Home>Finance>How Many Credit Hours Is An Associate’s Degree?


Finance
How Many Credit Hours Is An Associate’s Degree?
Published: January 7, 2024
Find out how many credit hours are required for an associate's degree in finance and plan your educational journey. Get the essential information on credit requirements and career opportunities.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of higher education, where countless opportunities await you in the pursuit of knowledge and career advancement. If you are considering pursuing an associate’s degree, you might be wondering how many credit hours are required to obtain this valuable credential. In this article, we will explore the credit hour requirement for an associate’s degree and delve into the various factors that can influence the number of credit hours needed.
An associate’s degree is a two-year undergraduate degree offered by community colleges, technical schools, and some four-year colleges and universities. It is a popular choice for students who are looking to gain practical skills and knowledge in a specific field or who plan to transfer to a four-year institution to pursue a bachelor’s degree.
While the specific requirements for an associate’s degree vary based on the institution and the program of study, credit hours are a common metric used to measure academic progress and completion. Credit hours represent the amount of time spent in class or engaged in academic activities, and they are typically assigned to individual courses.
In general, an associate’s degree requires completion of around 60 credit hours. This means that students must successfully earn credit for a predetermined number of courses, each typically worth 3 or 4 credit hours, to fulfill the degree requirements. However, it is essential to note that the actual number of credit hours can vary based on the specific program of study, the institution’s policies, and any transfer credits that may be applied towards the degree.
Now that we have a basic understanding of what an associate’s degree entails and the role credit hours play in its completion, let us dive deeper into the factors that can affect the number of credit hours needed to earn this valuable credential.
What is an Associate’s Degree?
An associate’s degree is a two-year undergraduate degree that provides individuals with a solid foundation in a specific field of study. It is typically offered by community colleges, technical schools, and even some four-year colleges and universities. This degree is a popular choice for individuals seeking to gain practical skills and knowledge in a shorter timeframe compared to a bachelor’s degree.
An associate’s degree is often divided into two categories: the Associate of Arts (AA) and the Associate of Science (AS). The choice between these two degrees depends on the field of study and the educational goals of the individual.
The Associate of Arts (AA) degree is commonly pursued by students with an interest in humanities, social sciences, or liberal arts. It emphasizes a well-rounded education and typically includes coursework in subjects such as English, history, psychology, and sociology. The AA degree is often designed to transfer to a four-year institution, allowing students to continue their education and pursue a bachelor’s degree in a related field.
The Associate of Science (AS) degree, on the other hand, is geared towards individuals interested in scientific and technical fields. It places a greater emphasis on mathematics, natural sciences, and applied sciences. Students pursuing an AS degree may study subjects such as biology, chemistry, computer science, engineering, or allied health professions. Like the AA degree, the AS degree can also serve as a stepping stone to a four-year degree program.
Associate’s degree programs typically consist of a mix of general education courses and courses specific to the chosen field of study. General education courses cover a broad range of subjects and help develop essential skills such as critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving. Field-specific courses delve deeper into the subject matter, providing students with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level positions or further education in their chosen field.
Overall, an associate’s degree offers a valuable educational experience for individuals seeking to gain specialized knowledge, explore career options, or save time and money on their educational journey. It serves as a stepping stone to higher education or can provide the skills and qualifications needed to enter the workforce directly after completion.
Credit Hours and Degree Requirements
Credit hours play a crucial role in determining the completion requirements for an associate’s degree. Each college or university sets its own credit hour requirements for graduation, which can vary depending on the institution’s policies and the specific program of study.
In general, an associate’s degree requires the completion of approximately 60 credit hours. These credit hours are earned by successfully completing a combination of general education courses, core courses specific to the chosen field of study, and electives. It is important to note that the credit hours required may differ for different programs or majors within the associate’s degree.
