
Finance
What Is A Pro Forma Capital Structure
Published: December 25, 2023
Discover the importance of pro forma capital structures in finance and how they impact financial planning and decision-making.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Pro Forma Capital Structure
- Purpose of Pro Forma Capital Structure
- Examples of Pro Forma Capital Structure
- Importance of Pro Forma Capital Structure
- Factors to Consider in Creating a Pro Forma Capital Structure
- Benefits and Limitations of Pro Forma Capital Structure
- How to Calculate Pro Forma Capital Structure
- Role of Pro Forma Capital Structure in Financial Analysis
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to navigating the complex world of finance, understanding the concept of a pro forma capital structure is crucial. Whether you’re a business owner, investor, or financial analyst, having a firm grasp on pro forma capital structure can greatly impact your decision-making process and overall financial success. In this article, we will delve into the depths of pro forma capital structure, exploring its definition, purpose, examples, importance, calculation methods, and its role in financial analysis.
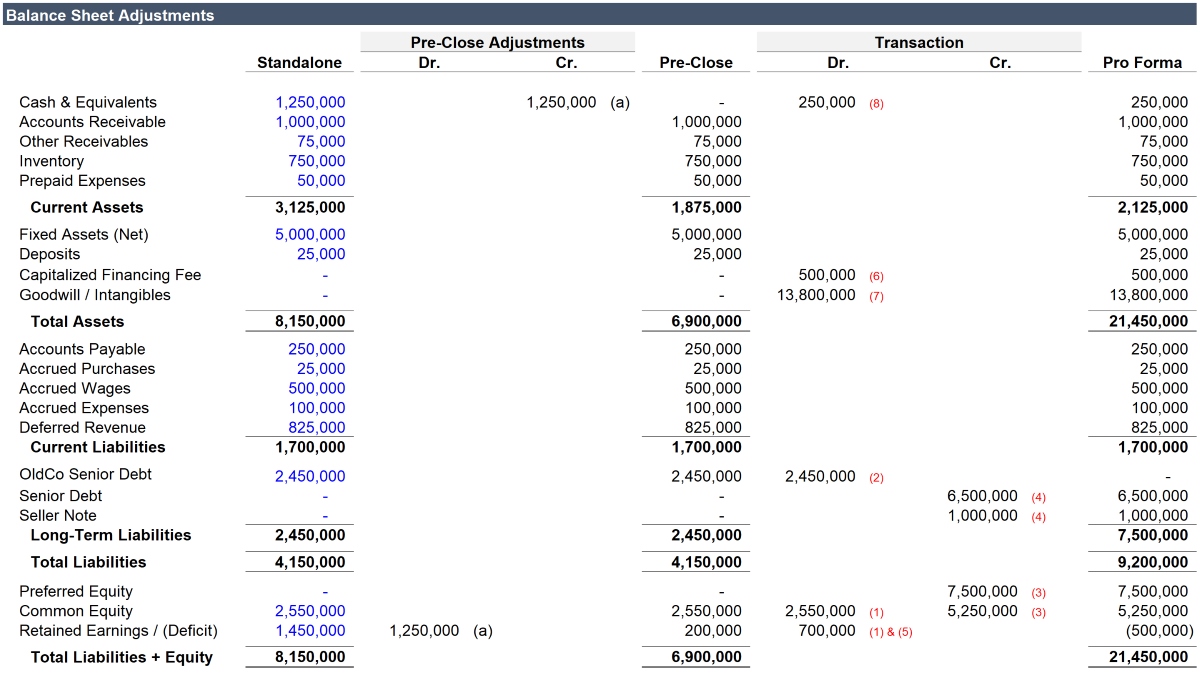
Pro forma capital structure refers to a hypothetical or projected capital structure that reflects the potential financing mix a company may adopt in the future. It essentially outlines the composition of a company’s long-term financing, including the proportion of debt, equity, and other financial securities. It takes into account the funds required to support the company’s growth plans, investment projects, and overall financial objectives.
