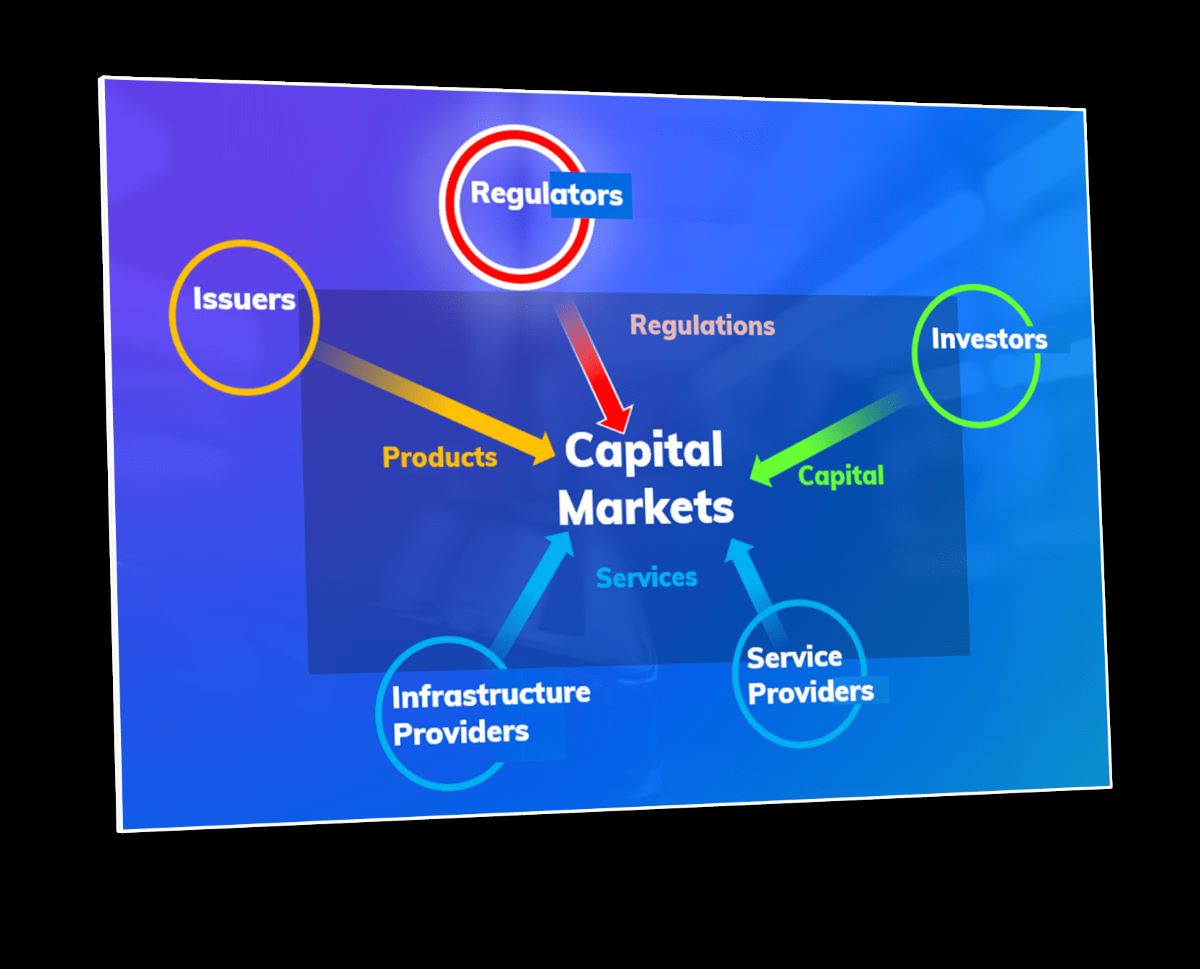
Finance
What Is The M&A Market
Published: February 23, 2024
Explore the current trends and dynamics of the M&A market in the finance industry. Understand the impact of mergers and acquisitions on businesses and the economy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
**
Introduction
**
The M&A market is a dynamic and integral component of the global economy. Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) play a pivotal role in shaping the business landscape, driving growth, and fostering innovation across various industries. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the M&A market, encompassing its definition, types of transactions, underlying reasons, the intricate process involved, factors influencing the market, and current trends.