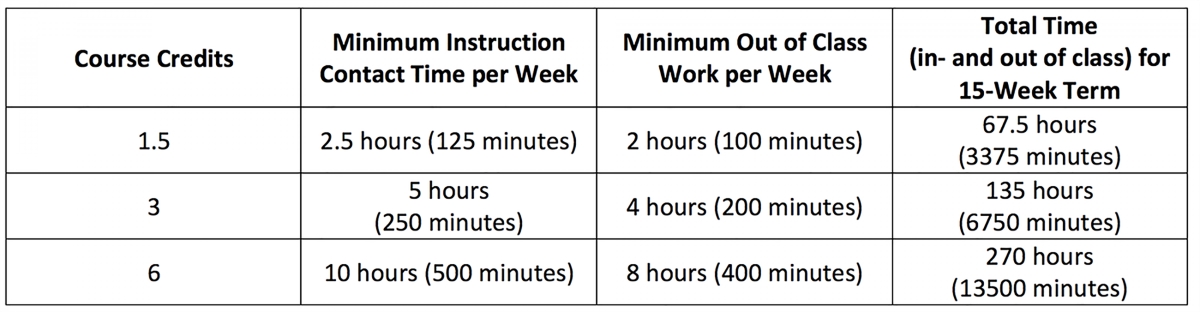
When considering the credit hour requirement for an associate’s degree, it is essential to understand that the number of credit hours assigned to each course can vary. Typically, courses range from 3 to 4 credit hours, depending on the depth and intensity of the subject matter and the amount of time spent in class. Some courses, such as laboratory-based or hands-on courses, may have higher credit hours to account for additional instructional time and practical application of knowledge.
Furthermore, specific degree programs may have additional requirements beyond credit hours. These requirements can include internships, capstone projects, portfolios, or comprehensive exams that students must successfully complete to fulfill the degree requirements. It is crucial for students to consult their academic advisors or program coordinators to gain a clear understanding of the credit hours and additional requirements needed to earn their associate’s degree.
Transfer credits from previous coursework or exams such as Advanced Placement (AP), College Level Examination Program (CLEP), or International Baccalaureate (IB) can also impact the number of credit hours required. Institutions often have policies in place that allow students to transfer applicable credits from accredited institutions or receive credit for prior learning through assessments. These transfer credits can reduce the number of credit hours needed to earn an associate’s degree, enabling students to expedite their educational journey.
In summary, earning an associate’s degree requires the successful completion of a specific number of credit hours, typically around 60. The credit hours are earned by completing general education courses, core courses in the chosen field of study, and electives. Additionally, students must consider any additional requirements specific to their program and the potential for transfer credits or prior learning assessment to impact the total credit hour requirement.
Average Credit Hours for Associate’s Degrees
While the credit hour requirements for an associate’s degree can vary depending on the institution and program of study, there is an average range that can provide a general guideline for students pursuing this degree.
On average, an associate’s degree typically requires the completion of around 60 credit hours. This translates to approximately 15-20 courses, assuming each course is worth 3-4 credit hours. However, it’s important to note that this is just a rough estimate, and the actual number of credit hours can vary.
The specific credit hour requirements for an associate’s degree depend on various factors, such as the program’s curriculum, the institution’s policies, and any transfer credits that may be applicable. Some associate’s degree programs may have slightly higher or lower credit hour requirements based on the depth and breadth of coursework required in the field of study.
It’s worth noting that some programs may offer accelerated options or allow students to complete their degree requirements in less time. These accelerated programs often involve a higher load of coursework per semester or offer flexible scheduling options such as summer classes or online courses. On the other hand, part-time students may take longer than the standard two years to complete their associate’s degree, as they typically enroll in fewer credit hours per semester.
Students pursuing specific fields of study may also experience variations in credit hour requirements. Certain specialized programs, such as nursing, computer science, or engineering technology, may have higher credit hour requirements due to additional hands-on or laboratory-based coursework.
It’s important for students to consult their academic advisors or program coordinators to obtain the exact credit hour requirements for their specific program of study. They can provide detailed information about the required courses, credit hours, and any additional requirements for graduation.
