Finance
What Is The Minimum Payment For A Credit Card
Published: February 27, 2024
Learn about the minimum payment for credit cards and its impact on your finances. Find out how to manage your credit card payments effectively. Gain valuable insights into personal finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Importance of Minimum Payments on Credit Cards
- Deciphering the Significance of Minimum Payments
- Influential Elements in Determining Minimum Credit Card Payments
- The Long-Term Ramifications of Minimum Credit Card Payments
- Empowering Approaches to Navigate Credit Card Obligations
- Navigating Credit Card Minimum Payments: A Path to Financial Empowerment
Introduction
Understanding the Importance of Minimum Payments on Credit Cards
Credit cards have become an integral part of modern financial transactions, offering convenience and flexibility to consumers. However, the convenience of using credit cards comes with the responsibility of managing payments effectively. One crucial aspect of credit card management is understanding and addressing the minimum payment requirement.
When individuals receive their monthly credit card statements, they are often presented with a minimum payment due. This minimum payment represents the smallest amount that cardholders are required to pay by a specific due date to keep their account in good standing. While making the minimum payment may seem like a manageable option, it is essential to recognize its implications on overall financial well-being.
In this article, we will delve into the significance of minimum payments on credit cards, explore the factors that influence these payments, and discuss the potential consequences of only paying the minimum amount. Additionally, we will provide practical strategies for effectively managing credit card minimum payments to maintain financial stability and avoid unnecessary debt accumulation.
Understanding the dynamics of minimum payments is vital for individuals seeking to make informed financial decisions and cultivate healthy credit habits. By shedding light on this topic, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the complexities of credit card management effectively. Let's embark on this insightful journey to unravel the intricacies of credit card minimum payments and their impact on personal finance.
Understanding Minimum Payments
Deciphering the Significance of Minimum Payments
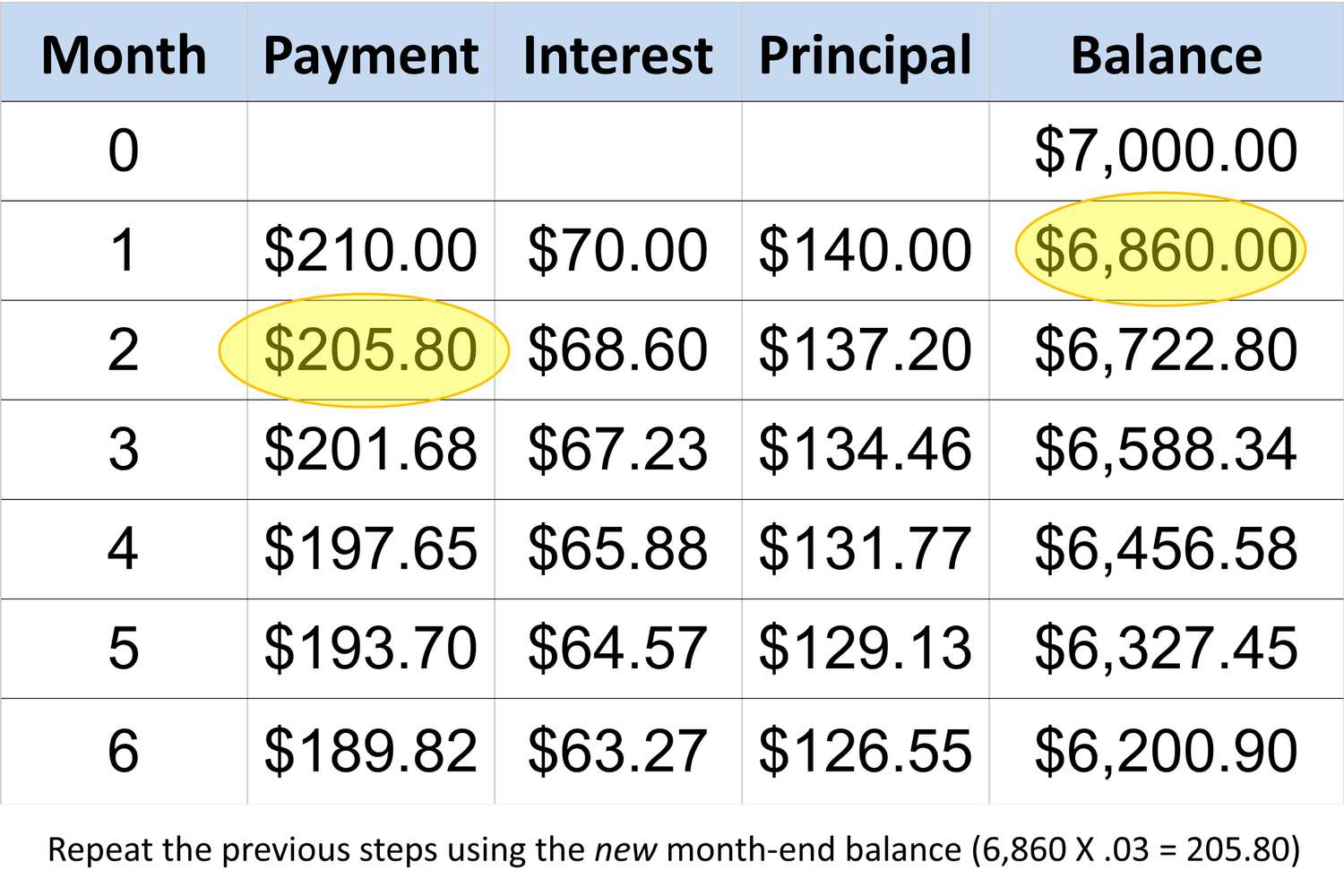
Minimum payments on credit cards represent the baseline amount that cardholders are required to pay each month to maintain their accounts in good standing. This minimum sum is typically calculated as a percentage of the outstanding balance, often ranging from 1% to 3% of the total amount owed. While the specific calculation method may vary among credit card issuers, understanding the rationale behind minimum payments is crucial for responsible financial management.