The primary purpose of establishing a pro forma capital structure is to estimate the financial implications, risks, and benefits associated with various financing options. By creating a hypothetical capital structure, companies can evaluate the viability of different capital raising strategies, determine the most optimal mix of debt and equity, and assess the impact on profitability, liquidity, and shareholder value.
Let’s consider an example to illustrate the concept of pro forma capital structure. An eCommerce startup, ABC Electronics, is planning to expand its operations to new markets and launch innovative product lines. To finance this growth, ABC Electronics may consider different financing options, such as bank loans, issuing bonds, or raising additional equity capital. Through pro forma analysis, the company can assess the potential outcomes of each financing option, estimate the cost of capital, and evaluate the impact on the company’s financial position.
The importance of pro forma capital structure lies in its ability to provide valuable insights into the financial health and stability of a company. By examining different capital structures, companies can identify the most suitable financing mix to achieve their strategic objectives and maintain a healthy balance between debt and equity. Pro forma analysis also aids in projecting future cash flows, determining the return on investment for shareholders, and assessing the financial risks associated with various financing decisions.
Creating a pro forma capital structure involves considering several key factors. Companies need to evaluate their current financial position, growth plans, industry dynamics, market conditions, and regulatory requirements. Additionally, they need to determine the appropriate levels of debt and equity, considering factors such as interest rates, repayment terms, cost of capital, dilution of ownership, and financial flexibility.
While pro forma capital structure analysis offers numerous benefits, it is important to recognize its limitations. The accuracy of projections may be influenced by unforeseen market conditions, changes in interest rates, regulatory changes, or shifts in investor sentiment. Therefore, it is important to regularly update and reassess the pro forma capital structure as new information becomes available.
In the next section, we will explore the calculation methods for determining a pro forma capital structure and discuss how it is utilized in financial analysis.
Definition of Pro Forma Capital Structure
The pro forma capital structure is a financial analysis tool that allows businesses to project a hypothetical or estimated composition of their long-term financing. It outlines the potential mix of debt, equity, and other financial securities that a company may adopt in the future to support its growth plans, investment projects, and overall financial objectives.
By creating a pro forma capital structure, companies can assess the potential implications, risks, and benefits associated with different financing options. It serves as a roadmap for determining the most optimal mix of debt and equity that aligns with the company’s strategic goals and financial stability.
The pro forma capital structure incorporates both existing and potential sources of capital. It takes into consideration the company’s current debt level, equity ownership, and any anticipated changes in the future. This allows companies to evaluate the potential impact on their capitalization, capital structure ratios, and financial viability.
Moreover, the pro forma capital structure aids in estimating the cost of capital for the company. It takes into account factors such as interest rates on debt, dividend rates for equity, and the overall risk profile of the business. By understanding the costs associated with different financing options, companies can make informed decisions that optimize their financial resources.
The pro forma capital structure is not a static snapshot but rather a dynamic model that can be adjusted and revised as circumstances change. It provides a framework for scenario planning and sensitivity analysis, allowing companies to evaluate the potential outcomes of different financing strategies under varying market conditions.
Overall, the pro forma capital structure is a powerful financial tool that enables businesses to forecast their future capital needs and make informed decisions regarding their financing mix. By considering factors such as debt, equity, interest rates, and risk profiles, companies can develop a comprehensive understanding of their financial structure and chart a path towards sustainable growth and profitability.
Purpose of Pro Forma Capital Structure
The purpose of the pro forma capital structure is to provide companies with a strategic framework for assessing and planning their long-term financing. By creating a hypothetical or projected capital structure, businesses can evaluate the potential impact of different financing options on their financial position, profitability, and overall sustainability.
One key purpose of the pro forma capital structure is to estimate the financial implications of various financing strategies. It allows companies to assess the costs associated with different types of financing, such as debt or equity, and helps determine the most optimal mix that aligns with the company’s growth plans and financial objectives.
