
Finance
What Is Suffix In Banking
Published: November 2, 2023
Discover the meaning of suffix in banking and how it impacts financial transactions. Explore the role of suffix in finance and its significance for banking operations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to understanding the intricate world of banking and finance, it is important to familiarize oneself with the various terms and concepts used in the industry. One such concept is the use of suffixes in banking. While suffixes may seem like a small and insignificant detail, they play a crucial role in organizing and identifying different types of accounts and transactions within the banking system.
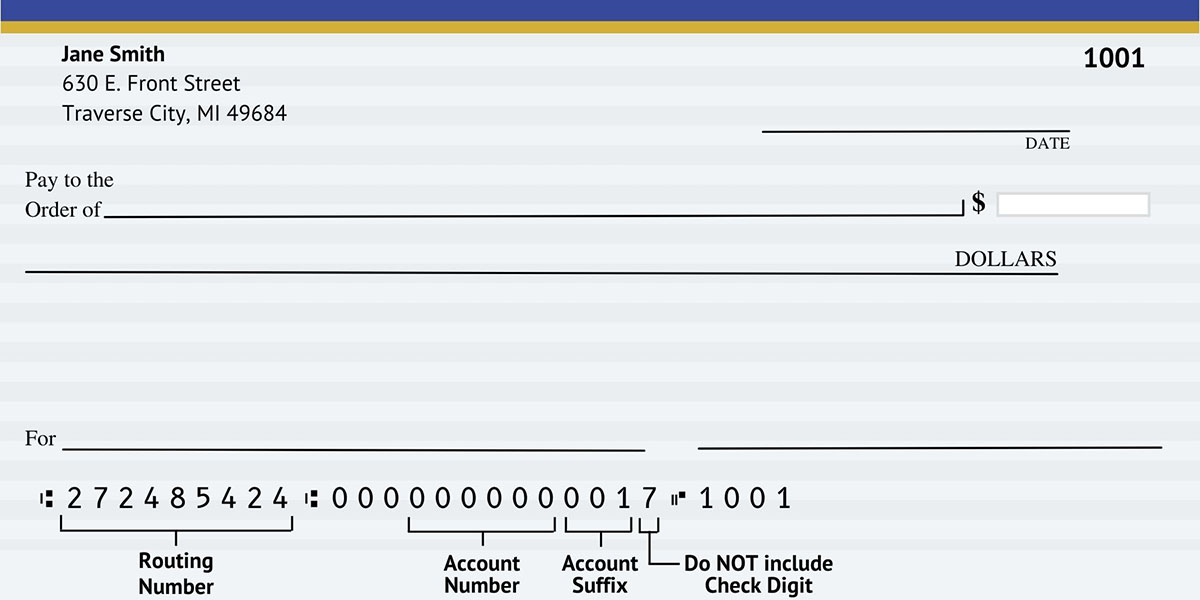
A suffix, in the context of banking, refers to a string of characters that is added at the end of an account number or a transaction code to provide additional information or categorization. These suffixes are used to differentiate between various account types, distinguish different transactions, and streamline processes within the banking system.
Whether you are a customer, a bank employee, or an industry professional, understanding the purpose and significance of suffixes in banking can greatly enhance your overall knowledge of the financial landscape. In this article, we will dive into the world of suffixes in banking, exploring their role, importance, and practical applications. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of why these small additions hold significant value in the banking industry.
Definition of a Suffix
Before delving into the role of suffixes in banking, let’s start by understanding what a suffix actually is. In linguistic terms, a suffix is a word part that is added to the end of a base word to create a new word with a different meaning. For example, in the word “happiness,” the suffix “-ness” is added to the base word “happy” to indicate a state or condition.
In the context of banking, a suffix refers to a string of characters that is added at the end of an account number or a transaction code. These additional characters serve a specific purpose, providing valuable information or categorization related to the account or transaction. Suffixes allow banks to differentiate between various types of accounts, track specific transactions, and streamline the management of financial operations.
Suffixes in banking can vary in length and composition, depending on the specific requirements and systems used by each financial institution. They can include combinations of numbers, letters, or symbols, all designed to convey specific meanings or classifications.
It is worth noting that suffixes in banking are not limited to just account numbers and transaction codes. They can also be used in other areas of banking, such as in the names of financial products, identification codes for bank branches or departments, or even in codes used for financial reporting and analysis.
Overall, suffixes in banking serve as a valuable tool for organizing, categorizing, and differentiating various aspects of the financial system. By adding a suffix to an account number or transaction code, banks can provide additional context and clarity, facilitating smooth and efficient banking operations.
Suffixes in Banking
Suffixes play a significant role in the banking industry by providing an efficient way to categorize and differentiate various accounts and transactions. These suffixes help banks manage and organize their operations, ensuring accuracy, consistency, and ease of reference.
