Finance
What Is EDD In Banking
Published: October 11, 2023
Discover how EDD in banking empowers financial institutions to enhance risk management and compliance. Gain comprehensive insights into the role of finance in ensuring a secure and transparent banking ecosystem.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the world of banking, risk management and regulatory compliance are of utmost importance. Financial institutions face the constant challenge of ensuring the security of their operations and protecting themselves from fraudulent activities and money laundering. This is where Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) comes into play.
In simple terms, EDD refers to the advanced and intensified scrutiny that financial institutions undertake when dealing with high-risk customers or transactions. It is a methodical process that involves gathering additional information and conducting enhanced analysis to thoroughly evaluate the risks associated with specific individuals, companies, or transactions.
As the complexity of financial crimes increases, banks and other financial institutions must stay ahead of potential threats and proactively mitigate risks. EDD provides them with the necessary tools to achieve this goal, ensuring that they comply with regulatory requirements and maintain the integrity of their operations.
In this article, we will delve into the world of EDD in banking, exploring its definition, purpose, benefits, practices, challenges, and the regulatory framework that governs its implementation. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of EDD and its critical role in the banking industry.
Definition of EDD in Banking
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is a risk management practice employed by financial institutions to assess and scrutinize high-risk customers or transactions more comprehensively. The purpose of EDD is to gain a deeper understanding of the potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with these individuals or activities.
EDD involves gathering additional information beyond the basic customer identification and verification processes. This includes collecting detailed data on the customer’s background, business affiliations, source of funds, and any potential red flags or adverse information that may be indicative of illicit activities.
The scope of EDD can vary depending on the nature and complexity of the customer or transaction. It may involve conducting in-depth research, utilizing specialized databases and screening tools, and seeking clarification on any potentially suspicious or unusual activities.
The objective of EDD is to enable financial institutions to make informed decisions by assessing the level of risk associated with a particular customer or transaction. It helps identify any heightened risks, such as money laundering, terrorist financing, fraud, or other financial crimes, and allows for appropriate risk mitigation measures to be implemented.
EDD is typically applied to customers or transactions that meet specific risk criteria, such as high-value transactions, politically exposed persons (PEPs), businesses operating in high-risk jurisdictions, or customers with a history of suspicious activities.
By conducting enhanced due diligence, banks and other financial institutions can better protect themselves from potential financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties. EDD acts as a crucial component of an overall risk management framework, ensuring that financial institutions can effectively detect, prevent, and address any illicit activities within their operations.
Purpose of EDD
The primary purpose of Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) in banking is to significantly reduce the risks associated with high-risk customers or transactions. EDD goes beyond the basic customer identification and verification processes to provide a more thorough evaluation of potential risks and vulnerabilities. Let’s explore the key purposes of EDD in banking:
1. Identify and mitigate financial crime risks: EDD helps financial institutions identify and assess the risks of money laundering, terrorist financing, fraud, and other financial crimes. By gathering comprehensive information and conducting enhanced analysis, banks can develop a clearer understanding of the potential risks related to specific customers or transactions.
2. Protect against reputational and regulatory risks: Financial institutions face significant reputational damage and regulatory penalties if they inadvertently facilitate illicit activities. EDD allows banks to implement proper risk management practices and safeguards to protect their reputation and comply with regulatory requirements. By identifying and mitigating risks, banks can maintain the integrity of their operations and meet legal obligations.
3. Strengthen compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations: EDD is an essential tool for meeting AML and KYC requirements set by regulatory bodies. It helps banks ensure that their due diligence processes are robust, effective, and compliant with regulatory guidelines. EDD provides the necessary evidence and documentation to demonstrate diligent efforts in preventing financial crimes.
4. Enhance the accuracy of risk assessments: By conducting EDD, financial institutions can collect more detailed information on customers and transactions. This leads to more accurate risk assessments, allowing banks to differentiate between low-risk and high-risk customers and tailor their risk mitigation measures accordingly. Enhanced accuracy in risk assessments aids in making informed decisions and allocating resources effectively.