Additionally, the pro forma capital structure aids in evaluating the financial risks and benefits associated with different financing options. Companies can use it to analyze the potential impact on their debt-to-equity ratio, interest expense, cash flow, and other key financial indicators. This enables them to make informed decisions about their financing mix to ensure financial stability and minimize risk.
Another purpose of the pro forma capital structure is to provide insights into the potential return on investment for shareholders. By analyzing the projected capital structure, companies can estimate the cost of equity, the dilution of ownership, and the expected return for shareholders. This information is crucial for attracting and retaining investors and ensuring their potential for value appreciation.
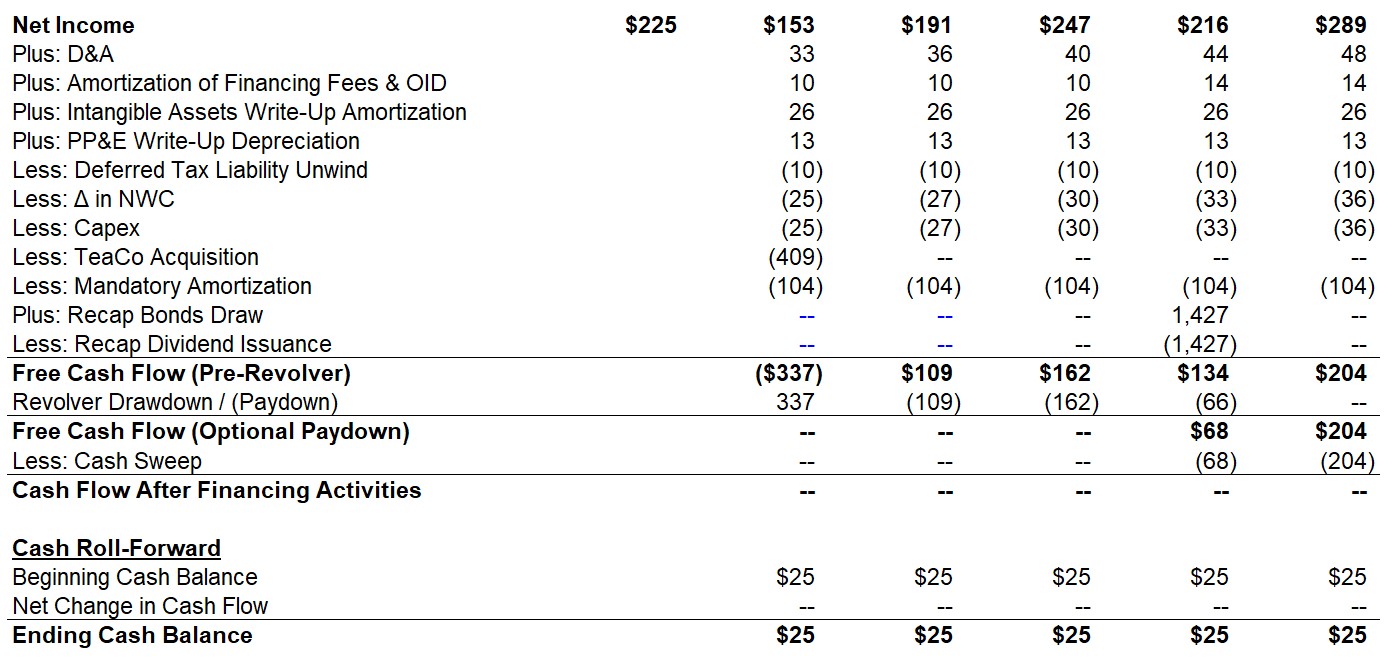
The pro forma capital structure also helps companies project future cash flows and assess their ability to meet their debt obligations. By considering the potential financing mix, companies can estimate the impact on interest payments and principal repayments. This allows them to gauge their financial sustainability and plan for any potential liquidity challenges.
