Finance
How Does Inflation Affect Businesses?
Published: October 19, 2023
Learn how inflation impacts businesses and what it means for finance. Find out strategies to navigate the effects of inflation on your business.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Inflation is a fundamental economic concept that affects businesses of all sizes and industries. It refers to the general rise in prices of goods and services over time, resulting in a decrease in the purchasing power of money. While inflation can be a natural part of a growing economy, its impact on businesses can be complex and far-reaching. Understanding how inflation affects businesses is crucial for companies to make informed decisions and develop strategies to mitigate its effects.
There are several factors that contribute to inflation, including increased production costs, changes in consumer spending habits, monetary policy, and global economic conditions. As inflation rises, businesses face various challenges that can impact their profitability, operations, and overall growth.
In this article, we will delve into how inflation affects businesses and explore the implications it has on production costs, consumer demand, pricing strategies, investments, and financing. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these effects, businesses can better adapt and navigate the dynamic economic landscape.
Understanding Inflation and Its Causes
Before delving into how inflation affects businesses, it is essential to grasp a basic understanding of what inflation is and the factors that contribute to its occurrence. As mentioned earlier, inflation refers to the general increase in prices of goods and services over time, resulting in a decrease in the purchasing power of money.
Inflation can occur due to various reasons, with the most common being:
- Increased production costs: When the cost of raw materials, labor, or other inputs required for production rises, businesses may be forced to pass on these increased costs to consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Changes in consumer spending habits: Shifts in consumer preferences, demographics, or economic conditions can lead to changes in the demand for specific goods and services. If the demand for certain products rises faster than their supply, it can result in inflation for those specific items.
- Monetary policy: When central banks engage in expansionary monetary policies by increasing the money supply or lowering interest rates, it can stimulate spending and economic growth, but also potentially lead to inflationary pressures.
- Global economic conditions: Fluctuations in global commodity prices, exchange rates, or geopolitical factors can influence the prices of imported goods and impact domestic inflation rates.
Inflation is typically measured by inflation indices such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or the Producer Price Index (PPI). These indices calculate the average price changes of a basket of goods and services over time, providing a measure of inflation.