The realm of M&A is characterized by intricate negotiations, strategic alliances, and transformative transactions that reshape the corporate world. As businesses continually seek opportunities for expansion, diversification, and market consolidation, the M&A market remains a fundamental avenue for achieving these objectives. Understanding the dynamics and nuances of M&A transactions is crucial for entrepreneurs, investors, and industry professionals alike, as it empowers them to navigate the complexities of this dynamic marketplace.
By delving into the intricacies of M&A, we can gain valuable insights into the forces driving the global economy, the competitive strategies adopted by businesses, and the evolving trends that shape various industries. This article aims to demystify the multifaceted nature of M&A, shedding light on its significance and impact on the corporate landscape. Whether you are a seasoned professional or an aspiring entrepreneur, exploring the world of M&A can provide valuable perspectives and strategic acumen that are indispensable in today's fast-paced and competitive business environment.
The subsequent sections will delve into the fundamental aspects of the M&A market, offering a comprehensive exploration of its various dimensions. From understanding the diverse types of M&A transactions to analyzing the underlying motives that drive such activities, this article is designed to provide a holistic and insightful perspective on the dynamic realm of mergers and acquisitions. Let's embark on this enlightening journey to unravel the intricacies of the M&A market and gain a deeper appreciation for its profound impact on the global business landscape.
**
Word count: 265
**
Definition of M&A
**
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) refer to the consolidation of companies or assets through various financial transactions, such as mergers, acquisitions, consolidations, or tender offers. In essence, M&A activities involve the combination of two or more entities to form a single, integrated business entity or the acquisition of one company by another.
**
At its core, a merger occurs when two separate entities amalgamate to form a new, single entity, thereby combining their operations, resources, and strategic objectives. On the other hand, an acquisition involves one company purchasing another, leading to the acquirer gaining control over the acquired company’s assets, operations, and intellectual property. Both mergers and acquisitions are strategic initiatives undertaken by businesses to achieve synergies, expand market presence, enhance capabilities, or gain a competitive advantage.
**
M&A transactions can take various forms, including horizontal mergers where companies operating in the same industry combine forces, vertical mergers involving entities within the same supply chain or distribution network, and conglomerate mergers that involve companies operating in unrelated business domains. Additionally, acquisitions can be categorized as friendly or hostile, depending on the willingness of the target company to be acquired.
**
From a financial perspective, M&A activities are driven by the pursuit of strategic objectives, such as achieving economies of scale, accessing new markets, diversifying product portfolios, or leveraging complementary strengths. These transactions are often facilitated through cash payments, stock swaps, or a combination of both, with the aim of creating value for the stakeholders of the involved entities.
**
Understanding the nuances of M&A is crucial for businesses, investors, and industry professionals, as it enables them to navigate the complexities of corporate restructuring, strategic partnerships, and market expansion. By comprehending the intricacies of M&A transactions, stakeholders can make informed decisions, assess potential risks, and capitalize on the opportunities presented by these transformative business endeavors.
**
Word count: 305
**
Types of M&A Transactions
**
Mergers and acquisitions encompass a diverse array of transaction types, each serving distinct strategic objectives and operational synergies. Understanding the various forms of M&A transactions is essential for comprehending the strategic rationale behind each type and the potential impact on the involved entities and the broader market landscape.
**
1. Merger: A merger involves the consolidation of two or more companies to form a new entity, thereby combining their operations, resources, and organizational structures. Mergers can be categorized into several subtypes, including:
- Horizontal Merger: This type of merger occurs between companies operating in the same industry or sector, aiming to achieve economies of scale, expand market share, and enhance competitiveness.
- Vertical Merger: In a vertical merger, companies within the same supply chain or distribution network merge to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and gain greater control over the production and distribution process.
- Conglomerate Merger: Conglomerate mergers involve companies operating in unrelated business domains, allowing for diversification and risk reduction through the combination of distinct business lines.
**
2. Acquisition: An acquisition occurs when one company purchases another, thereby gaining control over the acquired entity’s assets, operations, and intellectual property. Acquisitions can take various forms, including:
- Friendly Acquisition: In a friendly acquisition, the target company consents to the acquisition, and negotiations are conducted in a cooperative and mutually agreeable manner.