Furthermore, the pro forma capital structure is essential for strategic planning and decision-making. It provides a framework for evaluating different financing scenarios, such as raising additional capital, restructuring existing debt, or initiating stock repurchase programs. By utilizing the pro forma capital structure, companies can assess the potential outcomes of these decisions and choose the most optimal course of action.
Overall, the purpose of the pro forma capital structure is to guide companies in making informed financial decisions. It helps them assess the potential implications, risks, and benefits associated with different financing options and provides a roadmap for sustainable growth and financial success.
Examples of Pro Forma Capital Structure
To better understand how the pro forma capital structure works, let’s explore a few examples of how it can be applied in different scenarios:
1. Start-up Company: A tech start-up is looking to raise capital to fund its product development, marketing efforts, and expansion plans. The pro forma capital structure analysis will help the company assess the most effective financing mix. It may consider a combination of equity financing from angel investors or venture capitalists, as well as debt financing through bank loans or issuing bonds. By projecting the potential capital structure, the start-up can evaluate the impact on its liquidity, profitability, and future growth prospects.
2. Established Corporation: A well-established manufacturing company wants to diversify its product line and enter new markets. The management team is considering various financing options, such as issuing additional shares, taking on long-term debt, or utilizing retained earnings. Through pro forma analysis, the company can estimate the impact of each financing option on its capitalization, debt-to-equity ratio, and return on equity. This information will help the company make an informed decision about the most suitable financing mix that aligns with its growth objectives.
3. Acquisition or Merger: In the case of an acquisition or merger, both companies involved need to assess the potential capital structure of the combined entity. Pro forma analysis allows them to evaluate the impact on their respective capitalization levels, debt coverage ratios, and financial performance. By considering factors such as financing costs, interest rates, and synergies, the companies can determine the optimal financing mix and the potential benefits of the transaction.
4. Capital Restructuring: A company with a high level of debt may consider a capital restructuring to improve its financial position. Through pro forma analysis, the company can evaluate the impact of various restructuring options, such as refinancing debt with lower interest rates or converting debt into equity. The analysis helps the company determine the potential reduction in interest expense, improvement in debt-to-equity ratio, and the overall impact on its financial stability.
These examples demonstrate how the pro forma capital structure analysis can be applied in various contexts. By considering different financing options, estimating their impact on financial ratios, profitability, and growth prospects, companies can make well-informed decisions that optimize their capital structure and drive long-term success.
Importance of Pro Forma Capital Structure
The pro forma capital structure holds significant importance in the realm of finance, as it plays a pivotal role in guiding strategic decision-making and assessing the financial health of a business. Let’s explore why understanding and analyzing the pro forma capital structure is crucial:
1. Strategic Planning: The pro forma capital structure provides valuable insights that enable companies to chart a strategic course. By evaluating different financing options and their potential impact, businesses can align their capital structure with their growth objectives and long-term plans. It helps them determine the most optimal financing mix to support expansion, new product development, and market entry strategies.
2. Financial Viability: A well-balanced and sustainable capital structure is essential for a company’s financial viability. The pro forma analysis allows businesses to assess the potential risks and benefits associated with different financing options. By considering factors such as debt levels, interest rates, and equity ownership, companies can optimize their capital structure in a way that supports profitability, maximizes shareholder value, and minimizes financial risk.
3. Investor Confidence: The pro forma capital structure plays a crucial role in attracting and retaining investors. By projecting the potential return on investment and estimating the impact on share ownership, companies can demonstrate their financial stability and potential for value appreciation. This builds investor confidence and enhances the company’s ability to raise capital or issue stock in the market.
4. Risk Management: The pro forma capital structure analysis helps companies evaluate the potential financial risks associated with different financing options. By considering factors such as interest rates, debt-to-equity ratios, and repayment terms, businesses can assess their ability to meet their debt obligations and manage their cash flow. It allows them to plan for any potential liquidity challenges in advance and develop strategies to mitigate financial risks.
