Home>Finance>Asset Allocation Fund: Definition, Investments, Types & Examples


Finance
Asset Allocation Fund: Definition, Investments, Types & Examples
Modified: December 30, 2023
Learn about asset allocation funds in finance. Explore the definition, types, examples, and various investment strategies involved in asset allocation.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Asset Allocation Fund: Definition, Investments, Types & Examples
Are you a finance enthusiast looking to expand your investment options? If so, then you may be interested in learning about asset allocation funds. In this blog post, we will dive deep into the world of asset allocation funds, discussing their definition, investments, types, and providing examples. By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of asset allocation funds and how they can fit into your investment portfolio.
Key Takeaways:
- An asset allocation fund is a type of mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that invests in a diverse range of asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash.
- These funds aim to manage risk and maximize returns by diversifying investments across different asset classes based on market conditions and the investor’s risk tolerance.
Definition of Asset Allocation Fund
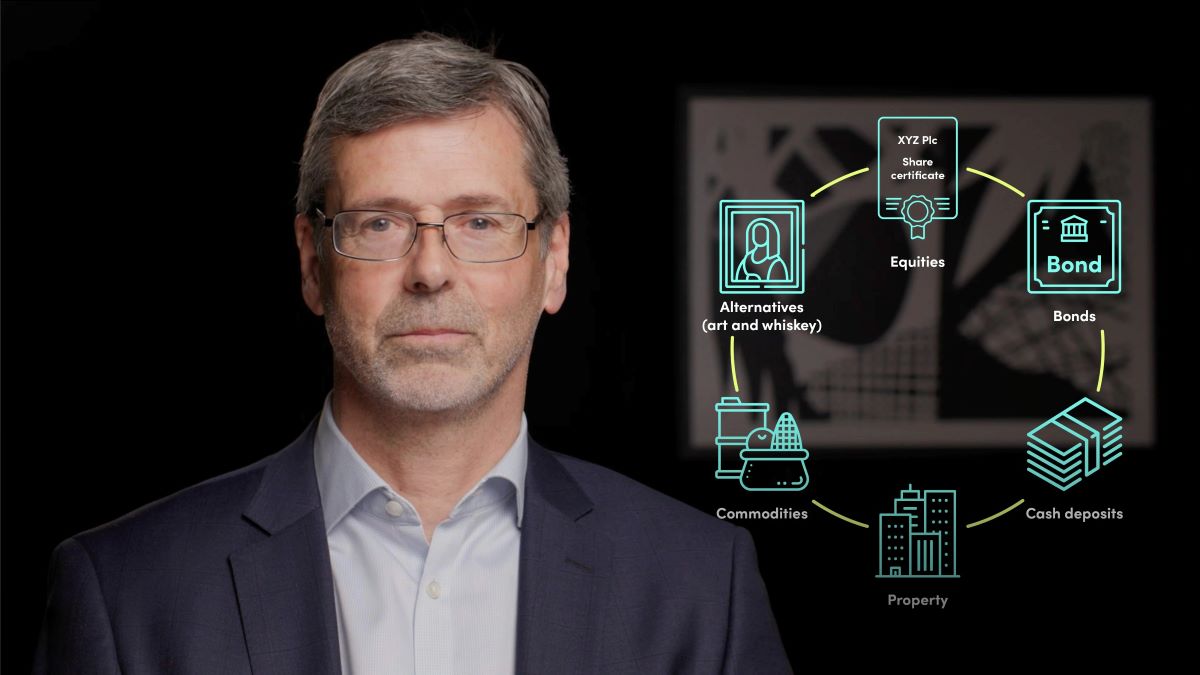
An asset allocation fund is a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that aims to diversify investments across different asset classes to manage risk and maximize returns. These funds hold a mix of stocks, bonds, and cash, with the allocation varying depending on market conditions and the investor’s risk appetite.
Asset allocation funds are designed to provide investors with a one-stop solution for diversifying their investment portfolios. Instead of picking individual stocks or bonds, investors can rely on asset allocation funds to make the investment decisions on their behalf.
Investments in Asset Allocation Funds
Asset allocation funds typically invest in a combination of three main asset classes:
- Stocks: Equity investments provide potential for long-term growth but also come with higher risk.
- Bonds: Fixed-income investments, such as government or corporate bonds, offer more stability and income but with less growth potential.
- Cash: Money market instruments like Treasury bills or short-term certificates of deposit (CDs) provide liquidity and act as a cushion during market downturns.
The specific mix of these assets is determined by the fund manager based on their investment strategy and market conditions. Typically, asset allocation funds aim to strike a balance between growth and stability, tailored to the desired risk level of the investor.
Types of Asset Allocation Funds
There are various types of asset allocation funds, each catering to different risk tolerance levels and investment objectives:
- Conservative Asset Allocation Funds: These funds allocate a larger portion of the portfolio towards fixed-income investments and a smaller percentage towards equities, aiming for lower volatility and stable returns.
- Moderate Asset Allocation Funds: These funds strike a balance between growth and stability, with a moderate allocation between stocks, bonds, and cash.
- Aggressive Asset Allocation Funds: These funds have a higher proportion of equities, aiming for higher growth potential but also exposing investors to higher risk.
- Target-Date Retirement Funds: These funds are designed for retirement planning and gradually shift the asset allocation to become more conservative as the target retirement date approaches.
Examples of Asset Allocation Funds
Here are a few examples of well-known asset allocation funds:
- T. Rowe Price Capital Appreciation Fund: A moderate asset allocation fund that invests in a mix of stocks, bonds, and cash instruments with the goal of long-term capital appreciation.
- Vanguard LifeStrategy Growth Fund: An aggressive asset allocation fund that primarily invests in stocks to pursue long-term capital growth.
- Fidelity Freedom Index 2055 Fund: A target-date retirement fund that allocates investments based on a target retirement year and progressively becomes more conservative over time.
In Conclusion
Asset allocation funds serve as a convenient and efficient way for investors to diversify their portfolios across different asset classes. By investing in these funds, investors can benefit from professional management and the ability to adjust their risk exposure based on market conditions and personal preferences. Whether you are a conservative investor or seeking higher growth potential, there is likely an asset allocation fund that suits your investment goals.
Remember, understanding and assessing your own risk tolerance and investment objectives is crucial before investing in any asset allocation fund. It is always recommended to speak with a qualified financial advisor who can guide you in making informed investment decisions.