Finance
When Were Defined Contribution Plans Created
Published: January 2, 2024
Learn about the history and origin of defined contribution plans in the world of finance. Explore how these plans were created to benefit individuals and plan for retirement.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Defined contribution plans have become a popular and widely-used investment vehicle, providing individuals with an opportunity to save for retirement while enjoying potential tax advantages. These plans, such as 401(k) plans, have revolutionized the way individuals approach retirement savings and have had a significant impact on the financial landscape. In this article, we will explore the origins and evolution of defined contribution plans and their current prominence in the retirement savings landscape.
A defined contribution plan is a retirement savings plan in which an individual, and often their employer, contribute a set amount to a retirement account. The contributions are invested in various assets, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, with the goal of accumulating wealth over time to support individuals during their retirement years. The key characteristic of defined contribution plans is that the contributions made by individuals and employers are defined, while the eventual payout during retirement is dependent on the performance of the investments.
The concept of defined contribution plans can be traced back to the early roots of retirement savings programs. However, it was not until the mid-20th century that the modern form of defined contribution plans started to emerge. These plans were initially designed as a supplement to traditional pension plans, which were prominent during that time.
Continued in next section…
Early Roots of Defined Contribution Plans
The origins of defined contribution plans can be traced back to the early 19th century when employee savings plans began to gain popularity in Europe. These plans allowed workers to contribute a portion of their wages towards a retirement fund, which would be invested on their behalf. However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that defined contribution plans started taking shape in the United States.
One of the earliest examples of a defined contribution plan in the U.S. was the creation of the TIAA (Teachers Insurance and Annuity Association) in 1918. The TIAA was established to provide retirement benefits for teachers, and it operated as a fully funded defined contribution plan. Teachers would make contributions to the plan, and those contributions would be invested in a diversified portfolio managed by the TIAA. The success of the TIAA paved the way for other similar defined contribution plans in various industries.
During the Great Depression in the 1930s, the government introduced the Social Security Act, which provided a form of defined contribution plan for retirement benefits. Under this Act, workers would contribute a portion of their wages to a government-run fund, which would then provide them with retirement benefits. While Social Security is primarily a pay-as-you-go system, with current workers funding the benefits of current retirees, it can be seen as an early form of defined contribution plan.
Continued in next section…
Rise of Pension Plans
In the mid-20th century, pension plans emerged as the dominant retirement savings vehicle. These plans were known as defined benefit plans, where employers would promise to pay retirees a specific monthly income for the rest of their lives. The responsibility of investing and managing the funds to meet these payment obligations rested on the employer.
Pension plans gained popularity among employers as they provided a stable and predictable retirement income for their employees. They offered a sense of security and alleviated the burden of retirement savings from the individual. Companies that offered pension plans attracted top talent and fostered employee loyalty.
During the post-World War II era, pension plans became more prevalent and widespread. The passage of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) in 1974 further solidified their importance in the retirement landscape. ERISA established guidelines and regulations to protect the rights and interests of employees participating in these plans.
However, despite the many advantages of pension plans, they also had some drawbacks. The burden of funding these plans fell solely on the employers, placing a considerable financial strain on them. As the workforce demographics shifted and life expectancies increased, pension plans became increasingly expensive to maintain. Furthermore, they provided limited flexibility for individuals in terms of managing and investing their retirement funds.
Continued in next section…
Advent of 401(k) Plans
The advent of 401(k) plans in the early 1980s was a game-changer in the retirement savings landscape. These plans were named after a section of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code and initially started as a provision to allow employees to defer a portion of their salary into a tax-advantaged retirement account.
Originally, 401(k) plans were seen as a supplement to traditional pension plans, giving employees an opportunity to save additional funds for retirement. However, over time, they gained popularity and started replacing pension plans as the primary retirement savings vehicle offered by employers.
One of the key benefits of 401(k) plans is the ability for individuals to control their retirement savings. Unlike pension plans, where the employer assumes the responsibility of managing investments, 401(k) plans allow employees to choose from a range of investment options to tailor their portfolio to their risk tolerance and financial goals.
Another significant advantage of 401(k) plans is the tax advantages they offer. Contributions to these plans are typically made on a pre-tax basis, meaning that the income contributed to the plan is not taxed until it is withdrawn during retirement. This provides individuals with an opportunity to reduce their taxable income during their working years and potentially benefit from lower tax obligations.