- Hostile Takeover: A hostile takeover involves the acquisition of a company against the wishes of its management, often through direct overtures to the target company’s shareholders.
- Asset Acquisition: In an asset acquisition, the acquiring company purchases specific assets or divisions of the target company, rather than acquiring the entire entity.
**
3. Consolidation: Consolidation refers to the combination of two or more companies to form a new, integrated entity, typically resulting in the dissolution of the original entities. This process involves the reorganization of assets, operations, and corporate structures to create a unified and synergistic business entity.
**
Each type of M&A transaction serves distinct strategic objectives, ranging from achieving market dominance and operational efficiency to diversifying business lines and accessing new markets. By comprehending the nuances of these transaction types, businesses and investors can strategically navigate the complexities of M&A activities and leverage them to drive growth, innovation, and value creation.
**
Word count: 340
**
Reasons for M&A Activity
**
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are driven by a myriad of strategic motives and operational imperatives that compel businesses to engage in transformative transactions. Understanding the underlying reasons for M&A activity is crucial for discerning the strategic rationale behind such endeavors and the potential impact on the involved entities and the broader market landscape.
**
1. Strategic Expansion: M&A activities often serve as a vehicle for strategic expansion, allowing companies to penetrate new markets, gain access to untapped customer segments, and diversify their geographic presence. Through mergers and acquisitions, businesses can achieve rapid market entry and establish a stronger foothold in regions where organic growth may be challenging or time-consuming.
**
2. Economies of Scale: Achieving economies of scale is a compelling driver for M&A transactions, as the consolidation of operations, resources, and infrastructure can lead to cost efficiencies, enhanced productivity, and improved profitability. By leveraging combined strengths and shared resources, merged entities can optimize their cost structures and gain a competitive advantage in their respective industries.
**
3. Synergistic Capabilities: Mergers and acquisitions enable companies to harness synergistic capabilities, combining complementary strengths, expertise, and intellectual assets to create a more formidable and innovative entity. By integrating diverse skill sets, technological proficiencies, and market insights, merged companies can enhance their competitive positioning and drive collaborative innovation.
**
4. Diversification: For businesses seeking to diversify their product portfolios, customer base, or revenue streams, M&A activities offer a strategic pathway to achieve diversification. Through mergers and acquisitions, companies can expand into new industry segments, acquire complementary product lines, and mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on a single market or product category.
**
5. Market Consolidation: M&A transactions are often driven by the imperative to consolidate market share, achieve industry leadership, and fortify competitive positioning. By combining forces with competitors or complementary players, businesses can solidify their market presence, exert greater influence on industry dynamics, and capitalize on emerging opportunities in their respective sectors.
**
6. Access to Resources: Accessing critical resources, such as advanced technologies, intellectual property, distribution networks, or talent pools, is a compelling rationale for engaging in M&A activities. By acquiring entities with valuable resources, companies can bolster their capabilities, drive innovation, and gain a strategic edge in an increasingly competitive business landscape.
**
By comprehending the diverse reasons driving M&A activity, businesses, investors, and industry professionals can gain valuable insights into the strategic imperatives shaping the corporate landscape. These motives underscore the multifaceted nature of M&A transactions and the profound impact they wield on the global business ecosystem.
**
Word count: 370
**
M&A Process
**
The M&A process is a complex and multifaceted endeavor that encompasses various stages, from strategic planning and due diligence to post-merger integration. Understanding the intricacies of the M&A process is essential for businesses embarking on such transactions, as it enables them to navigate the challenges, mitigate risks, and maximize the value created through these transformative endeavors.
**
1. Strategic Planning: The M&A process commences with strategic planning, wherein businesses identify their objectives, assess potential targets or partners, and devise a coherent roadmap for the transaction. This phase involves evaluating the strategic fit, financial feasibility, and synergistic potential of the proposed M&A activity.
**
2. Due Diligence: Conducting comprehensive due diligence is a critical phase of the M&A process, wherein the involved entities meticulously assess each other’s financial, operational, and legal facets. This entails scrutinizing financial records, evaluating assets and liabilities, and appraising the market positioning and growth prospects of the target company.
