Home>Finance>What Is Long-Term Debt? Definition And Financial Accounting


Finance
What Is Long-Term Debt? Definition And Financial Accounting
Published: December 20, 2023
Learn about long-term debt in finance, its definition, and its impact on financial accounting. Understand its importance for financial planning and management.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Long-Term Debt: Definition and Financial Accounting
Have you ever wondered what long-term debt is and how it affects individuals, businesses, or even entire economies? In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of finance to unravel the definition and financial accounting aspects of long-term debt. So, whether you are a finance enthusiast or a curious individual looking to expand your knowledge, keep reading to uncover the secrets behind long-term debt!
Key Takeaways:
- Long-term debt refers to any financial obligation that extends beyond a one-year period.
- It plays a crucial role in financing capital investments, funding operations, and supporting growth strategies.
Defining Long-Term Debt
Let’s start with the basics. Long-term debt is any financial obligation, such as loans or bonds, that extend beyond a one-year period. Unlike short-term debt, which typically has a repayment term of less than one year, long-term debt provides borrowers with a longer period to repay the borrowed funds. This lengthier repayment period enables individuals, businesses, and governments to finance significant investments, acquisitions, or expansions that require substantial capital.
The Significance of Long-Term Debt
Long-term debt plays a crucial role in the world of finance. Here are a few reasons why:
- Financing Capital Investments: Businesses often rely on long-term debt to fund capital investments, such as purchasing property, manufacturing equipment, or expanding their operations. By utilizing long-term debt, companies can spread the cost of these investments over several years, making them more manageable.