5. Safeguard the institution and its stakeholders: EDD serves as a proactive measure to protect the institution, shareholders, and other stakeholders. By identifying potential risks early on and implementing appropriate risk management measures, banks can reduce the likelihood of financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences. EDD plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and sustainability of the institution.
Overall, the purpose of EDD in banking is to enable financial institutions to identify, assess, and manage the risks associated with high-risk customers or transactions. It is a proactive approach to mitigating potential financial crimes, protecting the institution’s reputation, and ensuring compliance with regulatory obligations.
Benefits of EDD in Banking
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) in banking offers several key benefits to financial institutions. It enables them to effectively manage risks, ensure regulatory compliance, and protect their reputation. Let’s explore the benefits of EDD:
1. Risk mitigation: EDD plays a pivotal role in identifying and mitigating risks associated with high-risk customers or transactions. By conducting enhanced analysis and gathering comprehensive information, banks can make informed decisions and implement appropriate risk management measures. This helps minimize the exposure to financial crimes such as money laundering, fraud, and terrorist financing.
2. Enhanced customer protection: EDD not only protects the financial institution, but it also safeguards the interests of genuine customers. By adhering to stringent due diligence processes, banks can ensure that their customer base remains free from individuals involved in illicit activities. This contributes to maintaining a safe, secure, and trustworthy banking environment.
3. Regulatory compliance: EDD is an essential component of meeting regulatory requirements, particularly in the areas of anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations. Financial institutions that implement robust EDD practices demonstrate their commitment to compliance and reduce the risk of regulatory penalties and reputational damage.
4. Reputation management: A strong reputation is vital for banks and financial institutions. EDD helps protect the reputation of the institution by effectively detecting and preventing involvement in financial crimes. By maintaining a high standard of due diligence, banks can preserve the trust and confidence of their customers, shareholders, and the wider public.
5. Improved risk assessment: EDD results in more accurate risk assessments by providing additional information and insights. This allows banks to differentiate between high-risk and low-risk customers and transactions, enabling them to allocate resources more effectively. With enhanced risk assessments, banks can make better decisions and optimize their risk management strategies.
6. Competitive advantage: Implementing robust EDD practices can provide a competitive edge in the banking industry. Banks that prioritize risk management, regulatory compliance, and customer protection position themselves as reliable and trustworthy institutions. This can attract new customers, enhance existing customer relationships, and differentiate them from competitors.
