Finance
What Is The Middle Credit Score
Modified: March 6, 2024
Learn the importance of your middle credit score in finance and how it impacts your eligibility for loans and credit cards. Improve your creditworthiness by understanding the factors that influence this crucial score.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Credit Score
- Importance of Credit Scores
- What Is the Middle Credit Score?
- Why Is the Middle Credit Score Important?
- How to Find Your Middle Credit Score
- Factors That Affect the Middle Credit Score
- How Lenders Use the Middle Credit Score
- Tips for Improving Your Middle Credit Score
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of credit scores! When it comes to managing your finances, understanding your credit score is crucial. Whether you’re applying for a loan, purchasing a car, or renting an apartment, lenders and creditors rely on your credit score to assess your creditworthiness and determine whether you qualify for financial assistance.
But what exactly is a credit score, and why is it important? In this article, we’re going to delve into the concept of the middle credit score, its significance, and how it impacts your financial decisions.
A credit score is a three-digit number that represents your creditworthiness. It is an evaluation of your credit history and financial behavior, providing insights into how likely you are to repay your debts. The most commonly used credit scoring model is the FICO score, which ranges from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating better creditworthiness.
Your credit score is calculated based on various factors, including your payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit accounts, and recent credit inquiries. Lenders use this score as a quick snapshot of your creditworthiness, allowing them to make informed decisions about granting you credit.
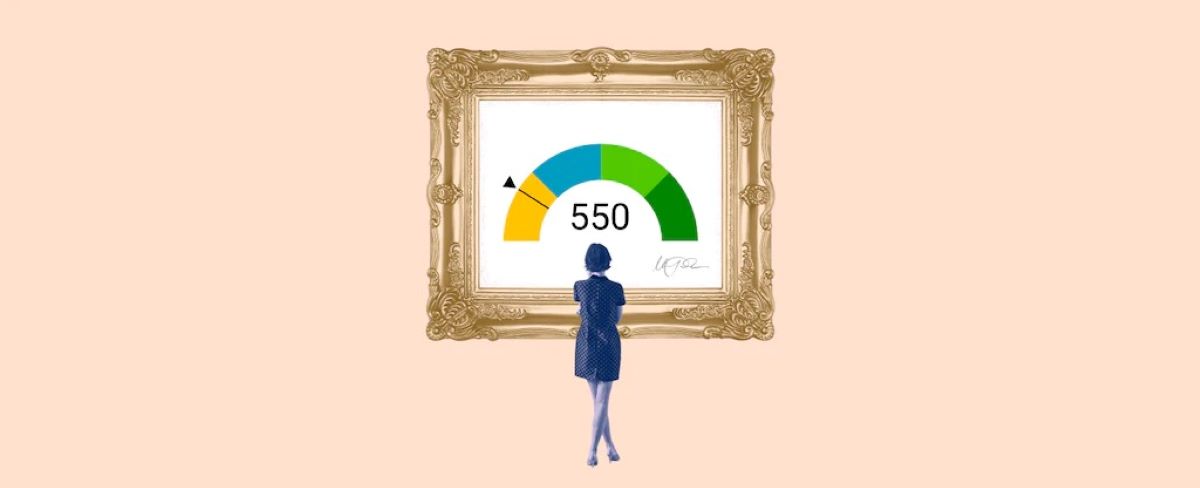
Now, let’s talk about the middle credit score. As the name implies, it refers to the middle value of the credit scores from the three major credit bureaus: Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion. When you apply for credit, the lender typically looks at all three credit scores. The middle credit score is the one that falls in the middle range of the three scores.
This middle credit score is crucial because it serves as a benchmark for lenders. It provides a more balanced representation of your creditworthiness compared to just considering the highest or lowest score. Let’s say your three credit scores are 720, 690, and 650. In this case, the middle credit score would be 690, which lenders may use as the basis for their loan approval process.
Understanding your middle credit score is important for several reasons. Firstly, it gives you a clearer picture of how lenders may view your creditworthiness. If your middle credit score is high, you are more likely to be eligible for better interest rates and loan terms. Conversely, a lower middle credit score may result in higher interest rates or even loan denial.
In addition, monitoring your middle credit score allows you to identify any discrepancies or errors in your credit reports. If you notice a significant discrepancy between your middle credit score and the other two, it may be a sign of inaccurate or outdated information that needs to be addressed to ensure fair representation of your creditworthiness.
Now that you understand the importance of the middle credit score, let’s explore how you can find this crucial piece of information and the factors that can impact your score.