- Funding Operations: In addition to financing capital investments, long-term debt also helps finance day-to-day operations of businesses. From covering payroll expenses to purchasing inventory, companies may utilize long-term debt to ensure a smooth flow of cash in their operations.
- Supporting Growth Strategies: Long-term debt can be instrumental in supporting a company’s growth strategies. Whether it’s entering new markets, acquiring competitors, or investing in research and development, businesses often turn to long-term debt as a means to fund these expansion initiatives.
Financial Accounting for Long-Term Debt
When it comes to financial accounting, long-term debt has several important aspects:
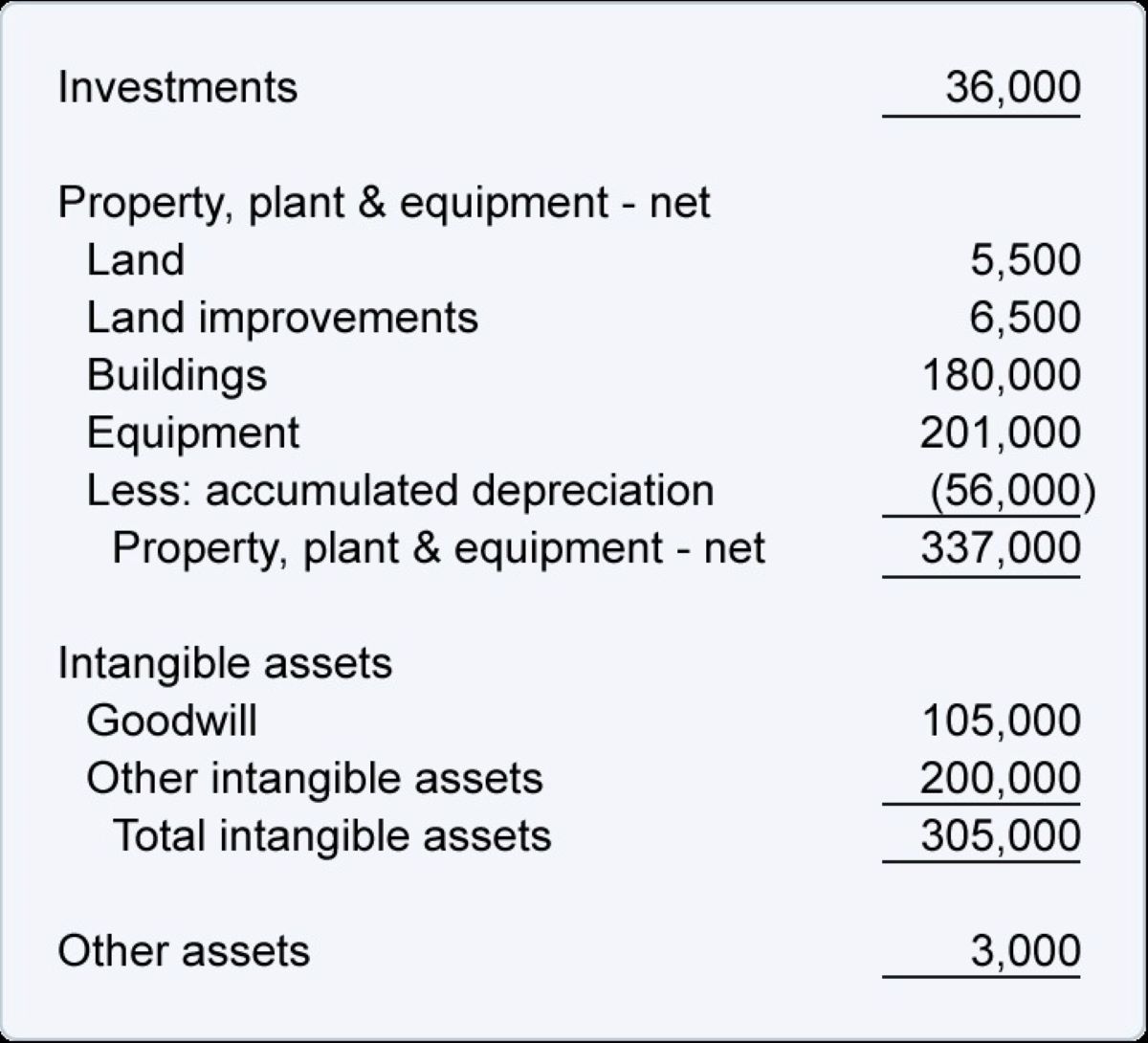
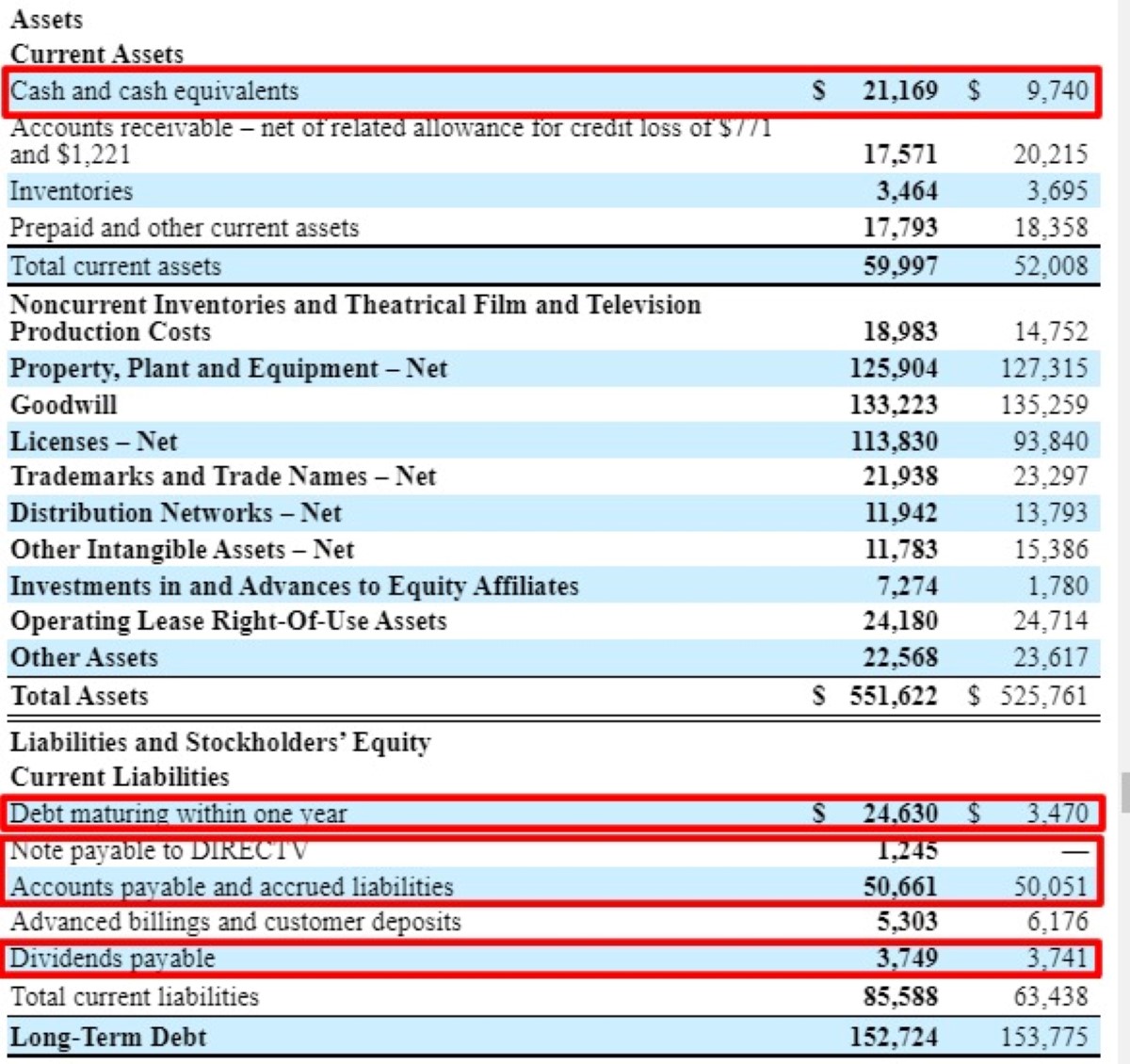
- Recognition: Long-term debt is recognized on a company’s balance sheet as a liability. This highlights the obligation to repay the borrowed funds over an extended period.
- Amortization: Long-term debt is typically amortized, which means that the principal and interest payments are spread out over the loan’s term. This allows borrowers to make regular, manageable payments.
- Interest Expense: Borrowers must also account for the interest expense associated with long-term debt. This expense is recorded on the income statement and reflects the cost of borrowing funds.
Understanding long-term debt is essential for individuals and businesses alike. It not only enables borrowers to finance significant investments and operations but also affects their overall financial health. By comprehending the intricacies of long-term debt, one can make informed financial decisions and plan for a prosperous future.
So, the next time you come across the term “long-term debt,” you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of its definition and how it impacts finance. Happy borrowing and investing!