Home>Finance>What Is The Minimum Payment On $2000 Credit Card


Finance
What Is The Minimum Payment On $2000 Credit Card
Published: February 27, 2024
Learn about the minimum payment on a $2000 credit card and manage your finances wisely. Find out how to handle credit card payments effectively in this finance guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to managing credit card debt, understanding the concept of minimum payments is crucial. Many credit cardholders are familiar with the term “minimum payment,” but the specifics of how it is calculated and its implications are often overlooked. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of minimum payments, particularly in the context of a $2000 credit card balance. By shedding light on this topic, we aim to equip readers with the knowledge needed to make informed financial decisions and effectively manage their credit card obligations.
Understanding the minimum payment requirements is essential for maintaining a healthy financial standing. Failing to grasp the significance of minimum payments can lead to prolonged debt, increased interest charges, and potential damage to one’s credit score. As such, gaining a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing minimum payments and the methods for calculating them is paramount for responsible credit card management.
Moreover, by exploring practical tips for managing credit card payments, we can provide readers with actionable strategies to navigate their financial responsibilities effectively. Whether it’s budgeting, prioritizing payments, or seeking professional guidance, the insights shared in this article will empower individuals to take control of their credit card debt and work towards financial stability.
Understanding Minimum Payments
Minimum payments represent the lowest amount a credit cardholder must pay by a specified due date to keep the account in good standing. This mandatory payment is typically calculated as a percentage of the outstanding balance, along with any interest and fees accrued during the billing cycle. While the exact formula for determining minimum payments may vary among credit card issuers, it is crucial for cardholders to comprehend the implications of making only the minimum payment each month.
One key aspect to consider is that making only the minimum payment can result in a prolonged repayment period and significantly higher interest charges. This is due to the fact that a substantial portion of the minimum payment goes towards covering the interest accrued, with only a fraction contributing to reducing the principal balance. As a result, carrying a balance while consistently making minimum payments can lead to a cycle of debt that becomes increasingly challenging to overcome.
Furthermore, relying solely on minimum payments can have adverse effects on one’s credit score. Credit utilization, which is the ratio of credit card balances to credit limits, plays a significant role in credit scoring models. By maintaining high balances relative to their credit limits and making only minimum payments, individuals may experience a negative impact on their credit scores, potentially limiting their access to favorable credit terms in the future.
It is important for credit cardholders to recognize that while minimum payments offer short-term relief by meeting the immediate payment obligation, they can result in long-term financial strain. By understanding the implications of minimum payments, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their credit card repayment strategies and work towards minimizing the overall cost of debt.
Factors Affecting Minimum Payments
The calculation of minimum payments is influenced by several key factors, each of which can significantly impact the amount due each billing cycle. Understanding these factors is essential for credit cardholders seeking to manage their repayment obligations effectively.
- Outstanding Balance: The outstanding balance on a credit card directly influences the minimum payment amount. Typically, minimum payments are calculated as a percentage of the total balance, meaning that higher balances result in larger minimum payment requirements.
- Interest Rate: The annual percentage rate (APR) applied to the credit card balance plays a critical role in determining the minimum payment. Higher interest rates lead to increased interest charges, thereby elevating the minimum payment amount required to cover both the interest and a portion of the principal balance.
- Fixed Fees and Penalties: Certain credit card issuers impose fixed fees and penalties for specific actions, such as late payments or exceeding the credit limit. These additional charges contribute to the minimum payment amount and can inflate the overall repayment obligation.
- Regulatory Requirements: In some jurisdictions, financial regulations dictate the minimum payment calculation methodology. These requirements may stipulate a minimum percentage of the total balance or establish specific guidelines for how interest and fees are factored into the minimum payment.
- Issuer Policies: Credit card issuers have the discretion to set their own policies for minimum payments, subject to regulatory constraints. As a result, the specific formula used to calculate minimum payments can vary among different card issuers, leading to differences in the minimum payment amounts for similar balances and interest rates.
By considering these factors, credit cardholders can gain insight into the variables influencing their minimum payment obligations. This understanding empowers individuals to assess the impact of these factors on their overall repayment strategy and take proactive measures to manage their credit card debt effectively.