Definition of Credit Score
A credit score is a three-digit number that represents your creditworthiness and financial reliability. It is a numerical assessment of your credit history and payment behavior, providing lenders with a quick snapshot of your ability to manage debt responsibly. Your credit score is a crucial factor in determining whether you will be approved for credit, and it also plays a significant role in determining the interest rates and terms you may be offered.
The most commonly used credit scoring model is the FICO score, developed by the Fair Isaac Corporation. FICO scores range from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating better creditworthiness. The higher your credit score, the more likely you are to be approved for credit and offered favorable terms.
Various factors contribute to the calculation of your credit score. The five main factors considered are:
- Payment history: Your track record of making timely payments on credit accounts, such as loans and credit cards, is a crucial element in determining your credit score. Consistently making payments on time positively impacts your credit score, while late payments or delinquencies can have a negative impact.
- Credit utilization: The amount of credit you use compared to your available credit limit, also known as your credit utilization ratio, is another significant factor. Keeping your credit utilization low, ideally below 30%, demonstrates responsible credit management and can positively affect your credit score.
- Length of credit history: The length of time you have been using credit also influences your credit score. The longer your credit history, the more valuable it becomes in assessing your creditworthiness. Lenders prefer to see a longer credit history to evaluate your repayment patterns and responsible credit management.
- Types of credit: The variety of credit accounts you have, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages, can impact your credit score. Having a mix of credit types can show that you can responsibly handle different forms of credit.
- New credit inquiries: When you apply for new credit, it results in a hard inquiry on your credit report. Multiple inquiries within a short period can negatively impact your credit score, as it may indicate a higher risk of potential debt accumulation.
Keep in mind that these factors may carry different weights depending on your individual credit profile. While the FICO scoring model is widely used, other credit bureaus and lenders may employ alternative scoring models that consider additional factors or use different scoring ranges.
Understanding the components and calculation of your credit score is essential in managing your financial health. It allows you to identify areas for improvement and take proactive steps to maintain or enhance your creditworthiness. Regularly monitoring your credit score and reviewing your credit reports can help you stay informed and detect any inaccuracies or fraudulent activity that may affect your credit standing.
Importance of Credit Scores
Your credit score plays a crucial role in your financial life. It impacts your ability to secure loans, obtain favorable interest rates, and even influences decisions related to renting an apartment or getting approved for a credit card. Here are some key reasons why credit scores are important:
1. Loan Approval: Lenders use your credit score to assess your creditworthiness when you apply for a loan. A higher credit score increases your chances of being approved for a loan, while a lower score may result in loan denials or limited borrowing options. A strong credit score demonstrates your ability to manage debt responsibly, making lenders more confident in your repayment capability.
2. Interest Rates: Your credit score can significantly impact the interest rates you are offered on loans. A higher credit score may enable you to secure loans at more favorable interest rates, saving you money over the life of the loan. On the other hand, a lower credit score may lead to higher interest rates, increasing the cost of borrowing.
3. Credit Card Approval: When applying for a credit card, issuers evaluate your credit score to determine the level of risk associated with extending you credit. A strong credit score increases your chances of approval and may enable you to access credit cards with higher credit limits and better rewards programs.
4. Rental Applications: Landlords and property management companies often review credit scores as part of the rental application process. A higher credit score can enhance your chances of being approved for a rental property, as it demonstrates financial responsibility and a higher likelihood of making rent payments on time.
5. Insurance Premiums: In some cases, insurance companies consider credit scores when determining the premiums you pay for auto, home, or renters insurance. A high credit score may result in lower insurance premiums, as it is seen as an indicator of responsible behavior that may translate to fewer insurance claims.
6. Employment Opportunities: Certain employers may review credit scores as part of their hiring process, especially for positions that require financial responsibility or involve handling money. While credit scores cannot be used as the sole basis for hiring decisions, they can influence an employer’s perception of an applicant’s reliability and attention to financial matters.
7. Financial Future: Building and maintaining a good credit score is essential for your long-term financial well-being. A strong credit history opens doors to better financial opportunities, including access to favorable loan terms, lower interest rates, and increased financial flexibility.
It’s crucial to monitor and manage your credit score regularly to ensure accuracy and identify areas of improvement. By practicing responsible financial habits, such as making payments on time, keeping credit utilization low, and avoiding excessive credit inquiries, you can build and maintain a strong credit score that sets the foundation for a healthy financial future.
What Is the Middle Credit Score?
