
Finance
What Is The Utah State Income Tax Rate
Published: November 2, 2023
Discover the current Utah state income tax rate and how it may impact your finances. Stay informed and plan your finances accordingly.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of state income taxes! If you’re a working professional or a business owner, understanding the ins and outs of state income taxes is crucial. In this article, we will focus on the Utah state income tax rate and provide you with all the information you need to navigate this financial landscape.
State income taxes play a significant role in funding state governments and providing essential services to residents. These taxes are separate from federal income taxes and vary from state to state. Each state determines its own tax rates, brackets, deductions, and credits, resulting in a unique tax landscape for residents.
Utah, often referred to as the “Beehive State,” is known for its stunning landscapes, thriving economy, and low unemployment rates. Understanding Utah’s state income tax system is essential for both residents and businesses within the state.
In this article, we will cover various aspects of the Utah state income tax, including the tax rates, deductions, and credits. We’ll also guide you through the process of calculating and filing your Utah state income taxes. Whether you’re a resident looking to file your annual tax return or a business owner interested in the tax implications of doing business in Utah, this article has got you covered.
So, let’s dive in and explore the Utah state income tax rate in detail, ensuring you have all the information needed to make informed financial decisions and fulfill your tax obligations.
Understanding State Income Taxes
State income taxes are taxes imposed by individual states on the income earned by residents and businesses within their jurisdiction. These taxes are separate from federal income taxes, which are imposed by the U.S. federal government. While federal income taxes are uniform across all states, state income taxes can vary significantly.
State income taxes are a vital source of revenue for state governments, allowing them to fund various services and programs such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and public safety. The amount of state income tax you owe is typically based on your taxable income, which is the amount of income you earn after subtracting any allowable deductions and exemptions.
Each state has its own tax laws, tax rates, and tax brackets, which determine how much tax you pay based on your income level. Some states have a flat tax rate, meaning that everyone pays the same percentage of their income in taxes. Other states have a progressive tax system, where tax rates increase as income levels rise, resulting in higher taxes for higher earners.
It is important to understand the nuances of state income taxes, as they can significantly impact your financial situation. By understanding how these taxes work and the specific rules and regulations in your state, you can take advantage of potential deductions and credits and ensure you are fulfilling your tax obligations.
When it comes to state income taxes, it’s not just residents who are affected. Businesses operating within a state’s jurisdiction are also subject to state income taxes. This can include both small businesses and large corporations. Depending on the state, businesses may be subject to different tax rates and regulations, such as corporate income tax or franchise tax.
As a resident or business owner, it is important to stay informed about state income tax laws and any updates or changes that may impact your financial situation. By understanding state income taxes, you can make informed decisions, take advantage of available deductions and credits, and fulfill your tax obligations while managing your finances effectively.
Overview of Utah State Income Tax
Utah is known for its picturesque landscapes, thriving economy, and business-friendly environment. Understanding the basics of Utah’s state income tax system is essential for residents and businesses in the state.
Utah follows a progressive income tax system, which means that tax rates increase as income levels rise. The Utah state income tax is based on taxable income, which is determined by subtracting deductions and exemptions from total income earned.
