Finance
What Does RDC Mean In Banking
Published: October 13, 2023
Learn the meaning of RDC in banking and how it impacts financial transactions. Stay informed about the latest developments in the finance industry.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to banking, technology has revolutionized the way we handle financial transactions. One such innovation is Remote Deposit Capture, or RDC, which has transformed the banking experience for individuals and businesses. RDC allows customers to deposit checks without having to physically visit a bank branch, bringing convenience and efficiency to the banking industry.
In this article, we will explore the meaning of RDC in banking, its benefits, the way it works, advancements in security measures, and the differences between RDC and traditional banking methods. We will also delve into the challenges faced in implementing RDC and its overall impact on the financial landscape.
With the advent of RDC, the once time-consuming and cumbersome process of physically depositing checks has been streamlined, enabling customers to deposit funds from the comfort of their homes or offices. This advancement has not only saved time and effort but has also played a significant role in reducing the reliance on physical banking branches.
As we move forward, it is crucial to understand the intricacies of RDC as well as its impact on the banking ecosystem. So, let’s delve into the world of RDC in banking and uncover the advantages, functionalities, and challenges associated with this innovative technology.
Definition of RDC
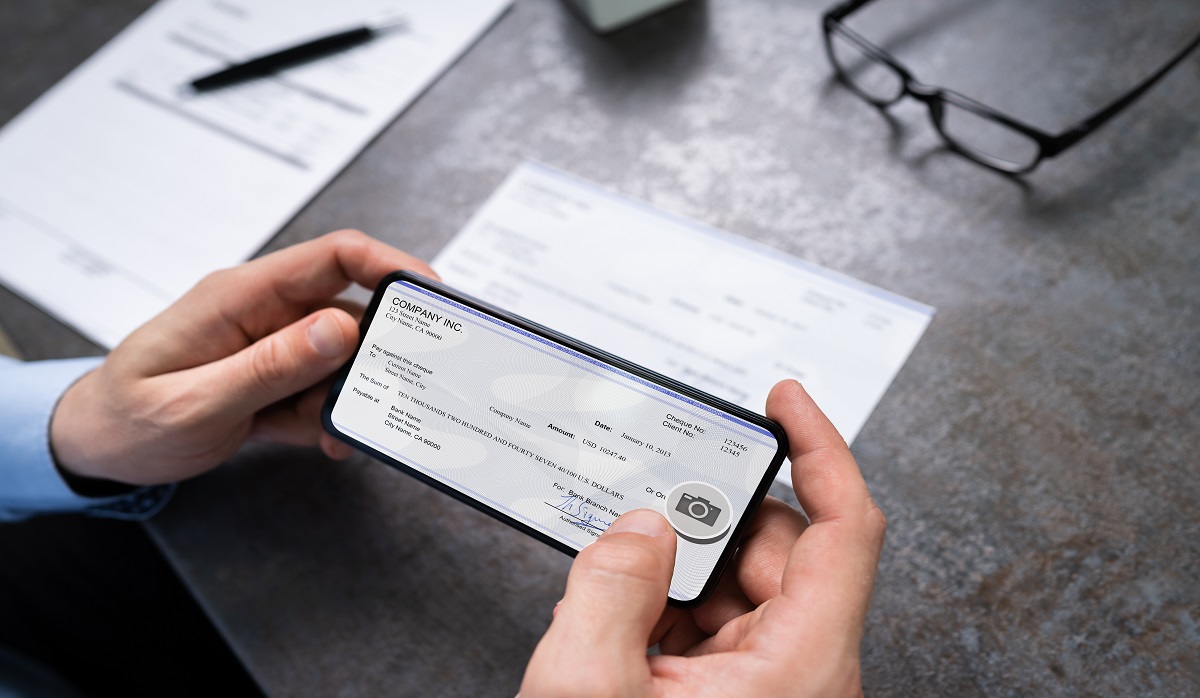
Remote Deposit Capture, commonly known as RDC, is a technology-based service offered by financial institutions that allows customers to deposit checks electronically without the need for physical presence at a bank branch. This digital method of depositing funds offers convenience, speed, and efficiency to both businesses and individuals.
RDC works by utilizing a desktop scanner or a mobile application equipped with the necessary imaging technology. These tools enable users to capture images of the front and back of a check and transmit the images securely to their financial institution for processing.
