Finance
Contract Market Definition
Published: November 2, 2023
Learn about the contract market with our comprehensive definition. Gain insights into how finance professionals navigate this integral aspect of the industry.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Contract Market Definition: Understanding the Basics of Financial Contracts
When it comes to the world of finance, there are numerous terms and concepts that can often be confusing. One such term is contract market. But what exactly does this term mean and how does it affect the financial industry? In this blog post, we will explore the definition of contract market and shed light on its importance in the financial world. So, let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways:
- A contract market refers to a platform or exchange where standardized financial contracts or commodities are traded between buyers and sellers.
- These contracts are typically regulated and governed by specific rules and regulations to ensure fair trading practices.
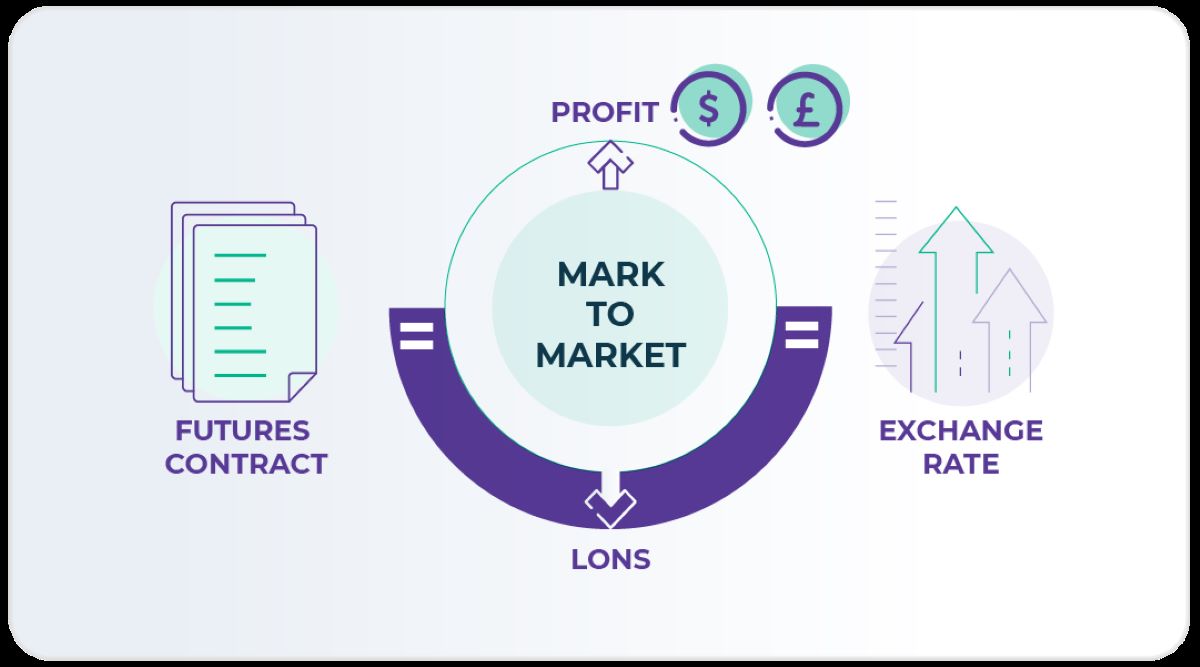
A contract market can be understood as a platform or exchange where standardized financial contracts or commodities are traded between buyers and sellers. These contracts often include futures contracts, options contracts, or other derivatives. Just like a stock market exchange, a contract market serves as a marketplace where traders can enter into agreements to buy or sell a specific asset at a specified price and time in the future.
Now, you might be wondering why contract markets are important and how they function. Well, here are a few key points to help you better understand:
1. Standardization:
Contract markets play a vital role in bringing standardization to financial contracts. Standardization means that the terms and conditions, such as contract size, maturity date, and settlement procedures, are predetermined and cannot be negotiated between participants. This allows for greater liquidity and ease of trading, as market participants can easily compare and exchange these standardized contracts.
2. Regulated Trading:
Contract markets are typically regulated by relevant authorities to ensure fair trading practices and protect both buyers and sellers. The rules and regulations set by these regulatory bodies guide the trading activities on the contract market, ensuring transparency and maintaining market integrity.
It’s important to note that contract markets can operate in various formats, such as physical exchanges or electronic platforms. These platforms provide the necessary infrastructure, technology, and clearings to facilitate trading activities smoothly and securely.
In Conclusion
Understanding contract markets is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the world of finance. By providing a standardized platform for trading financial contracts and commodities, contract markets promote transparency, liquidity, and fair trading practices. Whether you are an investor, trader, or simply interested in finance, knowing the basics of contract markets can help you make informed decisions and stay up-to-date with the ever-changing financial landscape.