It is worth noting that not all inflation is inherently negative. Moderate and stable levels of inflation can indicate a healthy economy with increasing wages, investment, and consumption. However, high and volatile inflation can create uncertainty and pose significant challenges for businesses.
Now that we have a better understanding of inflation and its causes, let’s explore the specific impact it has on businesses.
The Impact of Inflation on Businesses
Inflation can have a significant impact on businesses across various aspects of their operations. Let’s explore the key ways in which inflation affects businesses:
- Increase in Production Costs: When inflation occurs, the cost of raw materials, labor, and other inputs tends to rise. This increase in production costs can directly impact a business’s profitability. Businesses may face the challenge of maintaining their profit margins while facing higher expenses. In some cases, businesses may be forced to absorb these additional costs, leading to reduced profits.
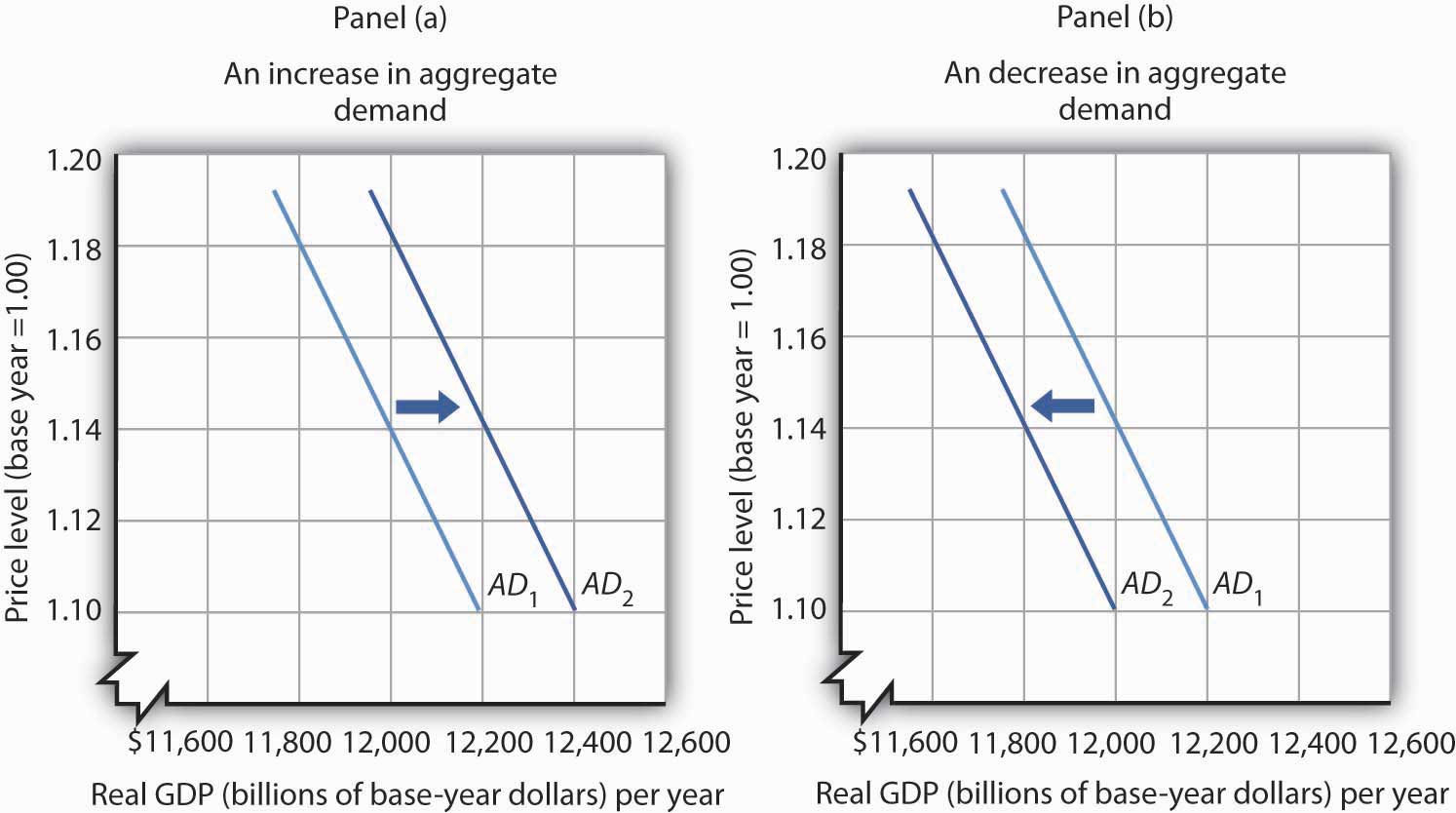
- Effect on Consumer Demand: Inflation can alter consumer spending habits and impact the overall demand for goods and services. When prices rise, consumers may become more cautious with their spending and prioritize essential purchases. This shift in consumer behavior can result in reduced demand for non-essential goods and discretionary services. Businesses in industries such as luxury products or travel and hospitality may experience a decrease in sales as a result.
- Impact on Pricing and Profit Margins: Inflation can create challenges for businesses in determining pricing strategies. While it may be necessary to increase prices in order to maintain profitability, businesses must carefully consider the potential impact on consumer demand. If prices increase too much, it may deter customers and result in decreased sales. Additionally, businesses that rely on long-term contracts or fixed pricing agreements may find it difficult to adjust prices in line with inflation, leading to squeezed profit margins.
- Implications for Investments and Financing: Inflation can also affect investment decisions and financing options for businesses. In a high-inflation environment, businesses may choose to invest in assets that can serve as hedges against inflation, such as real estate or commodities. Furthermore, inflation can impact interest rates, making borrowing more expensive. Businesses seeking financing may face higher interest costs, reducing their access to capital and potentially limiting growth opportunities.
Overall, the impact of inflation on businesses can vary depending on the industry, the specific market conditions, and the ability of businesses to adapt to changing economic realities. It is essential for businesses to monitor inflation rates, adjust their strategies accordingly, and implement measures to mitigate the adverse effects of inflation.