It is important to recognize that making only the minimum payment prolongs the time it takes to repay the outstanding balance and results in increased interest charges. By primarily addressing the interest and a small portion of the principal balance, individuals may find themselves trapped in a cycle of debt accumulation. Moreover, failing to meet the minimum payment requirement can lead to late fees, penalty interest rates, and a negative impact on credit scores.
When assessing the implications of minimum payments, it is essential to grasp the concept of credit utilization ratio. This ratio, a key factor in credit scoring models, compares the amount of credit used to the total available credit. By making only the minimum payment, individuals may inadvertently elevate their credit utilization ratio, potentially diminishing their credit scores and limiting access to favorable financial opportunities in the future.
Understanding the intricacies of minimum payments empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their credit card obligations. By recognizing the long-term consequences of solely meeting the minimum payment requirement, cardholders can proactively strategize to mitigate unnecessary interest charges and debt accumulation. In the subsequent sections, we will explore the factors influencing minimum payments and equip readers with effective strategies for managing their credit card obligations responsibly.
Factors Affecting Minimum Payments
Influential Elements in Determining Minimum Credit Card Payments
Several factors contribute to the calculation of minimum payments on credit cards, shaping the amount that cardholders are required to pay each month. Understanding these elements is pivotal for individuals seeking to manage their credit card obligations effectively and make informed financial decisions.
- Outstanding Balance: The outstanding balance on a credit card directly influences the minimum payment due. Typically, minimum payments are calculated as a percentage of the total amount owed, with the specific percentage varying among credit card issuers.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate associated with the credit card significantly impacts the minimum payment. Higher interest rates result in increased minimum payments, as a larger portion of the payment is allocated to addressing the accruing interest.
- Credit Card Terms and Conditions: Each credit card comes with its unique terms and conditions, which outline the specific method for calculating minimum payments. It is imperative for cardholders to review these terms to comprehend how their minimum payments are determined.
- Regulatory Requirements: Regulatory guidelines may influence the minimum payment calculation, with certain jurisdictions imposing specific standards for credit card issuers regarding minimum payments and associated fees.
- Financial Hardship Programs: In some cases, individuals facing financial challenges may be eligible for hardship programs offered by credit card issuers. These programs may temporarily adjust minimum payments to accommodate the cardholder’s financial circumstances.
By considering these influential factors, individuals can gain insight into the dynamics of minimum payments and strategize to manage their credit card obligations effectively. Recognizing the interplay between the outstanding balance, interest rate, and credit card terms empowers cardholders to make informed decisions regarding their monthly payments, thereby fostering financial stability and responsible credit management.
Consequences of Making Only the Minimum Payment
The Long-Term Ramifications of Minimum Credit Card Payments
Opting to make only the minimum payment on a credit card can have far-reaching consequences that extend beyond the immediate financial implications. While it may offer temporary relief by meeting the basic requirement, this approach often leads to a cascade of adverse outcomes that impact an individual’s overall financial well-being.
Extended Debt Repayment: By solely addressing the minimum payment, cardholders prolong the duration required to repay the outstanding balance. This protracted repayment period results in increased interest charges, amplifying the total cost of the debt and potentially leading to a cycle of persistent indebtedness.
Accumulation of Interest Charges: Making only the minimum payment means a significant portion of the payment is allocated to covering the accruing interest, with minimal impact on reducing the principal balance. Consequently, individuals incur substantial interest charges, further exacerbating the financial burden associated with the outstanding debt.