The middle credit score refers to the numerical value that falls in the middle range of the credit scores generated by the three major credit bureaus: Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion. When you apply for credit or a loan, lenders usually review your credit history and assess your creditworthiness using the information provided by these credit bureaus. Each credit bureau may generate a different credit score based on variations in their scoring models and the data they have on file.
To arrive at the middle credit score, the lender takes the three scores provided by the credit bureaus and selects the one that falls in the middle. For example, if your credit scores from the three bureaus are 720, 690, and 650, the middle credit score would be 690. In some cases, if two of the scores are the same, the middle credit score will be the same as well.
The middle credit score is used by lenders to acquire a more balanced assessment of your creditworthiness. By focusing on the middle score rather than just the highest or lowest score, lenders can mitigate the potential bias caused by extreme scores. The middle credit score is considered a more accurate representation of your overall credit profile and financial stability.
It is important to note that not all lenders use the middle credit score. Some may use the highest or lowest score instead, depending on their internal policies or specific loan programs. However, the middle credit score is commonly used by many lenders as a benchmark for evaluating loan applications and determining the terms and interest rates offered to borrowers.
Understanding your middle credit score is essential as it provides insight into how lenders may view your creditworthiness. A higher middle credit score indicates a stronger credit profile, increasing your chances of obtaining favorable loan terms, higher credit limits, and lower interest rates. Conversely, a lower middle credit score may result in limited borrowing options or higher interest rates.
Now that you understand what the middle credit score is, let’s explore why it is important in the lending process and how you can find your middle credit score.
Why Is the Middle Credit Score Important?
The middle credit score holds significant importance in the lending process and can greatly impact your borrowing options and loan terms. Here are some key reasons why the middle credit score is crucial:
1. Balanced Representation: The middle credit score provides a balanced representation of your creditworthiness compared to just considering the highest or lowest score. It takes into account the information from all three major credit bureaus and helps lenders get a more accurate assessment of your overall credit profile.
2. Risk Assessment: Lenders use the middle credit score as part of their risk assessment process. A higher middle credit score demonstrates a lower level of risk, indicating that you are more likely to repay your debts responsibly and on time. This can lead to more favorable loan terms, such as lower interest rates and higher credit limits.
3. Loan Approval: Many lenders use the middle credit score as the basis for loan approvals. If your middle credit score meets their minimum requirement, you are more likely to be approved for credit. Lenders prefer a borrower with a solid middle credit score, as it implies a lower likelihood of defaulting on the loan.
4. Better Loan Terms: A higher middle credit score can lead to better loan terms and interest rates. Lenders are more inclined to offer favorable terms to borrowers with strong credit profiles, as they are considered less risky. With a higher middle credit score, you may have access to lower interest rates, which can save you money over the life of the loan.
5. Negotiating Power: When you have a solid middle credit score, you have more negotiating power with lenders. You can confidently request better loan terms or interest rates based on your strong creditworthiness. Lenders are more likely to consider your requests when they see that you have a favorable middle credit score.
6. Loan Program Eligibility: Different loan programs may have specific requirements regarding credit scores. By knowing your middle credit score, you can determine if you meet the minimum criteria for specific loan programs. Without a satisfactory middle credit score, you may not qualify for certain loan options.
7. Credit Card Approval: Credit card issuers may also consider the middle credit score when evaluating credit card applications. A higher middle credit score can increase your chances of approval and may even qualify you for credit cards with better rewards programs and higher credit limits.
Understanding the importance of the middle credit score empowers you to take steps to improve and manage your credit profile effectively. Maintaining a good middle credit score not only provides you with more borrowing options but also sets the stage for a financially secure future.
How to Find Your Middle Credit Score
Discovering your middle credit score is crucial for understanding how lenders may perceive your creditworthiness. Here are a few steps to help you find your middle credit score:
- Obtain your credit reports: Start by obtaining your credit reports from all three major credit bureaus: Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion. You are entitled to receive a free credit report from each bureau once a year, which you can request online or by mail. Reviewing your credit reports will give you an overview of your credit history and the information that is being used to calculate your credit scores.
- Check your credit scores: After obtaining your credit reports, check the credit scores provided by each credit bureau. Some credit monitoring services may also provide you with access to your credit scores. Make note of the three scores: one from Experian, one from Equifax, and one from TransUnion.
- Identify the middle credit score: Compare the three credit scores you obtained. Arrange them in ascending order from lowest to highest. The middle credit score is the number that falls in the middle of the range. For example, if your credit scores are 720, 690, and 650, the middle credit score would be 690.
