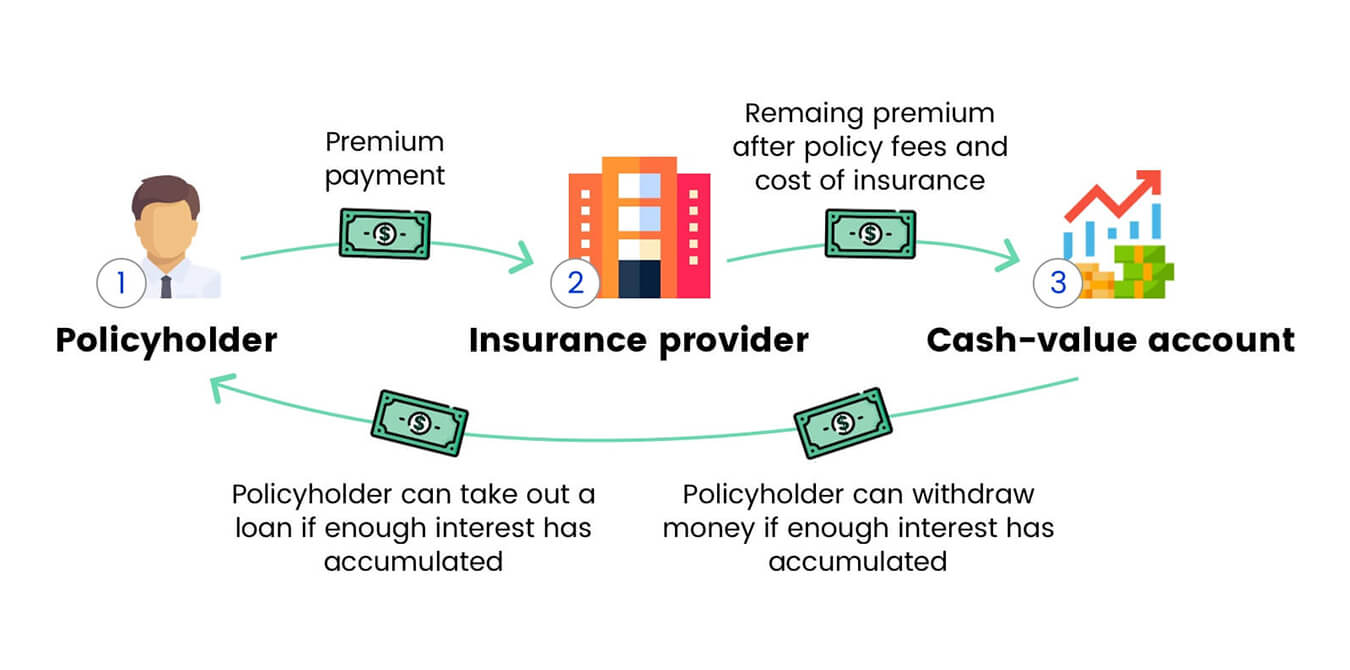
Home>Finance>Under A Life Insurance Policy, What Does The Insuring Clause State?


Finance
Under A Life Insurance Policy, What Does The Insuring Clause State?
Published: October 15, 2023
Discover what the insuring clause in a life insurance policy entails and its role in protecting your financial future. Ensure your peace of mind with a comprehensive understanding of this essential finance component.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of an Insuring Clause
- Purpose of an Insuring Clause
- Key Components of an Insuring Clause
- Types of Coverage Provided by an Insuring Clause
- Conditions and Limitations of an Insuring Clause
- Importance of Understanding the Insuring Clause
- Case Studies: Interpretation of Insuring Clauses
- Conclusion
Introduction
Life insurance is a financial tool that provides protection against the uncertainties of life by offering a death benefit to the beneficiaries of the policyholder. When purchasing a life insurance policy, it is essential to understand the various components and terms mentioned within the policy document. One crucial component of a life insurance policy is the insuring clause.
The insuring clause is a fundamental provision in a life insurance policy that outlines the coverage and terms offered by the insurer. It is often referred to as the heart of the contract as it sets the foundation for the entire policy. Understanding the insuring clause is crucial as it defines the scope of coverage, the types of risks covered, and the conditions under which the policy will pay out.
In this article, we will delve into the ins and outs of the insuring clause in a life insurance policy. We will explore its definition, purpose, key components, and the types of coverage provided. Additionally, we will discuss the conditions and limitations associated with the insuring clause and highlight the importance of understanding this clause when purchasing life insurance.
Furthermore, to illustrate the practical implications of the insuring clause, we will analyze a few case studies that will shed light on the interpretation and application of the clause in real-life scenarios.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the insuring clause and its significance within a life insurance policy. Let’s dive in!