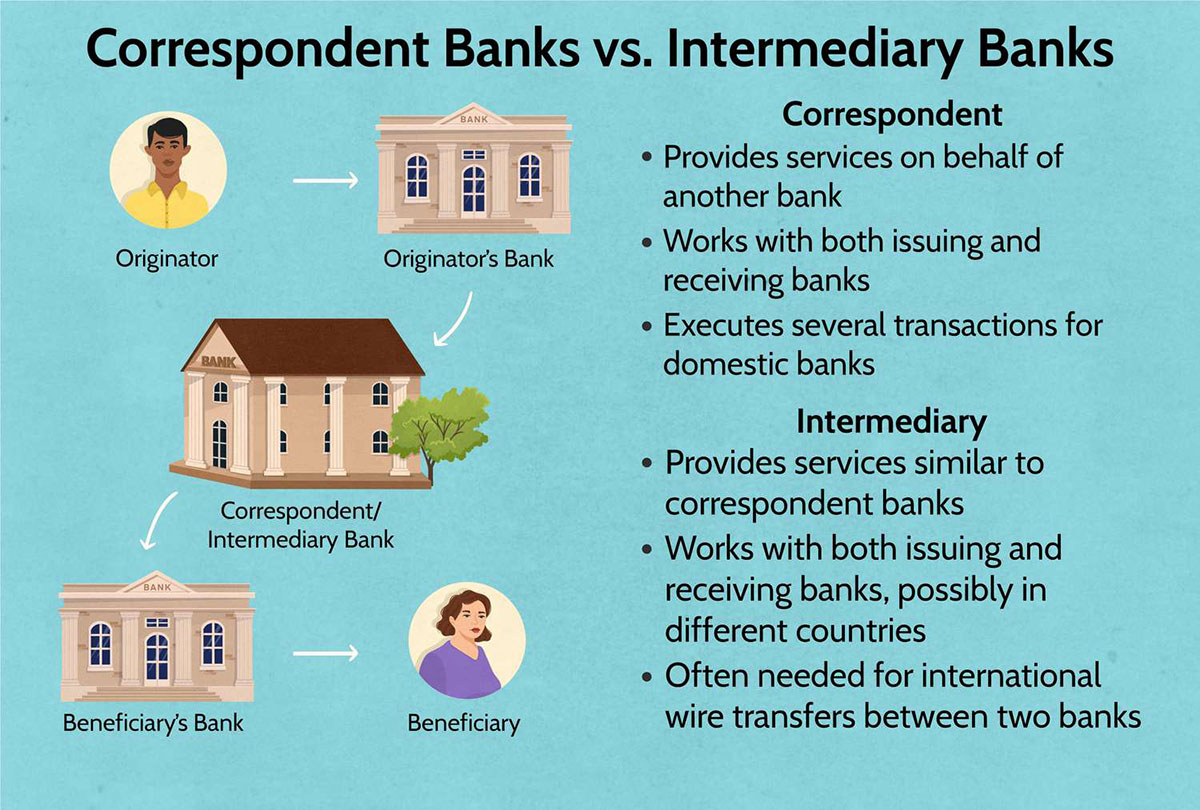
7. Strengthened relationships with correspondent banks: Correspondent banking relationships rely on trust, transparency, and adherence to anti-money laundering standards. By implementing rigorous EDD processes, banks can establish and maintain strong relationships with correspondent banks, facilitating seamless financial transactions and access to global financial markets.
Overall, EDD offers numerous benefits to financial institutions, including effective risk mitigation, regulatory compliance, reputation management, improved risk assessments, and a competitive advantage. By implementing robust EDD practices, banks can protect themselves and their customers while maintaining a strong position in the competitive banking landscape.
EDD Practices in the Banking Industry
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) practices in the banking industry involve a systematic approach to gather additional information, conduct in-depth analysis, and implement enhanced risk management measures for high-risk customers or transactions. These practices aim to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, mitigate risks, and protect the integrity of the financial institution. Let’s take a closer look at some common EDD practices:
1. Comprehensive customer identification: EDD starts with a thorough verification and identification process to establish the true identity of the customer. This involves obtaining and validating official identification documents, such as passports or driver’s licenses, and conducting extensive checks to verify the information provided.
2. Enhanced customer profiling: EDD requires a more robust customer profiling process, focusing on gathering detailed information about the customer’s personal, professional, and financial background. This may include information such as employment history, business affiliations, beneficial ownership, and source of funds.
3. Enhanced scrutiny of high-risk customers: Financial institutions identify high-risk customers based on predetermined risk criteria, such as those operating in high-risk jurisdictions or engaging in high-value transactions. These customers undergo a more thorough due diligence process, including enhanced background checks, ongoing transaction monitoring, and periodic reviews of their profile.
4. Additional data collection and analysis: EDD goes beyond basic customer information and involves collecting additional data from reliable sources. This may include reviewing public records, conducting media searches, and utilizing specialized databases to uncover any adverse information or red flags associated with the customer.
5. Heightened transaction monitoring: EDD involves implementing enhanced transaction monitoring systems to detect suspicious activities conducted by high-risk customers. These systems utilize advanced analytics, machine learning, and AI algorithms to identify unusual patterns, large transactions, or inconsistent behavior that may indicate potential financial crimes.
