Home>Finance>What Is The Minimum Payment On A Citi Credit Card


Finance
What Is The Minimum Payment On A Citi Credit Card
Published: February 25, 2024
Learn about the minimum payment on a Citi credit card and manage your finances wisely. Find out how to handle your credit card payments effectively.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding the dynamics of credit card payments is crucial for responsible financial management. When it comes to Citi credit cards, comprehending the concept of minimum payments is paramount. This article aims to shed light on the intricacies of minimum payments on a Citi credit card, providing readers with valuable insights into this fundamental aspect of credit card usage.
Navigating the world of credit cards can be daunting, especially for those new to the realm of personal finance. However, with the right information at your disposal, managing credit card payments can become a more manageable task. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of minimum payments on Citi credit cards, exploring the factors that influence them, how they are calculated, and why paying more than the minimum is essential for long-term financial well-being.
By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the minimum payment requirements for Citi credit cards, empowering them to make informed decisions regarding their credit card payments. Whether you are a seasoned credit card user or a newcomer to the world of personal finance, the insights provided here will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the realm of credit card minimum payments with confidence and prudence.
Understanding Minimum Payments
Minimum payments on a Citi credit card represent the lowest amount a cardholder must pay by the due date to keep the account in good standing. While it may seem like a convenient way to manage monthly expenses, it is essential to recognize that making only the minimum payment can lead to long-term financial repercussions.
When cardholders make only the minimum payment, they are essentially carrying a balance forward to the next billing cycle, incurring interest charges on the remaining balance. This can result in the accumulation of substantial interest over time, potentially leading to a cycle of debt if the pattern persists.
Understanding the implications of minimum payments is crucial for maintaining financial health. It is not merely a matter of meeting the basic payment requirement; rather, it involves grasping the impact of interest accrual and the potential prolongation of debt repayment. By comprehending the significance of minimum payments, cardholders can make more informed decisions about their financial obligations and strive towards more sustainable and responsible credit card usage.
Factors Affecting Minimum Payments
Several factors influence the calculation of minimum payments on Citi credit cards. Understanding these factors is essential for cardholders seeking to manage their credit card payments effectively. The following are key elements that can impact the minimum payment requirement:
- Outstanding Balance: The amount owed on the credit card significantly affects the minimum payment. As the outstanding balance increases, the minimum payment also rises, reflecting the higher amount due.
- Interest Rate: The annual percentage rate (APR) on the credit card plays a crucial role in determining the minimum payment. Higher interest rates lead to increased minimum payment amounts, as a larger portion of the payment goes towards covering the interest charges.
- Fixed Percentage: Credit card issuers often set a minimum payment as a fixed percentage of the outstanding balance. This percentage can vary among different credit card companies and is an important factor in the minimum payment calculation.
- Fees and Penalties: Additional fees, such as late payment fees or over-limit charges, can impact the minimum payment due. These fees add to the total amount owed and consequently affect the minimum payment requirement.
- Credit Utilization: The ratio of the credit card balance to the credit limit, known as credit utilization, can influence the minimum payment. Higher credit utilization may lead to a higher minimum payment as it indicates a greater reliance on credit.
By considering these factors, cardholders can gain insight into the variables that contribute to the determination of minimum payments on their Citi credit cards. Awareness of these elements empowers individuals to make informed financial decisions and take proactive steps towards managing their credit card obligations responsibly.
How to Calculate Minimum Payment
The calculation of the minimum payment on a Citi credit card involves a combination of factors, and understanding the methodology is essential for cardholders. While the specific formula may vary between credit card issuers, including Citi, the following general approach is often utilized:
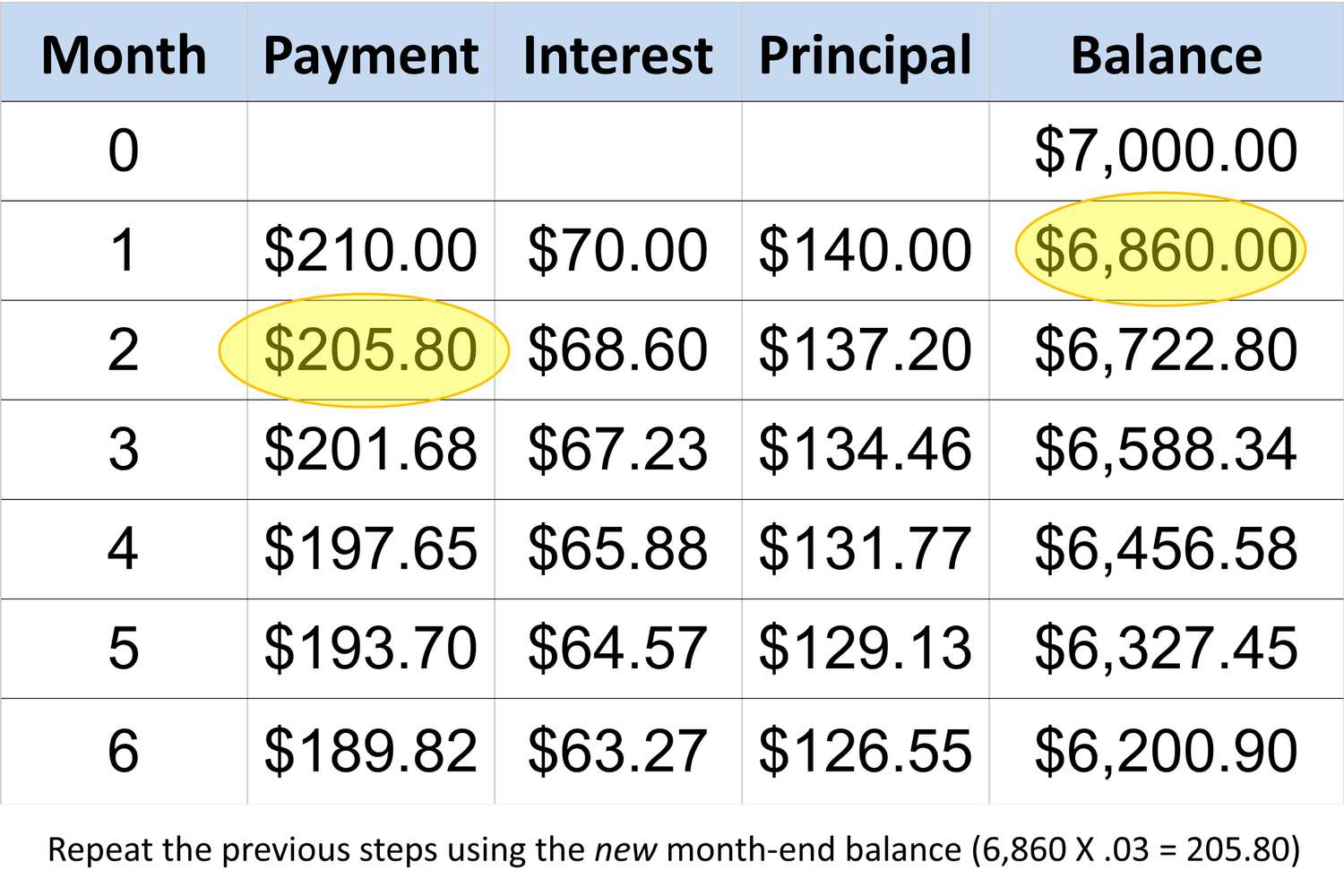