Employers often provide matching contributions to 401(k) plans, where they contribute a certain percentage of the employee’s salary into the retirement account. This matching feature serves as an additional incentive for employees to participate in the plan and maximizes the potential for greater retirement savings.
Continued in next section…
Evolution and Expansion of Defined Contribution Plans
Since their inception, defined contribution plans have evolved and expanded to meet the changing needs and preferences of individuals and employers. One notable development is the increasing popularity of employer-sponsored 401(k) plans, which have become the de facto retirement savings option for many Americans.
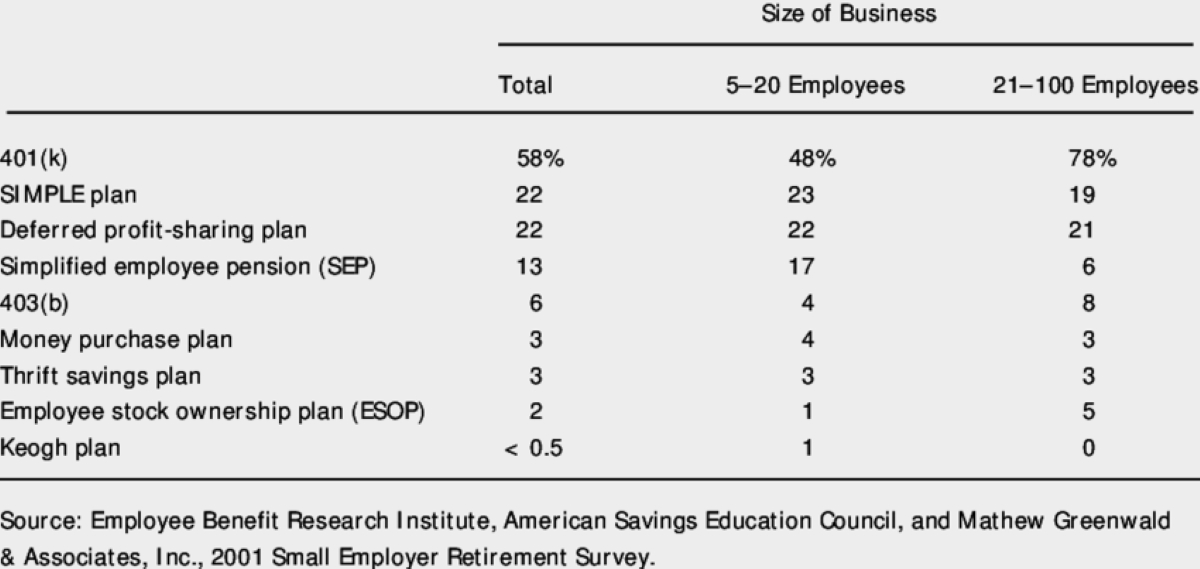
In addition to traditional 401(k) plans, other types of defined contribution plans have emerged, such as the SIMPLE IRA (Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees), SEP IRA (Simplified Employee Pension Individual Retirement Account), and the Roth 401(k). These variations provide individuals and employers with more flexibility and customized options to cater to their specific circumstances.
Technological advancements have also played a role in the evolution of defined contribution plans. Online platforms and mobile apps have made it easier for individuals to track their contributions, monitor their investments, and make adjustments to their portfolios. This accessibility and transparency have empowered individuals to take a more active role in managing their retirement savings.
Furthermore, the concept of automatic enrollment has gained popularity in recent years. Automatic enrollment features allow employers to automatically enroll eligible employees in the company’s 401(k) plan, with the option to opt-out if desired. This has proven to be an effective strategy in increasing plan participation and ensuring more individuals are saving for retirement.
Additionally, the passage of legislation, such as the Pension Protection Act of 2006 in the United States, has further influenced the expansion of defined contribution plans. This act introduced features like target-date funds, which automatically adjust the asset allocation based on an individual’s age and retirement date. It aimed to simplify the investment process and provide individuals with a more hands-off approach to managing their retirement savings.
Continued in next section…
Current Landscape of Defined Contribution Plans
In the present-day financial landscape, defined contribution plans continue to dominate the retirement savings arena. They have become a cornerstone for retirement planning, offering individuals and employers a flexible and customizable approach to long-term financial security.
Employer-sponsored 401(k) plans remain the most prevalent type of defined contribution plan. According to recent statistics, around 80% of large companies and over 50% of small businesses offer a 401(k) plan to their employees. These plans allow individuals to contribute a portion of their salary while enjoying potential tax advantages and employer matching contributions.