Increase in Production Costs
One of the significant impacts of inflation on businesses is the increase in production costs. When inflation occurs, the prices of raw materials, labor, and other inputs typically rise over time. This rise in production costs can have several consequences for businesses:
- Higher cost of raw materials: Inflation can lead to an increase in the prices of raw materials that businesses rely on for their production processes. This can be particularly challenging for businesses in industries that heavily depend on commodity inputs, such as manufacturing or construction. As the cost of these materials rises, businesses may need to either find alternative suppliers or pass on the increased costs to their customers, potentially affecting their competitiveness.
- Increased wages and labor costs: Inflation often translates into higher wages as employees demand increased compensation to keep up with the rising cost of living. Businesses may be required to offer higher wages to attract and retain quality talent. This can have a significant impact on labor-intensive industries, such as retail and hospitality, which rely heavily on manpower. The rise in labor costs can directly affect a business’s bottom line, reducing profitability if price increases cannot be passed on to customers.
- Escalation in energy and utility expenses: Inflation can also drive up the prices of energy and utilities, such as electricity, fuel, and water. These are critical inputs for many businesses, especially those in manufacturing, transportation, and agriculture sectors. As energy prices increase, businesses may face higher operational costs, impacting their profit margins. Finding ways to optimize energy usage or exploring alternative energy sources becomes crucial to mitigate the impact of rising energy costs.
- Impact on supply chain: When production costs increase, it can disrupt the entire supply chain. Suppliers may pass on their increased costs to businesses, which can have a ripple effect on the prices of intermediate goods and services. This can lead to supply chain disruptions and challenges in maintaining consistent inventory levels. Businesses may need to re-evaluate their supplier relationships, renegotiate contracts, or explore alternative sourcing options to mitigate the impact of rising production costs.
In order to address the challenge of increased production costs, businesses can adopt various strategies. This can include renegotiating contracts with suppliers, implementing cost-cutting measures, investing in technology and automation to streamline operations, and diversifying their supplier base to reduce reliance on specific inputs.
By closely monitoring inflation rates and proactively adjusting their production processes, businesses can mitigate the impact of rising costs and maintain their competitiveness in a changing economic environment.
Effect on Consumer Demand
Inflation has a direct impact on consumer demand, which can significantly affect businesses across various sectors. When prices rise, consumers may adjust their spending habits and prioritize essential purchases over non-essential goods and services. This change in consumer behavior can have several effects:
- Reduced purchasing power: As the cost of goods and services increases due to inflation, consumers may find that their purchasing power diminishes. This can lead to a decrease in overall consumer spending and may prompt individuals to cut back on discretionary expenses. Businesses that offer non-essential products or luxury items may experience a decline in sales as consumers become more cautious with their spending.
- Shifts in consumer preferences: Inflation can also result in changes in consumer preferences and buying patterns. As prices increase, consumers may opt for lower-priced alternatives or choose products and services that provide better value for their money. This shift in preferences can have implications for businesses that rely on specific brands or premium offerings. Adapting to the changing preferences and offering more affordable options can help businesses maintain demand.
- Impact on discretionary sectors: Certain industries, such as travel, hospitality, and entertainment, are particularly susceptible to changes in consumer demand during inflationary periods. As consumer budgets become tighter, individuals may cut back on leisure and travel expenses, leading to decreased demand for services in these sectors. Companies in these industries may need to adjust their pricing strategies or diversify their offerings to cater to cost-conscious consumers.
- Inflation and consumer confidence: Inflation can also impact consumer confidence, which plays a crucial role in driving consumer spending. When prices rise rapidly, consumers may become more uncertain about the future, leading to a decrease in their confidence levels. This hesitancy can result in reduced consumer spending, which can have a profound impact on businesses across industries.
To navigate the effects of inflation on consumer demand, businesses can consider a few strategies. Firstly, offering value-oriented pricing, promotions, and discounts can attract cost-conscious consumers. Secondly, focusing on product innovation and differentiation to provide unique value propositions can help businesses maintain customer loyalty. Lastly, investing in targeted marketing and communication campaigns to educate consumers about the value and benefits of their products or services can help mitigate the decline in demand during inflationary periods.
By understanding and adapting to changing consumer preferences and behaviors during inflation, businesses can effectively navigate the challenges posed by reduced consumer demand and maintain their competitiveness.
