Finance
How Many Credit Hours Is A Bachelor Degree
Published: January 11, 2024
Discover the credit hours required for a bachelor's degree in finance. Find out the number of classes needed to obtain your finance degree and plan your academic journey.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Obtaining a bachelor’s degree is a significant milestone in one’s academic journey. It opens up a world of opportunities and is often considered the first step towards a successful career. However, one question that often arises when considering a bachelor’s degree is how many credit hours it requires.
A credit hour is a unit that represents the amount of time spent in a classroom or engaged in coursework. It is a measure of the academic load and determines the amount of work a student needs to complete to earn a degree. The number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree can vary depending on various factors, such as the specific program and the institution offering the degree.
In this article, we will explore what constitutes a bachelor’s degree, understand the concept of credit hours, and delve into the typical credit hour requirements for bachelor’s degrees across different fields. Additionally, we will examine the factors that can affect credit hour requirements and discuss flexible credit options that students may have. Understanding credit hour requirements is crucial in navigating the path towards earning a bachelor’s degree and ensuring a successful academic journey.
What Constitutes a Bachelor Degree
A bachelor’s degree is an undergraduate academic degree conferred upon completion of a specific program of study. It typically signifies the completion of a comprehensive course of study in a specific field, such as business, engineering, psychology, or any other discipline offered by a university or college.
To earn a bachelor’s degree, students are required to fulfill a set of academic requirements, which may include completing a certain number of credit hours, passing specific courses, and fulfilling general education requirements. The exact structure and requirements of a bachelor’s degree can vary based on the institution and the chosen field of study.
Most bachelor’s degree programs consist of a combination of major-specific courses and general education or elective courses. Major-specific courses focus on developing expertise in a particular discipline and delve deeper into advanced concepts and theories. General education courses, on the other hand, aim to provide students with a well-rounded education by covering subjects outside their major, such as humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences.
Furthermore, some bachelor’s degree programs may also require students to complete a capstone project, internship, or thesis to demonstrate their mastery of the subject matter. These requirements not only serve as a culmination of the student’s academic journey but also help prepare them for real-world applications and challenges in their chosen field.
Overall, a bachelor’s degree encompasses a comprehensive curriculum that combines specialized knowledge in a chosen field with a broad understanding of various subjects. It equips students with the skills, knowledge, and critical thinking abilities necessary to pursue further education or enter the workforce in their desired career path.
Credit Hours and Bachelor Degrees
Credit hours play a crucial role in determining the workload and requirements of a bachelor’s degree. They are a measure of the time and effort a student needs to invest in their coursework to progress towards completing their degree.
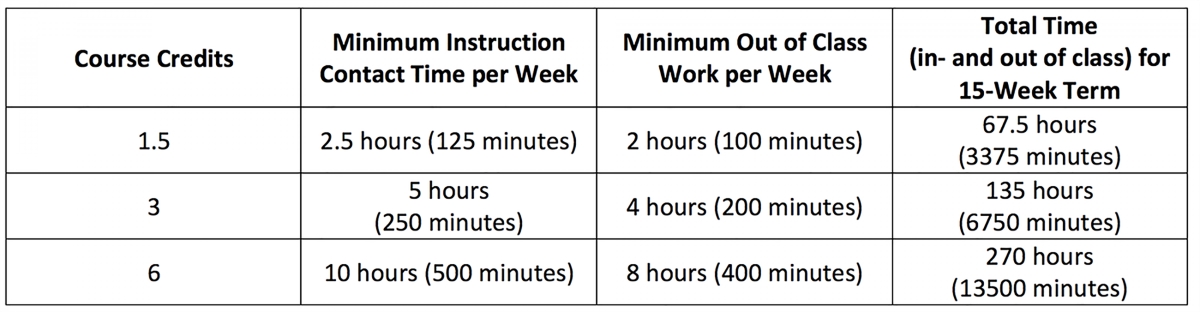
Typically, each course in a bachelor’s degree program is assigned a specific number of credit hours. The total number of credit hours required to earn a degree depends on the institution and the specific program of study. It is important to note that credit hour requirements can vary significantly across different fields of study.
For example, a bachelor’s degree in liberal arts may require around 120 credit hours for completion, while a bachelor’s degree in engineering or a STEM discipline might require a higher number due to the technical nature of the coursework. The number of credit hours for each course may also vary, ranging from one to six credit hours, depending on factors such as the complexity and depth of the subject matter.
As students progress through their bachelor’s degree program, they accumulate credit hours by successfully completing their courses. These credit hours contribute towards fulfilling the overall degree requirements. In addition to major-specific courses, students are usually required to take a certain number of credit hours in general education courses to ensure a well-rounded education.
It is essential for students to carefully plan their course selections to ensure they fulfill the necessary credit hour requirements for their chosen degree program. Academic advisors and department faculty are valuable resources who can guide students in selecting the appropriate courses to meet their degree requirements and academic goals.
