
Finance
How Do Interest Rates Affect Businesses?
Published: November 1, 2023
Learn how interest rates impact businesses and discover the crucial role of finance in managing economic fluctuations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Interest Rates
- Overview of Businesses and Borrowing
- Interest Rates and Business Investment
- Interest Rates and Business Expenses
- Interest Rates and Consumer Borrowing
- Interest Rates and Business Financing Options
- Interest Rates and Pricing Strategies
- Interest Rates and Business Profitability
- Interest Rates and Economic Conditions
- Conclusion
Introduction
When analyzing the dynamics of the business world, one cannot overlook the significant role that interest rates play. Interest rates affect businesses in various ways, influencing their borrowing decisions, investment strategies, expenses, and ultimately, their profitability. Understanding how interest rates impact businesses is vital for entrepreneurs, investors, and financial professionals alike.
Interest rates refer to the cost of borrowing money or the return on investment for lenders. They are determined by the supply and demand for capital in the economy, as well as macroeconomic factors such as inflation and monetary policy. Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, have a significant influence on interest rates through their control of the money supply and monetary policy adjustments.
In this article, we will delve into the multifaceted relationship between interest rates and businesses. We will explore how interest rates affect borrowing decisions and investment strategies, and how they impact business expenses and profitability. Additionally, we will examine the interplay between interest rates and consumer borrowing, as well as the different financing options available to businesses. Lastly, we will discuss how interest rates influence pricing strategies and are influenced by overall economic conditions.
It is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners to develop a comprehensive understanding of how interest rates can impact their operations. By staying informed about interest rate trends and their implications, businesses can make strategic decisions that potentially minimize risks and maximize profitability.
Definition of Interest Rates
Interest rates are a fundamental concept in finance and economics. They represent the percentage at which a lender charges a borrower for the use of their funds. In other words, interest rates reflect the cost of borrowing money or the compensation received on investments.
Interest rates are influenced by various factors, including the supply and demand for loanable funds, inflation expectations, and central bank policies. As the demand for borrowing increases, interest rates tend to rise due to the higher competition among borrowers. Conversely, when the supply of loanable funds exceeds demand, interest rates may decline as lenders compete for borrowers.
The central bank, often responsible for setting key benchmark interest rates, plays a significant role in shaping interest rate levels. By adjusting interest rates, central banks can influence the overall economy. For example, during periods of economic expansion, central banks may increase interest rates to prevent inflation from rising too rapidly. Conversely, during economic downturns, central banks may lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and investment and promote economic growth.
Interest rates can be divided into two primary categories: nominal interest rates and real interest rates. Nominal interest rates are the rates reported and quoted by lenders and borrowers and are usually expressed annually. Real interest rates, on the other hand, take into account inflation. By subtracting the inflation rate from the nominal interest rate, we can determine the real return on an investment after accounting for the eroding effects of inflation.
It is important to note that interest rates can vary across loan types and borrowers’ creditworthiness. Lenders assess the risk profiles of borrowers and adjust interest rates accordingly. Borrowers with higher creditworthiness generally receive more favorable interest rates, reflecting the lenders’ confidence in their ability to repay the loan.
Interest rates play a critical role in the economy and financial markets. Businesses and individuals make borrowing, spending, investing, and saving decisions based on prevailing interest rates. Understanding the dynamics of interest rates is essential in managing personal finances and business operations.
Overview of Businesses and Borrowing
Borrowing is an essential component of business operations. Businesses often require capital to finance their operations, expand their offerings, invest in new projects, or manage cash flow fluctuations. Borrowing allows businesses to access funds that they may not currently have, enabling growth and strategic initiatives.
Businesses can borrow funds from various sources, including banks, financial institutions, private lenders, and even individuals. The terms of borrowing, such as interest rates, repayment schedules, and collateral requirements, may vary depending on the lender and the borrower’s creditworthiness.
Borrowing decisions are influenced by a range of factors, and interest rates play a central role. When interest rates are low, businesses are more likely to seek financing to take advantage of favorable borrowing conditions. On the other hand, when interest rates are high, businesses may be more hesitant to borrow due to the increased cost of capital.
The purpose of borrowing also determines the type of financing a business may seek. For example, businesses needing short-term funds to cover temporary cash flow gaps may opt for a line of credit or a business credit card. These types of borrowing arrangements typically have higher interest rates but offer flexibility in terms of borrowing and repayment.
