
Finance
What Is RPA In Banking
Published: October 12, 2023
Discover what RPA in banking is and how it revolutionizes finance processes. Streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance customer experience with automated solutions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
In an era where digital transformation is reshaping industries, the banking sector is no exception. With the constant need to streamline operations, cut costs, and enhance customer experience, banks are turning to innovative technologies to stay competitive. One such technology that is gaining traction in the banking sector is Robotic Process Automation (RPA).
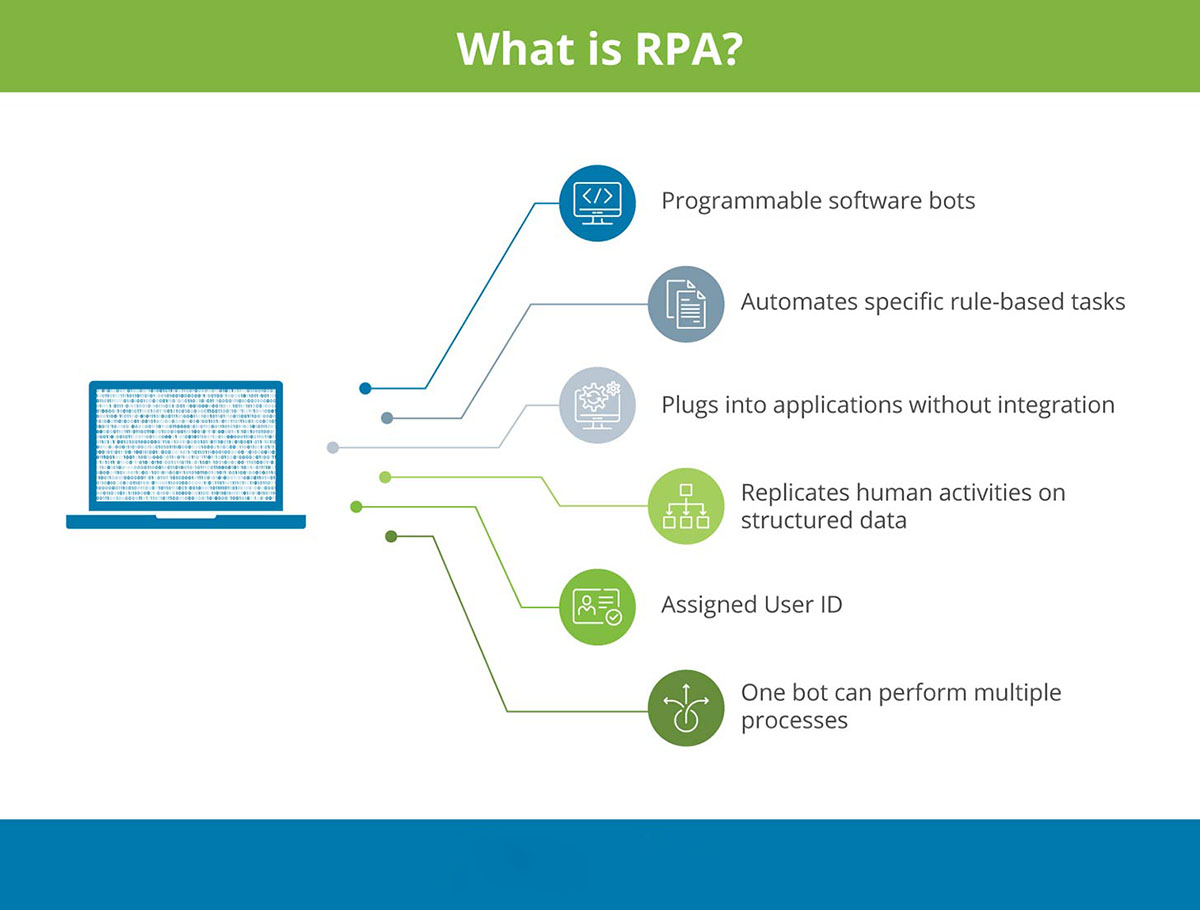
RPA is a cutting-edge solution that leverages software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks. These bots can mimic human actions, interact with systems, and execute tasks in a fraction of the time it would take a human to complete the same task. This enables banks to improve efficiency, accuracy, and speed, ultimately leading to cost savings and enhanced customer service.
