Finance
Income Bond Definition
Modified: February 21, 2024
Discover the definition of income bonds and how they can be an effective financial tool for generating regular income. Learn more about income bonds in the field of finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Income Bonds: A Complete Guide
When it comes to investing, there are a plethora of options available in the financial market. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, it’s crucial to have a good understanding of the different investment vehicles. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of income bonds and provide you with a comprehensive guide on what they are and how they work.
Key Takeaways:
- Income bonds are a type of fixed-income security that pays interest to bondholders.
- Unlike traditional bonds, income bonds may not pay interest on a regular basis and the interest payment is contingent upon the issuer’s ability to generate income.
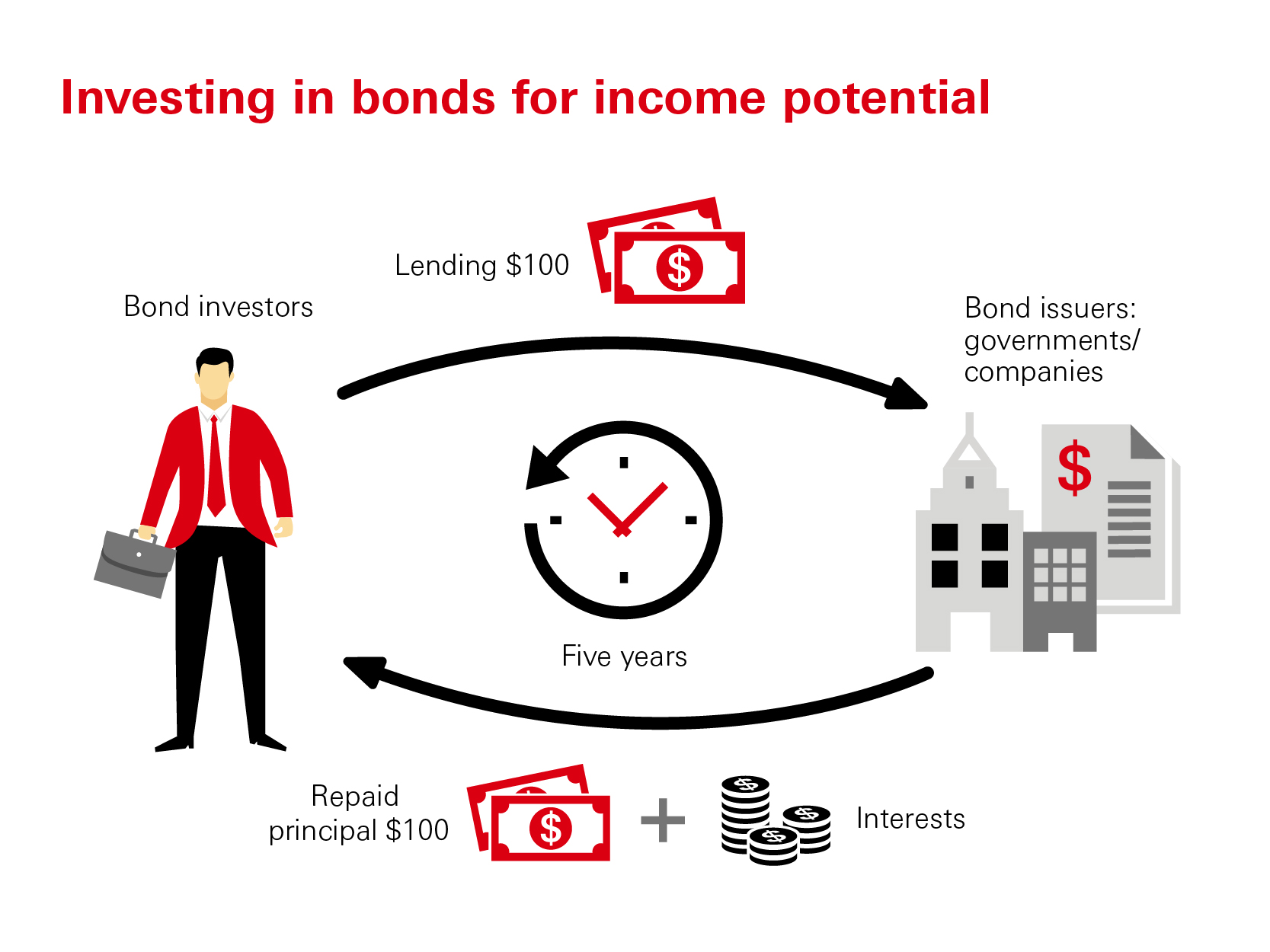
What are Income Bonds?
Income bonds are a type of financial instrument that offer regular interest payments to bondholders. These bonds are issued by companies or governments to raise capital and are typically considered a safer investment option compared to stocks. Unlike traditional bonds, income bonds may not pay interest on a regular basis.
Income bonds are often used by corporations that are currently experiencing financial difficulties or have a negative cash flow. Since the interest payments on income bonds are contingent upon the issuer’s ability to generate income, investors must carefully assess the financial health and stability of the issuing entity before investing in income bonds.
How Do Income Bonds Work?
Income bonds work differently from other types of bonds. Here’s how they operate:
- Interest Payment: The interest payment on income bonds is dependent on the issuer’s ability to generate income. Unlike traditional bonds that pay interest at fixed intervals, income bonds may not pay interest on a regular basis, as it relies on the issuer’s earnings.
- No Fixed Maturity Date: Income bonds also differ from traditional bonds in terms of maturity. While traditional bonds have a defined maturity date, income bonds may not have a fixed maturity date. The issuer has the option to redeem the bond at any time, subject to the terms and conditions of the bond agreement.
- Potential for Higher Returns: Investing in income bonds carries a higher level of risk compared to traditional bonds. However, due to the higher risk involved, income bonds often offer higher interest rates to compensate investors for the potential lack of regular interest payments or the delayed return of principal.
- Investor’s Due Diligence: As an investor, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research and analysis before investing in income bonds. Carefully evaluate the issuer’s financial situation, credit rating, and the specific terms and conditions of the bond agreement. This will help you make an informed decision based on your risk appetite and investment goals.
Conclusion
Income bonds can be a viable investment option for investors seeking regular interest payments. However, it’s essential to understand the risks associated with these types of bonds and to conduct thorough due diligence before investing. By carefully assessing the financial health of the issuer, you can make informed investment decisions that align with your financial goals.
Do you have any further questions about income bonds? Leave them in the comments below, and we’ll be happy to assist you!