Home>Finance>Commodity Futures Modernization Act (CFMA) Definition


Finance
Commodity Futures Modernization Act (CFMA) Definition
Published: October 30, 2023
Learn about the Commodity Futures Modernization Act (CFMA) and its impact on finance. Explore the definition and implications of this crucial legislation.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding the Commodity Futures Modernization Act (CFMA) Definition
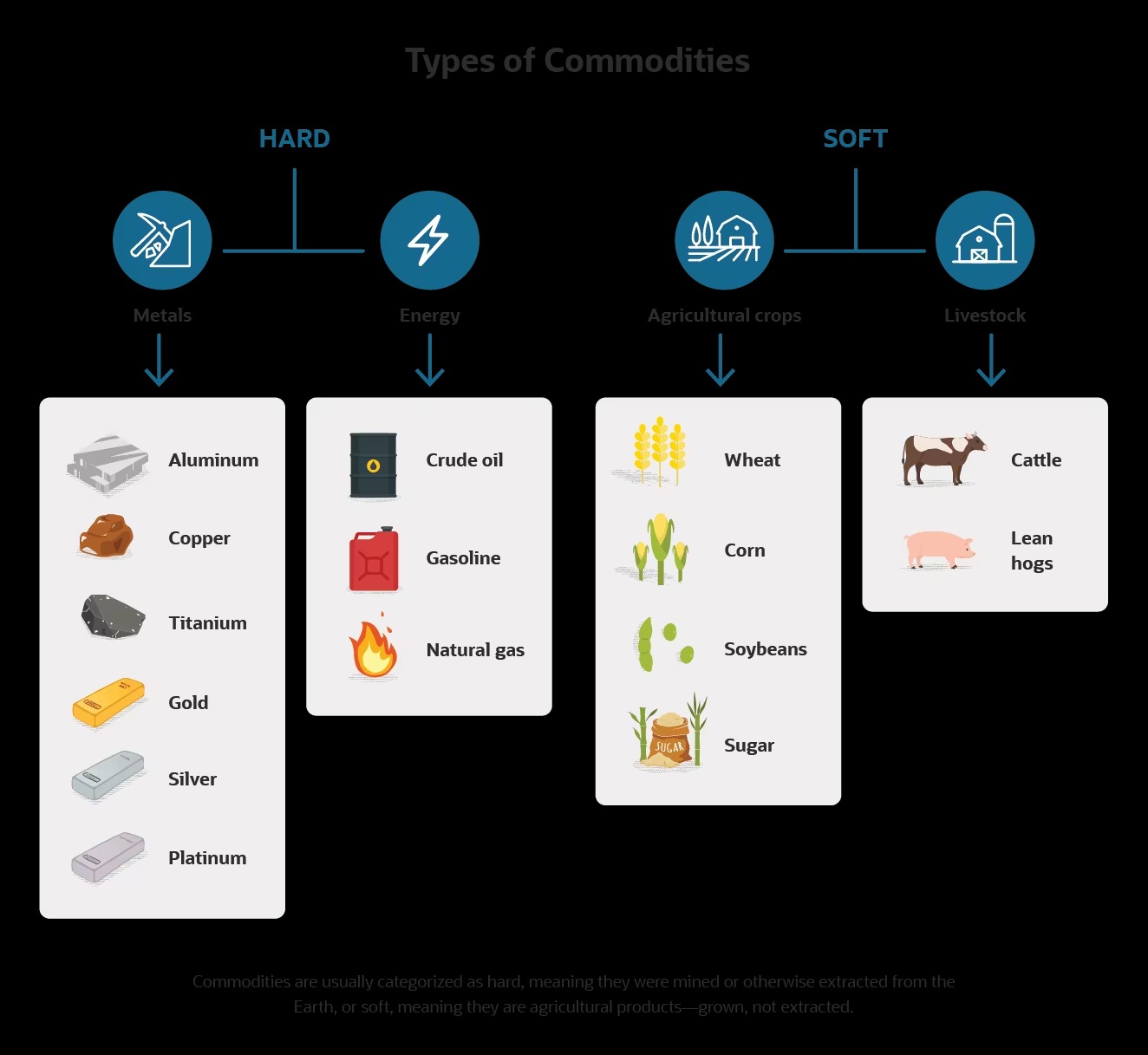
Finance is a broad field that encompasses various aspects of managing and investing money. One important area within finance is the regulation of financial derivatives and commodities trading. In this blog post, we will delve into the Commodity Futures Modernization Act (CFMA) and explore its definition, impacts, and significance in the finance industry.
Key Takeaways:
- The Commodity Futures Modernization Act (CFMA) was enacted in 2000 to provide regulatory framework for financial derivatives and commodities trading.
- CFMA facilitated the expansion of the derivatives market, leading to increased innovation and risk-taking in the financial industry.
The CFMA, passed by the United States Congress in 2000, was a significant piece of legislation that brought about a fundamental change in the regulation of financial derivatives and commodities trading. Its main purpose was to update and modernize existing laws to accommodate the rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Prior to the CFMA, the regulatory framework for these markets was fragmented and outdated, causing regulatory inefficiencies and hindering the growth of financial markets. The Act sought to address these issues by establishing a comprehensive regulatory framework tailored to the complexities of financial derivatives and commodities trading. It aimed to strike a balance between market efficiency and investor protection.
One of the key impacts of the CFMA was the facilitation of the expansion of the derivatives market. By providing legal certainty and regulatory clarity, it encouraged financial institutions to engage in more derivatives transactions. This led to increased innovation and risk-taking, as well as greater market liquidity. The Act also introduced exemptions and exclusions for various types of derivatives, allowing for customized contracts to meet the specific needs of market participants.
The CFMA also introduced the concept of “qualified eligible participants” (QEPs), which exempted certain sophisticated investors from certain regulatory requirements. This provision allowed institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals to actively participate in the derivatives market without being subject to stringent regulations designed for retail investors.
Overall, the Commodity Futures Modernization Act (CFMA) played a momentous role in reshaping the regulation of financial derivatives and commodities trading in the United States. It facilitated market growth, encouraged innovation, and adjusted regulations to better suit the evolving financial landscape. While it provided significant benefits, it also brought challenges and risks, which required continuous monitoring and adaptation in subsequent years.
As we navigate the complex world of finance, it’s crucial to understand important legislation like the CFMA and its impact on the industry. By staying informed and aware, we can make better-informed decisions about our investments and contribute to a more robust and resilient financial system.