Impact on Pricing and Profit Margins
Inflation can have a significant impact on pricing strategies and profit margins for businesses. As the overall price level increases, businesses may face various challenges and considerations when determining product or service prices:
- Cost pass-through: When businesses experience an increase in production costs due to inflation, they may choose to pass on these costs to consumers by raising prices. However, it is essential for businesses to carefully evaluate the price elasticity of demand, as significant price increases can lead to a decline in consumer demand. Balancing the need to maintain profitability with the risk of losing customers requires a careful analysis of the market dynamics.
- Competitive pressures: Inflation affects not only a single business but often the entire market. Competitors faced with rising costs may also increase their prices, creating a delicate balance between remaining competitive and maintaining profit margins. In highly competitive industries, businesses may need to find alternative ways to differentiate their offerings, such as through quality, service, or unique value propositions.
- Negotiating power: Inflation can impact the balance of power in supplier-customer relationships. Suppliers facing higher costs may attempt to negotiate higher prices, potentially further squeezing the profit margins of businesses. In such cases, businesses need to explore alternative sourcing options, renegotiate contracts, or develop strategic partnerships to ensure the sustainability of their operations.
- Long-term contracts: Businesses that operate under long-term contracts or fixed pricing agreements may face challenges when inflation occurs. If their input costs rise significantly, they may find it difficult to adjust their prices accordingly, potentially leading to squeezed profit margins. To mitigate this, businesses can consider incorporating escalation clauses in contracts that allow for periodic price adjustments based on inflation indices or renegotiate pricing terms to reflect changing market conditions.
To navigate the impact of inflation on pricing and profit margins, businesses can adopt certain strategies. Firstly, cost optimization measures, such as streamlining operations and implementing efficiency improvements, can help mitigate the impact of rising costs on profit margins. Secondly, businesses can explore alternative sourcing options, negotiate better prices with suppliers, or invest in technology and automation to improve productivity and reduce expenses. Lastly, implementing value-added services or product enhancements can provide justification for price increases and help maintain profit margins while providing added benefits to customers.
By carefully considering the market dynamics, competitive landscape, and customer expectations, businesses can adjust their pricing strategies to minimize the impact of inflation on profit margins while continuing to meet customer demands.
Implications for Investments and Financing
Inflation not only affects day-to-day operations and pricing strategies but also has implications for the long-term investments and financing decisions of businesses. Understanding the impact of inflation on investments and financing is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions and manage their financial stability:
- Interest rates: Inflation can lead to changes in interest rates set by central banks as a monetary policy tool. When inflation rises, central banks may raise interest rates to curb inflationary pressures. Higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive for businesses, affecting their financing costs. This can limit their access to capital for investments or require them to allocate more resources towards servicing debt, potentially impacting their profitability and growth plans.
- Investment decisions: Inflation has implications for investment decisions as well. In a high-inflation environment, businesses may seek to invest in assets that can act as hedges against inflation, such as real estate or commodities. These investments can preserve value during periods of rising prices and provide a potential source of income or protection against inflationary pressures. Businesses need to carefully evaluate their investment portfolio, considering the potential returns and risks associated with different asset classes in an inflationary economic environment.
- Foreign exchange considerations: Inflation can impact exchange rates, which can also have implications for investments and financing for businesses engaged in international trade. If local inflation rates differ significantly from those of trading partners, it can affect currency exchange rates, impacting the profitability of exporting or importing goods or services. Businesses need to monitor exchange rate fluctuations and implement appropriate hedging strategies to manage the risks associated with currency fluctuations.
- Financing options: Inflation can influence the availability and terms of financing options for businesses. Lenders and investors may factor in inflation expectations when determining interest rates, loan terms, or investment returns. Businesses may face higher borrowing costs, stricter lending criteria, or less favorable terms during periods of high inflation. This can impact their ability to secure adequate financing for growth initiatives or require them to explore alternative financing options, such as equity financing or strategic partnerships.
To address the implications of inflation on investments and financing, businesses can take several measures. Firstly, conducting thorough financial analyses, including sensitivity analysis based on different inflation scenarios, can help businesses understand the potential impact on their cash flows, profitability, and loan repayment capacity. Secondly, exploring diversification strategies by investing in assets with different risk-return profiles can help businesses navigate the uncertainty associated with inflation. Lastly, actively monitoring inflation rates, interest rate trends, and market conditions can enable businesses to make timely adjustments to their investment and financing strategies.