**
3. Transaction Structuring: Once due diligence is completed, the transaction structuring phase ensues, wherein the terms of the deal, including the purchase price, payment structure, and post-acquisition governance, are meticulously delineated. This phase involves negotiations, contractual agreements, and regulatory compliance to formalize the transaction.
**
4. Regulatory Approval: Depending on the scale and nature of the M&A transaction, obtaining regulatory approvals from relevant authorities may be necessary. This phase involves navigating antitrust regulations, industry-specific compliance requirements, and other legal considerations to secure the necessary approvals for the transaction.
**
5. Integration and Synergy Realization: Following the completion of the transaction, the integration and synergy realization phase comes into play, wherein the merged entities embark on harmonizing their operations, organizational structures, and strategic initiatives. This phase aims to capture synergies, optimize resource utilization, and foster a cohesive and unified corporate entity.
**
6. Post-Merger Evaluation: Post-merger evaluation involves assessing the performance, operational efficacy, and strategic alignment of the merged entities. This phase entails monitoring key performance indicators, addressing operational challenges, and refining the integration strategy to ensure the realization of the intended synergies and strategic objectives.
**
The M&A process is a dynamic and intricate journey that demands meticulous planning, rigorous analysis, and adept execution. By comprehensively understanding the various stages of the M&A process, businesses can adeptly navigate the complexities of these transactions, capitalize on strategic opportunities, and drive sustainable value creation.
**
Word count: 350
**
Factors Affecting the M&A Market
**
The M&A market is influenced by a multitude of factors that shape the landscape of mergers and acquisitions, driving trends, transaction volumes, and strategic imperatives for businesses. Understanding the diverse factors affecting the M&A market is essential for discerning the dynamics of this domain and anticipating the evolving trends that impact corporate transactions and market consolidation.
**
1. Economic Conditions: Fluctuations in macroeconomic conditions, such as interest rates, GDP growth, and market stability, significantly impact M&A activity. Favorable economic conditions, characterized by low interest rates and robust growth, often spur heightened M&A transactions, as businesses capitalize on conducive financial environments to pursue strategic expansion and consolidation.
**
2. Regulatory Environment: The regulatory landscape, encompassing antitrust laws, industry-specific regulations, and cross-border compliance requirements, profoundly influences M&A transactions. Changes in regulatory policies, government interventions, and compliance complexities can either facilitate or impede the execution of M&A activities, shaping the strategic considerations and feasibility of such transactions.
**
3. Market Valuations: Fluctuations in asset valuations, stock market performance, and industry benchmarks impact the attractiveness and feasibility of M&A transactions. Market valuations influence deal pricing, stock-swap ratios, and the perceived value of potential targets, thereby shaping the strategic calculus and financial viability of mergers and acquisitions.
**
4. Technological Disruption: The advent of disruptive technologies, digital transformation, and industry innovation plays a pivotal role in shaping M&A trends. Businesses often engage in M&A activities to acquire technological capabilities, intellectual property, and innovative startups, positioning themselves to capitalize on emerging trends and gain a competitive edge in rapidly evolving markets.
**
5. Geopolitical Considerations: Geopolitical factors, including trade policies, geopolitical tensions, and global market dynamics, exert a significant influence on cross-border M&A transactions. Geopolitical stability, trade agreements, and diplomatic relations impact the feasibility and strategic rationale for international mergers and acquisitions, shaping the global M&A landscape.
**
6. Industry Dynamics: Sector-specific trends, competitive forces, and industry disruptions play a pivotal role in driving M&A activities within distinct sectors. Industry consolidation, technological convergence, and shifting consumer preferences contribute to the strategic imperatives and transaction volumes within various industries, shaping the M&A market dynamics.
**
By comprehending the multifaceted factors influencing the M&A market, businesses, investors, and industry stakeholders can gain valuable insights into the strategic imperatives, market trends, and operational dynamics that underpin mergers and acquisitions. These factors underscore the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of the M&A landscape, shaping the strategic considerations and transactional dynamics within the global business ecosystem.
**
Word count: 350
**
Current Trends in the M&A Market
**
The M&A market is characterized by evolving trends that reflect the dynamic interplay of economic, technological, and strategic forces shaping corporate transactions and market consolidation. Understanding the current trends in the M&A market is crucial for discerning the prevailing dynamics, strategic imperatives, and transformative shifts that influence business transactions and industry landscapes.
