Finance
Which Is The Largest Stock Exchange In India
Published: January 17, 2024
Discover the largest stock exchange in India and gain valuable insights into the world of finance. Learn about key players and market trends.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to investing in the stock market, it’s essential to have an understanding of the various stock exchanges operating in the country. In India, the stock market plays a crucial role in the country’s economy, providing individuals and businesses with the opportunity to invest in publicly traded companies. The Indian stock market consists of several stock exchanges, but the two most prominent players are the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
These two stock exchanges have a significant impact on the Indian economy, serving as vital platforms for facilitating the buying and selling of securities. They provide a transparent and regulated environment for investors to trade shares, bonds, and other financial instruments. Understanding the differences between these exchanges can help investors make informed decisions and navigate the world of stock market investments more effectively.
In this article, we will explore the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), highlighting their historical backgrounds, their features and functions, and how they compare to each other. Additionally, we will provide an overview of other notable stock exchanges in India.
Whether you are a seasoned investor or a beginner looking to enter the stock market, understanding these stock exchanges’ workings is essential. So, let’s dive deeper into the fascinating world of the Indian stock market and discover which stock exchange is the largest in India.
Historical Background
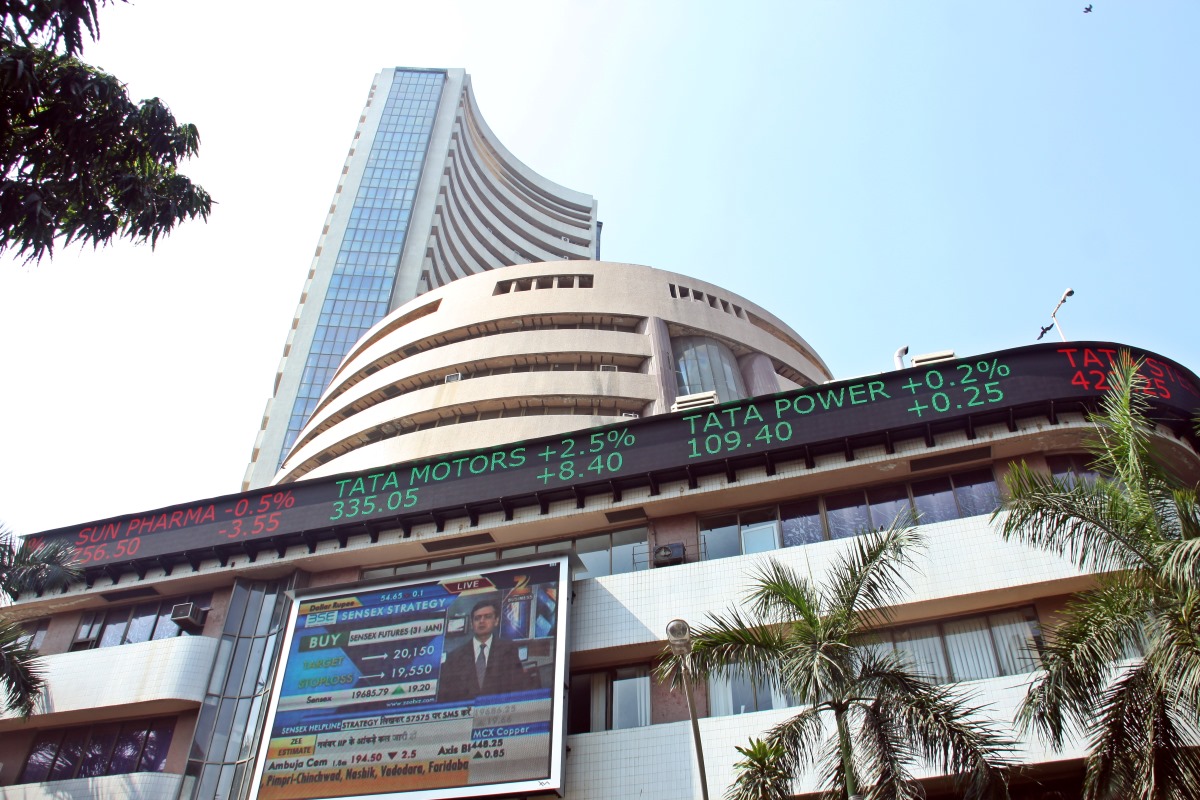
The history of stock exchanges in India can be traced back to the 19th century during the British colonial rule. The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) holds the distinction of being the oldest stock exchange in Asia, established in 1875. It was initially known as “The Native Share & Stock Brokers’ Association” and later renamed to BSE in 1956. The BSE played a crucial role in the development of the Indian capital market and continues to be at the forefront of stock trading in India.