Definition of an Insuring Clause
The insuring clause, also known as the coverage clause or grant of coverage, is a crucial provision in a life insurance policy that specifies what risks are covered and the conditions under which the insurer will pay out a death benefit to the beneficiaries. Essentially, it outlines the scope and extent of the coverage provided by the policy.
Within the insuring clause, the insurance company clearly states its commitment to pay a benefit upon the death of the insured individual. It specifies the amount that will be paid out, which is typically the face value or the sum assured of the policy. Additionally, it establishes the circumstances under which the policyholder or beneficiaries are eligible to receive the death benefit.
The language used in the insuring clause is crucial, as it may define the period of coverage, any exclusions, and any specific conditions or requirements that must be met. It is essential to read this clause carefully to ensure that you fully understand the coverage provided by the policy.
For example, an insuring clause may state that, “In the event of the death of the insured individual during the policy term, the insurer agrees to pay a death benefit equal to the sum assured to the designated beneficiaries.” This clearly establishes the insurer’s commitment to providing a benefit upon the insured individual’s death.
It is important to note that the insuring clause is a standard feature of life insurance policies but may vary in its wording from one policy to another. Each insurance company may have its own specific language and terminology within the insuring clause. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully review and understand the insuring clause for the specific policy you are considering.
Now that we have defined the insuring clause, let’s explore its purpose and why it is such a critical component of a life insurance policy.
Purpose of an Insuring Clause
The insuring clause in a life insurance policy serves several important purposes that benefit both the policyholder and the insurance company. Let’s explore the key purposes of an insuring clause:
- Clearly defines the coverage: The primary purpose of an insuring clause is to clearly outline the risks and events that are covered under the policy. It specifies the circumstances under which the insurance company will pay out the death benefit. This helps both the policyholder and the beneficiaries understand the scope of coverage and the situations in which they may be eligible for a payout.
- Establishes the obligations of the insurance company: The insuring clause establishes the contractual obligation of the insurance company to pay the death benefit upon the insured individual’s death. It sets the terms and conditions for the insurer’s responsibility and creates a legal obligation to fulfill the promised coverage.
- Provides clarity on the payout amount: The insuring clause specifies the amount that will be paid out upon the insured individual’s death. This amount is typically referred to as the sum assured or the face value of the policy. It ensures that the policyholder and beneficiaries have a clear understanding of the financial protection provided by the policy.
- Creates transparency and trust: By clearly stating the coverage and obligations of both parties, the insuring clause helps establish transparency and build trust between the policyholder and the insurance company. It ensures that the policyholder understands the terms of the policy and can make informed decisions when purchasing life insurance.
- Guides underwriting and risk assessment: The insuring clause plays a crucial role in the underwriting process, where the insurance company assesses the risk associated with an individual’s life. By clearly defining the coverage, the insuring clause helps the insurer determine the premium amount and evaluate the insurability of the applicant.
In summary, the insuring clause serves to clearly define the coverage, establish the insurer’s obligations, provide clarity on the payout amount, create transparency and trust, and guide the underwriting process. Understanding the purpose of the insuring clause is essential for policyholders to make informed decisions and ensure they have the appropriate coverage for their needs.
Now that we understand the purpose of an insuring clause, let’s explore the key components that are typically included in this important provision.
Key Components of an Insuring Clause
The insuring clause in a life insurance policy consists of several key components that provide specific details about the coverage being offered. These components help establish the terms and conditions under which the insurer will pay out the death benefit. Let’s explore the key components typically found in an insuring clause:
- Statement of coverage: The insuring clause begins by explicitly stating the coverage being provided by the policy. It outlines the risks or events that are covered, such as death due to illness, accident, or natural causes.
- Payout amount: The insuring clause specifies the amount that will be paid out to the beneficiaries upon the death of the insured individual. This amount is typically referred to as the sum assured or the face value of the policy.
- Designated beneficiaries: The clause identifies and specifies the beneficiaries who are entitled to receive the death benefit. It can be one or multiple individuals, and their full names or relationship to the insured may be mentioned.
- Policy conditions and requirements: The insuring clause may outline any specific conditions or requirements that must be met for the death benefit to be paid out. This can include factors such as the policy being in force, premium payments being up to date, and the insured’s death occurring within the policy term.
- Exclusions or limitations: The insuring clause may also mention any exclusions or limitations to the coverage provided. These are specific situations or circumstances in which the policy will not pay out the death benefit. Common exclusions include suicide within a certain period after policy issuance and death due to engaging in high-risk activities.
The language used in the insuring clause is crucial as it outlines the mutual obligations of the insured and the insurer. It is essential to read this clause carefully to ensure that you understand the coverage being offered and any specific conditions or limitations that may apply.