Negative Impact on Credit Score: Failing to manage credit card obligations beyond the minimum requirement can detrimentally affect an individual’s credit score. This can limit access to favorable lending terms, impact insurance premiums, and even hinder employment opportunities, as credit scores are increasingly utilized as a measure of financial responsibility and trustworthiness.
Escalation of Credit Utilization Ratio: By making only the minimum payment, individuals may inadvertently elevate their credit utilization ratio, potentially diminishing their credit scores. This can restrict access to additional credit and favorable financial opportunities, as lenders often view high credit utilization as a red flag for potential financial distress.
Accrual of Late Fees and Penalty Interest Rates: Failing to meet the minimum payment deadline can result in the imposition of late fees and penalty interest rates, further exacerbating the financial strain associated with credit card debt. These additional charges compound the existing debt burden, making it increasingly challenging to achieve financial stability.
By comprehending the extensive repercussions of exclusively meeting the minimum payment requirement, individuals can proactively strategize to manage their credit card obligations responsibly. In the subsequent section, we will explore effective strategies for navigating credit card minimum payments and mitigating the adverse consequences associated with this approach.
Strategies for Managing Credit Card Minimum Payments
Empowering Approaches to Navigate Credit Card Obligations
Effectively managing credit card minimum payments is essential for maintaining financial stability and cultivating responsible credit habits. By implementing strategic approaches, individuals can proactively address their credit card obligations, mitigate unnecessary interest charges, and work towards debt reduction. Here are practical strategies to navigate credit card minimum payments:
- Pay More Than the Minimum: Whenever feasible, strive to pay more than the minimum amount due. By allocating additional funds towards the outstanding balance, individuals can expedite debt repayment and minimize the accumulation of interest charges.
- Create a Budget and Payment Plan: Develop a comprehensive budget that prioritizes credit card payments. Establish a structured payment plan to ensure timely and consistent payments, aligning with your financial capabilities.
- Consolidate High-Interest Debt: Explore options for consolidating high-interest credit card debt, such as transferring balances to a card with a lower interest rate or leveraging a debt consolidation loan. This can help reduce interest expenses and streamline debt management.
- Communicate with Credit Card Issuers: In cases of financial hardship, communicate with credit card issuers to explore potential hardship programs or negotiate more favorable repayment terms. Many issuers offer assistance to individuals facing temporary financial challenges.
- Monitor Credit Card Statements Closely: Regularly review credit card statements to ensure accuracy and identify any unauthorized charges or errors. By promptly addressing discrepancies, individuals can safeguard their financial well-being and avoid unnecessary expenses.
- Limit New Credit Card Charges: Exercise prudence in utilizing credit cards for new purchases, particularly if struggling to meet minimum payments. Minimizing new charges can alleviate the burden of additional debt and facilitate focused efforts towards debt reduction.
- Seek Financial Counseling: Consider seeking guidance from reputable financial counselors or advisors to gain insights into effective debt management strategies and develop a personalized plan for addressing credit card obligations.
By incorporating these strategies into their financial approach, individuals can proactively navigate credit card minimum payments and work towards achieving greater financial stability. It is imperative to approach credit card management with diligence and foresight, leveraging these strategies to mitigate the adverse consequences associated with solely meeting the minimum payment requirement.
Conclusion
Navigating Credit Card Minimum Payments: A Path to Financial Empowerment
Understanding the intricacies of credit card minimum payments is fundamental for individuals seeking to cultivate responsible financial habits and safeguard their long-term financial well-being. By unraveling the significance of minimum payments, exploring influential factors in their calculation, and elucidating the consequences of solely meeting the minimum requirement, this article has provided valuable insights into the realm of credit card management.
It is evident that making only the minimum payment on a credit card can lead to a myriad of adverse outcomes, including extended debt repayment, increased interest charges, negative impacts on credit scores, and the accrual of late fees and penalty rates. However, armed with this knowledge, individuals can proactively implement strategies to navigate credit card minimum payments effectively and mitigate the associated risks.
By prioritizing timely and consistent payments, striving to pay more than the minimum, and exploring options for consolidating high-interest debt, individuals can take proactive steps towards debt reduction and financial stability. Additionally, maintaining open communication with credit card issuers, monitoring statements diligently, and seeking financial counseling when needed are instrumental in fostering a resilient approach to credit card management.
As individuals embrace these strategies and insights, they can empower themselves to navigate credit card minimum payments with prudence and foresight. By fostering a proactive and informed approach to credit card management, individuals can work towards achieving financial empowerment and cultivating a solid foundation for long-term financial success.
Ultimately, the journey towards effective credit card management is marked by diligence, informed decision-making, and a commitment to financial well-being. By leveraging the knowledge and strategies presented in this article, individuals can embark on a path towards responsible credit card management, debt reduction, and enhanced financial resilience.