
Finance
How To Avoid APR On A Credit Card?
Published: March 2, 2024
Learn effective strategies to avoid APR on your credit card and save money. Discover smart financial tips and tricks to manage your finances wisely.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
**
Introduction
**
Credit cards have become an integral part of modern financial transactions, offering convenience and flexibility to users. However, the allure of credit cards often comes with the potential burden of high-interest rates, commonly referred to as the Annual Percentage Rate (APR). Understanding and managing APR is crucial for responsible credit card usage. By delving into the intricacies of APR and implementing effective strategies, individuals can navigate the credit card landscape with confidence and financial acumen.
This article aims to demystify the concept of APR on credit cards and provide actionable tips to avoid falling into the APR trap. Whether you're a seasoned credit card user or just starting to build your credit history, the insights shared here will empower you to make informed decisions and mitigate the impact of APR on your financial well-being.
Navigating the world of credit cards can be daunting, especially when faced with the prospect of accruing interest. However, armed with the right knowledge and proactive measures, you can harness the benefits of credit cards without succumbing to the pitfalls of high APR. Let's embark on a journey to unravel the nuances of APR and equip ourselves with practical strategies to sidestep its financial implications.
Understanding APR on Credit Cards
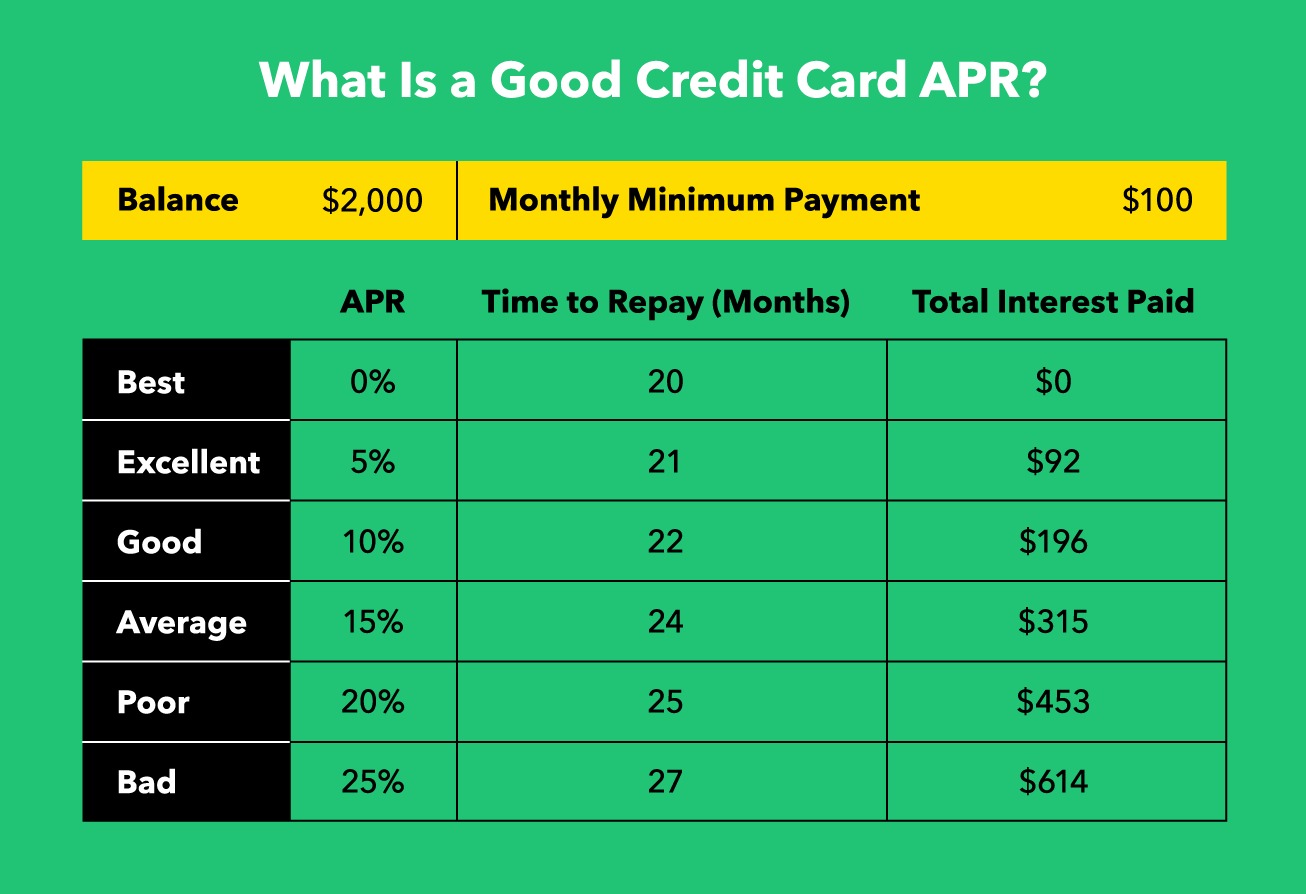
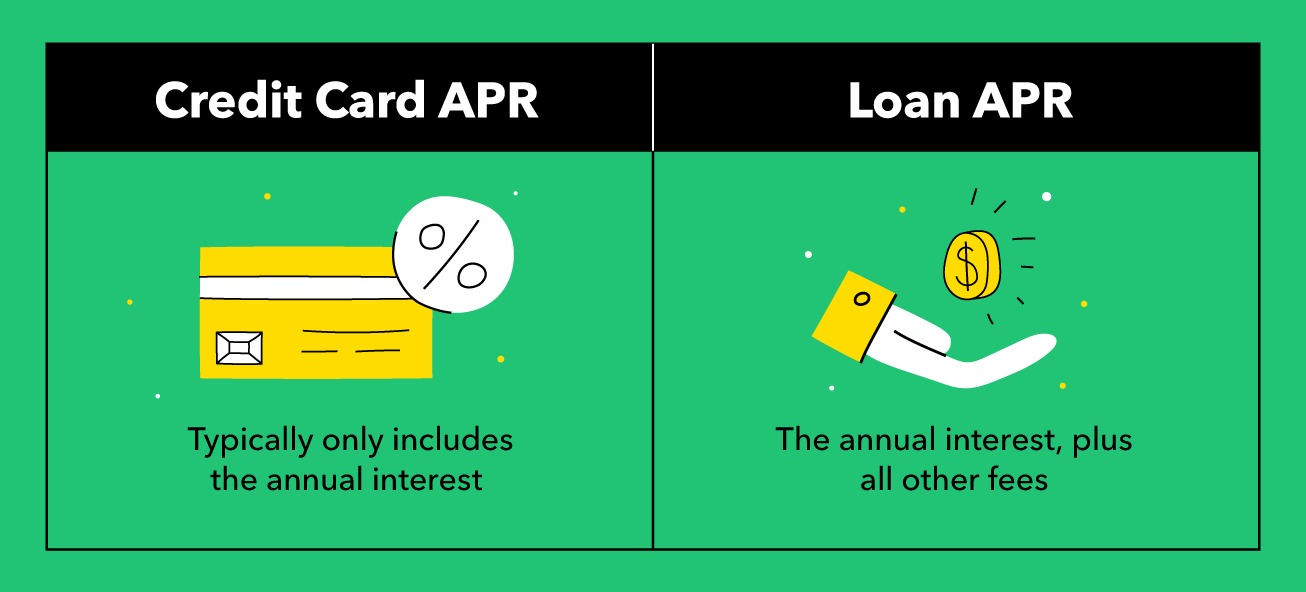
Annual Percentage Rate (APR) is a critical component of credit card terms and refers to the annualized interest rate applied to outstanding balances. Essentially, it represents the cost of borrowing on a credit card, encompassing not only the interest charged by the issuer but also any additional fees or finance charges. It’s important to note that APR can vary based on the type of transaction, such as purchases, balance transfers, or cash advances.
When evaluating credit card offers, understanding the nuances of APR is paramount. The APR can significantly impact the overall cost of using a credit card, especially if balances are carried from month to month. Moreover, credit card companies may apply different APRs based on the cardholder’s creditworthiness, leading to a wide spectrum of potential rates.