- Focus on the middle score: Understand that lenders often base their decisions on the middle credit score. While it’s essential to keep an eye on all your credit scores, focusing on the middle score will give you a better understanding of how lenders may view your creditworthiness.
- Regular credit monitoring: To stay informed about changes in your credit scores, consider using credit monitoring services or signing up for free credit score tracking through various online platforms. These services can provide you with regular updates on your credit scores and alert you to any significant changes that could impact your creditworthiness.
Remember that credit scores may vary slightly among the credit bureaus due to differences in their scoring models and data reporting. By knowing and monitoring your middle credit score, you can better gauge your creditworthiness and make informed decisions when seeking credit or loans.
Keep in mind that improving your credit takes time and consistent effort. By practicing responsible financial habits, such as making timely payments, keeping credit utilization low, and minimizing new credit applications, you can work towards raising your middle credit score and strengthening your overall credit profile.
Factors That Affect the Middle Credit Score
Several factors influence your middle credit score, which lenders consider when assessing your creditworthiness. Understanding these factors can help you identify areas for improvement and take proactive steps to enhance your credit score. Here are some key factors that can affect your middle credit score:
- Payment History: One of the most critical factors is your payment history. Making timely payments on credit accounts, such as loans and credit cards, positively impacts your credit score. Late payments, defaults, or accounts sent to collections can significantly lower your credit score.
- Credit Utilization: The amount of credit you use compared to your available credit limit, known as credit utilization, also plays a significant role. Keeping your credit utilization low, ideally below 30%, shows responsible credit management and can positively affect your credit score. High utilization can indicate a higher risk of overextending your credit.
- Length of Credit History: The length of your credit history is another crucial factor. Lenders prefer to see a longer credit history as it demonstrates your ability to manage credit over an extended period. A shorter credit history may limit your credit score. It’s important to establish and maintain credit accounts responsibly to build a strong credit history.
- Types of Credit: The diversity of credit accounts you have can impact your credit score. Lenders like to see a healthy mix of credit, including credit cards, loans, and mortgages. Demonstrating experience managing various types of credit can positively contribute to your credit score.
- New Credit Applications: Opening multiple new credit accounts within a short period can negatively impact your credit score. Each time you apply for new credit, it results in a hard inquiry on your credit report. Limiting new credit applications can help maintain a higher credit score.
- Derogatory Marks and Negative Information: Certain negative marks on your credit report, such as bankruptcies, foreclosures, or collections, can significantly impact your credit score. These derogatory marks may remain on your credit report for several years and can lower your credit score. It’s essential to address and resolve any negative information to improve your creditworthiness.
- Credit Account Age: The age of your credit accounts also affects your credit score. Older accounts that have been open for a longer period contribute positively to your credit history. Closing old accounts may lower the average age of your accounts and potentially impact your credit score.
It’s important to note that each credit bureau may weigh these factors differently, leading to slight variations in your credit scores from each bureau. However, understanding the overall impact of these factors can help you take action to improve your creditworthiness and raise your middle credit score.
By practicing responsible financial habits such as making timely payments, keeping credit utilization low, and avoiding excessive new credit applications, you can positively impact these factors and work towards a stronger middle credit score.
How Lenders Use the Middle Credit Score
Lenders play a critical role in the borrowing process, and they rely on the middle credit score as a key factor in assessing your creditworthiness. Here’s how lenders use the middle credit score when making lending decisions:
Loan Eligibility: Lenders often set minimum credit score requirements for loan eligibility. They use the middle credit score to determine whether you meet their criteria and have a credit history that aligns with their lending guidelines. If your middle credit score falls below their threshold, you may be considered a higher risk borrower, resulting in potential loan denials or limited borrowing options.
Loan Terms and Interest Rates: Your middle credit score is also influential in determining the terms and interest rates offered by lenders. A higher middle credit score generally results in more favorable terms, such as lower interest rates, extended repayment periods, and higher credit limits. Lenders view borrowers with higher credit scores as lower risk and are willing to provide better loan terms and conditions.
Creditworthiness Assessment: The middle credit score gives lenders a snapshot of your creditworthiness and how likely you are to repay your debts. It provides them with insights into your past credit behavior, including your payment history, utilization ratios, and overall credit management. Lenders interpret a higher middle credit score as a positive indicator of responsible financial behavior, increasing their confidence in your ability to manage future debt obligations.