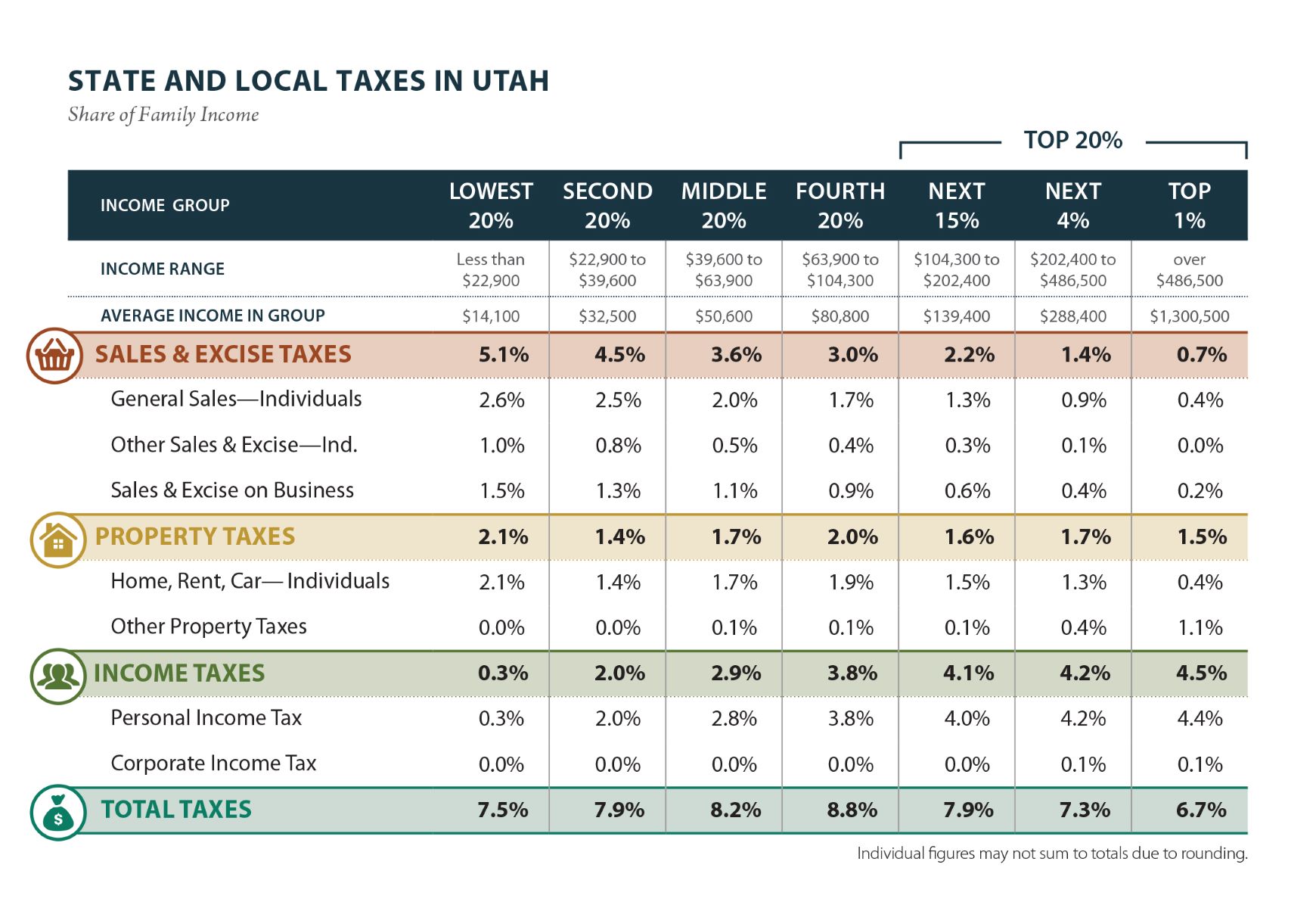
Utah has a relatively low state income tax rate compared to many other states. As of 2021, the Utah state income tax rates range from 4.95% to 4.95% for individuals and married couples filing jointly. The flat tax rate of 4.95% applies to all income levels, making it a simple and straightforward tax structure.
It’s important to note that Utah’s state income tax is separate from federal income tax. Individuals and businesses in Utah must file both federal and state income tax returns each year. The federal income tax forms the basis for determining the Adjusted Gross Income (AGI), which is then used to calculate the Utah state income tax liability.
Utah also offers various deductions and credits to help taxpayers reduce their overall tax liability. Some common deductions include mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and medical expenses. Additionally, there are specific credits available for individuals, such as the Child and Dependent Care Credit and the Retirement Credit.