Long-term financing options include term loans and commercial mortgages. These types of loans are often used for significant investments, such as purchasing real estate, buying equipment, or funding expansion projects. Interest rates for long-term loans may be lower compared to short-term financing, as the repayment period is longer and the collateral provided by the borrower reduces the lender’s risk.
Businesses also have the option of borrowing through bonds or issuing corporate debt. These are more complex and typically used by larger corporations to raise significant amounts of capital. The interest rates on corporate bonds are determined by various market factors, such as prevailing interest rates, the company’s credit rating, and the overall demand for bonds in the market.
Overall, businesses must carefully assess the cost-benefit analysis of borrowing. They must consider the potential benefits of borrowing for growth and investment opportunities against the costs associated with interest payments and potential risks. Monitoring interest rate trends and staying informed about market conditions are crucial in making informed borrowing decisions that align with the business’s financial objectives.
Interest Rates and Business Investment
Interest rates have a significant impact on business investment decisions. When interest rates are low, businesses are more inclined to undertake investment projects or expand their operations. This is because the cost of borrowing funds to finance investments is lower, making such projects more financially viable.
Lower interest rates reduce the cost of capital for businesses. They make it more affordable for companies to access funding for various investment activities, such as purchasing new equipment, expanding facilities, or developing new products. With lower borrowing costs, businesses have greater financial flexibility and can allocate more resources towards growth and innovation.
Additionally, low interest rates stimulate consumer spending and aggregate demand in the economy. This increased demand can create opportunities for businesses to expand their customer base and generate more revenue. With the potential for higher sales and profits, businesses are more likely to embark on investment projects.
On the other hand, high interest rates can discourage business investment. When interest rates are high, borrowing costs increase, making it more expensive for businesses to finance investment projects. Higher interest rates also reduce consumers’ purchasing power, as the cost of borrowing for personal expenses such as mortgages and car loans increases. This decrease in consumer spending can lead to reduced demand for businesses’ products or services, impacting their profitability and investment plans.
Interest rates also play a role in determining the attractiveness of alternative investment opportunities. When interest rates are low, the potential returns from investing in financial markets may be relatively low as well. This makes tangible investments, such as expanding facilities or purchasing new equipment, more appealing for businesses seeking higher returns.
It is worth noting that the relationship between interest rates and business investment is not solely determined by the absolute level of interest rates. Expectations and confidence about future interest rate movements also influence investment decisions. Businesses consider long-term financing implications when planning for investment projects. If businesses anticipate that interest rates will rise in the future, they may be more motivated to invest before borrowing costs increase.
In summary, interest rates significantly impact business investment decisions. Lower interest rates make investment projects more affordable, allowing businesses to allocate resources towards growth and innovation. Conversely, higher interest rates increase borrowing costs, potentially discouraging businesses from undertaking new investments. Consideration of interest rate trends, along with analysis of financial feasibility and market conditions, is crucial for businesses when evaluating investment opportunities.
Interest Rates and Business Expenses
Interest rates have a direct impact on business expenses, particularly in relation to borrowing and debt servicing costs. When interest rates are low, businesses can benefit from reduced borrowing costs, resulting in lower interest expense payments and overall expenses.
Lower interest rates make borrowing more affordable for businesses. Whether a company needs short-term financing for working capital or long-term financing for major investments, the cost of borrowing is influenced by prevailing interest rates. When interest rates are low, businesses can secure loans at more favorable terms, including lower interest rates and potentially reduced fees.
Reduced borrowing costs can have a significant impact on a business’s bottom line. With lower interest expenses, businesses can allocate more resources towards other areas, such as research and development, marketing, and employee wages. This increased flexibility allows businesses to invest in growth initiatives and potentially expand their operations.
On the contrary, when interest rates are high, borrowing becomes more expensive. Businesses may face higher interest rates on new loans or may see their existing variable-rate loans become more costly to service. This increases the overall expenses for businesses, potentially impacting their profitability and financial stability.
In addition to borrowing costs, interest rates can also influence other business expenses indirectly. For instance, higher interest rates can lead to an increase in the cost of raw materials or goods due to higher production and transportation expenses. This ripple effect can impact a business’s cost structure, potentially leading to higher prices for their products or services.