- Percentage of the Outstanding Balance: Credit card issuers typically set the minimum payment as a percentage of the outstanding balance. This percentage can range from 1% to 3% or more, depending on the terms and conditions of the credit card agreement. For example, if the outstanding balance is $1,000 and the minimum payment percentage is 2%, the minimum payment would be $20.
- Interest and Fees: In addition to the percentage of the outstanding balance, the minimum payment may include accrued interest for the billing cycle and any applicable fees, such as late fees or over-limit charges. These additional amounts contribute to the total minimum payment requirement.
- Minimum Fixed Amount: Some credit card issuers set a minimum fixed amount for the minimum payment, ensuring that the payment is not unreasonably low, regardless of the outstanding balance. This ensures a baseline for the minimum payment, even if the calculated percentage falls below a certain threshold.
By considering these components, cardholders can gain insight into how minimum payments are calculated on their Citi credit cards. It is important to review the terms and conditions of the credit card agreement to understand the specific methodology employed by Citi for minimum payment calculations. This knowledge empowers cardholders to plan their finances effectively and make informed decisions regarding their credit card payments.
Importance of Paying More Than the Minimum
While meeting the minimum payment requirement on a Citi credit card is essential for avoiding late fees and maintaining a positive payment history, it is equally crucial to recognize the benefits of paying more than the minimum. By exceeding the minimum payment, cardholders can experience several advantages that contribute to their financial well-being:
- Interest Savings: Paying more than the minimum amount reduces the outstanding balance, thereby lowering the amount on which interest accrues. This can lead to substantial interest savings over time, allowing cardholders to pay off their balances more efficiently.
- Debt Repayment Acceleration: Making larger payments accelerates the process of debt repayment. By allocating more funds towards reducing the principal balance, cardholders can work towards becoming debt-free at a faster pace, ultimately reducing financial stress and enhancing long-term financial stability.
- Credit Score Improvement: Lowering credit card balances through higher payments can positively impact credit scores. A lower credit utilization ratio, which is the ratio of credit card balances to credit limits, can enhance creditworthiness and contribute to an improved credit score over time.
- Financial Discipline and Freedom: Consistently paying more than the minimum reflects responsible financial behavior and discipline. It also provides greater financial freedom by reducing the burden of high-interest debt and fostering a proactive approach to managing credit card obligations.
By recognizing the importance of paying more than the minimum, cardholders can take proactive steps towards achieving financial stability and reducing the overall cost of credit card usage. While meeting the minimum payment is a crucial starting point, going beyond this requirement can yield significant long-term benefits and contribute to a healthier financial outlook.
Conclusion
Understanding the minimum payment requirements on a Citi credit card is a fundamental aspect of responsible credit card usage. By grasping the dynamics of minimum payments, including their calculation, influencing factors, and the importance of paying more than the minimum, cardholders can take proactive steps towards managing their credit card obligations effectively.
While the minimum payment serves as the baseline requirement to avoid late fees and maintain account status, it is crucial to recognize that paying only the minimum can lead to long-term financial challenges due to accruing interest and extended debt repayment periods. By comprehending the impact of minimum payments and the benefits of exceeding this requirement, cardholders can make informed decisions that contribute to their financial well-being.
Ultimately, responsible credit card usage involves not only meeting minimum payment obligations but also striving to pay more than the minimum whenever possible. By doing so, cardholders can reduce interest expenses, accelerate debt repayment, improve their credit standing, and cultivate financial discipline. These actions contribute to a more secure financial future and empower individuals to make the most of their credit card usage while minimizing the associated costs and risks.
In conclusion, by gaining a comprehensive understanding of minimum payments and their implications, Citi credit cardholders can navigate their financial responsibilities with confidence, ensuring that their credit cards remain valuable financial tools rather than sources of long-term financial strain.