For businesses operating in Utah, there are different tax requirements and regulations depending on the business structure. Corporations are subject to Utah’s Corporate Income Tax, which is calculated based on the net income earned by the corporation. Other business entities, such as partnerships, limited liability companies (LLCs), and sole proprietorships, may be required to file Utah’s Business Income Tax return.
It’s important for individuals and businesses in Utah to stay updated with any changes or updates in the state income tax laws. The Utah State Tax Commission provides resources and information on their website to help taxpayers navigate the tax system and fulfill their obligations.
Understanding the overview of Utah’s state income tax is a crucial step in managing your finances and ensuring compliance with tax laws. By knowing the tax rates, deductions, and credits available, individuals and businesses can make informed financial decisions and accurately calculate their tax liability.
Calculating Utah State Income Tax
Calculating your Utah state income tax is an essential step in understanding and fulfilling your tax obligations. To determine your state income tax liability in Utah, you will need to follow a few key steps.
The first step is to calculate your taxable income. Taxable income is the amount of income subject to taxation after deducting any allowable deductions and exemptions. Common deductions include student loan interest, alimony payments, and contributions to retirement accounts.
Once you have determined your taxable income, you can refer to Utah’s state income tax rate schedule to determine the applicable tax rate. As of 2021, Utah has a flat tax rate of 4.95%. This means that regardless of your income level, you will pay the same percentage of tax on your taxable income.
To calculate your state income tax, simply multiply your taxable income by the applicable tax rate. For example, if your taxable income is $50,000, you would multiply this by 4.95% (or 0.0495) to find your Utah state income tax liability, which would be $2,475.
It’s essential to keep in mind that this calculation is simplified for individuals and married couples filing jointly. If you have a more complex tax situation, such as self-employment income or itemized deductions, it may be beneficial to consult a tax professional or utilize tax software to ensure accurate calculations.
In addition to the basic state income tax calculation, individuals and businesses in Utah may also need to consider other factors. For example, Utah has a nonrefundable and nontransferable Renter’s Credit, designed to provide tax relief for individuals who rent their homes. This credit can help lower the overall tax liability for eligible individuals.
It’s important to note that Utah’s state income tax is due on the same filing deadline as federal income taxes, typically April 15th, unless an extension has been granted. Utah taxpayers can file their state income tax returns electronically or through traditional paper filing methods. It’s recommended to file your state income tax return alongside your federal return to ensure accuracy and streamline the filing process.
By understanding how to calculate your Utah state income tax, you can estimate your tax liability, plan your finances accordingly, and ensure compliance with tax laws. Remember to keep accurate records, seek professional advice if needed, and stay updated with any changes in Utah tax laws that may affect your calculations.
Utah State Income Tax Rates by Income Bracket
Understanding the Utah state income tax rates by income bracket is essential for accurately calculating your tax liability and planning your finances. As of 2021, Utah follows a flat tax rate structure, meaning that all income levels are taxed at the same rate. The current flat tax rate for Utah state income tax is 4.95%.
This flat tax rate ensures simplicity in the tax system, as taxpayers do not need to navigate different tax brackets based on their income level. Regardless of your income, you will pay 4.95% of your taxable income as state income tax.
However, it’s worth noting that Utah’s flat tax rate of 4.95% applies only to individuals and married couples filing joint returns. Other filing statuses might have different rates, such as trusts and estates, with a flat tax rate of 5%.
The flat tax rate structure in Utah eliminates the need to calculate tax liability based on different income brackets, making tax planning and estimation relatively straightforward. It ensures a consistent tax burden for all taxpayers, regardless of their income level.
While Utah’s flat tax rate does not distinguish between income brackets, it’s still important to understand how your overall income may impact your tax liability. Higher earners may have a higher tax liability in absolute terms due to their higher income, even at the same tax rate.