By automating routine tasks, RPA allows banking professionals to focus on more complex and value-added activities. For example, bots can handle mundane tasks like data entry, document processing, and customer onboarding, freeing up employees to dedicate their time and skills to strategic decision-making and providing personalized services to customers.
The implementation of RPA in banking not only transforms operational processes but also adds agility to business operations. Banks can respond rapidly to changing market dynamics, regulatory requirements, and customer demands. RPA brings the potential to revolutionize service delivery, reduce errors, and improve compliance.
In this article, we will explore the definition of RPA in banking, delve into the benefits it offers, examine use cases of RPA in banking, discuss the challenges of implementing RPA, provide best practices for successful implementation, and look into the future of RPA in the banking sector.
Definition of RPA in Banking
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) refers to the use of software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks within the banking industry. These bots are capable of mimicking human actions, interacting with various systems, and executing tasks with speed and accuracy. RPA technology allows banks to automate routine processes, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic and customer-oriented activities.
RPA in banking involves the use of software robots to perform tasks such as data entry, document verification, account reconciliation, compliance reporting, and customer onboarding, among others. The bots are trained to follow predefined rules and algorithms to execute these tasks, making them highly efficient and reliable.
These software robots typically work on the user interface (UI) level, interacting with the same applications and systems that humans use. They can navigate through different screens, input data, extract information, and perform calculations. With RPA, banks can automate processes that involve repetitive steps across multiple systems, reducing human errors and improving operational efficiency.
One of the key advantages of RPA in banking is its non-invasive nature. Unlike other automation solutions, RPA does not require changes to the underlying IT infrastructure or significant integration efforts. It can be implemented as an overlay to existing systems, working seamlessly with legacy systems and modern applications.
Furthermore, RPA in banking can be applied to various departments and functions within a bank, including retail banking, corporate banking, loan processing, risk management, compliance, finance, and accounting. It offers a scalable and flexible solution that can be tailored to the specific needs and processes of each bank.
Overall, RPA in banking brings significant efficiency gains, cost savings, and improved customer service. By automating repetitive and manual tasks, banks can enhance operational productivity, reduce turnaround times, minimize errors, and ensure regulatory compliance. With the potential to transform the banking landscape, RPA is increasingly becoming a strategic technology for banks aiming to stay competitive in the digital age.
Benefits of RPA in Banking
RPA has emerged as a game-changing technology in the banking sector, offering numerous benefits that drive operational efficiency and improve customer experience. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of implementing RPA in banking:
- Cost Savings: RPA enables banks to significantly reduce operational costs by automating repetitive tasks that were previously performed by humans. This eliminates the need for manual labor, resulting in cost savings and improved efficiency. Furthermore, RPA can operate 24/7, reducing the need for overtime or additional staff in handling time-sensitive operations.
- Improved Accuracy: By leveraging RPA, banks can reduce the risk of errors caused by human intervention. Software robots follow predefined rules and algorithms, ensuring consistent and accurate execution of tasks. This leads to improved data quality, reduced compliance risks, and enhanced regulatory reporting.
- Enhanced Productivity: RPA eliminates manual and repetitive tasks from employees’ workload, freeing up their time to focus on more value-added activities. It empowers banking professionals to dedicate their expertise to strategic decision-making, customer engagement, and problem-solving. This increases overall productivity and employee satisfaction.
- Faster Processing and Turnaround Times: RPA enables banks to expedite time-consuming processes that involve multiple systems and data entry. Software robots can handle tasks in parallel and operate at high speeds, significantly reducing processing times. This leads to faster turnaround times for customer requests, loan approvals, account opening, and other critical operations.