In some cases, students may have the opportunity to earn credit hours through alternative means, such as Advanced Placement (AP) courses, Dual Enrollment programs, or credit for prior learning assessment. These options allow students to earn credits before enrolling in a bachelor’s degree program or demonstrate proficiency in a subject to bypass certain course requirements. Such flexible credit options can help students expedite their degree completion or tailor their coursework to align with their specific interests and goals.
Overall, credit hours are an integral part of bachelor’s degree programs, serving as a quantifiable measure of academic progress and a key determinant of degree completion. Understanding the credit hour requirements for a specific program is vital for students to plan their academic journey effectively and make informed decisions regarding course selection and workload.
Typical Credit Hour Requirements for Bachelor Degrees
The credit hour requirements for a bachelor’s degree can vary depending on the field of study, the institution, and the specific program. However, there are some general guidelines and common trends when it comes to typical credit hour requirements for bachelor degrees.
On average, most bachelor’s degree programs require anywhere between 120 to 130 credit hours for completion. This usually translates to about 40 to 45 courses in total. These credit hours are distributed among major-specific courses, general education requirements, electives, and any additional requirements specific to the program.
Major-specific courses make up a significant portion of the credit hour requirements and can range from 50 to 70 credit hours in total. These courses are designed to provide in-depth knowledge and skills in the chosen field of study and may be further divided into lower-level and upper-level courses.
General education requirements typically account for around 30 to 45 credit hours and aim to give students a well-rounded education by exposing them to various disciplines outside their major. These requirements often include courses in areas such as English composition, mathematics, natural sciences, social sciences, arts, and humanities.
Elective courses provide students with the flexibility to explore other areas of interest or specialize further within their major. The number of credit hours allotted to electives can vary, but it is typically around 15 to 25 credit hours. These courses can be chosen from a range of options offered by the institution, allowing students to customize their degree based on their interests and career goals.
It is important to note that credit hour requirements can be influenced by accreditation standards and specific program requirements. For example, some professional or highly specialized fields may have additional prerequisites or clinical or practical components that require more credit hours.
Additionally, credit hour requirements may also vary based on the mode of study. For students pursuing a bachelor’s degree on a part-time basis or through online programs, the credit hour requirements may be spread out over a longer period, allowing for more flexibility and accommodating work or other commitments.
Ultimately, the credit hour requirements for a bachelor’s degree are designed to ensure that students acquire the necessary knowledge and skills in their chosen field and graduate with a well-rounded education. It is important for prospective students to review the specific credit hour requirements for the programs they are interested in to make informed decisions and plan their academic journey accordingly.
Factors Affecting Credit Hour Requirements
The credit hour requirements for a bachelor’s degree can be influenced by several factors. These factors can vary depending on the field of study, the institution, and the specific program. Understanding these factors is essential for students to have a clear understanding of the workload and time commitment required to complete their degree.
1. Field of Study: Different fields of study have varying credit hour requirements. Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) disciplines often have higher credit hour requirements due to the complex and technical nature of the coursework. On the other hand, liberal arts or social sciences programs may have relatively lower credit hour requirements.
2. Program Accreditation: Accreditation bodies may set specific credit hour requirements for certain programs to ensure that graduates meet the industry standards and requirements. These requirements aim to maintain the quality and rigor of the program and ensure that graduates are well-prepared for their chosen profession.
3. Program Requirements: Some programs may have additional requirements or prerequisites that can impact the credit hour requirements. For example, a nursing program may have clinical rotations and practical components that require additional credit hours to be completed.
4. Credit Transfer: Transfer students who have completed coursework at another institution may have some of their credits transferred towards their bachelor’s degree. The acceptance of transfer credits can affect the total credit hour requirements, allowing students to complete their degree in a shorter time frame.
5. Prior Learning Assessment: Some institutions offer the option of assessing prior learning through examinations or portfolio evaluations. This can allow students to earn credit hours for knowledge and skills they have acquired outside of formal coursework, further impacting the credit hour requirements.
6. Dual Enrollment or Advanced Placement (AP) Courses: High school students who have taken dual enrollment courses or AP courses and have earned college credits may have these credits applied towards their bachelor’s degree. This can reduce the credit hour requirements and expedite the degree completion process.
7. Study Mode: The mode of study, such as full-time, part-time, or online, can also impact credit hour requirements. Part-time or online programs often provide more flexibility, allowing students to spread out their coursework over a longer period, resulting in lower credit hour requirements per semester.
It is important for students to consult with academic advisors or program coordinators to understand the specific factors affecting credit hour requirements for their chosen program. They can provide guidance on credit transfer policies, prerequisites, and any other requirements that may impact the credit hour workload for each semester.
Flexible Credit Options for Bachelor Degrees
Flexible credit options provide students with alternative pathways to earning credits towards their bachelor’s degree. These options allow students to tailor their educational experience, expedite their degree completion, or gain credit for prior learning. Here are some common flexible credit options:
1. Advanced Placement (AP) Courses: High school students can take AP courses and exams, which assess their mastery of college-level material. Depending on the exam score, students may be eligible to receive college credits, reducing the overall credit hour requirements for their bachelor’s degree.