6. Ongoing monitoring and periodic reviews: EDD is not a one-time process but requires continuous monitoring and periodic reviews of high-risk customers. This ensures that banks stay updated on any changes in the customer’s profile, business activities, or risk level. Regular reviews also help identify and address any emerging risks promptly.
7. Collaboration with external agencies: Financial institutions may collaborate with external agencies, such as regulatory bodies, law enforcement agencies, or specialized financial crime units, to obtain additional insights and intelligence. This collaboration strengthens the EDD process by leveraging expertise and resources outside the bank’s scope.
8. Training and awareness programs: Banks invest in training and awareness programs to educate employees about EDD practices, regulatory requirements, and emerging financial crime trends. This ensures that staff members are adequately equipped to identify, report, and escalate any suspicious activities or potential risks they may come across.
By adopting these EDD practices, financial institutions can significantly enhance their ability to detect and prevent financial crimes, comply with regulations, and effectively manage risks associated with high-risk customers or transactions. EDD practices form a fundamental part of a comprehensive risk management framework within the banking industry.
Challenges and Limitations of EDD in Banking
While Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) practices are crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring regulatory compliance in the banking industry, they also come with their own set of challenges and limitations. It’s important for financial institutions to be aware of these challenges in order to navigate them effectively. Let’s explore some common challenges and limitations of EDD in banking:
1. Resource-intensive process: EDD requires a significant amount of time, effort, and resources. Conducting thorough background checks, gathering additional information, and implementing enhanced risk management measures can be resource-intensive for financial institutions. Small- to medium-sized banks may struggle with the additional costs and operational burdens associated with EDD implementation.
2. Compliance with evolving regulations: Regulatory requirements related to EDD are constantly evolving. Financial institutions need to stay updated with changing regulations and ensure that their EDD practices remain compliant. Adapting to new regulatory guidelines and implementing necessary changes can be challenging, particularly for banks operating across multiple jurisdictions.
3. Data quality and availability: EDD heavily relies on the availability and quality of data. Financial institutions may face challenges in accessing reliable sources of data, particularly when dealing with international customers or complex ownership structures. Limited availability or poor data quality can hinder the effectiveness of EDD processes and compromise risk assessments.
4. Balancing risk and customer experience: The rigorous nature of EDD practices can sometimes result in a more cumbersome customer onboarding experience. Striking a balance between thorough due diligence and a streamlined customer experience can be challenging. Financial institutions need to find ways to effectively manage risk while maintaining a positive customer journey.
5. Evolving nature of financial crimes: Financial criminals are constantly adapting their methods and strategies to bypass detection. This poses a challenge for financial institutions, as they need to continuously update their EDD practices to stay ahead of emerging risks. Traditional monitoring tools and techniques may not always be effective in detecting sophisticated financial crimes.
6. False positives and false negatives: EDD processes may generate false positives, flagging legitimate customers or transactions as high risk. This can result in unnecessary delays, additional scrutiny, and inconvenience for customers. Conversely, false negatives may occur, where high-risk customers or transactions go undetected. Financial institutions need to fine-tune their EDD systems and processes to minimize false alerts and ensure accurate risk assessments.
7. Inconsistent implementation across jurisdictions: EDD practices may vary across different jurisdictions due to variations in regulatory frameworks and requirements. This can create challenges for banks with a global presence, as they need to navigate different regulatory landscapes. Harmonizing EDD practices across jurisdictions can be complex and time-consuming.
While EDD is an essential risk management practice, financial institutions need to navigate these challenges and limitations effectively. By allocating sufficient resources, staying updated on regulatory changes, leveraging technology and data analytics, and maintaining a customer-centric approach, banks can overcome these challenges and ensure robust EDD processes.
Regulatory Framework for EDD in Banking
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) practices in the banking industry are closely regulated to ensure the prevention of financial crimes and the protection of the integrity of the financial system. Regulatory bodies around the world have established frameworks and guidelines that govern the implementation of EDD. Let’s explore the regulatory framework for EDD in banking:
1. Financial Action Task Force (FATF): The Financial Action Task Force is an intergovernmental organization that sets international standards and develops policies to combat money laundering, terrorist financing, and other related threats to the integrity of the global financial system. The FATF provides recommendations and guidelines that countries can adopt to implement effective EDD practices.
2. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Regulations: AML regulations set out by regulatory authorities require financial institutions to implement robust EDD measures. These regulations require banks to conduct enhanced due diligence on high-risk customers, maintain comprehensive customer records, and report any suspicious transactions to the relevant authorities. AML regulations also mandate the implementation of effective AML compliance programs within financial institutions.
3. Know Your Customer (KYC) Requirements: KYC requirements mandate banks to gather sufficient information about their customers to verify their identities, assess their risk levels, and ensure compliance with AML regulations. EDD is an integral part of KYC processes, focusing on more rigorous identification and risk assessment for high-risk customers or transactions.
4. Risk-Based Approach (RBA): Many regulatory frameworks emphasize the importance of implementing a risk-based approach to EDD. This approach requires financial institutions to assess and categorize customers and transactions based on their perceived risk levels. The level of EDD scrutiny is then determined based on this risk assessment. A risk-based approach allows banks to allocate resources more effectively and apply EDD practices proportionately to the level of risk involved.
5. Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Requirements: CDD requirements dictate that financial institutions should conduct due diligence procedures to gather and verify customer information. EDD goes a step further by requiring additional information and analysis for high-risk customers. CDD requirements are often enforced through regulations and guidelines established by regulatory bodies.
6. Enhanced Monitoring and Reporting Obligations: Regulatory frameworks often require financial institutions to establish robust monitoring systems to detect and report suspicious activities. EDD plays a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of monitoring systems, allowing banks to identify potential risks and report them to the appropriate authorities in a timely manner.
7. Cross-Border Cooperation: Given the global nature of financial crimes, regulatory frameworks emphasize the importance of cross-border cooperation and information sharing among regulatory bodies. This allows for coordinated efforts to combat money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes that transcend jurisdictional boundaries. Cross-border collaboration ensures that EDD practices are consistent and aligned across different regions.
It’s essential for financial institutions to stay abreast of the regulatory frameworks and guidelines pertaining to EDD in their respective jurisdictions. Adhering to these regulations not only ensures compliance but also helps banks mitigate risks, protect their reputation, and contribute to the overall integrity of the financial system.
Conclusion
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) plays a crucial role in the banking industry, enabling financial institutions to effectively manage risks, ensure regulatory compliance, and protect their reputation. Through comprehensive customer identification, enhanced analysis, and robust risk management practices, EDD helps banks identify and mitigate potential financial crimes, such as money laundering, fraud, and terrorist financing.
EDD offers several key benefits to financial institutions, including improved risk mitigation, enhanced customer protection, regulatory compliance, reputation management, and strengthened risk assessments. By implementing EDD practices, banks can confidently navigate the complex landscape of financial risks and maintain a competitive edge.
However, EDD is not without its challenges and limitations. Financial institutions may face resource-intensive processes, the need to adapt to evolving regulations, data quality and availability issues, and the delicate balance between risk management and customer experience. Despite these challenges, banks can overcome them through strategic allocation of resources, ongoing training programs, and leveraging technology and data analytics.
The regulatory framework for EDD in banking is comprehensive and governed by international standards set by organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF). AML regulations, KYC requirements, risk-based approaches, and enhanced monitoring and reporting obligations form the core of the regulatory framework. Cross-border cooperation and information sharing further strengthen the effectiveness of EDD practices.
In conclusion, EDD in banking is a vital component of risk management and regulatory compliance. By implementing robust EDD practices, financial institutions can effectively mitigate risks, protect their reputation, comply with regulations, and contribute to the integrity of the financial system. While there are challenges and limitations, strategic implementation and alignment with regulatory frameworks enable banks to navigate these hurdles successfully and focus on building a secure and trustworthy banking environment.