- Improved Compliance: Compliance is a critical aspect of the banking sector. RPA ensures that regulatory processes and reporting are executed accurately and in a timely manner. Bots can validate data, perform risk assessments, and generate compliance reports, reducing the risk of manual errors and compliance violations. This enhances transparency, auditability, and overall compliance posture.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: RPA enables banks to deliver faster and more accurate services to their customers. With automated processes, customers experience shorter wait times and faster response rates. Additionally, RPA allows for customized and personalized interactions, as employees have more time to focus on building relationships and providing tailored solutions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: RPA offers scalability and flexibility, allowing banks to expand automation to meet their evolving needs. Banks can easily scale the implementation of bots to handle increased volumes or new processes without significant infrastructure changes. RPA also integrates seamlessly with existing systems, allowing for flexibility in adopting new technologies and adapting to changing business requirements.
Overall, the benefits of RPA in banking are profound. It revolutionizes operational processes, drives cost savings, improves accuracy, boosts productivity, ensures compliance, enhances customer experience, and provides the agility needed to thrive in today’s competitive banking landscape.
Use Cases of RPA in Banking
The adoption of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in the banking sector has expanded to various areas, delivering tangible benefits and transforming traditional processes. Let’s explore some common use cases where RPA is revolutionizing banking operations:
- Account Opening and Onboarding: RPA can automate the account opening process by extracting customer information from various sources, performing KYC (Know Your Customer) checks, and populating account details in the banking systems. This streamlines the onboarding process, reduces manual errors, and accelerates customer acquisition.
- Loan Processing: RPA can streamline loan origination processes by automating tasks such as data collection, verification, document processing, credit scoring, and loan decisioning. Bots can gather relevant information, perform credit checks, and generate loan agreement documents, improving processing times and accuracy.
- Data Entry and Validation: RPA can automate data entry and validation tasks, eliminating the need for manual input and reducing human errors. Bots can extract data from multiple sources, validate it against predefined rules, and populate the relevant fields in banking applications and databases.
- Compliance and Reporting: RPA can automate compliance processes, such as anti-money laundering (AML) checks, fraud detection, and regulatory reporting. Bots can monitor transactions in real-time, flag suspicious activities, generate compliance reports, and ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Customer Service: RPA can enhance customer service by automating routine inquiries and requests. Bots can handle tasks like balance inquiries, account transfers, password resets, and account statement generation. This reduces waiting times, improves response rates, and allows customer service representatives to focus on complex issues and personalized interactions.
- Reconciliation and Settlement: RPA can automate reconciliation processes, comparing data from different systems to identify discrepancies and ensure accurate settlement. Bots can match transactions, verify balances, and generate reconciliation reports, reducing the risk of errors and minimizing manual intervention.
- Credit Card Processing: RPA can automate credit card processing tasks, including credit limit checks, dispute resolution, and payment processing. Bots can validate transactions, update account information, and generate payment confirmations, improving efficiency and reducing processing times.
- Account Closure and Deactivation: RPA can automate the account closure and deactivation process. Bots can verify customer details, close accounts, update records, and notify relevant parties. This simplifies the account closure process, reduces manual effort, and ensures compliance with regulations.
These use cases highlight the versatility of RPA in the banking sector. By automating repetitive and rule-based tasks, RPA enables banks to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and deliver better service to customers.
Challenges of Implementing RPA in Banking
While the implementation of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in the banking sector brings numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges. Let’s explore some of the key challenges that banks may face when adopting RPA:
- Process Identification: Identifying suitable processes for automation can be a challenge. Banks need to carefully analyze their operations to determine which processes are repetitive, rule-based, and high-volume enough to benefit from RPA.