Furthermore, credit card APRs can be categorized as variable or fixed. A fixed APR remains constant, providing predictability for cardholders, while a variable APR is tied to an underlying financial index, making it susceptible to fluctuations in the market. This distinction underscores the need for vigilance in monitoring changes to the APR and its potential impact on outstanding balances.
It’s essential to recognize that APR is not solely determined by the interest rate; rather, it encompasses the full spectrum of costs associated with credit card usage. This includes annual fees, late payment penalties, and other charges that contribute to the overall APR. By comprehensively grasping the multifaceted nature of APR, individuals can make informed choices regarding their credit card utilization and minimize the financial implications of high APR.
Tips to Avoid APR on Credit Cards
While APR is an inherent aspect of credit card usage, there are several proactive strategies that individuals can employ to mitigate its impact and, in some cases, avoid it altogether. By integrating these tips into your financial management approach, you can navigate the credit card landscape with prudence and minimize the potential burden of high APR.
1. Paying the Full Statement Balance
One of the most effective ways to sidestep APR charges is to pay the full statement balance every month. By doing so, you eliminate the accrual of interest on carried balances, effectively rendering the APR inconsequential. This approach not only fosters disciplined financial habits but also ensures that you harness the benefits of a credit card without incurring unnecessary costs.
2. Leveraging Interest-Free Periods
Many credit cards offer interest-free periods, typically ranging from 21 to 25 days, during which no interest is charged on new purchases if the previous month’s balance was paid in full. By strategically timing your purchases within this window and promptly settling the outstanding balance, you can capitalize on interest savings and circumvent the imposition of APR.
3. Exploring Balance Transfer Offers
If you are contending with high APR on an existing credit card, exploring balance transfer offers can be a viable option. Some credit card issuers extend promotional periods with minimal or zero APR on transferred balances for a specified duration. By leveraging these offers judiciously, you can consolidate high-interest debts onto a card with more favorable terms, providing temporary respite from APR-related expenses.
4. Negotiating with Credit Card Issuers
Engaging in proactive communication with credit card issuers can yield favorable outcomes, especially if you have a history of responsible financial conduct. In some cases, cardholders have successfully negotiated lower APRs or secured temporary waivers on interest charges, thereby alleviating the financial burden associated with high APR. Building a rapport with your card issuer and articulating your commitment to prudent financial management can open avenues for mitigating the impact of APR.
5. Embracing Financial Discipline
Ultimately, cultivating sound financial habits and exercising prudence in credit card usage form the bedrock of avoiding APR-related challenges. By adhering to budgetary constraints, making timely payments, and steering clear of unnecessary debt accumulation, you can preemptively mitigate the influence of APR on your financial well-being.
By integrating these tips into your financial repertoire, you can proactively manage the impact of APR on credit cards and navigate the financial landscape with confidence and astuteness.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on credit cards is pivotal for prudent financial management. While APR is an inherent component of credit card usage, it need not be a source of undue financial strain. By embracing a proactive approach and implementing targeted strategies, individuals can effectively mitigate the impact of APR and, in some instances, circumvent it altogether.
Through the conscientious application of these tips, such as paying the full statement balance, leveraging interest-free periods, exploring balance transfer offers, negotiating with credit card issuers, and embracing financial discipline, individuals can navigate the credit card landscape with resilience and fiscal sagacity. By doing so, they can harness the benefits of credit cards while minimizing the potential burden of high APR.
Moreover, fostering financial discipline and cultivating prudent financial habits serve as enduring safeguards against the adverse implications of APR. By adhering to these principles, individuals can fortify their financial resilience and steer clear of unnecessary interest expenses, thereby enhancing their overall financial well-being.
Ultimately, the insights shared in this article empower individuals to approach credit card usage with discernment and acumen, transcending the specter of high APR. By integrating these strategies into their financial toolkit, individuals can embark on a journey of financial empowerment, leveraging credit cards as a facilitator of convenience and financial flexibility without succumbing to the pitfalls of exorbitant APR.
Armed with this knowledge and fortified by proactive measures, individuals can chart a course toward financial prudence, leveraging credit cards as a tool for financial empowerment while evading the potential entanglements of high APR.