It’s important to note that tax rates and brackets may change over time, so it’s crucial to stay updated with any changes in Utah’s state income tax laws. The Utah State Tax Commission provides resources and information on their website to help taxpayers understand the latest tax rates and brackets.
Overall, knowing the Utah state income tax rate by income bracket is essential for understanding your tax liability and effectively planning your finances. The flat tax rate of 4.95% makes it easier for taxpayers to calculate their state income tax without the complexity of multiple tax brackets. Remember to consult a tax professional or utilize tax software if you have a more complex tax situation to ensure accurate calculations and compliance with Utah’s state income tax laws.
Utah State Income Tax Deductions and Credits
When it comes to reducing your Utah state income tax liability, understanding the available deductions and credits can be beneficial. Utah offers various deductions and credits that can help lower your overall tax burden. Here are some key deductions and credits to be aware of:
Deductions:
1. Standard Deduction: Utah allows taxpayers to claim a standard deduction, which is a set amount subtracted from your taxable income. As of 2021, the standard deduction is $12,800 for married couples filing jointly and $6,400 for individuals filing as single or married filing separately.
2. Itemized Deductions: Utah taxpayers who have deductible expenses that exceed the standard deduction amount may choose to itemize their deductions. Allowable itemized deductions include mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and certain medical expenses, among others.
3. Educator Expense Deduction: Eligible educators in Utah can deduct up to $2,500 of qualified unreimbursed expenses incurred for classroom supplies and materials.
Credits:
1. Child and Dependent Care Credit: Utah provides a credit for childcare expenses incurred while working or looking for work. The credit amount is based on a percentage of qualifying expenses, up to certain limits, and is meant to assist with the cost of caring for children or dependents.
2. Retirement Credit: Individuals who contribute to eligible retirement accounts in Utah may qualify for a retirement credit. The credit amount is based on a percentage of the contributions made, up to certain limits, encouraging individuals to save for retirement.
3. Renter’s Credit: If you are a renter in Utah, you may be eligible for the nonrefundable and nontransferable Renter’s Credit. This credit is designed to provide tax relief for individuals who pay rent on their primary residence. The credit amount is based on a percentage of qualifying rent paid, up to certain limits.
It’s important to note that the availability and eligibility criteria for deductions and credits may vary. Ensure that you meet the requirements outlined by the Utah State Tax Commission and consider consulting a tax professional to maximize your tax deductions and credits efficiently.
Remember to keep accurate records of your expenses and maintain necessary documentation to support your deductions and credits claimed on your Utah state income tax return. Staying informed about available deductions and credits can significantly reduce your overall tax liability and help you effectively manage your finances.
Filing and Paying Utah State Income Tax
Filing and paying your Utah state income tax is an important responsibility for residents and businesses in the state. Here are the key steps to follow:
Filing Requirements:
Most Utah residents are required to file a state income tax return if they meet certain income thresholds. As of 2021, you generally need to file a return if your income exceeds the following thresholds:
- Single filers: $12,800
- Married filers (filing jointly): $25,600
- Married filers (filing separately): $12,800
- Head of household: $18,300
These thresholds may change over time, so it’s essential to stay updated with the current guidelines from the Utah State Tax Commission.
Filing Methods:
You have the option to file your Utah state income tax return electronically or through traditional paper filing methods. Electronic filing is generally faster, more convenient, and can help ensure accuracy. Utah offers an e-filing system called “tap.utah.gov,” which allows individuals and businesses to file their state income tax returns online.
If you prefer to file a paper return, you can download the necessary forms from the Utah State Tax Commission’s website. Be sure to carefully follow the instructions provided and attach any required schedules or documentation.
Payment Options:
Utah provides several payment options to settle your state income tax liability:
- Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT): You can make an electronic payment through the Utah State Tax Commission’s website by providing your banking information. This is a convenient and secure way to pay your tax obligation.
- Credit or Debit Card: Utah accepts credit or debit card payments. However, keep in mind that there may be associated service fees for using this payment method.