5. Decision-Making: The pro forma capital structure analysis aids in making informed financial decisions. It provides a framework for evaluating the financial implications, costs, and benefits of different financing options. By understanding the potential impact on profitability, cash flow, and capitalization, companies can make sound decisions that align with their strategic objectives, maximize financial resources, and optimize shareholder value.
6. Financial Performance Evaluation: The pro forma capital structure acts as a benchmark for assessing the financial performance of a company. By comparing the projected capital structure with the actual results, businesses can identify any deviations and make necessary adjustments. It helps them monitor the effectiveness of their financing strategies, evaluate the utilization of funds, and identify areas for improvement.
In summary, the pro forma capital structure is of utmost importance in finance. It enables companies to strategically plan their financial future, optimize their capital structure, manage financial risks, attract investors, and make informed decisions that drive sustainable growth and financial success.
Factors to Consider in Creating a Pro Forma Capital Structure
Creating a pro forma capital structure requires careful consideration of several key factors. These factors influence the composition of a company’s long-term financing and play a critical role in determining the optimal mix of debt, equity, and other financial securities. Let’s explore some important factors to consider when creating a pro forma capital structure:
1. Current Financial Position: Evaluating the company’s current financial position is essential when creating a pro forma capital structure. This includes assessing factors such as existing debt levels, equity ownership, and cash flow. Understanding the starting point helps in projecting the potential capital structure and determining how it relates to the company’s present financial health.
2. Growth Plans and Objectives: The company’s growth plans and objectives should inform the pro forma capital structure. Consider the company’s future investment projects, expansion plans, and anticipated capital requirements. These factors help determine the amount of financing needed and the appropriate proportion of debt and equity to support the growth trajectory.
3. Industry Dynamics and Market Conditions: Consider the specific dynamics of the industry in which the company operates. Factors such as industry growth rates, competitive landscape, and market conditions can influence the financing mix. For example, companies in a rapidly evolving tech industry may need to allocate more resources towards research and development, potentially leading to a higher equity component in the capital structure.
4. Regulatory Requirements: Take into account any regulatory requirements or restrictions that may impact the company’s financing options. For example, certain industries may have specific guidelines on debt-to-equity ratios or limitations on foreign ownership. Adhering to these requirements is crucial when determining the appropriate capital structure.
5. Cost of Capital: Evaluate the cost of different financing options, such as interest rates on debt and dividend rates on equity. Consider both short-term and long-term financing costs. Balancing the desire for lower financing costs with the need for sustainable profitability is important when selecting the financing mix.
6. Dilution of Ownership: Consider how the various financing options may dilute existing shareholders’ ownership in the company. Issuing new equity or convertible debt may result in a decrease in ownership percentages for current shareholders. Balancing the need for capital infusion with maintaining a reasonable level of ownership dilution is critical.
7. Financial Flexibility: Assess the company’s need for financial flexibility. Determine how the capital structure affects the company’s ability to respond to market changes, unforeseen challenges, or future investment opportunities. Evaluate the trade-offs between fixed obligations, such as debt repayments, and the ability to maneuver and adapt to changing circumstances.
These factors provide guidance when creating a pro forma capital structure. However, it’s important to note that no single approach fits all companies. The specific circumstances and goals of each company will influence the weight given to each factor and the resulting optimal capital structure. Regularly reviewing and reassessing the capital structure is essential as market conditions, regulatory requirements, and business objectives may change over time.
Benefits and Limitations of Pro Forma Capital Structure
The pro forma capital structure analysis offers several benefits to companies in evaluating their long-term financing decisions. However, it is important to recognize its limitations as well. Let’s delve into the benefits and limitations of the pro forma capital structure:
Benefits:
1. Decision Support: The pro forma capital structure provides valuable insights that support strategic decision-making. It helps companies assess the potential financial implications, risks, and benefits of different financing options. With this information at hand, businesses can make informed choices that align with their growth plans, financial objectives, and shareholder interests.