The investment options available within defined contribution plans have also expanded significantly. Participants can choose from a range of mutual funds, target-date funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and even self-directed brokerage options, providing individuals with more control over their investment strategies.
Furthermore, the rise of digital investment platforms, often referred to as robo-advisors, has made the process of managing investments within defined contribution plans more accessible and cost-effective. Robo-advisors use algorithmic technology to provide personalized portfolio recommendations based on an individual’s goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Employers are increasingly recognizing the importance of financial wellness programs and integrating them into their defined contribution plans. These programs provide resources and education to help employees make informed financial decisions, including retirement planning, budgeting, and debt management. By promoting financial literacy, employers aim to improve overall employee financial well-being.
Another notable development in the current landscape is the focus on automatic features within defined contribution plans. Auto-enrollment and auto-escalation features have gained traction, aiming to increase employee participation and savings rates. Auto-enrollment automatically enrolls eligible employees in the plan, while auto-escalation gradually increases their contribution rate over time.
Continued in next section…
Impact and Future Trends of Defined Contribution Plans
The impact of defined contribution plans on retirement savings and financial planning cannot be overstated. These plans have empowered individuals to take control of their retirement future, providing flexibility, tax advantages, and investment options. However, there are both positive and negative implications to consider.
On the positive side, defined contribution plans have expanded access to retirement savings for a broader population. Individuals who may not have had access to traditional pension plans now have the opportunity to participate in employer-sponsored plans and accumulate wealth over time. This helps promote a culture of saving and financial responsibility.
Furthermore, defined contribution plans provide individuals with the flexibility to customize their investment strategy and actively manage their retirement savings. They have the potential to build substantial wealth over time, especially when coupled with employer matching contributions and diligent investment choices.
However, there are some concerns associated with defined contribution plans. One significant issue is the responsibility and burden of investment decisions falling on the individuals. Not everyone may have the knowledge, expertise, or time to effectively manage their retirement portfolio, leading to suboptimal investment outcomes.
Another challenge is the potential for inadequate savings rates. Individuals may not contribute enough to their defined contribution plans, which could result in insufficient funds for retirement. This highlights the importance of education and financial wellness programs to encourage appropriate contributions and promote long-term financial planning.
In terms of future trends, several factors are shaping the evolution of defined contribution plans. One prominent trend is the increasing integration of digital technology and artificial intelligence in retirement planning. Robo-advisory platforms and online tools will likely continue to enhance the user experience, providing personalized recommendations and simplified investment management.
Additionally, the focus on financial wellness programs is expected to grow. Employers will continue to offer comprehensive financial education and resources within their defined contribution plans, helping employees make informed decisions and improve their overall financial well-being.
The concept of sustainable investing is also gaining traction within defined contribution plans. More individuals are seeking to align their investments with their values, focusing on companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices. This trend is likely to shape the investment options available within defined contribution plans in the future.
Continued in next section…
Conclusion
Defined contribution plans have revolutionized the retirement savings landscape, providing individuals with flexible and customizable options to build wealth for their future. From their early roots in the 20th century to the prevalence of 401(k) plans today, these retirement savings vehicles have had a profound impact on how individuals plan and save for retirement.
Defined contribution plans have brought about a shift in responsibility, placing the onus on individuals to actively manage their retirement savings. While this increased control allows for personalized investment strategies, it also places the burden of investment decisions and potential risks on individuals themselves. Therefore, financial education and support are crucial to ensure individuals make informed decisions and maximize the potential of their defined contribution plans.
The current landscape of defined contribution plans showcases the dominance of 401(k) plans, along with advancements in technology and the availability of a wide range of investment options. Additionally, the emphasis on financial wellness programs and automatic features demonstrates the ongoing efforts to improve participant outcomes and increase retirement savings rates.
Looking ahead, future trends in defined contribution plans will continue to leverage technology, providing individuals with more accessible tools and personalized recommendations. Financial wellness programs will play a vital role in promoting financial literacy and helping individuals make sound financial decisions.
While defined contribution plans have their advantages and challenges, they have undoubtedly transformed the retirement savings landscape, offering individuals more control over their financial futures. With continued innovation and focus on participant outcomes, defined contribution plans will likely remain a cornerstone of retirement planning for years to come.