By having an understanding of the average credit hour range for an associate’s degree, students can plan their course schedules, manage their time effectively, and ensure they are on track to meet the requirements for degree completion.
Factors Affecting Credit Hours
The number of credit hours required for an associate’s degree can vary based on several factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for students as they plan their academic journey and navigate the requirements for degree completion.
1. Program of Study: Different fields of study have varying credit hour requirements. Programs that have extensive and specialized coursework, such as healthcare, engineering, or technology, may require more credit hours to ensure students acquire the necessary skills and knowledge.
2. Institution’s Policies: Colleges and universities often have their own policies regarding credit hours and degree requirements. Each institution sets its own guidelines based on accreditation standards and the desired outcomes for their programs. It is important for students to research and understand the specific policies of their institution.
3. Transfer Credits: Students who have previously completed coursework at another institution or have obtained credits through exams such as AP, CLEP, or IB may be eligible to transfer those credits towards their associate’s degree. The acceptance of transfer credits can reduce the number of credit hours required for graduation.
4. Prior Learning Assessment: Some institutions provide opportunities for students to earn credits based on their prior learning or professional experience. Prior learning assessment may involve portfolios, examinations, or other forms of evaluation. This assessment can result in the awarding of credit hours, which can shorten the time required to complete an associate’s degree.
5. Course Load: The number of credit hours taken per semester can impact the time required to complete an associate’s degree. Full-time students typically take a higher course load each semester and may complete their degree requirements in a shorter timeframe. Part-time students, on the other hand, enroll in fewer credit hours per semester, which can extend the time needed to earn their degree.
6. Academic Performance: Some programs require students to meet certain GPA or grade requirements to progress and graduate. Failing a course or needing to retake a course can result in additional credit hours needed to fulfill degree requirements.
7. Individual Pace: Each student has their own unique learning style and pace. Some students may choose to take a lighter course load to balance work or family responsibilities, while others may opt for an accelerated program to complete their degree faster. The pace at which a student completes their coursework can impact the total credit hours required.
It’s important for students to consult with academic advisors, program coordinators, or admissions offices to fully understand the factors that can affect credit hours and ensure they are on track to meet the requirements for an associate’s degree.
Full-Time vs. Part-Time Study
When pursuing an associate’s degree, students have the flexibility to choose between full-time and part-time study based on their personal preferences, commitments, and educational goals. The decision between full-time and part-time study can significantly impact the credit hours earned and the time required to complete the degree.
Full-Time Study:
Full-time study refers to enrolling in a higher number of credit hours per semester, typically between 12-15 credit hours. This course load allows students to focus primarily on their academic pursuits with fewer external obligations. Full-time students may take a more traditional path and complete their associate’s degree within the standard two-year timeframe.
Advantages of full-time study include:
- Accelerated completion: Full-time students can complete their degree requirements more quickly due to the higher credit hours taken per semester.
- Continuous learning: With a higher course load, full-time students are consistently engaged in their coursework, enabling them to build upon knowledge and skills acquired in previous courses.
- Access to resources: Full-time students often have greater access to academic support services, such as tutoring, library resources, and extracurricular activities on campus.
- Potential cost savings: Graduating earlier can reduce overall tuition costs and allow students to enter the workforce or pursue higher education sooner.
Part-Time Study:
Part-time study involves enrolling in a lower number of credit hours per semester, usually below 12 credit hours. Part-time students typically balance their academic pursuits with work, family responsibilities, or other commitments.
Advantages of part-time study include:
- Flexibility: Part-time study allows students to create a more manageable schedule, accommodating external obligations such as work or family responsibilities.
- Reduced course load: Taking fewer credit hours per semester can lighten the academic workload and allow for a more balanced approach to learning.
- Extended timeline: Part-time students have the flexibility to spread their coursework over a longer period, allowing for a more gradual and manageable approach to earning their associate’s degree.