- Data Quality: RPA requires high-quality data to work efficiently and accurately. If the data is incomplete, inconsistent, or outdated, it can lead to errors and hinder the effectiveness of RPA. Banks must ensure data cleanliness and integrity before implementing automation solutions.
- System Compatibility: RPA bots need to integrate and interact with various banking systems, applications, and databases. Ensuring compatibility and seamless integration can be a challenge, especially when dealing with legacy systems that may have limited API capabilities.
- Security and Privacy: RPA introduces potential security risks, as bots interact with sensitive customer data and perform critical financial tasks. Banks must implement robust security measures to protect data privacy, prevent unauthorized access, and mitigate the risk of cyber threats.
- Change Management: Implementing RPA in banking requires a cultural shift and change management efforts. Employees may resist or fear automation, fearing job losses or changes to their roles. It is crucial to communicate the strategic objectives and advantages of RPA to gain buy-in from internal stakeholders.
- Regulatory Compliance: Banks operate in a highly regulated environment, and implementing RPA must comply with various regulatory requirements. Banks need to ensure that bots adhere to compliance standards and maintain proper audit trails to demonstrate adherence to regulations.
- Process Standardization: RPA works best when processes are standardized and well-defined. Banks may face challenges in standardizing processes and ensuring consistency across multiple departments and systems. Process standardization efforts may require significant time and resources.
- Bot Management and Monitoring: Banks need to establish effective governance and monitoring mechanisms to manage the bots. This includes tracking bot performance, addressing exceptions, handling scalability, and ensuring that bots are functioning as intended and delivering the expected results.
These challenges are not insurmountable, but they require careful planning, collaboration, and proactive management to address. By anticipating and proactively mitigating these challenges, banks can successfully implement RPA and maximize its benefits.
Best Practices for Implementing RPA in Banking
Implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in the banking sector can bring significant benefits, but it requires careful planning, execution, and governance. Here are some best practices to consider when implementing RPA in banking:
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define the objectives and expected outcomes of the RPA implementation. Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the automation initiative.
- Start with Pilot Projects: Begin with smaller pilot projects to validate the effectiveness and feasibility of RPA. Select processes that are suitable for automation, have a high volume of transactions, and can deliver quick wins.
- Engage Stakeholders and Employees: Involve stakeholders, including employees, from the beginning of the RPA journey. Communicate the benefits of RPA, address concerns, and provide training to ensure a smooth transition and acceptance of the new technologies.
- Thoroughly Assess Processes: Conduct a thorough process assessment to identify suitable processes for automation. Evaluate their complexity, suitability, and potential ROI to prioritize automation efforts.
- Ensure Data Quality: Before implementing RPA, ensure data quality and integrity. Cleanse and standardize data to ensure accuracy, as RPA relies on high-quality data for effective automation.
- Design Scalable and Flexible Solutions: Develop RPA solutions that can scale and handle increasing volumes of transactions. Design them to be flexible enough to accommodate process changes and adapt to evolving business requirements.
- Ensure Security and Compliance: Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data and comply with regulatory requirements. Securely manage user access rights, encrypt data, and implement appropriate controls to mitigate cyber risks.
- Establish Governance Framework: Establish a governance framework to manage RPA implementations effectively. Define roles and responsibilities, create standard operating procedures, and implement controls for bot management, monitoring, and exception handling.
- Continuously Monitor and Optimize: Regularly monitor the performance of RPA bots and the outcomes of the automated processes. Proactively address exceptions, analyze data, and continuously optimize the automation solutions for better efficiency and effectiveness.
- Maintain a Continuous Improvement Mindset: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. Encourage feedback from employees, monitor industry trends, and explore advanced RPA capabilities to continually enhance and expand automation capabilities.
Following these best practices can help banks achieve successful RPA implementations. With well-planned strategies, stakeholder engagement, and effective governance, RPA has the potential to revolutionize banking operations, improve efficiency, and drive sustainable growth.
