Home>Finance>What Is An Asset? Definition, Types, And Examples


Finance
What Is An Asset? Definition, Types, And Examples
Published: October 9, 2023
Learn the definition, types, and examples of assets in finance. Discover the importance of assets for your financial well-being.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
What Is an Asset? Definition, Types, and Examples
Have you ever wondered what exactly an asset is? When it comes to finance, understanding the concept of assets is essential. In this blog post, we will dive deep into the world of assets, exploring their definition, different types, and providing real-life examples. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of assets and how they play a crucial role in managing your finances.
Key Takeaways:
- An asset is something of value that an individual or organization owns. It can be tangible or intangible.
- Understanding the various types of assets – such as financial, physical, and intellectual assets – is vital for effective financial planning.
Defining an Asset
An asset, in simple terms, is something that holds value and is owned by an individual or organization. Assets can be tangible, meaning they have physical existence, or intangible, referring to non-physical assets such as intellectual property.
Assets play a key role in finance as they contribute to a person’s or company’s overall net worth. They can range from personal possessions like a car or a house to financial investments like stocks, bonds, or even a patent for an invention. In essence, assets are resources that provide future economic benefits.
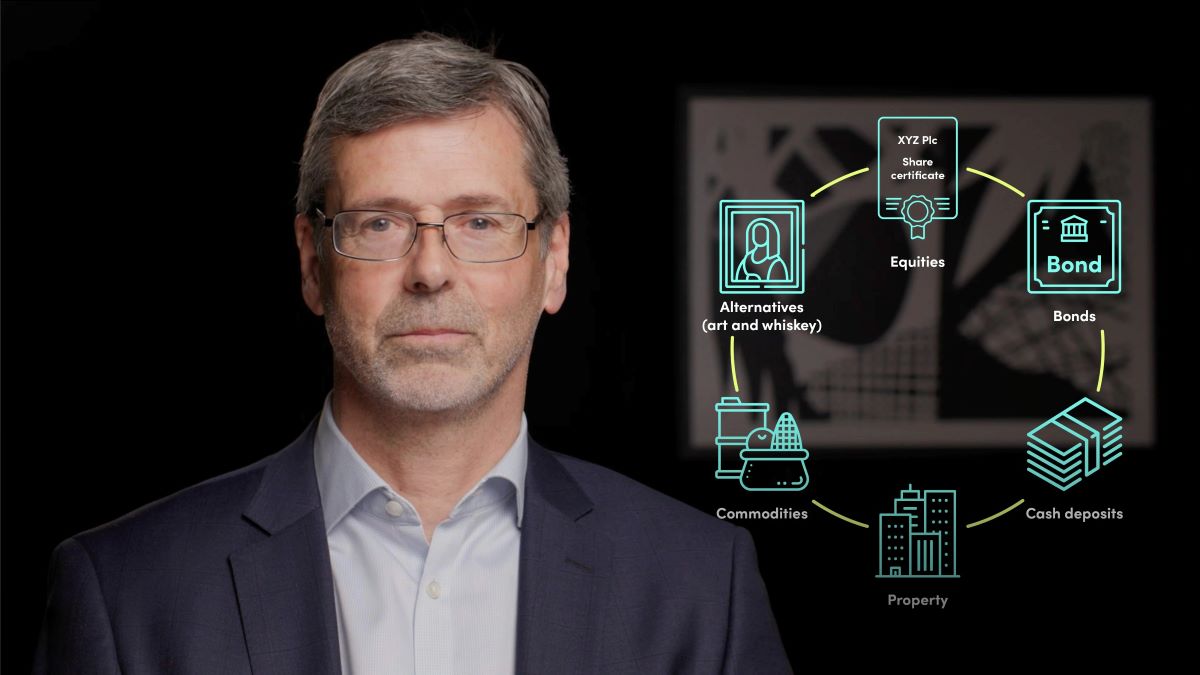
Types of Assets
Now that we understand what an asset is, let’s explore the different types:
- Financial Assets: These include cash, stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other investments that have a monetary value.
- Physical Assets: Tangible assets such as real estate, vehicles, machinery, and equipment fall under this category.
- Intangible Assets: These assets lack physical form but hold significant value. Examples include patents, trademarks, copyrights, and intellectual property.
- Current Assets: Assets that are expected to be consumed or converted into cash within a year, such as inventory or accounts receivable, are categorized as current assets.
- Fixed Assets: Also known as long-term assets, they have a useful life of more than one year, like buildings, land, and large machinery.
Examples of Assets
Let’s put theory into practice with a few real-life examples of assets:
- John owns a house, which serves as a physical asset.
- Sara invests in stocks and bonds, making them financial assets.
- XYZ Corp registers a patent for their innovative product, establishing an intangible asset.
- ABC Corporation acquires a building to expand their operations, demonstrating a fixed asset.
- ABC Corp also purchases inventory to sell in their retail store, classifying it as a current asset.
Assets can vary greatly depending on individual circumstances and business ventures. However, they all share the common characteristic of holding value and contributing to wealth accumulation.
Conclusion
In summary, assets are valuable resources that individuals and organizations own. They can take the form of tangible or intangible assets and play a critical role in financial planning. Being aware of the different types of assets empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their wealth and build a secure future.
By understanding the definition and importance of assets, you now have the knowledge to navigate the complex world of finance with confidence. Remember, investments in various assets can help you grow your net worth and secure a prosperous future.