Comparison to Industry Standards: Lenders often compare your middle credit score to industry standards and benchmarks. These standards help them determine whether your creditworthiness is in line with borrowers in similar financial situations. If your middle credit score exceeds the average or falls below the industry standard, it can influence their loan decisions and the terms they offer you.
Risk Assessment: Lenders use the middle credit score as part of their risk assessment process. A lower middle credit score may raise concerns about your ability to repay the loan, resulting in higher perceived risk. This may lead lenders to offer less favorable terms or require additional collateral or a cosigner to mitigate their risk exposure.
Loan Approval Decisions: Ultimately, the middle credit score heavily influences loan approval decisions. Lenders use this score, among other factors, to determine whether to approve your loan application. A higher middle credit score increases your chances of loan approval, while a lower score may result in denials or require you to explore alternative lending options.
It’s important to note that lenders may also consider other aspects of your financial profile, such as income, employment history, and debt-to-income ratio, alongside the middle credit score. They evaluate multiple factors to make well-informed lending decisions that balance risk and profitability.
By understanding how lenders use the middle credit score, you can prioritize improving and maintaining a strong credit profile. This will increase your chances of loan approvals and enable you to secure more favorable loan terms and interest rates in the future.
Tips for Improving Your Middle Credit Score
If you want to improve your middle credit score and strengthen your overall creditworthiness, here are some effective tips to consider:
- Make Timely Payments: Pay all your bills and credit accounts on time. Late payments can have a detrimental impact on your credit score. Set up automatic payments or reminders to ensure you never miss a due date.
- Reduce Credit Utilization: Aim to keep your credit card balances low and your credit utilization ratio below 30%. High credit utilization can signal a higher risk of overextending your credit and can negatively affect your score. Consider paying off balances in full each month or making multiple payments to keep utilization low.
- Manage Credit Accounts Responsibly: Keep credit accounts open and active, even if you pay them off. The longer your credit history, the better it reflects on your credit score. Avoid closing old accounts unless absolutely necessary.
- Diversify Your Credit Mix: Having a mix of credit accounts, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages, can demonstrate responsible credit management. However, don’t open new accounts just for the sake of diversification. Only take on credit you need and can manage effectively.
- Limit New Credit Applications: Avoid applying for multiple new credit accounts within a short period. Each application typically generates a hard inquiry on your credit report, which can temporarily lower your score. Only apply for credit when necessary, and do some research to find lenders who offer pre-approval options without hard inquiries.
- Check Your Credit Reports Regularly: Review your credit reports from all three major credit bureaus to ensure accuracy. Dispute any errors you find promptly to prevent them from negatively impacting your credit score. You are entitled to a free credit report from each bureau annually.
- Manage Debt Responsibly: Keep your debt levels under control and avoid overextending yourself financially. Prioritize paying down existing debts and avoid accumulating unnecessary debt. A healthy debt-to-income ratio can positively impact your credit score.
- Build a Positive Credit History: Establish a positive credit history by consistently using credit responsibly. Make small purchases on credit cards and pay them off in full. This demonstrates your ability to manage credit effectively and builds a positive credit history over time.
- Be Patient and Persistent: Improving your credit score takes time and persistence. Focus on building good credit habits, and over time you will see your credit score rise. Stay committed to your financial goals and avoid practices that can harm your score.
By following these tips, you can gradually improve your middle credit score and enhance your overall creditworthiness. Remember, improving your credit score is a journey that requires consistent effort and responsible financial management. The rewards of maintaining a healthy credit score are worth the time and dedication.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of the middle credit score is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the world of credit and loans. Your middle credit score serves as a benchmark for lenders, providing them with a more balanced representation of your creditworthiness compared to just the highest or lowest score. It plays a vital role in loan approvals and the terms and interest rates offered by lenders.
Your credit score is influenced by various factors, including payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit, and new credit applications. By managing these factors responsibly, you can work towards improving your middle credit score and strengthening your overall credit profile.
Monitoring your credit score regularly and checking your credit reports for accuracy are essential steps towards maintaining good credit health. By doing so, you can identify any discrepancies or errors and take appropriate actions to rectify them. Additionally, practicing sound financial habits, such as making timely payments, keeping credit utilization low, and limiting new credit applications, can positively impact your credit score.
Remember, building and maintaining a strong middle credit score takes time and effort. It’s a reflection of your financial responsibility and reliability. By prioritizing good credit practices, you can enhance your creditworthiness, access better loan terms, and open doors to a more secure financial future.