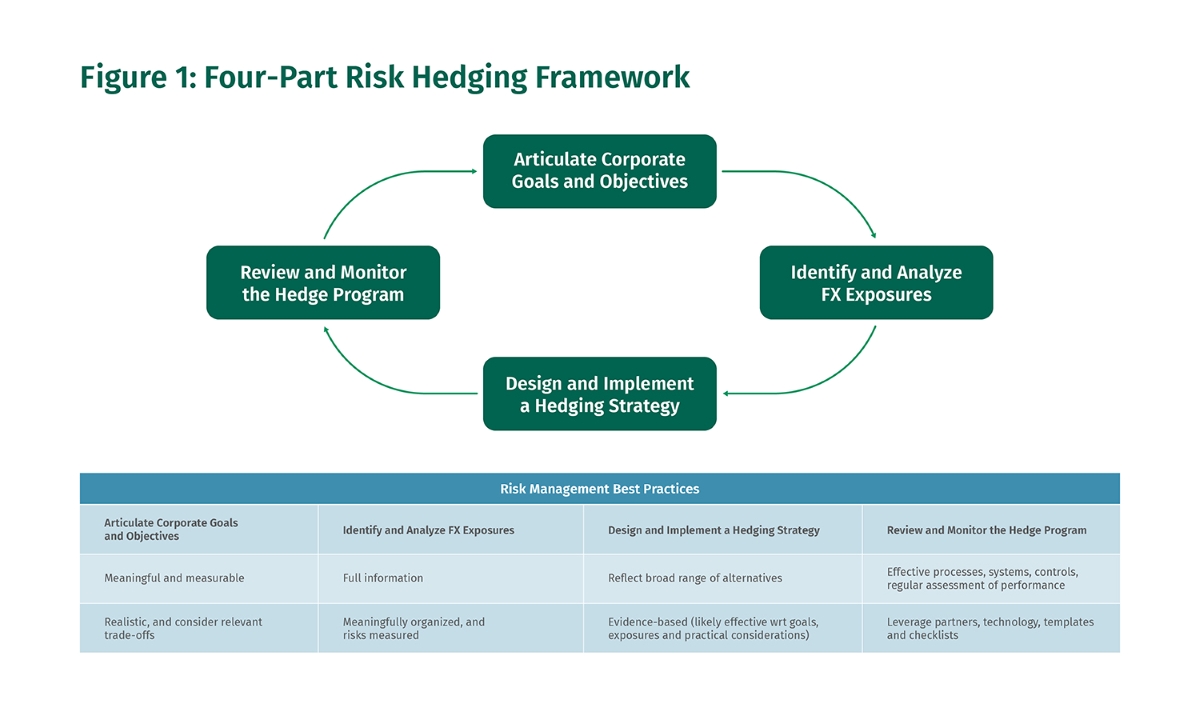
Home>Finance>Line Graph: Definition, Types, Parts, Uses, And Examples


Finance
Line Graph: Definition, Types, Parts, Uses, And Examples
Published: December 18, 2023
Learn about the definition, types, parts, uses, and examples of line graphs in finance. Find out how line graphs can visually represent financial data.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Welcome to the world of finance!
Are you ready to dive into the exciting world of finance? Look no further. In this post, we will explore everything you need to know about finance. Let’s kick off this journey by understanding what finance is and how it impacts us in our daily lives.
Key Takeaways:
- Finance is the discipline concerned with the management of money, investments, and other financial instruments.
- Understanding finance can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions regarding their finances and investments.
What is Finance?
Finance is a broad term that encompasses various aspects of managing money and making financial decisions. It includes activities such as budgeting, investing, banking, lending, and more. Whether you are an individual, a small business owner, or a large corporation, understanding finance is crucial for achieving financial stability and success.
Types of Finance:
Finance can be divided into several subcategories, each serving different purposes. Here are some common types of finance:
- Personal Finance: This type of finance relates to individuals and their financial decisions. It involves managing personal budgets, savings, investments, retirement planning, and handling personal debts.
- Corporate Finance: Corporate finance focuses on the financial decisions made by businesses. It includes investment analysis, capital budgeting, financial planning, and managing the company’s finances.
- Public Finance: Public finance refers to the financial management of government entities, including taxation, public expenditure, debt management, and budgeting.
- International Finance: International finance deals with financial transactions between countries and the management of cross-border investments, foreign exchange rates, and trade finance.
Parts of Finance:
To fully comprehend finance, you need to understand its key components. Here are the main parts of finance:
- Financial Markets: These are platforms where individuals and institutions trade financial assets such as stocks, bonds, derivatives, and commodities.
- Financial Institutions: Banks, credit unions, investment firms, and insurance companies are examples of financial institutions. They provide various financial services to individuals and businesses.
- Financial Instruments: These are contracts and securities that represent a monetary value. Examples include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, options, and futures.
- Financial Analysis: Financial analysis involves evaluating the financial health and performance of individuals, businesses, and investment opportunities. It utilizes various techniques and metrics to assess profitability, liquidity, solvency, and growth potential.
Why is Finance Important?
Finance plays a crucial role in our lives, shaping our financial well-being and influencing economic growth. Here are some reasons why finance is important:
- Proper financial management allows individuals to budget effectively, save for their goals, and make informed investment decisions.
- Businesses rely on finance to fund their operations, invest in growth opportunities, manage risks, and generate profits.
- Government entities use finance to allocate resources, implement fiscal policies, and promote economic stability.
- Understanding finance helps individuals and businesses navigate through the complexities of taxation, debt management, and financial regulations.
Examples of Finance in Action:
Let’s look at a few examples to illustrate how finance influences our everyday lives:
- Home Mortgage: When purchasing a house, most individuals require a home loan. Finance allows banks to provide these loans, allowing people to own their dream homes.
- Investment Portfolios: Finance enables individuals to invest in stocks, bonds, and mutual funds to grow their wealth over time.
- Business Loans: Small businesses often rely on loans and lines of credit to fund their operations and expand their activities. Finance provides the means for these funds.
- Government Budgets: Finance allows governments to allocate funds for infrastructure development, healthcare, education, and other public services.
So, whether you’re planning your personal budget or analyzing investment opportunities, finance is the backbone that supports sound financial decision-making. By understanding its various components and applications, you’ll be equipped to navigate the world of finance with confidence.