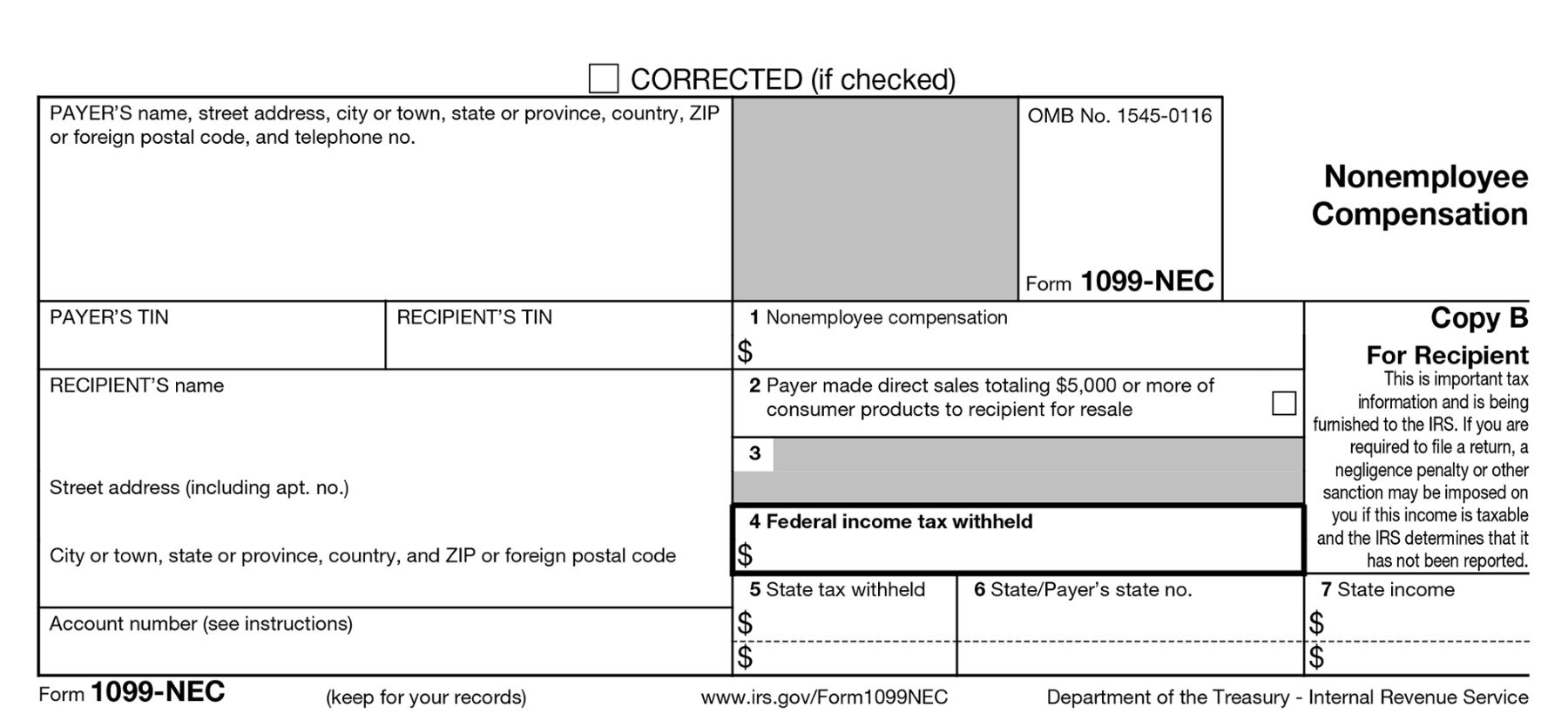
Home>Finance>FHA 203(k) Loan: Definition, Use, Types, Pros, And Cons


Finance
FHA 203(k) Loan: Definition, Use, Types, Pros, And Cons
Published: November 23, 2023
Learn about the FHA 203(k) loan, its definition, use, types, and the pros and cons associated with it. Explore how this financing option can help you in your financial needs.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
FHA 203(k) Loan: Definition, Use, Types, Pros, and Cons
Are you considering purchasing a fixer-upper? Do you dream of transforming a run-down property into your dream home? If so, then an FHA 203(k) loan might be the right financing option for you. In this blog post, we will dive deep into the world of FHA 203(k) loans, exploring their definition, uses, types, as well as their pros and cons. So, let’s get started and uncover everything you need to know about this innovative loan program.
Key Takeaways:
- FHA 203(k) loans are backed by the Federal Housing Administration and designed to help individuals purchase and renovate homes in need of repair.
- They offer two primary types: the Limited 203(k) and the Standard 203(k), catering to different levels of renovation projects.
What is an FHA 203(k) Loan?
An FHA 203(k) loan is a specialized mortgage loan program designed to assist homebuyers in financing both the purchase of a property and the cost of renovations or repairs. This government-backed loan is insured by the Federal Housing Administration, providing lenders with reassurance and borrowers with flexible financing options.
Types of FHA 203(k) Loans
There are two primary types of FHA 203(k) loans: the Limited 203(k) loan and the Standard 203(k) loan. Let’s take a closer look at each:
1. Limited 203(k) Loan
The Limited 203(k) loan is ideal for smaller renovation projects that do not exceed $35,000. This type of loan is often used for minor home improvements, such as replacing flooring, repainting walls, or upgrading appliances. The application process is typically less complex compared to the Standard 203(k) loan, making it more accessible for individuals seeking to make modest adjustments to their new property.
2. Standard 203(k) Loan
The Standard 203(k) loan is suitable for more extensive renovation projects, including structural alterations or major repairs. If you’re planning a comprehensive home transformation, such as adding a room, remodeling the kitchen, or replacing the entire HVAC system, the Standard 203(k) loan offers the necessary financial support. While the application process may be more involved, this type of loan provides greater flexibility and higher loan limits.
Pros of FHA 203(k) Loans
- Financing for Purchase and Renovation: With an FHA 203(k) loan, you can finance both the purchase of the property and the cost of renovations with a single loan. This eliminates the need for separate loans or additional financial burdens.
- Accessible Loan Approval: FHA 203(k) loans have more lenient credit and income requirements compared to conventional loans, making them more accessible to a broader range of borrowers.
- Lower Down Payments: These loans typically require a lower down payment than traditional mortgages, allowing borrowers to conserve their financial resources for repairs and other expenses.
- Housing Value Potential: By renovating a distressed property, you have the opportunity to increase its value and potentially build equity right from the start.
Cons of FHA 203(k) Loans
- Stringent Borrower Requirements: While the loan program itself is more lenient, borrowers still need to meet certain criteria, including sufficient income and creditworthiness.
- Additional Paperwork: The application process for an FHA 203(k) loan can be more time-consuming than a traditional mortgage due to the additional paperwork required for renovation plans and contractor estimates.
- Appraisal Challenges: The property must meet specific valuation and safety criteria, which could pose challenges if the initial condition of the property is significantly deteriorated.
- Loan Limits: FHA 203(k) loans have maximum loan limits, which may restrict the extent of renovations possible for high-cost properties.
As with any financial decision, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons to determine if an FHA 203(k) loan aligns with your specific needs and aspirations. Consulting with a mortgage professional can provide valuable guidance and help you make an informed decision.
In conclusion, an FHA 203(k) loan can be an excellent financing solution for individuals looking to purchase and renovate a fixer-upper property. Whether you choose the Limited 203(k) or Standard 203(k) loan, this program offers flexibility, accessibility, and the potential to turn your dream home into a reality. Just remember to carefully consider the pros and cons, and to consult with experts who can assist you throughout the process.