Furthermore, interest rates can influence the cost of leasing or renting office space, equipment, or vehicles. Landlords and lessors may adjust their rates based on prevailing interest rates, potentially impacting businesses’ rental expenses. When interest rates are high, the cost of leasing or renting may increase, putting additional financial strain on businesses.
Overall, businesses should closely monitor interest rate trends and assess the impact on their borrowing costs and overall expenses. By understanding the relationship between interest rates and business expenses, companies can strategically plan their financial management and budgeting, taking advantage of favorable interest rate environments and minimizing the impact of higher borrowing costs.
Interest Rates and Consumer Borrowing
Interest rates have a significant impact on consumer borrowing decisions and ultimately influence consumer spending patterns. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes more affordable for consumers, leading to increased consumer spending and economic growth.
Lower interest rates reduce the cost of borrowing for consumers. This means that obtaining loans for major purchases, such as homes, cars, or appliances, becomes more financially viable. Lower interest rates can also incentivize consumers to take on more debt, such as credit card debt or personal loans, to finance discretionary spending or cover unexpected expenses.
When consumers can borrow money at lower interest rates, they have more disposable income available to spend on goods and services. Increased consumer spending stimulates business activity and fuels demand for products, which can lead to higher sales and revenue for businesses.
In contrast, higher interest rates can discourage consumer borrowing. When interest rates increase, the cost of borrowing becomes more expensive, reducing consumers’ purchasing power. This can lead to decreased consumer spending and a slowdown in economic activity.
Higher interest rates not only impact consumers’ ability to borrow for major purchases but also affect the cost of carrying existing debt. For example, credit card balances or personal loans with variable interest rates can become more burdensome for consumers as interest rates rise, potentially resulting in higher monthly payments and increased financial strain.
Interest rates also play a role in influencing financial decisions related to saving and investing. When interest rates are low, consumers may be less incentivized to save because the return on savings accounts or certificates of deposit (CDs) is minimal. On the other hand, higher interest rates can encourage people to save more as they can earn a greater return on their savings.
Additionally, interest rates can influence consumer behavior in the housing market. Lower interest rates make mortgages more affordable, leading to increased demand for homes and potentially driving up property prices. Conversely, higher interest rates can make housing less affordable, leading to decreased demand and potentially cooling the housing market.
Overall, interest rates have a significant impact on consumer borrowing decisions and subsequent spending patterns. Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and stimulate consumer spending, while higher interest rates can constrain borrowing and dampen consumer demand. Monitoring interest rate trends is important for both businesses and consumers to make informed financial decisions and adapt to changing economic conditions.
Interest Rates and Business Financing Options
Interest rates are a key factor to consider when evaluating different financing options for businesses. The cost of borrowing funds is influenced by prevailing interest rates, making it important for businesses to assess the most suitable financing options based on their financial needs and the prevailing interest rate environment.
Bank Loans: Traditional bank loans are one of the most common financing options for businesses. Banks offer both short-term and long-term loans, with varying interest rates depending on factors such as the borrower’s creditworthiness and collateral provided. When interest rates are low, businesses can secure loans at more favorable terms, reducing their borrowing costs and improving their financial position.
Lines of Credit: Lines of credit provide businesses with a flexible source of financing that can be used as needed. Similar to bank loans, lines of credit have interest rates that can vary depending on the borrower’s credit profile and the lender’s assessment of risk. Lower interest rates make lines of credit more affordable for businesses, allowing them to access funds for ongoing expenses, working capital needs, or to seize opportunities quickly.
Trade Credit: Some businesses can negotiate trade credit terms with suppliers, allowing them to defer payment for goods and services. While trade credit terms typically do not involve interest charges, businesses need to assess the cost of delayed payments in terms of potential discounts foregone and the impact on their relationships with suppliers.
Private Financing: Private financing options, such as angel investors or venture capital, offer businesses funding in exchange for equity or a share of future profits. Interest rates may not apply directly, but the terms of equity investments can be influenced by prevailing interest rates or market conditions, impacting the overall cost of capital for businesses.
Crowdfunding: Crowdfunding platforms allow businesses to raise funds from a large number of individuals in exchange for products, services, or rewards. The interest rate does not apply in crowdfunding, but businesses need to carefully consider the costs associated with creating and delivering these offerings, as well as any platform fees.