Upon receipt of the digital check images, the bank processes the deposit, verifies the authenticity of the check, and credits the funds to the customer’s account. The entire process of depositing a check through RDC typically takes just a few minutes, eliminating the need for physical transportation and manual handling of paper checks.
It is important to note that RDC is not limited to personal or retail banking customers. Many financial institutions also offer RDC services tailored for businesses, allowing companies to streamline their accounts receivable processes and improve cash flow management.
In recent years, RDC technology has made significant advances, and many financial institutions have integrated it into their mobile banking apps. This means that customers can deposit checks anytime and anywhere by simply using their smartphones or tablets, making the process even more convenient and efficient.
Overall, RDC represents a fundamental shift in the way check deposits are handled in the banking industry. By embracing digital technology, financial institutions can offer their customers a seamless and secure method to deposit checks, making banking more accessible and convenient for all.
Benefits of RDC in Banking
The adoption of Remote Deposit Capture (RDC) technology in the banking industry has brought about numerous benefits for both financial institutions and their customers. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of RDC:
- Convenience: One of the main benefits of RDC is the convenience it offers to customers. With RDC, individuals and businesses can deposit checks anytime and anywhere through their desktop scanners or mobile applications. This eliminates the need to visit a bank branch, saving valuable time and effort.
- Efficiency: RDC drastically improves the speed and efficiency of check deposits. Instead of physically transporting checks to the bank, customers can simply scan and transmit the check images electronically. This reduces processing times and enables quicker access to funds.
- Cost Savings: RDC eliminates the costs associated with physically depositing checks, such as transportation expenses and potential fees for courier services. Additionally, businesses can reduce administrative costs by automating their accounts receivable processes through RDC, reducing manual data entry and paperwork.
- Flexibility: RDC offers flexibility in terms of deposit options. Customers can choose to deposit checks immediately or schedule deposits for a later date. This flexibility allows for better cash flow management, especially for businesses with varying incomes or seasonal fluctuations.
- Faster Access to Funds: By depositing checks digitally, customers can enjoy faster access to their funds. Financial institutions typically expedite the processing of RDC deposits, allowing customers to have quicker availability of funds compared to traditional check deposits.
- Enhanced Security: RDC incorporates robust security measures to protect sensitive financial information. Encryption technology, secure transmission protocols, and authentication measures ensure that check images are transmitted securely to the bank, minimizing the risk of fraud or unauthorized access.
These benefits make RDC an attractive option for individuals and businesses seeking efficiency, convenience, and cost savings in their banking activities. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further enhancements in RDC services, providing even more advantages to both customers and financial institutions.
How RDC Works in Banking
Remote Deposit Capture (RDC) technology works by allowing customers to digitally deposit checks without physically visiting a bank branch. Here is a step-by-step overview of how RDC works in banking:
- Account Setup: The customer must have an active account with a financial institution that offers RDC services. This can be a personal or business account, depending on the customer’s needs.
- Equipment and Software: To utilize RDC, customers need the appropriate equipment and software provided by their financial institution. This can include a desktop scanner, mobile application, or a combination of both. The equipment and software enable the customer to capture check images and transmit them securely.
- Check Capture: When ready to deposit a check, the customer positions the check on the scanner or uses the mobile application to capture images of the front and back of the check. The software guides the user to align the check properly and ensure a clear image is captured.
- Image Transmission: Once the check images are captured, the customer initiates the transmission of the images to their financial institution. This can be done through a secure connection using the provided software or mobile application.
- Check Processing: Upon receiving the check images, the financial institution’s processing system verifies the authenticity of the check and performs necessary validations. This includes verifying the account number, the amount written on the check, and comparing the signature to the records on file.
- Funds Availability: After the check is successfully processed, the financial institution credits the funds to the customer’s account. The availability of funds may vary depending on the financial institution’s policies, but in many cases, RDC deposits enjoy quicker availability compared to traditional check deposits.
- Check Retention and Disposal: Once the check has been successfully deposited through RDC, customers should follow the financial institution’s guidelines for retaining and disposing of the physical check. This often involves securely storing the check for a specific period and then properly disposing of it to prevent any potential misuse.
It’s important to note that each financial institution may have its own specific processes and procedures for RDC. However, the overall concept remains the same – the customer captures check images, transmits them electronically, and the financial institution processes the deposit and credits the funds to the customer’s account.