On the other hand, the National Stock Exchange (NSE) was established much later, in 1992. It was founded as a result of a wide-ranging reform initiative undertaken by the Indian government to modernize the Indian stock market and introduce electronic trading systems. The NSE focused on providing a more efficient and transparent trading platform.
The establishment of the NSE allowed for the shift from the traditional trading floor setup to a fully automated trading system. This automation brought in significant benefits, including faster trade executions, reduced errors, and enhanced transparency. The NSE’s technological advancements quickly gained traction among market participants, leading to its rapid growth and emergence as a major player in the Indian stock market.
Both the BSE and NSE have played vital roles in India’s economic development over the years. They have facilitated capital formation, attracted domestic and foreign investors, and provided a platform for companies to raise funds for growth and expansion.
As the Indian economy has grown, so have the stock exchanges, adapting to changing market dynamics and regulatory requirements. Today, the BSE and NSE continue to compete while collaborating to maintain the integrity and stability of the Indian stock market.
Now that we have a historical context, let’s delve into the specifics of the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) to understand their unique features and functions.
National Stock Exchange (NSE)
The National Stock Exchange (NSE) is one of the leading stock exchanges in India. It was established in 1992 and is headquartered in Mumbai. The NSE operates on a fully automated electronic trading platform, offering investors a seamless and efficient trading experience.
The key features of the NSE include:
- Largest Stock Exchange in India: The NSE is the largest stock exchange in India in terms of market capitalization and trading volume. It has a vast network of traders, investors, and listed companies, making it a leading platform for securities trading.
- Wide Range of Products: The NSE offers a diverse range of financial products for trading, including equities, derivatives (such as futures and options), mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). This enables investors to create diversified portfolios and manage risk effectively.
- Technology-driven Trading: The NSE is renowned for its advanced technology infrastructure, which ensures real-time market data dissemination, high-speed order execution, and robust risk management systems. The trading platform provides investors with access to a vast array of market information and enables instantaneous trade execution.
- NSE Indices: The NSE operates various widely followed indices, including the Nifty 50 and Nifty Bank. These indices track the performance of selected stocks and provide investors with benchmark references for evaluating the market’s overall performance.
- Investor Protection: The NSE places a strong emphasis on investor protection and market integrity. It has implemented stringent regulatory frameworks, surveillance mechanisms, and compliance standards to safeguard investor interests and maintain market transparency.
The NSE has played a significant role in transforming the Indian stock market landscape. Its technological advancements, robust infrastructure, and investor-friendly approach have positioned it as a preferred choice for domestic and international investors.
In the next section, we will explore the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and its unique features that distinguish it from the NSE.
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) is the oldest stock exchange in Asia, dating back to 1875. It is located in Mumbai, considered the financial capital of India. The BSE has played a vital role in the development of the Indian capital market and continues to be one of the leading stock exchanges in the country.
Here are some key features of the BSE:
- Legacy and Historical Significance: The BSE holds a rich history and is a symbol of India’s financial heritage. It has witnessed numerous milestones and has been influential in shaping the Indian stock market.
- Wide Range of Listed Companies: The BSE boasts a significant number of listed companies across various sectors, including large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks. This offers investors a diversified pool of investment opportunities.
- Trading Mechanism: The BSE facilitates trading through an electronic trading system known as the BOLT (BSE Online Trading) system. It provides a transparent and efficient platform for buying and selling securities, ensuring fair price discovery and quick trade executions.
- Sensex Index: One of the notable highlights of the BSE is its flagship index, the Sensex. Comprising 30 actively traded stocks, the Sensex is widely regarded as a barometer of the Indian stock market’s overall performance. It is tracked by investors and market participants to gauge market trends and sentiment.
- Investor Education and Awareness: The BSE takes several initiatives to educate and create awareness among investors. It conducts investor awareness programs, seminars, and workshops to enhance financial literacy and promote responsible investing in the stock market.
The BSE has evolved over the years and has successfully adapted to the changing needs of market participants. Its rich history, wide range of listed companies, and iconic Sensex index make it a distinctive player in the Indian stock market.
In the following section, we will compare the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) to understand their similarities and differences.
Comparison of NSE and BSE
While both the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) are prominent stock exchanges in India, there are notable differences between them. Let’s compare the two exchanges based on several key factors:
1. Market Size and Trading Volume: The NSE is generally considered the largest stock exchange in India in terms of market capitalization and trading volume. It has a wider reach and a broader spectrum of listed companies, attracting a larger number of investors. However, the BSE holds its own significance, especially with its heritage and historically significant listed companies.
2. Trading Mechanisms: Both the NSE and BSE operate on electronic trading platforms. The NSE uses an automated trading system known as NEAT (National Exchange for Automated Trading), while the BSE’s trading system is called BOLT (BSE Online Trading). Both platforms provide real-time trading and efficient order matching. However, the trading timings and circuit breaker mechanisms may differ between the two exchanges.