Government Programs: Government-sponsored programs and initiatives may provide businesses with financing options at favorable interest rates. These programs are often aimed at supporting specific industries, promoting economic development, or encouraging innovation. Businesses should explore these programs to access potentially cheaper financing alternatives.
Leasing: In some situations, businesses may consider leasing as a financing option. Whether it’s leasing equipment, vehicles, or office space, interest rates indirectly influence the leasing costs that businesses incur. Higher interest rates may lead to increased lease rates, impacting overall business expenses.
When evaluating financing options, businesses need to consider not only the interest rates but also other factors such as repayment terms, collateral requirements, fees, and the lender’s reputation and track record. Developing relationships with multiple lenders and staying informed about interest rate trends can empower businesses to make informed decisions and secure financing options that align with their financial objectives.
Interest Rates and Pricing Strategies
Interest rates can have a significant impact on a business’s pricing strategies. Understanding how interest rates influence pricing decisions is essential for businesses to effectively manage their costs, maintain competitiveness, and optimize profitability.
Cost of Borrowing: When interest rates are low, businesses can benefit from lower borrowing costs, reducing the expense associated with financing their operations. This can provide businesses with the opportunity to lower their prices or maintain competitive pricing while still achieving desired profit margins. By passing on the cost savings to customers in the form of lower prices, businesses can attract more customers and potentially increase their market share.
Credit Terms: Higher interest rates can lead to increased costs for businesses that offer credit terms to their customers. When businesses extend credit, they essentially become lenders themselves, and the interest rates they pay on their own borrowing can influence the interest rates they charge their customers. Higher interest rates may necessitate adjusting credit terms, such as shortening payment periods or increasing interest charges on late payments, to mitigate the increased cost of borrowing.
Inflation Considerations: Interest rates are often influenced by inflation expectations. Higher inflation can lead to higher interest rates as lenders seek compensation for the reduced purchasing power of the money they lend. Inflationary pressures can impact a business’s cost structure, including raw material costs, wages, and other operational expenses. To maintain profitability, businesses may need to adjust their pricing strategies to reflect inflationary pressures and accommodate higher costs associated with their products or services.
Competitive Positioning: Interest rates can also influence a business’s competitive positioning within the market. When interest rates are low, businesses that have taken advantage of lower borrowing costs may be able to set more competitive prices, potentially attracting customers away from competitors. On the other hand, higher interest rates may increase borrowing costs for businesses, making it more challenging to compete solely on price. In such cases, businesses may need to differentiate themselves through product quality, service, or unique value propositions.
Market Demand: Interest rates can impact consumer demand for products and services as they influence borrowing costs and disposable income. Businesses need to monitor consumer sentiment and purchasing power, taking into account the overall economic conditions. Higher interest rates can lead to decreased consumer spending, which may necessitate businesses to adjust their pricing strategies to maintain customer demand. Conversely, lower interest rates can stimulate consumer spending, potentially supporting higher price levels.
Foreign Exchange Rates: Interest rates and currency exchange rates are often interconnected. Changes in interest rates can influence foreign exchange rates, impacting businesses involved in international trade. Fluctuations in exchange rates can affect the cost of imported raw materials or finished goods, which may require adjustments in pricing strategies to ensure profitability.
It is crucial for businesses to regularly assess their pricing strategies in light of prevailing interest rates and market conditions. By considering the impact of interest rates on borrowing costs, credit terms, inflation, market demand, competitive positioning, and foreign exchange rates, businesses can make informed pricing decisions that support their financial objectives and maintain competitiveness in the marketplace.
Interest Rates and Business Profitability
Interest rates play a significant role in determining a business’s profitability. Fluctuations in interest rates can impact a company’s borrowing costs, customer demand, and overall financial performance, ultimately influencing its profitability.
Borrowing Costs: Interest rates directly affect the cost of borrowing for businesses. When interest rates are high, borrowing becomes more expensive, leading to higher interest payments and potentially reducing a company’s profitability. Conversely, when interest rates are low, businesses can benefit from lower borrowing costs, resulting in reduced interest expenses and improved profitability.
Leverage and Debt Servicing: Higher interest rates can put a strain on businesses with significant debt levels. Rising interest rates increase the cost of servicing existing debt, potentially reducing a company’s cash flows and profitability. Businesses with a large amount of debt or variable-rate loans should closely monitor interest rate trends to assess the impact on their debt servicing capacity and adjust their financial strategies accordingly.