RDC has transformed how banking customers handle check deposits, providing a faster, more convenient, and secure alternative to traditional methods. With the ongoing advancements in technology, we can expect RDC to continue evolving, offering even more seamless and efficient deposit experiences for individuals and businesses alike.
Security Measures in RDC Banking
Ensuring the security of customer information and transactions is of utmost importance in the banking industry, and Remote Deposit Capture (RDC) is no exception. Financial institutions have implemented robust security measures to protect the integrity of RDC transactions. Here are some key security measures in RDC banking:
- Encryption Technology: RDC transactions employ encryption technology to protect the sensitive data transmitted during the check deposit process. Encryption scrambles the data, making it unreadable to unauthorized individuals during transmission.
- Secure Transmission Protocols: Financial institutions utilize secure transmission protocols, such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS), to establish encrypted connections between the customer’s device and their servers. This ensures that check images are transmitted securely, preventing interception or tampering.
- Authentication Mechanisms: RDC systems implement authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of customers. This may involve the use of unique usernames, passwords, and additional security measures like two-factor authentication (2FA), which requires an additional verification step, such as a code sent to the customer’s mobile device.
- Image Analysis and Verification: Financial institutions employ sophisticated image analysis technology to verify the authenticity of check images. This includes automated checks for alterations, counterfeit attempts, or tampering. Suspicious or questionable images can be flagged for manual review by banking staff.
- Fraud Detection Systems: RDC systems often incorporate advanced fraud detection systems that use algorithms and machine learning to identify unusual or suspicious patterns in check deposits. These systems can quickly detect potential fraudulent activity and alert the appropriate personnel for further investigation.
- Data Privacy Policies: Financial institutions have stringent data privacy policies and compliance measures in place to protect customer information. These policies outline how customer data is collected, stored, and used, and they adhere to applicable data protection laws and regulations.
Overall, financial institutions make significant investments in technology and infrastructure to ensure the security of RDC transactions. While these measures provide a high level of security, customers also play a vital role in safeguarding their information. This includes using strong passwords, keeping software and devices up to date with the latest security patches, and being cautious of phishing attempts and suspicious online activities.
By implementing these security measures, financial institutions aim to instill confidence in RDC users, assuring them that their funds and personal information are protected throughout the deposit process. Continual advancements in security technology will further enhance the security of RDC banking, providing customers with a safe and secure way to deposit checks without the need to visit a physical banking location.
RDC vs. Traditional Banking Methods
Remote Deposit Capture (RDC) has revolutionized the way we deposit checks, offering a convenient and efficient alternative to traditional banking methods. Let’s compare RDC with traditional banking methods to understand the differences:
- Convenience: RDC provides unparalleled convenience compared to traditional banking methods. With RDC, customers can deposit checks anytime and anywhere using a desktop scanner or a mobile application. Traditional methods, on the other hand, require customers to physically visit a bank branch during business hours to make a check deposit.
- Time and Effort: RDC significantly reduces the time and effort required to deposit checks. With RDC, customers can complete the deposit process within minutes, eliminating the need to travel, stand in line, or fill out deposit slips. Traditional methods involve the physical transportation of checks to a bank branch and waiting in line to make the deposit, which can be time-consuming.
- Processing Speed: RDC offers faster processing times compared to traditional banking methods. Once the check images are transmitted through RDC, they can be processed and verified electronically, making the funds available quicker. In contrast, traditional check deposits may require manual processing, clearing, and verification, leading to longer processing times.
- Cut-off Times: RDC provides more flexibility in cut-off times for check deposits. Many financial institutions offer extended cut-off times for RDC deposits, allowing customers to initiate deposits later in the day and still have the funds credited on the same business day. Traditional banking methods often have earlier cut-off times for same-day processing.
- Cost Savings: RDC can result in cost savings compared to traditional banking methods. With RDC, customers can save on transportation costs associated with physically depositing checks, such as fuel expenses or courier fees. Additionally, businesses can reduce administrative costs by automating accounts receivable processes through RDC, minimizing manual data entry and paperwork.
While RDC offers numerous advantages over traditional banking methods, there are a few considerations to keep in mind. RDC relies on the availability and functionality of the required equipment and software, such as a desktop scanner or a compatible mobile application. Additionally, users must adhere to the guidelines and policies set by their financial institution to ensure a smooth and secure RDC experience.
