Home>Finance>Debt Spread: Definition, Example, Vs. Credit Spread


Finance
Debt Spread: Definition, Example, Vs. Credit Spread
Modified: January 15, 2024
Learn the definition and example of debt spread and how it compares to credit spread in the world of finance. Unlock your understanding of finance today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Debt Spread: Definition, Example, Vs. Credit Spread
In the world of finance, understanding different investment strategies is crucial for making informed decisions. One such strategy that investors often come across is the concept of debt spread. In this blog post, we will delve into the definition of debt spread, provide an example to illustrate its application, and differentiate it from another similar strategy known as credit spread.
Key Takeaways:
- Debt spread refers to the difference in interest rates between two debt instruments or securities.
- Investors utilize debt spread as a means to assess the risk and potential returns associated with different debt products.
What is Debt Spread?
Debt spread, in simple terms, is the variance in interest rates between two different debt instruments or securities. It serves as a valuable tool for investors to compare the risk and potential returns associated with various debt products. By analyzing the debt spread between two securities, investors can assess the overall attractiveness and viability of each investment option.
Think of debt spread as a financial metric that enables investors to gauge the difference in interest rates between two bonds, loans, or other forms of debt instruments. It can also be seen as a reflection of the perceived creditworthiness and overall market conditions.
Example of Debt Spread
Let’s consider an example to better understand debt spread. Suppose an investor is assessing two corporate bonds: Bond A and Bond B. Bond A has an annual interest rate of 4%, while Bond B offers an interest rate of 5%. In this scenario, the debt spread between Bond A and Bond B would be 1%, as the difference between their interest rates is 1 percentage point.
Based on the debt spread, investors can infer that Bond B carries a higher interest rate, suggesting that it may be associated with a higher level of risk. However, the higher interest rate also implies the potential for higher returns. By comparing the debt spread across different debt instruments, investors can make informed decisions that align with their risk appetite and investment goals.
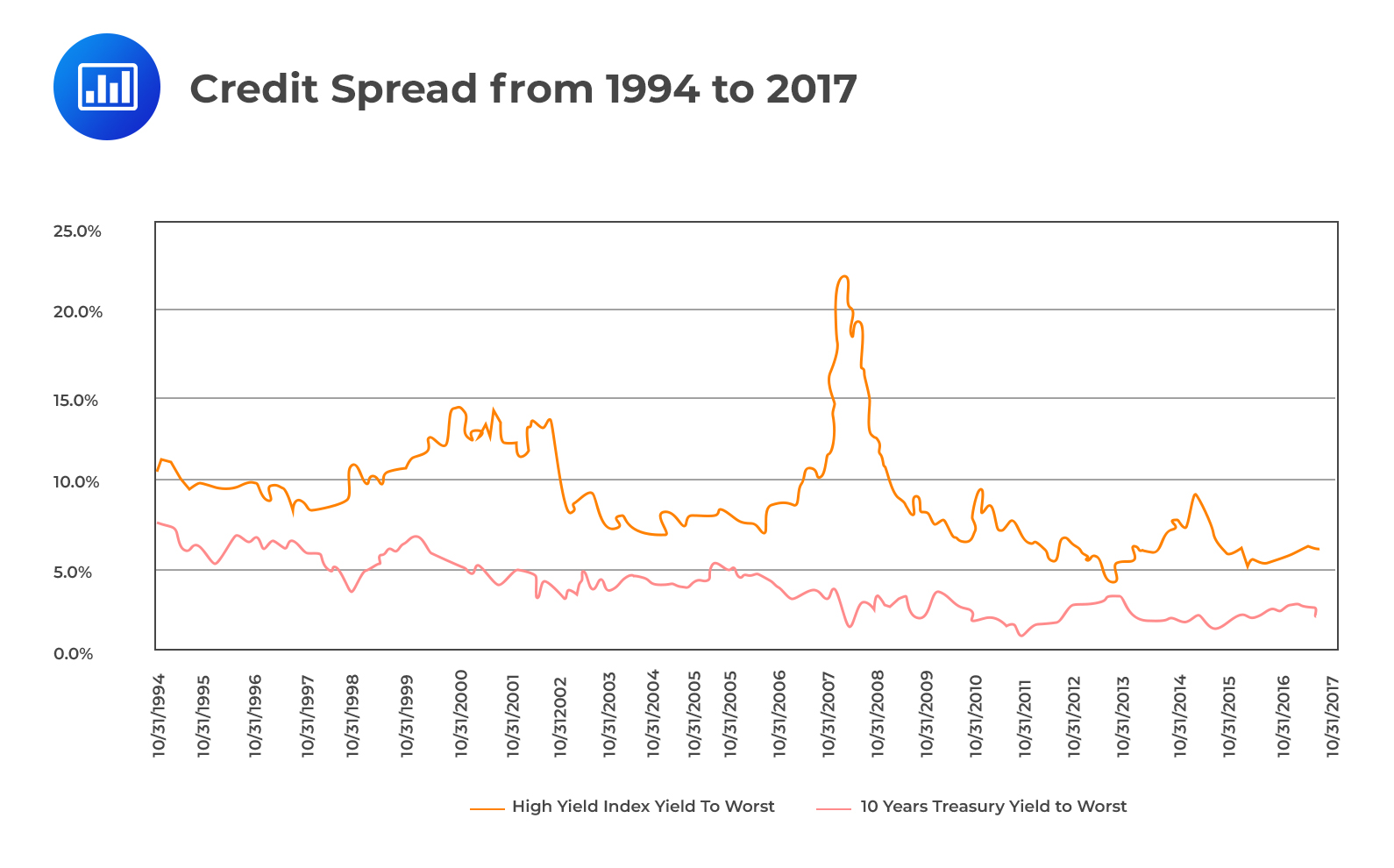
Debt Spread vs. Credit Spread
While debt spread and credit spread both relate to the variance in interest rates, there is a fundamental difference between the two. Debt spread refers to the difference in interest rates between two different debt instruments, whereas credit spread focuses on the difference in interest rates between a corporate bond and a risk-free security, such as a Treasury bond.
Essentially, debt spread provides insights into the variances between debt instruments, while credit spread sheds light on the additional compensation investors receive for taking on credit risk when investing in corporate bonds compared to risk-free securities.
- Debt Spread:
- Compares interest rates between two different debt instruments.
- Assesses the risk and potential returns associated with each debt product.
- Credit Spread:
- Compares interest rates between a corporate bond and a risk-free security.
- Reflects the compensation for taking on credit risk.
By understanding the distinctions between debt spread and credit spread, investors can gain a deeper understanding of the nuances within the world of finance and make better-informed investment decisions.
To summarize, debt spread is a valuable metric for assessing the variances in interest rates between different debt instruments. By comparing debt spreads, investors can evaluate the risk and potential returns associated with each investment option. It is also essential to differentiate debt spread from credit spread, as they focus on different aspects of interest rate variances. By grasping these concepts, investors can navigate the financial landscape with more confidence and make informed investment choices.