Future of RPA in Banking
The future of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in the banking sector is promising, as technology continues to evolve and banks increasingly recognize the value of automation. Here are some key trends and possibilities that highlight the future of RPA in banking:
- Advanced Intelligent Automation: The future of RPA in banking lies in combining it with other technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to create intelligent automation solutions. This integration will enhance the capabilities of RPA, enabling bots to make intelligent decisions, learn from experience, and perform cognitive tasks.
- Cognitive Document Processing: RPA will play a significant role in automating document processing tasks in banking. Intelligent bots will be able to extract information from unstructured documents, such as invoices, contracts, and financial statements, and perform complex analyses, reducing manual effort and errors.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: RPA will continue to be integral to the development of chatbots and virtual assistants in banking. Bots will handle customer inquiries, guide users through processes, and provide personalized support, enhancing the customer experience and reducing the workload of support teams.
- Hyperautomation: Hyperautomation, a concept that combines RPA with other automation technologies like process mining and analytics, will become more prevalent in the banking sector. This holistic approach will enable end-to-end automation of processes, uncover bottlenecks, and drive continuous improvement.
- RPA in Regulatory Compliance: As regulatory requirements continue to increase, RPA will become crucial in assisting banks with compliance. Bots can monitor and analyze large volumes of data, flag suspicious activities, generate compliance reports, and ensure adherence to regulatory standards in real-time.
- Scaling RPA: RPA will continue to scale in banking, expanding its reach to more processes, departments, and functions. Banks will embrace the adoption of automation across various divisions, such as risk management, anti-money laundering, customer service, and treasury operations.
- Collaborative Automation: Collaborative automation, where humans and bots work together in a symbiotic manner, will become more prevalent. Banks will leverage the unique strengths of bots and human employees, allowing them to collaborate on complex tasks and deliver superior results.
- Automation Centers of Excellence: Banks will establish dedicated Automation Centers of Excellence (CoEs) to drive RPA initiatives and provide guidance and expertise. These CoEs will ensure successful implementation, governance, and continuous improvement of automation efforts across the organization.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: RPA bots will continue to evolve and improve through continuous learning and adaptation. They will analyze data, identify patterns, and dynamically adjust their processes to optimize performance, accuracy, and efficiency.
- Expansion of Use Cases: With the advancements in RPA technology, the range of use cases in banking will expand. From customer onboarding to wealth management, from fraud detection to mortgage underwriting, RPA will find application in a wide array of banking processes.
The future of RPA in banking is a blend of exciting possibilities and transformative potential. Banks that leverage RPA effectively will gain a competitive edge, as they streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive sustained growth in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is revolutionizing the banking sector by automating repetitive and rule-based tasks, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing customer experiences. The benefits of RPA in banking are far-reaching, including cost savings, improved accuracy, enhanced productivity, faster processing times, and better compliance.
The application of RPA in banking spans various areas, from account opening and loan processing to compliance reporting and customer service. By automating these processes, banks can free up their employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities, ultimately driving innovation and improving customer satisfaction.
However, implementing RPA in banking does come with its challenges. Banks must carefully assess processes, ensure data quality, address system compatibility issues, and navigate security and compliance requirements. Change management and stakeholder engagement are also critical for successful implementation.
Looking to the future, RPA in banking will continue to evolve and bring exciting advancements. The integration of AI and ML will enhance the intelligence of RPA, enabling bots to handle cognitive tasks and provide more personalized support. Hyperautomation and collaborative automation will drive end-to-end process automation, resulting in improved operational efficiency.
As the banking industry continues to undergo digital transformation, RPA will play a crucial role in driving innovation and operational excellence. Banks that embrace RPA and strategically implement it across their operations will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape.
In conclusion, RPA is a transformative technology that holds immense potential for the banking sector. By harnessing the power of automation, banks can enhance their operational efficiency, deliver superior customer service, and achieve sustainable growth in an ever-evolving digital world.