2. Dual Enrollment Programs: Some high schools offer dual enrollment programs where students can take college-level courses while still in high school. These credits can often be transferred to a bachelor’s degree program, allowing students to start their college education and earn credits ahead of time.
3. Credit for Prior Learning Assessment: Some colleges and universities offer assessments to evaluate a student’s knowledge and skills acquired through work experience, military training, or self-study. If a student demonstrates proficiency in a particular subject, they may be granted credit hours for that coursework, thereby reducing the overall credit hour requirements.
4. Transfer Credits: Students who have completed coursework at another institution can transfer their credits towards their bachelor’s degree. The credits are evaluated for equivalency, and if approved, they can shorten the time and credit hour requirements needed to complete the degree.
5. Online and Accelerated Programs: Many universities now offer online or accelerated programs that allow students to complete their coursework at a faster pace. These programs often have flexible scheduling options and condensed courses, enabling students to complete their degree in a shorter time and with fewer credit hours.
6. Professionally-Based Experiences: Some bachelor’s degree programs offer opportunities for students to gain credit through internships, co-op programs, or fieldwork. These experiences allow students to apply their academic knowledge in real-world settings and earn credit hours while gaining practical skills and industry insights.
It is important for students to consult with their academic advisors or admissions office to understand the specific policies and guidelines for flexible credit options at their institution. They can provide information on eligibility criteria, credit transfer policies, and potential credit hour reductions.
By taking advantage of flexible credit options, students can personalize their educational journey, save time and money, and accelerate their progress towards earning a bachelor’s degree.
Importance of Credit Hour Requirements in Bachelor Degrees
Credit hour requirements play a crucial role in bachelor’s degree programs and are of significant importance for both students and institutions. Here are some key reasons why credit hour requirements are essential:
1. Structured Academic Progression: Credit hour requirements provide a structured framework for students to progress through their bachelor’s degree program. They ensure that students complete the necessary coursework and gain the required knowledge and skills in their field of study, ensuring a comprehensive education.
2. Time Management and Course Planning: Credit hour requirements help students effectively manage their time and plan their course selections. By having a clear understanding of the credit hours needed per semester, students can create a balanced schedule that aligns with their personal and professional commitments.
3. Graduation Completion and Degree Attainment: Credit hour requirements serve as a benchmark for students to track their progress towards degree completion. Meeting the specified credit hour requirements is a necessary step to receive a bachelor’s degree, ensuring that students have met the academic qualifications necessary for graduation.
4. Quality Assurance and Accreditation: Credit hour requirements are set and monitored by accreditation bodies to ensure the quality of education in bachelor’s degree programs. The completion of specific credit hours demonstrates that students have met the academic standards and requirements set by the accrediting agencies, ensuring the rigor and reputation of the institution and program.
5. Transferability and Mobility: Credit hour requirements play a crucial role in credit transfer and mobility. Consistent credit hour standards make it easier for students to transfer their credits between institutions if they decide to change their program or transfer to another educational institution, allowing them to continue their education seamlessly.
6. Career and Professional Advancement: Many professional fields and employers require a bachelor’s degree as a minimum qualification. Meeting the credit hour requirements and earning a bachelor’s degree enhances job prospects and opens up opportunities for career advancement and higher earning potential.
7. Validation of Learning Outcomes: Credit hour requirements ensure that students have completed a certain amount of coursework and have had the opportunity to demonstrate their learning outcomes in a structured academic setting. These requirements validate the acquisition of knowledge and skills necessary for success in the chosen area of study.
It is important for institutions to establish appropriate credit hour requirements that are aligned with industry standards, academic rigor, and the overall goals of the bachelor’s degree program. By setting clear credit hour requirements, institutions can ensure they are equipping students with the necessary knowledge and skills to thrive in their professional lives.
Conclusion
Credit hour requirements are a fundamental aspect of bachelor’s degree programs, providing structure and guidance to students as they progress towards earning their degree. Understanding these requirements is essential for students to plan their academic journey effectively and make informed decisions about their coursework and workload.
By completing the required credit hours, students ensure that they meet the academic qualifications necessary for graduation and gain the knowledge and skills necessary for success in their chosen field. Credit hour requirements also serve as a quality assurance measure, ensuring that institutions uphold the standards set by accrediting bodies and provide a rigorous education experience.
Flexible credit options, such as Advanced Placement (AP) courses, dual enrollment programs, and credit for prior learning assessments, provide students with opportunities to expedite their degree completion, personalize their educational experience, and gain credit for previous knowledge and skills.
Furthermore, factors such as the field of study, program requirements, transfer credits, and study mode can affect the specific credit hour requirements for a bachelor’s degree. It is important for students to consult with academic advisors and program coordinators to understand these factors and develop a plan that aligns with their academic goals and aspirations.
In conclusion, credit hour requirements are an essential aspect of bachelor’s degree programs, serving as a roadmap for students’ academic progress and degree attainment. By meeting these requirements, students gain a comprehensive education, fulfill accreditation standards, and enhance their career prospects. It is crucial for students to be well-informed and navigate their credit hour requirements strategically to make the most of their bachelor’s degree journey.