2. Financial Planning: By projecting the potential capital structure, companies can plan and allocate their financial resources more efficiently. The pro forma analysis aids in estimating future cash flows, determining the cost of capital, and assessing the company’s ability to meet its debt obligations. This allows for effective financial planning and mitigates the risk of cash flow shortages or liquidity challenges.
3. Optimal Financing Mix: The pro forma capital structure helps companies determine the optimal mix of debt and equity. By considering factors such as interest rates, dilution of ownership, and financial flexibility, companies can strike a balance between the costs and benefits of different financing options. This allows for capital structures that support growth, maintain financial stability, and optimize shareholder value.
4. Investor Confidence: The pro forma capital structure analysis builds investor confidence by providing transparency and a clear financial roadmap. It allows companies to illustrate the potential return on investment, value appreciation prospects, and the overall financial health of the business. This attracts potential investors and aids in capital raising efforts.
Limitations:
1. Uncertain Market Conditions: Pro forma capital structures are based on assumptions and projections, which are subject to change due to uncertain market conditions. External factors such as interest rate fluctuations, changes in industry dynamics, or economic downturns can impact the accuracy of pro forma analysis. Companies must regularly update and reassess the capital structure as new information becomes available.
2. Integration Challenges: In cases of mergers and acquisitions, creating a pro forma capital structure for the combined entity can be complex. It requires integrating the financials, capitalization, and debt levels of both companies, taking into account potential synergies and changes in ownership. Such integration challenges can add complexity to the pro forma analysis.
3. Limited Predictability: While a pro forma capital structure provides insights into the potential future financials, it does not guarantee actual performance. Unforeseen events or changes in the business environment can significantly impact the accuracy of projections. It is important to supplement the pro forma analysis with ongoing monitoring and adjustment as circumstances change.
4. Regulatory Constraints: Pro forma capital structures must comply with regulatory requirements and limitations. Industries and jurisdictions may place restrictions on debt-to-equity ratios, foreign ownership, or capitalization levels. Companies must ensure their pro forma capital structure aligns with these regulations to avoid potential fines or legal issues.
Despite its limitations, the pro forma capital structure remains a valuable tool for financial analysis and decision-making. Companies that understand its benefits and limitations can effectively utilize it to optimize their financing decisions and strive for long-term financial success.
How to Calculate Pro Forma Capital Structure
Calculating the pro forma capital structure involves estimating the composition of a company’s long-term financing by considering the proportion of debt, equity, and other financial securities. Here are the key steps involved in calculating the pro forma capital structure:
1. Identify Existing Capital Structure: Start by gathering information on the company’s current capital structure. This includes the current outstanding debt, equity ownership, and any other financial securities. This information serves as a baseline for projecting the potential capital structure.
2. Assess Financing Needs: Determine the financing needs of the company based on its growth plans, investment projects, and financial objectives. Evaluate the capital requirements and estimate the amount of funding required to support these initiatives.
3. Evaluate Financing Options: Consider the various financing options available to the company. This may include debt financing through bank loans, bonds, or other debt instruments, as well as equity financing through issuing new shares or seeking investment from venture capitalists or angel investors. Evaluate the costs, terms, and risks associated with each financing option.
4. Consider Cost of Capital: Assess the cost of each financing option to estimate the impact on the company’s overall cost of capital. Consider factors such as interest rates on debt, dividend rates for equity, and the risk profile of the company. Strive to understand the trade-offs between the costs and benefits of each financing option.
5. Determine Optimal Financing Mix: Analyze the potential impact of different financing options on the company’s capital structure ratios, such as debt-to-equity ratio or leverage ratio. Evaluate how each financing option aligns with the company’s growth plans, financial stability, and risk tolerance. Strive to achieve an optimal financing mix that supports the company’s strategic objectives.
6. Create Pro Forma Capital Structure: Based on the evaluation of financing options and the desired financing mix, project the potential composition of the company’s long-term financing. Estimate the proportion of debt, equity, and other financial securities that would constitute the pro forma capital structure.