**
1. Technology-Driven Transactions: The M&A landscape is witnessing a surge in technology-driven transactions, as businesses seek to acquire innovative startups, digital platforms, and disruptive technologies. Companies are strategically leveraging M&A activities to bolster their technological capabilities, enhance digital transformation initiatives, and gain a competitive edge in rapidly evolving markets.
**
2. Cross-Border Consolidation: Cross-border M&A transactions continue to be a prominent trend, driven by globalization, market access imperatives, and strategic expansion initiatives. Businesses are increasingly pursuing international mergers and acquisitions to gain access to new markets, diversify their geographic presence, and capitalize on emerging opportunities in a globalized business environment.
**
3. Sustainability-Driven M&A: Sustainability considerations are increasingly influencing M&A activities, with businesses prioritizing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in their strategic transactions. Companies are engaging in M&A endeavors to acquire sustainable technologies, enhance their ESG performance, and align their operations with evolving sustainability mandates and stakeholder expectations.
**
4. Healthcare and Biotech Consolidation: The healthcare and biotechnology sectors are experiencing heightened M&A activities, driven by the pursuit of innovative treatments, pharmaceutical advancements, and healthcare technology integration. Companies within these sectors are engaging in strategic mergers and acquisitions to bolster their research capabilities, expand their product portfolios, and address evolving healthcare needs.
**
5. SPAC Transactions: Special purpose acquisition company (SPAC) transactions are increasingly prevalent in the M&A market, offering companies an alternative pathway to go public and access capital. SPAC mergers enable businesses to expedite their listing process, raise funds for expansion, and pursue strategic partnerships, contributing to the diversification of M&A transaction structures.
**
6. Reshaping of Traditional Industries: Traditional industries, such as retail, energy, and manufacturing, are undergoing transformative M&A activities aimed at reshaping their operational models, embracing digitalization, and adapting to evolving consumer preferences. These industries are witnessing strategic consolidations, divestitures, and partnerships to foster resilience and innovation in a rapidly changing business landscape.
**
By staying attuned to the prevailing trends in the M&A market, businesses, investors, and industry professionals can gain strategic insights, anticipate market shifts, and capitalize on emerging opportunities. These current trends underscore the dynamic and transformative nature of the M&A landscape, reflecting the evolving strategies and imperatives that drive corporate transactions and industry realignments.
**
Word count: 350
**
Conclusion
**
The realm of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) embodies a dynamic and multifaceted landscape, characterized by strategic imperatives, transformative transactions, and evolving market trends. As businesses navigate the complexities of the M&A market, it becomes evident that understanding the intricacies of this domain is essential for driving growth, fostering innovation, and shaping the corporate landscape.
**
From the strategic expansion and synergistic consolidation to the pursuit of technological innovation and sustainability-driven transactions, the M&A market reflects the strategic acumen, economic dynamics, and operational imperatives that underpin corporate transactions. The current trends in the M&A market underscore the transformative shifts and strategic considerations shaping industry landscapes, reflecting the evolving strategies and market dynamics that drive corporate transactions and industry realignments.
**
As businesses, investors, and industry stakeholders navigate the M&A landscape, it becomes imperative to comprehend the diverse factors influencing this domain, including economic conditions, regulatory environments, technological disruptions, and industry dynamics. These factors underscore the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of the M&A market, shaping the strategic considerations and transactional dynamics within the global business ecosystem.
**
By delving into the intricacies of M&A, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into the forces driving the global economy, the competitive strategies adopted by businesses, and the evolving trends that shape various industries. Whether pursuing cross-border consolidation, embracing sustainability-driven transactions, or reshaping traditional industries, the M&A market serves as a catalyst for strategic expansion, operational optimization, and market consolidation.
**
As we conclude this exploration of the M&A market, it is evident that mergers and acquisitions play a pivotal role in shaping the business landscape, driving growth, and fostering innovation across various industries. By unraveling the intricacies of the M&A market, stakeholders can gain a deeper appreciation for its profound impact on the global business ecosystem, empowering them to navigate the complexities of this dynamic marketplace and capitalize on the strategic opportunities it presents.
**
Word count: 270
**