By staying informed, developing robust financial plans, and adapting investment and financing strategies to inflationary conditions, businesses can effectively manage their financial stability and position themselves for long-term success.
Strategies for Businesses to Address Inflation
Inflation can present significant challenges for businesses, but there are strategies they can employ to address its impact and navigate the changing economic landscape. Here are some strategies businesses can consider:
- Monitor and forecast inflation: Businesses should closely track inflation rates and economic indicators to anticipate future trends. By staying updated on inflation data and forecasts, businesses can proactively adjust their strategies and make informed decisions to mitigate the impact of rising costs and changing consumer behaviors.
- Optimize operational efficiency: In a high-inflation environment, it becomes crucial for businesses to streamline their operations and identify efficiency improvements. By optimizing processes, reducing waste, and improving productivity, businesses can mitigate the impact of rising production costs and maintain profitability. Automation and technology can play a vital role in driving operational efficiency.
- Implement pricing strategies: Businesses should carefully evaluate their pricing strategies to strike a balance between maintaining profitability and remaining competitive. This may involve analyzing price elasticity, considering value-added offerings, exploring alternative pricing models, or introducing promotions and discounts to attract price-conscious customers.
- Negotiate with suppliers and vendors: Building strong relationships with suppliers and vendors is crucial during periods of inflation. Businesses should engage in open and transparent communication to negotiate favorable pricing terms and explore alternative sourcing options. Collaborative partnerships can help mitigate the impact of rising input costs and ensure a more stable supply chain.
- Seek alternative financing options: As inflation can lead to higher borrowing costs and stricter lending criteria, businesses should explore alternative financing options. These can include seeking equity financing, crowdfunding, or strategic partnerships. Diversifying financing sources can provide greater flexibility and reduce reliance on traditional debt financing.
- Invest in research and development: Inflationary periods can present opportunities for businesses to innovate and develop new products or services. By investing in research and development, businesses can stay ahead of the competition, create new revenue streams, and adapt to changing consumer preferences and demands.
- Develop a risk management framework: Businesses should establish a comprehensive risk management framework that incorporates risks associated with inflation. This includes conducting risk assessments, implementing appropriate hedging strategies, and creating contingency plans to mitigate the impact of inflation on operations, supply chains, and financial performance.
- Focus on customer retention and loyalty: During inflationary periods, customer loyalty becomes even more critical. Businesses should prioritize customer retention by providing exceptional customer service, personalized experiences, and value-added offerings. Building long-term relationships with customers can help mitigate the impact of changing consumer behaviors and sustain business growth.
It is important for businesses to adopt a proactive and adaptive approach when addressing the challenges of inflation. By implementing these strategies, businesses can better position themselves to navigate the impact of inflation, maintain profitability, and continue to grow in a dynamic and evolving economic environment.
Conclusion
Inflation is a fundamental economic concept that has a significant impact on businesses across various industries. As prices rise and the purchasing power of money decreases, businesses face challenges related to increased production costs, changes in consumer demand, pricing strategies, investment decisions, and financing options.
To navigate the effects of inflation, businesses should adopt strategies such as monitoring and forecasting inflation, optimizing operational efficiency, implementing effective pricing strategies, and negotiating with suppliers. It is also critical for businesses to explore alternative financing options, invest in research and development, and develop a robust risk management framework.
By understanding the causes and implications of inflation, businesses can make informed decisions, adapt their strategies, and manage the challenges posed by rising prices. It is important to closely monitor economic indicators, consumer behaviors, and market dynamics to proactively respond to changing conditions. By addressing inflationary pressures head-on, businesses can maintain profitability, sustain growth, and remain competitive in a dynamic and evolving economic landscape.
Ultimately, businesses that successfully navigate the impact of inflation are those that demonstrate resilience, flexibility, and a proactive approach to managing costs, customer demands, and market conditions. Through strategic planning and adaptation, businesses can thrive even in an inflationary environment and continue to deliver value to their customers and stakeholders.