Investment and Expansion: Interest rates also influence businesses’ investment decisions. When interest rates are low, businesses are more likely to undertake investments in new projects or expansions. Lower borrowing costs make it more financially feasible to finance these initiatives, potentially leading to increased revenue and profitability. On the other hand, higher interest rates can curb investment and expansion plans due to increased borrowing costs, potentially impacting a company’s growth and profitability.
Consumer Demand: Interest rates can influence consumer spending patterns and, consequently, a business’s profitability. Lower interest rates can stimulate consumer borrowing and spending, which increases demand for goods and services. As a result, businesses may experience higher sales and greater profitability. Conversely, higher interest rates can lead to decreased consumer spending, reducing demand and potentially impacting a company’s profitability.
Competitive Positioning: Interest rates can also affect a business’s competitive positioning. When interest rates are low, businesses with lower borrowing costs may have the ability to offer more competitive prices compared to competitors. By attracting more customers through competitive pricing, businesses can potentially increase market share and profitability. Conversely, higher interest rates may put pressure on businesses’ pricing strategies, potentially impacting their competitiveness and profitability.
Currency Exchange Rates: Interest rates can indirectly affect a business’s profitability through their impact on currency exchange rates. Changes in interest rates can cause fluctuations in exchange rates, impacting businesses involved in international trade. Exchange rate fluctuations can affect production costs, import/export prices, and profitability for businesses operating in multiple currencies.
Overall, businesses need to carefully consider the impact of interest rates on their borrowing costs, investment decisions, customer demand, competitive positioning, and exchange rate exposure. By monitoring interest rate trends and proactively adjusting their financial strategies, businesses can optimize their profitability in a dynamic market environment.
Interest Rates and Economic Conditions
Interest rates are closely tied to prevailing economic conditions and serve as a barometer of the overall health of an economy. Changes in interest rates can reflect and influence the state of the economy, impacting various sectors and businesses in different ways.
Monetary Policy: Central banks use interest rates as a tool to regulate economic activity and manage inflation. During periods of economic expansion and rising inflation, central banks may increase interest rates to control inflationary pressures and prevent the economy from overheating. Conversely, during economic downturns, central banks may lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing, investment, and consumer spending, aiming to boost economic growth.
Consumer Confidence and Spending: Interest rates have a significant impact on consumer borrowing costs and disposable income, which can influence consumer confidence and spending. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes more affordable, leading to increased consumer spending and economic activity. Higher interest rates, on the other hand, can reduce consumer purchasing power and dampen consumer spending, potentially slowing economic growth.
Housing Market: Interest rates play a crucial role in the housing market. Lower interest rates make mortgages more affordable, leading to increased demand for homes and potentially driving up property prices. This can stimulate construction and related industries, supporting economic growth. Conversely, higher interest rates can curb demand for housing, potentially leading to a slowdown in the construction sector and the overall economy.
Investment and Business Activity: Interest rates influence businesses’ borrowing costs and investment decisions. Lower interest rates make it more financially viable for businesses to undertake capital investments and expand their operations, potentially boosting economic growth. Conversely, higher interest rates can increase borrowing costs, dampening investment and business activity, and potentially slowing economic growth.
Inflation and Price Stability: Interest rates are influenced by inflation expectations. Higher inflation expectations contribute to higher interest rates as lenders seek compensation for the reduced purchasing power of money in the future. Central banks may raise interest rates to control inflation and maintain price stability. By adjusting interest rates to manage inflation, central banks aim to ensure the long-term stability and health of the economy.
Foreign Exchange Rates: Interest rates can impact a country’s exchange rates. Higher interest rates can attract foreign investors seeking higher returns, potentially strengthening the country’s currency. Conversely, lower interest rates can reduce foreign investor demand, potentially weakening the currency. Exchange rate fluctuations can impact international trade and economic competitiveness, influencing businesses operating in global markets.
Overall, interest rates and economic conditions are interconnected. Changes in interest rates reflect and influence economic activity, consumer behavior, business investment decisions, and overall economic growth. Businesses should closely monitor interest rate trends and their implications for the broader economy to adapt their strategies and navigate the changing economic landscape effectively.
