Finance
What Are The Roles Of Pension Funds?
Published: January 22, 2024
Discover the crucial roles of pension funds in finance and retirement planning. Learn how these funds impact the financial market and individual wealth management.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
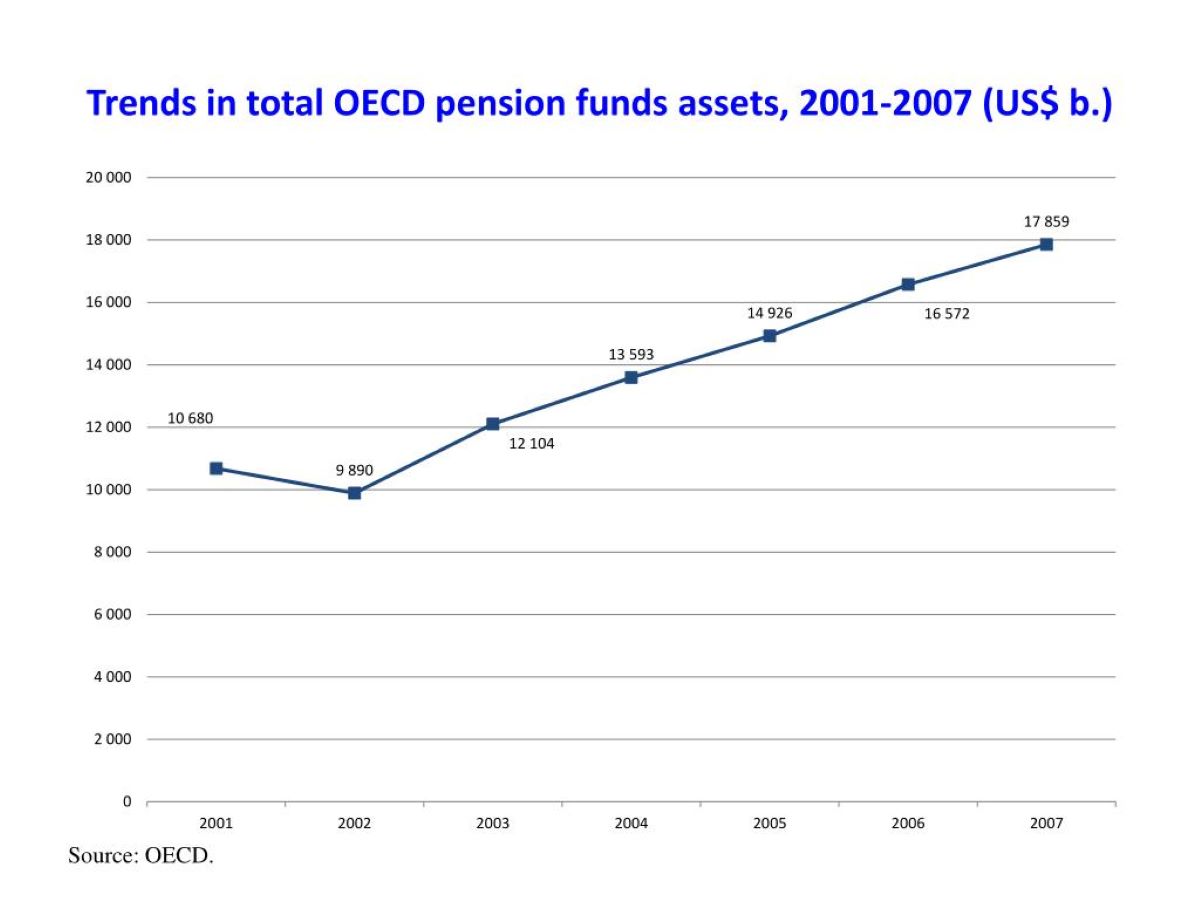
Pension funds play a pivotal role in the financial landscape, serving as a cornerstone for retirement planning and investment. These funds are designed to provide individuals with financial security during their retirement years, offering a range of benefits and opportunities for long-term wealth accumulation. By understanding the multifaceted roles of pension funds, individuals can make informed decisions about their financial futures and gain insight into the broader impact of these funds on the economy and society as a whole.
