Home>Finance>Interest Rate Sensitivity: Definition, What It Measures, And Types


Finance
Interest Rate Sensitivity: Definition, What It Measures, And Types
Published: December 11, 2023
Learn the definition and types of interest rate sensitivity in finance, and how it measures the impact of interest rate changes on investments and financial markets.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Interest Rate Sensitivity in Finance
When it comes to managing your finances, understanding interest rates is crucial. Whether you’re saving for the future or considering taking out a loan, the concept of interest rate sensitivity plays a significant role. In this article, we’ll dive into the definition of interest rate sensitivity, what it measures, and the different types you should be aware of.
Key Takeaways:
- Interest rate sensitivity measures the impact of interest rate changes on the value of financial instruments.
- It is an essential factor in decision-making for investors, borrowers, and financial institutions.
Definition of Interest Rate Sensitivity
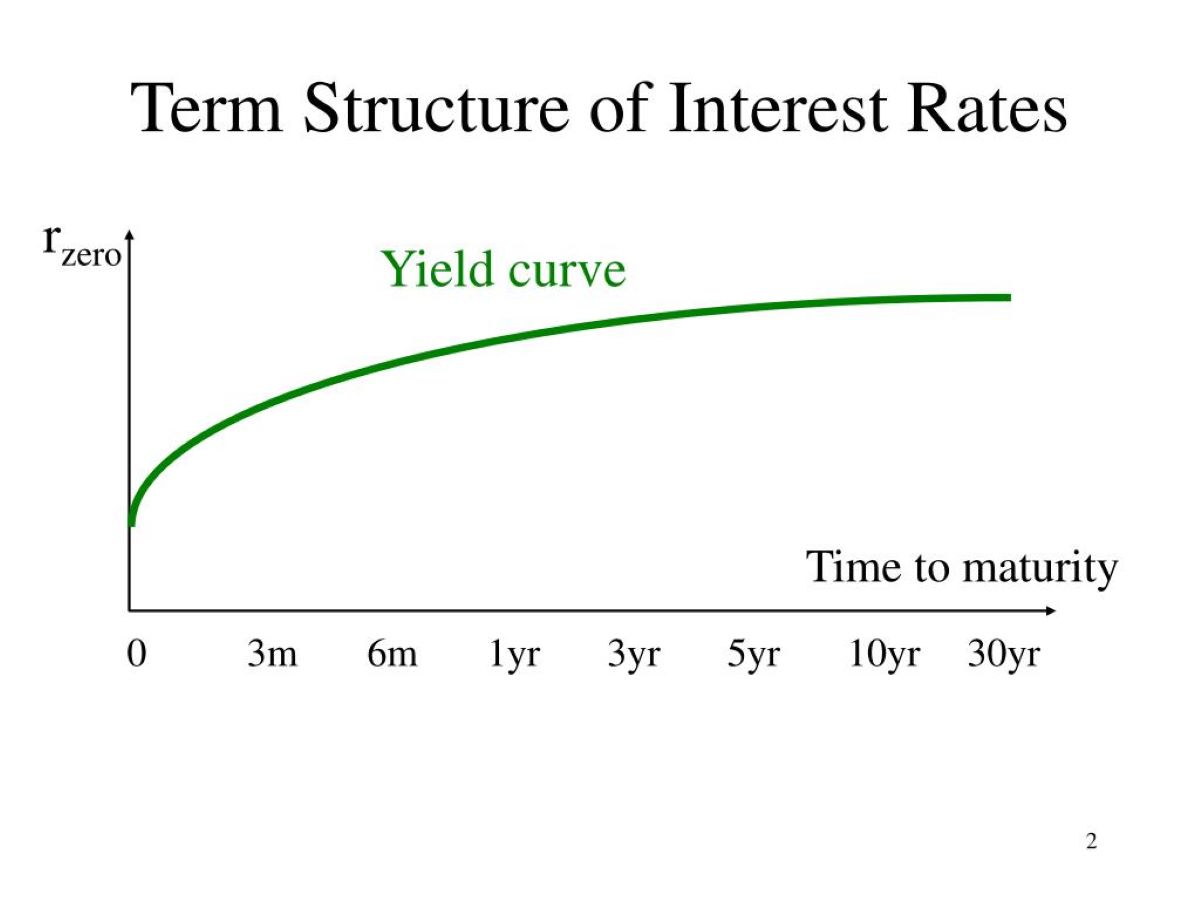
Interest rate sensitivity refers to the relationship between interest rates and the value of financial instruments. It is a measure of how much the value of these instruments changes in response to fluctuations in interest rates. The sensitivity is typically expressed as a percent change in value for a given change in interest rates.
Interest rate sensitivity affects various financial products and instruments, including bonds, mortgages, and loans. Understanding interest rate sensitivity is crucial for investors, borrowers, and financial institutions, as it helps them gauge the potential impact of interest rate changes on their portfolios, investments, and profitability.
What Does Interest Rate Sensitivity Measure?
Interest rate sensitivity measures the potential impact of interest rate changes on the value of financial instruments. It allows individuals and organizations to understand how the value of these instruments may fluctuate in response to changes in interest rates.
For example, if you own a savings account or a fixed-income investment such as a bond, interest rate sensitivity helps you assess how the value of your investment may change if interest rates rise or fall. Understanding this sensitivity enables you to make informed decisions about your investments and manage your financial risk effectively.
Types of Interest Rate Sensitivity
There are primarily two types of interest rate sensitivity:
- Price Sensitivity: Price sensitivity, also known as “duration,” measures the percentage change in the price of a financial instrument for a given change in interest rates. Bonds and fixed-income securities typically have a price sensitivity or duration associated with them. A higher duration indicates a higher price sensitivity or a more significant impact on the value of the instrument due to interest rate changes.
- Cash Flow Sensitivity: Cash flow sensitivity measures the impact of interest rate changes on the cash flows generated by financial instruments. It is particularly relevant for loans, mortgages, and other debt instruments, where changes in interest rates affect the amounts paid or received by borrowers and lenders. Higher cash flow sensitivity means that changes in interest rates have a substantial impact on the cash flows associated with the instrument.
Understanding the specific type of interest rate sensitivity is crucial for making informed financial decisions. For example, as a bond investor, if you are more concerned with price movements in response to interest rate changes, you would focus on duration. On the other hand, if you are a borrower with a variable-rate mortgage, understanding the cash flow sensitivity would help you anticipate changes in your monthly payments.
Conclusion
Interest rate sensitivity is a vital concept to grasp in the world of finance. It measures the impact of interest rate changes on the value and cash flows of various financial instruments, helping individuals and organizations make informed decisions.
Key Takeaways:
- Interest rate sensitivity determines how the value of financial instruments changes in response to interest rate fluctuations.
- It helps investors, borrowers, and financial institutions manage their portfolios, investments, and risk effectively.
By understanding interest rate sensitivity and its different types, individuals can make more informed decisions about their investments, loans, and overall financial strategies.