One key area where suffixes are used in banking is in account identification. Financial institutions use suffixes to denote specific types of accounts, such as savings accounts, checking accounts, or investment accounts. This allows customers and bank staff to easily identify the nature and purpose of each account, simplifying account management and providing a clearer understanding of the account’s characteristics.
Additionally, suffixes are utilized in the identification of different transactions within banking systems. For instance, when conducting electronic fund transfers, suffixes are often added to transaction codes to indicate the purpose or type of transaction. This enables banks to track and analyze different types of transactions, such as deposits, withdrawals, transfers, or payments, effectively capturing and organizing data related to each transaction.
Furthermore, suffixes are employed in various financial products and services offered by banks. For instance, in the case of loans, suffixes may be appended to loan account numbers to indicate specific loan types, such as personal loans, mortgages, or business loans. This simplifies loan management and allows for easy identification of the type of loan associated with each account.
Moreover, suffixes are utilized in banking systems to indicate the geographical location or branch of a particular account or transaction. This can assist in routing transactions correctly and helps banks monitor activity across different branches more effectively.
Overall, suffixes in banking serve as a valuable tool for categorizing, organizing, and managing accounts and transactions. By utilizing suffixes, banks can streamline operations, enhance customer experience, and maintain system integrity.
Importance of Suffixes
Suffixes may seem like minor details in the banking industry, but their importance should not be overlooked. These small additions have a significant impact on the efficiency, accuracy, and organization of banking operations. Here are some key reasons why suffixes are so important in banking:
- Account Differentiation: Suffixes allow banks to easily differentiate between different types of accounts. For example, suffixes can be used to indicate whether an account is a personal account, a business account, a joint account, or a specialized account such as a trust account or a retirement account. This helps banks accurately categorize and manage accounts, making it easier to provide customized services to customers based on their account type.
- Transaction Categorization: Suffixes are crucial in categorizing and tracking different types of transactions within the banking system. By adding a suffix to transaction codes, banks can identify whether a transaction is a deposit, withdrawal, transfer, payment, or any other specific type. This allows for accurate reporting, analysis, and reconciliation of financial transactions, ensuring transparency and accountability in the banking process.
- System Efficiency: Suffixes contribute to the overall efficiency of banking systems. By using suffixes to categorize and organize accounts and transactions, banks can streamline processes, reduce errors, and improve data management. This enables faster access to relevant information and enhances the speed and accuracy of customer service, ultimately improving the overall banking experience.
- Risk Management: Suffixes also play a role in risk management within the banking industry. By utilizing suffixes to identify certain types of accounts or transactions that may pose higher risk, banks can implement targeted risk mitigation strategies. For example, they can set specific controls or monitoring parameters for accounts with a suffix indicating a higher level of risk, reducing the potential for fraudulent activities or financial losses.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with regulatory requirements is a critical aspect of banking operations. Suffixes can assist in meeting these requirements by enabling banks to accurately report and classify accounts and transactions as required by regulatory bodies. This ensures banks remain in compliance with financial regulations and facilitates audits and regulatory inspections.
Overall, the use of suffixes in banking is of utmost importance as it contributes to accurate and efficient account management, transaction tracking, system optimization, risk mitigation, and regulatory compliance. By recognizing the significance of suffixes, banks can enhance their operational capabilities and provide better services to their customers.
How Suffixes are Used in Banking
Suffixes are utilized in various ways within the banking industry to streamline processes, enhance organization, and improve the overall management of accounts and transactions. Let’s explore some common use cases for suffixes in banking:
- Account Identification: Suffixes are added to account numbers to identify different types of accounts. For example, a suffix may indicate whether an account is a savings account, a checking account, a certificate of deposit (CD), or a money market account. This allows both customers and bank staff to easily recognize the purpose and features associated with each account.
- Transaction Classification: Suffixes are crucial in classifying and categorizing various transactions conducted within the banking system. They can be added to transaction codes to differentiate between different types of transactions such as deposits, withdrawals, transfers, payments, or specific transaction categories like loan repayments or utility bill payments. This enables banks to track and analyze transaction data more efficiently.
- Product Differentiation: Suffixes are used to classify and distinguish various financial products offered by banks. This includes loans, credit cards, investment accounts, and other specialized banking products. By adding a specific suffix to the product code, banks can easily identify and manage different product offerings, allowing for tailored customer services and improved product maintenance.
- Branch or Department Identification: Suffixes can be used to indicate the geographical location or specific department associated with an account or transaction. This aids in routing transactions correctly, assigning specific account management to designated branches, or identifying specific departments responsible for handling certain transactions or customer inquiries.
- Beneficiary Identification: In international banking, suffixes can be used to identify beneficiaries or beneficiary banks in cross-border transactions. These suffixes contain additional information such as the country code, institution code, or account type, to ensure accuracy and swift processing of international payments.
By utilizing suffixes in these various ways, banks are able to enhance their efficiency, provide personalized services, and maintain accurate records. Suffixes make it easier for both customers and bank staff to identify and manage different aspects of banking operations, ensuring a smooth and seamless experience for all parties involved.