As mentioned earlier, the specific wording and components within the insuring clause may vary from one insurance company to another. Therefore, it is important to carefully review the insuring clause of the policy you are considering to fully understand its provisions.
Now that we have explored the key components of an insuring clause, let’s move on to understanding the types of coverage provided by this important clause.
Types of Coverage Provided by an Insuring Clause
The insuring clause in a life insurance policy outlines the types of coverage provided by the insurer. These types of coverage determine the events or risks for which the death benefit will be paid out. Let’s explore the common types of coverage that are typically included in an insuring clause:
- Death Benefit: The primary coverage provided by an insuring clause is the death benefit. This coverage ensures that if the insured individual passes away, the designated beneficiaries will receive a payout. The death benefit is usually a lump sum payment and is typically equal to the sum assured or the face value of the policy.
- Accidental Death Benefit: Some life insurance policies may include an additional coverage option known as the accidental death benefit. This provides an extra amount in addition to the regular death benefit if the insured individual dies due to an accident covered by the policy. The accidental death benefit is typically a percentage of the base death benefit.
- Terminal Illness Benefit: Another type of coverage that may be included is the terminal illness benefit. This coverage allows the policyholder to access a portion of the death benefit if they are diagnosed with a terminal illness that is expected to result in death within a specified timeframe (as defined in the policy). The terminal illness benefit helps provide financial support during the individual’s remaining time.
- Waiver of Premium: Some policies may offer a waiver of premium feature within the insuring clause. This provision states that if the insured individual becomes permanently disabled or unable to work due to an illness or injury, the insurance company will waive future premium payments while keeping the policy in force. This helps ensure that the coverage continues even if the policyholder is unable to pay the premiums due to their disability.
- Additional Riders: An insuring clause may also mention any additional coverage options or riders that have been added to the base policy. Riders are optional additions to the policy that provide coverage for specific events or circumstances, such as critical illness, disability, or accidental death. These riders enhance the overall coverage and can be customized to fit the policyholder’s specific needs.
It is important to review the insuring clause and policy documentation thoroughly to understand the precise types of coverage provided by the policy. This will ensure that you have a clear understanding of the events or risks for which the death benefit will be paid out.
Now that we have explored the types of coverage provided by an insuring clause, let’s turn our attention to the conditions and limitations that may be associated with this important provision.
Conditions and Limitations of an Insuring Clause
While the insuring clause in a life insurance policy outlines the coverage being provided, it is important to understand that there may be certain conditions and limitations associated with this clause. These conditions and limitations establish the criteria that must be met for the insurer to pay out the death benefit. Here are some common conditions and limitations you may come across:
- Policy in force: The insuring clause typically requires that the policy be in force at the time of the insured individual’s death for the death benefit to be paid out. This means that the premium payments must be up to date, and the policy must not have lapsed or been cancelled.
- Waiting period: Some policies may have a waiting period, also known as the contestability period, during which the insurance company can investigate the information provided by the policyholder. If the insured individual dies within this waiting period (usually two years), the insurer may investigate the cause of death more rigorously before paying out the death benefit.
- Exclusions and limitations: The insuring clause may specify particular exclusions or limitations to coverage. For example, it may state that the death benefit will not be paid out if the insured individual dies by suicide within a certain period after the policy’s commencement. Similarly, engaging in certain hazardous activities or misrepresenting information in the application can lead to the denial of the death benefit under specific circumstances.
- Pre-existing conditions: Depending on the policy, there may be limitations or exclusions related to pre-existing medical conditions. This means that if the insured individual has a pre-existing condition, such as a chronic illness, the insurer may either exclude coverage for that specific condition or apply specific waiting periods before the condition is covered.
- Policy terms: The insuring clause may also include specific terms and conditions related to the duration of the policy. For example, if the policy term expires and the insured individual passes away after that, the death benefit may not be paid out.
It is important to carefully review the insuring clause and policy documentation to understand the specific conditions and limitations that apply to your life insurance coverage. This will help you determine whether the policy aligns with your needs and expectations.
Now that we have explored the conditions and limitations associated with an insuring clause, let’s discuss the importance of understanding this clause when purchasing life insurance.
Importance of Understanding the Insuring Clause
When purchasing a life insurance policy, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the insuring clause. This provision outlines the coverage being provided, the conditions under which the death benefit will be paid, and any limitations or exclusions that may apply. Here are some key reasons why understanding the insuring clause is of utmost importance:
- Clarity of Coverage: The insuring clause provides clarity on the scope of coverage offered by the policy. It outlines the risks or events for which the death benefit will be paid out. Understanding the insuring clause ensures that you know the specific circumstances in which your beneficiaries will be eligible to receive the death benefit.