- Check or Money Order: You can also mail a check or money order along with your completed tax return to the Utah State Tax Commission. Be sure to include your payment voucher, which can be obtained from the Utah State Tax Commission’s website.
It’s important to note that payments are due by the same deadline as the federal income tax filing deadline, typically April 15th. If you need more time to file your Utah state income tax return, you can request an extension. However, it’s crucial to remember that an extension to file does not extend the deadline to pay any tax owed. Interest and penalties may apply if you do not pay your tax liability by the due date.
Lastly, it’s recommended to keep copies of your filed tax return and any tax-related documents for your records. This can help if you need to refer to them in the future or if there are any issues with your tax return.
By understanding the filing and payment process for Utah state income taxes, you can meet your obligations and ensure compliance with state tax laws. Remember to file your return on time, pay any tax owed by the deadline, and consult a tax professional if you have specific questions or need assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions about Utah state income taxes:
1. Who needs to pay Utah state income tax?
Most Utah residents who meet certain income thresholds are required to pay state income tax. This includes individuals, married couples, and businesses operating within the state.
2. What is the current Utah state income tax rate?
The current Utah state income tax rate is a flat rate of 4.95% for individuals and married couples filing jointly. Other filing statuses, such as trusts and estates, have a flat tax rate of 5%.
3. Are there any deductions or credits available to Utah taxpayers?
Yes, Utah offers various deductions and credits to help taxpayers reduce their overall tax liability. Some common deductions include the standard deduction, itemized deductions, and educator expense deduction. There are also credits available, such as the Child and Dependent Care Credit, Retirement Credit, and Renter’s Credit.
4. When is the deadline to file and pay Utah state income taxes?
The deadline to file and pay Utah state income taxes is typically April 15th, the same as the federal income tax deadline. If you need more time to file your return, you can request an extension, but remember that the extension does not extend the deadline to pay any tax owed.
5. Can I file my Utah state income tax return electronically?
Yes, you can file your Utah state income tax return electronically using the e-filing system offered by the Utah State Tax Commission. Electronic filing is generally faster, more convenient, and can help ensure accurate calculations.
6. What if I can’t afford to pay my Utah state income tax liability?
If you are unable to pay your Utah state income tax liability in full, it’s still important to file your return and pay as much as you can by the deadline. You can explore payment options, such as installment agreements, or contact the Utah State Tax Commission to discuss potential solutions.
Remember, while this provides general information, it is always advisable to consult a tax professional or visit the Utah State Tax Commission’s website for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding Utah state income taxes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the Utah state income tax rate and its associated components is essential for residents and businesses in the Beehive State. Knowing how to calculate your tax liability, take advantage of deductions and credits, and fulfill your filing and payment obligations will help you navigate the Utah state income tax system with confidence.
Utah follows a simple and straightforward flat tax rate of 4.95% for individuals and married couples filing jointly. This allows for easier tax planning and estimation, as there are no complex income brackets to consider. However, it is still important to understand how your overall income may impact your tax liability.
Utah also offers various deductions and credits to help lower your tax burden. Whether it’s utilizing the standard deduction, itemizing deductions, or claiming credits such as the Child and Dependent Care Credit or Renter’s Credit, taking advantage of these opportunities can significantly reduce your overall tax liability.
Filing and paying your Utah state income tax can be done electronically or through traditional paper filing methods. Remember to file your return by the deadline, pay any tax owed, and keep accurate records of your tax-related documents.
By staying informed about the latest tax laws, deductions, and credits, you can effectively manage your finances, maximize your tax savings, and ensure compliance with Utah’s state income tax regulations.
If you have specific questions or need assistance with your tax situation, it’s always a good idea to consult a tax professional or visit the Utah State Tax Commission’s website for more information.
With this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the world of Utah state income taxes and make informed decisions while fulfilling your tax obligations. Remember, understanding and managing your tax liability is essential for maintaining financial stability and achieving your long-term financial goals.