Examples of Suffixes in Banking
Suffixes in banking can take on various forms and serve different purposes. Let’s explore some examples of suffixes commonly used in the banking industry:
- -SAV: This suffix is often added to the account number to indicate a savings account. For example, if an account number is 123456, a savings account with the same account number would be labeled as 123456-SAV.
- -CHK: The suffix “-CHK” is commonly used to denote a checking account. It differentiates a checking account from other types of accounts within a bank. For instance, an account number of 987654 may be labeled as 987654-CHK to identify it as a checking account.
- -INV: This suffix is often added to account numbers for investment accounts. For example, if an account number is 456789, adding the suffix “-INV” would indicate that it is an investment account: 456789-INV.
- -LOAN: This suffix is often used to identify loan accounts. For instance, if an account number is 567890, adding the suffix “-LOAN” would indicate that it is a loan account: 567890-LOAN.
- -BR: Suffixes can also be used to indicate a specific bank branch. Adding “-BR” to an account number helps to identify which branch the account is associated with. For example, if an account number is 7890123, the suffix “-BR” could be added to indicate that it belongs to a specific branch, making it 7890123-BR.
These examples demonstrate how suffixes can be used to provide additional information and categorization within the banking system. By adding these suffixes to account numbers or transaction codes, banks are able to clearly distinguish between different account types, track specific transactions, and optimize their operations.
It is important to note that the specific suffixes used in banking can vary between financial institutions. Each bank may have its own set of suffixes tailored to their internal systems and account management requirements. Therefore, it is crucial for both bank staff and customers to familiarize themselves with the specific suffixes used by their respective bank.
Benefits and Limitations of Suffixes in Banking
The use of suffixes in banking offers several benefits, but it also has its limitations. Let’s explore both aspects:
- Benefits:
- Enhanced Organization: Suffixes facilitate the categorization and organization of accounts and transactions within the banking system. They provide a clear way to differentiate between different account types, transactions, and products, making it easier for banks to manage and track financial operations.
- Efficient Account and Transaction Identification: Suffixes allow for streamlined identification and classification of accounts and transactions. This enables banks and customers to quickly recognize the purpose, type, and characteristics of each account or transaction, improving accuracy and reducing confusion.
- Improved Customer Service: With the use of suffixes, bank staff can easily identify and understand the specific needs of customers based on their account types or transaction suffixes. This enables personalized services, tailored recommendations, and efficient resolution of customer inquiries.
- Streamlined Reporting and Analysis: Suffixes contribute to accurate and consistent reporting and analysis of banking data. By categorizing transactions and accounts through suffixes, banks can generate comprehensive reports, conduct targeted data analysis, and facilitate regulatory compliance.
- System Integrity: Suffixes help maintain the integrity of banking systems by providing consistent and accurate data. They reduce the risk of errors, mismanagement, and confusion by ensuring that each account and transaction is correctly categorized and easily distinguishable.
- Limitations:
- Limited Standardization: There is no universal standard for suffixes in banking, and different banks may use different suffixes to classify accounts and transactions. This lack of standardization can lead to confusion when customers transfer accounts between institutions or when aggregating data across multiple banks.
- Potential Complexity: As the number of different suffixes increases, the complexity of account and transaction identification may also rise. This can become a challenge for both customers and bank staff to remember and understand the meaning behind each suffix, especially when dealing with a wide range of products and services.
- System Constraints: Banking systems must be equipped to handle the use of suffixes efficiently. Some legacy systems may have limitations that restrict the number of possible suffixes or the length of the account number. This can hinder the implementation of complex suffixing structures or require system upgrades to accommodate additional suffixes.
Although suffixes in banking offer significant benefits in terms of organization, identification, and reporting, it is important to recognize their limitations. Banks must carefully consider the trade-offs and ensure that the implementation of suffixes aligns with their operational capabilities and customer needs.
Conclusion
Suffixes in banking may seem like small details, but they play a vital role in categorizing, organizing, and managing accounts and transactions within the financial system. They enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and clarity of banking operations, benefiting both customers and financial institutions.
By utilizing suffixes, banks can easily differentiate between various types of accounts, track specific transactions, and provide personalized services tailored to customer needs. The use of suffixes enables efficient reporting, analysis, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
However, it is important to note that there are limitations to the use of suffixes, such as the lack of standardization and potential complexity. Banks need to carefully consider these factors and ensure that their systems can handle the use of suffixes effectively without creating confusion or operational constraints.
In conclusion, suffixes in banking are a valuable tool for organizing, categorizing, and managing accounts and transactions. They enhance the overall efficiency and accuracy of banking operations, improving customer service, facilitating regulatory compliance, and optimizing system integrity. By understanding and utilizing suffixes effectively, banks can streamline their processes and provide a seamless and enhanced banking experience for their customers.