- Informed Decision-making: By understanding the insuring clause, you can make informed decisions when selecting a life insurance policy. You can compare different policies based on their coverage provisions and conditions, ensuring that you choose the one that aligns with your needs and goals.
- Policy Suitability: Understanding the insuring clause helps you assess whether the policy meets your requirements. You can evaluate if the coverage provided aligns with your financial objectives and the level of protection you desire for your loved ones.
- Exclusions and Limitations: The insuring clause outlines any exclusions or limitations to coverage. By being aware of these, you can avoid potential surprises when it comes to filing a claim. You can assess whether any exclusions or limitations align with your lifestyle, health conditions, or specific concerns.
- Interpretation of Terms: Understanding the insuring clause allows you to interpret the terms and conditions of the policy correctly. It ensures that you are aware of any specific requirements or obligations that must be fulfilled to maintain coverage and secure the death benefit for your beneficiaries.
- Effective Financial Planning: With a clear understanding of the insuring clause, you can effectively plan your finances. You can assess the potential payout your beneficiaries will receive and determine how it fits into your overall financial strategy, such as estate planning and providing for your family’s future needs.
Reading and comprehending the insuring clause may seem complex, but it is essential to ensure that you have the right level of coverage and peace of mind. If you have any doubts or questions about the insuring clause or any other policy provisions, consider seeking guidance from an insurance professional who can provide expert advice based on your specific circumstances.
Now, let’s explore case studies that illustrate the interpretation of insuring clauses in real-life scenarios.
Case Studies: Interpretation of Insuring Clauses
To better understand the practical implications of an insuring clause, let’s analyze a few case studies that highlight the interpretation and application of this crucial provision in real-life scenarios:
- Case Study 1: Accidental Death Coverage
- Case Study 2: Suicide Exclusion
- Case Study 3: Pre-existing Condition Limitation
In this case, the insuring clause of a life insurance policy includes an accidental death benefit rider. The insured individual unfortunately passes away due to an accident covered by the policy. The beneficiaries submit a claim for the death benefit, including the additional amount from the accidental death coverage. The insurance company thoroughly investigates the cause of death to ensure that it meets the criteria for an accidental death. Once satisfied, the insurer pays out the death benefit along with the additional coverage specified in the insuring clause.
In this case, the insuring clause explicitly states that the policy will not pay out the death benefit if the insured individual dies by suicide within two years of the policy’s inception. Unfortunately, the insured individual takes their own life within the excluded timeframe. As a result, the insurance company is not liable to pay the death benefit as specified in the insuring clause. The exclusion outlined in the insuring clause allows the insurer to avoid covering suicides that occur shortly after policy issuance.
In this case, the insuring clause includes a provision that limits coverage for pre-existing medical conditions. The insured individual has a pre-existing heart condition that was disclosed during the application process. The policy explicitly states that any claims related to the pre-existing condition will be excluded for the first two years of the policy term. Unfortunately, the insured individual passes away due to a heart-related issue within the exclusion period. As a result, the insurance company denies the claim for the death benefit related to the pre-existing condition, in accordance with the insuring clause.
These case studies illustrate how the interpretation and application of insuring clauses can impact the payment of death benefits in different situations. It emphasizes the importance of carefully reviewing and understanding the insuring clause to ensure that you are aware of any specific exclusions, limitations, or conditions that may affect the policy’s coverage.
Now that we have examined these case studies, let’s wrap up our discussion on the significance of the insuring clause in a life insurance policy.
Conclusion
The insuring clause is a vital component of a life insurance policy as it defines the coverage, conditions, and limitations offered by the insurer. Understanding the insuring clause is crucial for policyholders to make informed decisions, ensure appropriate coverage for their needs, and be aware of any exclusions or limitations that may impact the payout of the death benefit. It provides clarity on the coverage being provided, establishes the obligations of the insurance company, and guides the underwriting process.
By carefully reading and comprehending the insuring clause, policyholders can ensure that they have a clear understanding of the types of coverage provided, the terms and conditions to be met, and any exclusions or limitations that may apply. This knowledge empowers individuals to effectively plan their financial future, assess the suitability of the policy, and make informed decisions about coverage options and riders.
It is essential to review the insuring clause in detail when purchasing a life insurance policy and to seek guidance from insurance professionals, if needed. By doing so, policyholders can ensure that their life insurance coverage aligns with their needs and goals, providing financial protection and peace of mind to their loved ones.
In conclusion, the insuring clause is the heart of a life insurance policy, outlining the coverage, conditions, and limitations associated with the death benefit. Understanding this clause is of utmost importance to make informed decisions, navigate policy provisions confidently, and secure the financial future of your beneficiaries.