7. Monitor and Review: Remember that calculating the pro forma capital structure is an ongoing process. Regularly monitor and review the capital structure to ensure its alignment with the company’s evolving needs and market conditions. Adjust the pro forma capital structure as necessary to reflect changes in financing requirements, market dynamics, or regulatory constraints.
It is important to note that calculating the pro forma capital structure involves making assumptions and projections, which are subject to uncertainties. Companies should conduct sensitivity analysis to understand the potential impact of different variables on the pro forma capital structure calculations. Regularly revisiting and adjusting the projections based on new information and market changes is crucial to maintaining an accurate and effective capital structure.
Role of Pro Forma Capital Structure in Financial Analysis
The pro forma capital structure plays a significant role in financial analysis by providing valuable insights into a company’s long-term financing and its impact on various financial metrics. Here are the key roles of the pro forma capital structure in financial analysis:
1. Assessing Financial Health: The pro forma capital structure allows analysts to evaluate the financial health and stability of a company. By considering the composition of debt and equity, analysts can assess the risk profile, solvency, and liquidity of the business. This information aids in understanding the company’s ability to meet its financial obligations and sustain its operations over the long term.
2. Evaluating Profitability and Return on Investment: The pro forma capital structure helps in evaluating profitability and return on investment for shareholders. Through projections of debt costs, interest payments, and equity return expectations, analysts can estimate the expected profitability and the potential return that investors can achieve by investing in the company. This information is crucial for attracting and retaining investors.
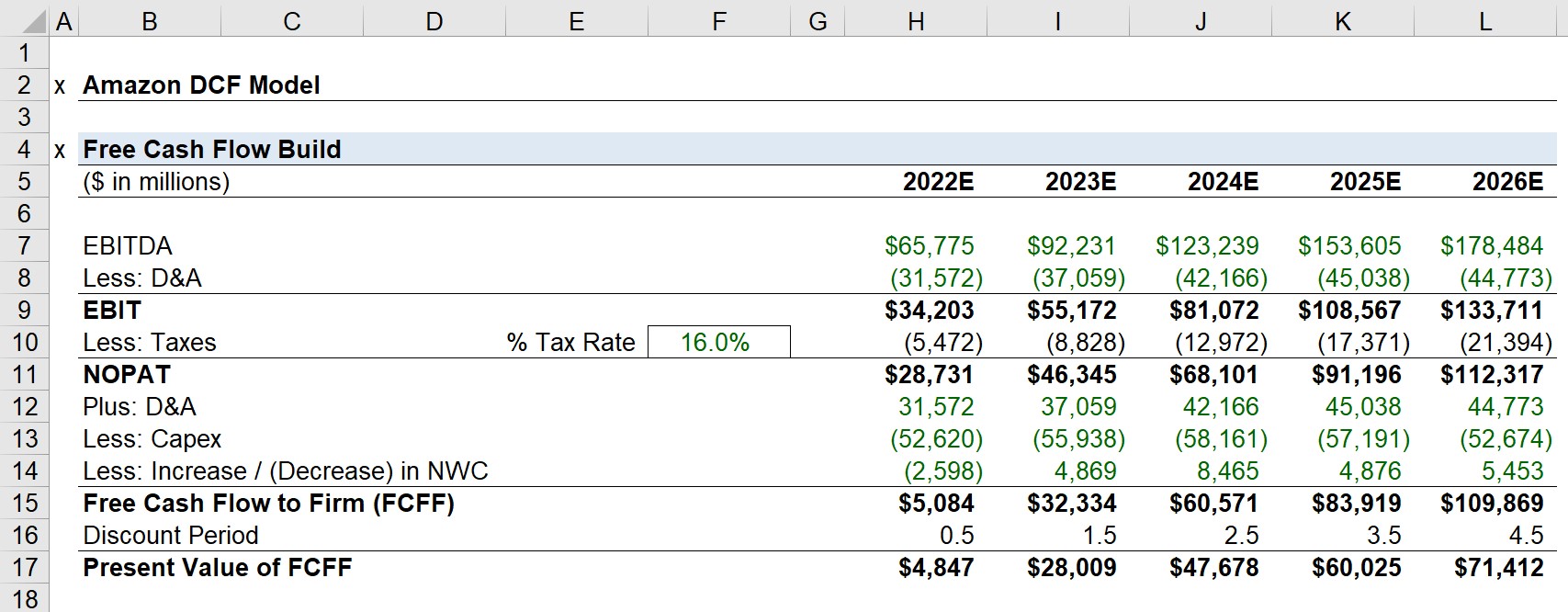
3. Estimating Cost of Capital: Companies can utilize the pro forma capital structure to estimate their cost of capital. By considering the cost of debt and equity, businesses can calculate their weighted average cost of capital (WACC). This measure provides guidance in evaluating projects or investments by determining the minimum rate of return required to create value for the company and its shareholders.