3. Indices: The NSE operates various indices, including the Nifty 50, Nifty Bank, and Nifty Midcap. On the other hand, the BSE has the iconic Sensex index. While the Nifty 50 and Sensex are both widely tracked indices, they represent different sets of stocks, leading to variations in their compositions and performance.
4. Investor Demographics: The NSE has a higher proportion of institutional investors, including mutual funds, foreign institutional investors (FIIs), and insurance companies. The BSE, on the other hand, has a relatively higher participation from individual and retail investors. This can result in different market dynamics and trading patterns between the two exchanges.
5. Regulatory Environment: Both the NSE and BSE are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and follow strict regulatory guidelines to ensure investor protection and market integrity. They adhere to similar rules and regulations and hold exchanges to high compliance standards.
6. Brand Recognition: The NSE has gained significant brand recognition over the years, becoming a preferred choice for many investors due to its technological advancements and transparency. However, the BSE, as the oldest stock exchange in Asia, holds a prestigious position and is often associated with India’s financial heritage.
It’s important to note that while these comparisons highlight the differences, both the NSE and BSE provide robust platforms for investors to trade securities, raise capital, and participate in the Indian stock market.
In addition to the NSE and BSE, there are other stock exchanges in India worth exploring. Let’s briefly touch upon these exchanges in the next section.
Other Stock Exchanges in India
In addition to the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), there are several other stock exchanges in India that contribute to the country’s vibrant capital market. While these exchanges may not be as prominent or have the same trading volumes as the NSE and BSE, they play a significant role in specific sectors or regions. Let’s take a look at a few notable stock exchanges in India:
- National Commodity & Derivatives Exchange (NCDEX): As the leading commodity exchange in India, the NCDEX provides a platform for trading agricultural commodities such as cereals, pulses, oilseeds, and spices. It enables farmers, traders, and other stakeholders to hedge their price risks and participate in the commodity market.
- Mutual Fund Exchange (MFEX): The Mutual Fund Exchange is an electronic platform that facilitates the buying and selling of mutual fund units. It offers investors a convenient way to invest in a wide range of mutual funds and track their investments through a single account.
- Indian Energy Exchange (IEX): The IEX is a specialized exchange that caters to the energy sector. It provides a transparent and competitive platform for trading electricity and renewable energy certificates, facilitating efficient electricity market operations.
- Calcutta Stock Exchange (CSE): The Calcutta Stock Exchange, established in 1908, is one of the oldest stock exchanges in India. While its trading volumes have declined over the years, it continues to operate and facilitate trading in securities.
- Ahmedabad Stock Exchange (ASE): Founded in 1894, the Ahmedabad Stock Exchange is another ancient stock exchange in India. Despite a decrease in trading activity, it persists in providing a platform for securities trading, particularly for the local business community in Ahmedabad and surrounding areas.
These are just a few examples of other stock exchanges in India. Each exchange serves a specific purpose or caters to a particular segment of the market. Together, they contribute to the overall growth and development of the Indian capital market by providing investors with diverse investment opportunities and specialized trading platforms.
Now that we have explored the different stock exchanges in India, let’s conclude our discussion.
Conclusion
The Indian stock market is a dynamic and thriving ecosystem, offering a plethora of investment opportunities for individuals and businesses. The National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) are the two primary stock exchanges in India, playing pivotal roles in the country’s economy. While the NSE is known for its technological advancements and larger market capitalization, the BSE holds a legacy of being the oldest stock exchange in Asia.
Both the NSE and BSE provide investors with efficient trading platforms, diverse financial products, and regulatory frameworks that prioritize investor protection. The NSE’s widespread reach and advanced trading infrastructure have made it the largest stock exchange in India. On the other hand, the BSE’s rich history, broad range of listed companies, and iconic Sensex index lend it a unique position in the market.
In addition to the NSE and BSE, there are other stock exchanges in India that cater to specific sectors or regions, contributing to the overall growth and diversity of the Indian capital market. These exchanges provide opportunities for trading commodities, mutual funds, and specialized securities.
As an investor, it is crucial to understand the nuances and differences between these exchanges, leveraging their distinct features to make informed investment decisions. Whether you prefer the technology-driven ecosystem of the NSE or value the historical significance of the BSE, both exchanges offer valuable avenues for investment and participation in the Indian stock market.
By recognizing the strengths and unique characteristics of each stock exchange, investors can navigate the Indian stock market with confidence, capitalizing on the opportunities presented by these thriving platforms. Ultimately, understanding the various stock exchanges in India provides a solid foundation for building a successful investment strategy and achieving financial goals.
So, whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting your journey in the stock market, explore the diverse offerings of the NSE, BSE, and other stock exchanges in India, and embark on a rewarding investment journey in one of the fastest-growing economies in the world.