- Opportunity for work experience: Part-time students may have the opportunity to gain work experience in their field of study while earning their degree, providing practical skills and networking opportunities.
It is important to note that the choice between full-time and part-time study should be based on individual circumstances, such as work commitments, family responsibilities, financial constraints, and the desired pace of learning. There is no one-size-fits-all approach, and students should carefully consider their options and consult with academic advisors to determine the best fit for their academic and personal goals.
Transfer Credits and Prior Learning Assessment
For students pursuing an associate’s degree, transfer credits and prior learning assessment can play a significant role in reducing the number of credit hours required for graduation.
Transfer Credits:
Transfer credits allow students to apply previously earned credits from accredited institutions toward their associate’s degree. Students who have completed coursework at another college or university may be eligible to transfer those credits, reducing the total number of credit hours needed for degree completion. It is important for students to check the transfer credit policies of their institution to understand which courses are eligible for transfer and the maximum number of credits that can be applied.
Many colleges and universities have established transfer agreements or articulation agreements with other institutions to facilitate a smooth credit transfer process. These agreements outline the specific courses and credits that will be accepted for transfer. It is advisable for students to work closely with their academic advisors and the appropriate transfer credit coordinators to ensure a seamless transition of credits.
Prior Learning Assessment:
Prior learning assessment (PLA) refers to the process of evaluating and awarding credits for learning that has occurred outside of a traditional classroom setting. PLA recognizes that individuals may have gained knowledge and skills through work experience, professional training, military service, or other non-academic activities.
Colleges and universities may offer various options for prior learning assessment, such as portfolio assessment, challenge exams, or credit by examination programs like the College Level Examination Program (CLEP) or Advanced Placement (AP) exams. These assessments allow students to demonstrate their proficiency in a subject and earn credits without having to take the corresponding course.
PLA provides an opportunity for students to leverage their existing knowledge and skills and accelerate their progress towards earning an associate’s degree. It is important to note that the availability and acceptance of prior learning assessment credits vary among institutions. Students should consult with their academic advisors and the PLA coordinators to determine the specific options and requirements for earning credits through prior learning assessment.
By taking advantage of transfer credits and prior learning assessment options, students can potentially reduce their time to degree completion, save on tuition costs, and tailor their educational journey to align with their prior experiences and knowledge.
Conclusion
Earning an associate’s degree is a significant accomplishment that can open doors to various career opportunities and serve as a stepping stone to further education. Understanding the credit hour requirements and the factors that can influence them is essential for students embarking on their journey towards an associate’s degree.
On average, an associate’s degree typically requires the completion of around 60 credit hours, but this can vary based on the program of study, institution’s policies, transfer credits, and prior learning assessment. Students should consult with their academic advisors to determine the specific credit hour requirements for their program.
Factors such as the chosen field of study, institution’s policies, transfer credits, prior learning assessment, course load, academic performance, and individual pace can all impact the number of credit hours needed to earn an associate’s degree. Students should carefully consider these factors and work closely with advisors to navigate their educational journey efficiently.
The choice between full-time and part-time study allows students to tailor their education around their personal commitments, with full-time study offering an accelerated timeline and potential cost savings, while part-time study provides flexibility and the opportunity to balance other responsibilities.
In addition, transfer credits and prior learning assessment can significantly reduce the number of credit hours required. Students should explore options for transferring credits from other institutions and taking advantage of assessments to receive credit for prior learning and work experience.
By understanding these factors and making informed decisions, students can effectively plan their course schedules, manage their time, and complete their associate’s degree with confidence. Whether pursuing an Associate of Arts or an Associate of Science degree, an associate’s degree provides valuable knowledge and skills that can launch successful careers or serve as a foundation for further academic pursuits.
Ultimately, earning an associate’s degree requires dedication, hard work, and a commitment to personal and professional growth. As students embark on this educational journey, they will gain invaluable knowledge, expand their horizons, and lay the groundwork for a promising future.