Pension funds are instrumental in shaping the financial well-being of retirees, offering a means to accumulate and grow savings over the course of one's career. As individuals contribute a portion of their earnings to these funds, they are essentially investing in their own future, with the goal of securing a comfortable and stable retirement. Moreover, pension funds serve as a crucial source of capital for various investment avenues, fostering economic growth and stability.
Understanding the significance of pension funds entails delving into their various roles, which extend beyond individual retirement planning. From investing for retirement to promoting corporate governance and contributing to infrastructure development, pension funds have far-reaching implications that warrant exploration. By examining these roles in depth, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the impact and importance of pension funds in the financial realm and society at large.
Investing for Retirement
One of the primary roles of pension funds is to facilitate investing for retirement. These funds serve as a vehicle for individuals to set aside a portion of their income during their working years, with the aim of building a substantial nest egg for their retirement. Through prudent investment strategies, pension funds endeavor to grow the contributions made by employees, ensuring that they yield favorable returns over time. This long-term approach to investing is geared towards providing retirees with a reliable source of income once they exit the workforce.
Pension funds allocate the pooled contributions from employees across a diverse portfolio of assets, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and other investment instruments. By spreading the investments across various sectors and industries, pension funds aim to mitigate risk and optimize returns, thereby safeguarding the financial future of retirees. Furthermore, the professional management of pension fund assets by experienced investment professionals is instrumental in maximizing growth potential while adhering to risk management principles.
Employing a disciplined and strategic investment approach, pension funds strive to generate substantial returns on the funds accumulated, thereby ensuring that retirees can maintain their standard of living and meet their financial obligations post-retirement. By harnessing the power of compounding and leveraging the expertise of investment managers, pension funds play a crucial role in securing the financial well-being of retirees and enabling them to enjoy a comfortable and fulfilling retirement.
Providing Retirement Income
Another vital role of pension funds is to provide retirees with a consistent and reliable source of income during their post-employment years. Through the accumulation of contributions and investment returns, pension funds are structured to offer a steady stream of payments to retirees, supplementing other sources of retirement income such as social security benefits. This regular income serves to sustain retirees’ financial well-being, enabling them to cover living expenses, healthcare costs, and other essential needs without undue financial strain.
Upon reaching retirement age, individuals who have contributed to a pension fund are often presented with various options for receiving their accumulated benefits. These may include receiving periodic payments over a predetermined period, opting for a lump sum distribution, or choosing a combination of both. The flexibility offered by pension funds empowers retirees to tailor their income stream according to their specific financial requirements and preferences, thereby enhancing their financial security and autonomy in retirement.
By providing a reliable source of income, pension funds alleviate the financial uncertainties that retirees may face, allowing them to enjoy their post-employment years with peace of mind and stability. This aspect of pension funds underscores their pivotal role in safeguarding the economic well-being of retirees and underscores the importance of prudent retirement planning and investment management throughout one’s career.
Corporate Governance
Pension funds wield significant influence in the realm of corporate governance, exerting their power as institutional investors to advocate for sound governance practices within the companies in which they hold stakes. As substantial shareholders, pension funds have a vested interest in promoting transparency, accountability, and ethical conduct among corporate entities, thereby safeguarding the interests of their beneficiaries and the broader investment community.
Through active engagement with the management teams and boards of directors of publicly traded companies, pension funds strive to influence decision-making processes, encourage responsible business practices, and align corporate strategies with the long-term interests of shareholders. This involvement may encompass voting on key corporate resolutions, participating in shareholder meetings, and collaborating with other institutional investors to effect positive changes in corporate policies and operations.