That being said, the benefits of RDC in terms of convenience, time-saving, processing speed, flexibility, and cost savings make it a compelling choice for individuals and businesses alike. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in RDC, making it an integral part of the modern banking experience, transforming check deposits for the better.
Implementation Challenges of RDC in Banking
While Remote Deposit Capture (RDC) has transformed the way we deposit checks, its implementation in the banking industry comes with its fair share of challenges. Let’s explore some of the key challenges faced in implementing RDC:
- Technological Infrastructure: Implementing RDC requires financial institutions to invest in the necessary technological infrastructure, including scanners, software, and secure transmission systems. Upgrading existing systems and ensuring compatibility with various devices can pose implementation challenges.
- User Adoption and Training: Encouraging customers to adopt and utilize RDC can be a challenge. Some customers may be resistant to change or uncomfortable with using technology for financial transactions. Financial institutions must provide sufficient training, clear instructions, and ongoing support to ensure a smooth transition to RDC.
- Security Concerns: Ensuring the security of RDC transactions is paramount. Financial institutions must continuously invest in robust security measures to protect customer data and prevent fraud. As technology advances, new security threats may arise, necessitating a proactive approach to stay ahead of potential risks.
- Compliance and Regulation: The banking industry operates under strict compliance and regulatory frameworks. Implementing RDC requires financial institutions to navigate these regulations related to check processing, data privacy, anti-money laundering (AML), and fraud prevention. Compliance with these regulations can be complex and involves ongoing monitoring and reporting.
- Check Image Quality: Clear and high-quality check images are essential for accurate processing. However, customers may face challenges in capturing clear images due to various factors such as lighting conditions, check quality, or user error. Financial institutions must provide clear guidelines and educate customers on best practices for capturing acceptable check images.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating RDC technology seamlessly into existing banking systems can be a complex process. Financial institutions need to ensure compatibility and smooth integration with various backend systems, including deposit processing, fraud detection, and account management, to provide a seamless and efficient RDC experience.
Despite these challenges, financial institutions recognize the value and benefits that RDC offers. They continue to invest in overcoming these challenges to provide customers with convenient and secure deposit options. Ongoing innovation, collaboration with technology providers, and continuous improvement in security measures will contribute to the successful implementation and widespread adoption of RDC in banking.
As the banking landscape evolves, it is crucial to address these challenges proactively and adapt to the changing needs and expectations of customers. By doing so, financial institutions can leverage the advantages of RDC while maintaining a secure and efficient banking experience for their customers.
Conclusion
Remote Deposit Capture (RDC) has revolutionized the way we deposit checks in the banking industry. This technology-driven service offers convenience, efficiency, and cost savings for individuals and businesses alike. RDC eliminates the need to physically visit a bank branch and reduces the time and effort required to deposit checks.
Throughout this article, we have explored the meaning of RDC in banking, its benefits, how it works, security measures, and the differences compared to traditional banking methods. The convenience of RDC allows customers to deposit checks anytime and anywhere, providing flexibility and faster access to funds.
Financial institutions have implemented robust security measures to protect the integrity of RDC transactions, including encryption technology, secure transmission protocols, and authentication mechanisms. These measures work together to ensure the security of customer information and prevent unauthorized access and fraud.
While RDC offers numerous advantages, its implementation comes with its fair share of challenges. Financial institutions must overcome obstacles related to technological infrastructure, user adoption, security concerns, compliance and regulation, check image quality, and integration with existing systems.
Despite these challenges, financial institutions are committed to providing a seamless and secure RDC experience for their customers. Ongoing investment in technology, security measures, and customer education will contribute to the continued growth and adoption of RDC in the banking industry.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in RDC, making it even more efficient and accessible. RDC has transformed the way we handle check deposits, bringing convenience and time savings to individuals and businesses. With RDC, the process of depositing checks has become streamlined, allowing customers to focus more on their financial goals and less on administrative tasks.
In conclusion, Remote Deposit Capture has ushered in a new era of convenience and efficiency in the banking industry. It is a testament to the power of technology to simplify and enhance our financial transactions. As customers embrace RDC, they can enjoy the benefits of faster, easier, and more secure check deposits, improving their overall banking experience.