Conclusion
Interest rates play a crucial role in shaping the financial landscape for businesses. Understanding the impact of interest rates on borrowing decisions, investment strategies, expenses, and profitability is essential for businesses to navigate the complex world of finance and maximize their potential for success.
Lower interest rates create favorable conditions for businesses, reducing borrowing costs and facilitating investment and expansion initiatives. They stimulate consumer spending and aggregate demand, providing opportunities for businesses to grow their customer base and increase revenue. Lower interest rates also support pricing strategies, allowing businesses to offer competitive prices and potentially gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Conversely, higher interest rates can pose challenges for businesses. They increase borrowing costs, potentially squeezing profit margins and lowering business investment and expansion plans. Higher interest rates can also dampen consumer spending, which can impact overall demand for products and services, affecting businesses’ profitability.
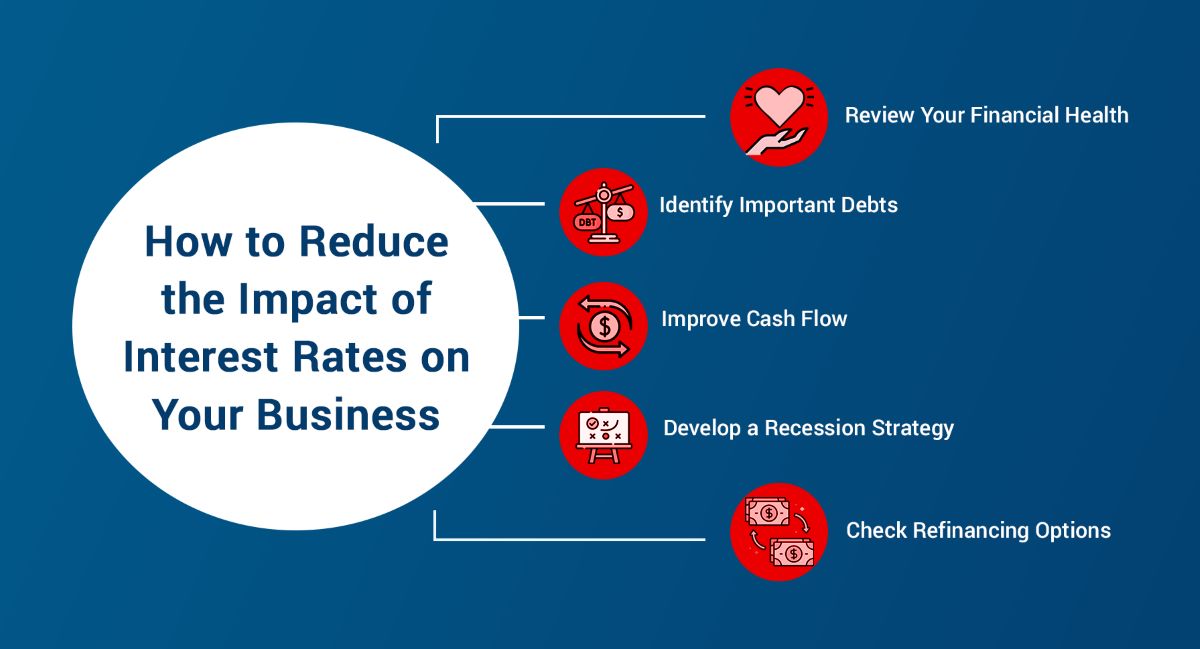
Businesses need to carefully monitor interest rate trends and their impact on financing options, consumer behavior, and market conditions. By understanding the relationship between interest rates and various aspects of their operations, businesses can make informed financial decisions, adjust their strategies, and proactively manage risks.
It is important for businesses to regularly assess their borrowing needs, evaluate the suitability of different financing options, and consider the potential impact of interest rates on their profitability. By staying informed and proactive, businesses can position themselves to take advantage of favorable interest rate environments, mitigate the impact of higher borrowing costs during periods of rising interest rates, and optimize their financial performance.
In conclusion, interest rates have far-reaching implications for businesses. They influence borrowing decisions, investment strategies, expenses, pricing strategies, and overall profitability. Understanding the dynamics of interest rates and their impact on business operations is crucial for businesses to adapt to changing economic conditions, manage their finances effectively, and ultimately thrive in the ever-evolving business landscape.