By advocating for strong corporate governance standards, pension funds seek to enhance the overall performance and sustainability of the companies in which they invest, thereby bolstering the value of their investment portfolios. Furthermore, by promoting ethical conduct and responsible management practices, pension funds contribute to fostering a business environment that prioritizes integrity, transparency, and long-term value creation, benefitting not only their beneficiaries but also the broader economy and society.
Infrastructure Investment
Pension funds play a crucial role in financing infrastructure projects that are vital for economic development and societal progress. By allocating a portion of their investment portfolios to infrastructure assets, such as transportation networks, energy facilities, and public utilities, pension funds contribute to the expansion and maintenance of essential infrastructure that underpins economic activity and quality of life.
Infrastructure investments offer pension funds the opportunity to generate long-term, stable returns while simultaneously fulfilling a societal need for robust infrastructure. These investments often exhibit characteristics of long asset life, predictable cash flows, and inflation-hedging qualities, aligning with the long-term liabilities and objectives of pension funds. Additionally, infrastructure projects can have a tangible impact on communities by creating jobs, improving connectivity, and enhancing overall productivity.
By channeling capital into infrastructure development, pension funds not only seek to achieve attractive risk-adjusted returns for their beneficiaries but also contribute to the advancement of public infrastructure, addressing critical gaps and modernizing essential facilities. This dual benefit underscores the significance of infrastructure investment as a strategic avenue for pension funds to deploy capital in a manner that aligns with their long-term investment objectives while fulfilling broader societal needs.
Social Responsibility
Beyond their financial objectives, pension funds embrace a role of social responsibility, leveraging their influence and resources to promote sustainable and ethical investment practices. By integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into their investment decisions, pension funds seek to drive positive change and contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future.
Through the incorporation of ESG considerations, pension funds aim to align their investment strategies with principles that prioritize environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and ethical governance. This approach not only reflects a commitment to responsible investing but also underscores the recognition of the interconnectedness between financial performance and broader societal and environmental impacts.
Furthermore, pension funds engage in active stewardship of the companies and assets in which they invest, advocating for sustainable business practices, diversity and inclusion, and transparent governance. By promoting responsible corporate behavior and sustainable business models, pension funds play a pivotal role in influencing the conduct of investee companies and fostering a culture of responsible capitalism.
By embracing social responsibility as a fundamental tenet of their investment approach, pension funds align their financial objectives with broader societal and environmental imperatives, thereby contributing to positive change while pursuing long-term value creation for their beneficiaries and the society at large.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pension funds fulfill multifaceted roles that extend beyond individual retirement planning, encompassing vital contributions to the economy, society, and the broader investment landscape. These funds serve as instrumental vehicles for investing for retirement, enabling individuals to accumulate savings and build a secure financial foundation for their post-employment years. Through strategic investment management, pension funds aim to generate favorable returns and provide retirees with a reliable source of income, thereby fostering financial security and stability.
Moreover, pension funds exert influence in the realm of corporate governance, advocating for sound governance practices and ethical conduct within the companies in which they invest. By promoting transparency and accountability, pension funds contribute to the long-term sustainability and value creation of corporate entities, thereby safeguarding the interests of their beneficiaries and the broader investment community.
Furthermore, pension funds play a pivotal role in infrastructure investment, channeling capital into essential projects that drive economic development and enhance societal well-being. By financing critical infrastructure, pension funds contribute to the advancement of public assets while pursuing attractive risk-adjusted returns for their beneficiaries.
Embracing social responsibility as a core principle, pension funds integrate environmental, social, and governance considerations into their investment strategies, aiming to drive positive change and contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future. Through responsible investing and active stewardship, pension funds seek to align their financial objectives with broader societal and environmental imperatives, thereby fostering a culture of responsible capitalism and sustainable value creation.
Overall, the roles of pension funds encompass not only the prudent management of retirement savings but also the promotion of ethical governance, infrastructure development, and social responsibility. By understanding and appreciating the diverse roles of pension funds, individuals can gain valuable insights into the broader impact of these funds on the economy and society, empowering them to make informed decisions about their financial futures and retirement planning.