4. Analyzing Financial Ratios: The pro forma capital structure aids in analyzing financial ratios that provide insights into a company’s financial performance. Ratios such as debt-to-equity ratio, leverage ratio, and interest coverage ratio are derived from the capital structure and offer a quantitative assessment of a company’s capitalization, financial structure, and ability to service its debt obligations. These ratios help analysts assess risk, financial stability, and potential profitability.
5. Facilitating Risk Management: The pro forma capital structure enables companies to assess the financial risks associated with different financing options. It aids in evaluating interest rate risk, debt repayment obligations, and the impact of leverage on the company’s financial position. By conducting scenario analysis, companies can identify potential risks and develop risk management strategies to mitigate their impact on the business.
6. Supporting Strategic Decision-Making: The pro forma capital structure serves as a crucial tool for strategic decision-making. It helps companies evaluate the potential impact of different financing options on their growth plans, investment projects, and overall financial goals. By considering the financial implications and risks associated with each option, companies can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives and maximize their financial resources.
7. Assessing Capital Structure Optimization: The pro forma capital structure allows companies to evaluate and optimize their capital structure. Through analysis, businesses can determine the appropriate mix of debt and equity that balances the costs, risks, and benefits of each financing option. This optimization aids in achieving an efficient capital structure that supports the company’s growth objectives while maintaining financial stability.
In summary, the pro forma capital structure plays a pivotal role in financial analysis by providing insights into a company’s long-term financing, financial health, profitability, and risk management. Analysts and companies alike utilize the pro forma capital structure to make informed decisions, evaluate financial metrics, and optimize the company’s financial structure for sustainable growth and success.
Conclusion
The pro forma capital structure is a vital tool in the world of finance, allowing companies to project their future long-term financing and assess its impact on their financial health, profitability, and strategic decision-making. By considering factors such as debt, equity, cost of capital, and financial goals, companies can create a roadmap for optimizing their capital structure and achieving sustainable growth.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition and purpose of the pro forma capital structure, as well as its importance in financial analysis. We have also discussed the factors involved in creating a pro forma capital structure and the benefits and limitations associated with its use.
The pro forma capital structure serves as a guide for companies in making informed financial decisions. It aids in evaluating different financing options, estimating the cost of capital, and assessing the potential risks and benefits. By understanding the projected capital structure, companies can align their financing mix with their growth plans and strategic objectives, attracting investors and ensuring long-term financial sustainability.
However, it is important to recognize the limitations of the pro forma capital structure. External factors such as market conditions, regulatory changes, and unforeseen events can impact the accuracy of projections. Regular monitoring, reassessment, and adjustment are necessary to ensure the pro forma capital structure remains relevant and effective.
In conclusion, the pro forma capital structure is a powerful tool that enables companies to navigate the complexities of long-term financing. It provides the framework for evaluating different financing options, assessing financial health, and supporting strategic decision-making. By utilizing the pro forma capital structure, businesses can optimize their capital structure, manage financial risks, and pave the way for sustainable growth and financial success.