Calculating the Minimum Payment on a $2000 Credit Card
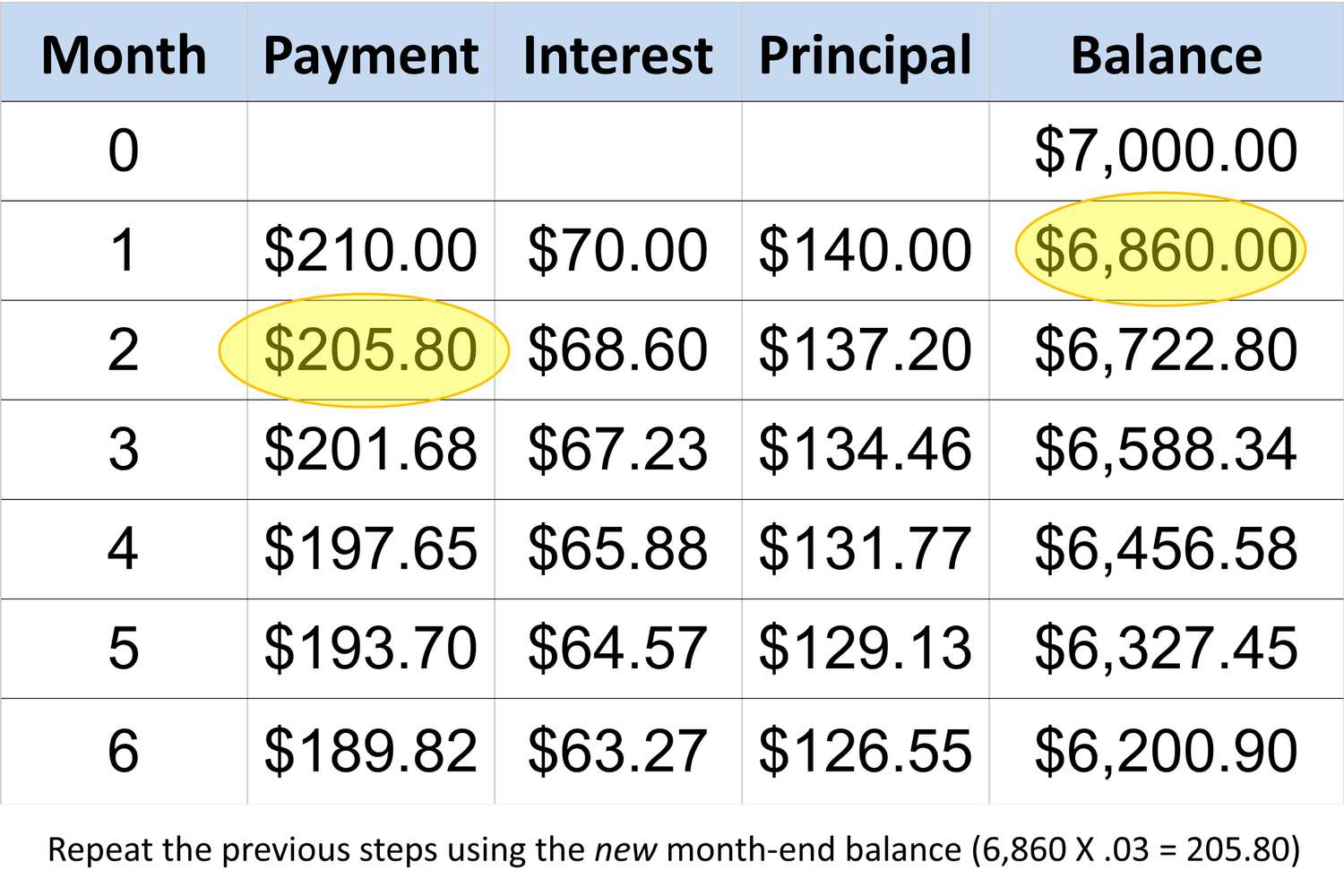
When determining the minimum payment on a $2000 credit card balance, it is essential to consider the factors that contribute to the calculation of this mandatory payment. While specific credit card issuers may employ varying methodologies for minimum payment determination, a common approach involves a calculation based on the outstanding balance, interest accrued, and any applicable fees. To illustrate the potential minimum payment requirements for a $2000 credit card balance, let’s explore a hypothetical scenario.
Assuming a credit card issuer sets the minimum payment at 3% of the outstanding balance or $25, whichever is greater, the minimum payment for a $2000 balance would be $60 (3% of $2000). However, if the calculated 3% falls below the predetermined minimum of $25, the minimum payment would be $25 instead. It is important to note that this example serves to demonstrate a hypothetical minimum payment scenario, and actual minimum payment calculations may differ based on the specific terms and conditions outlined by the credit card issuer.
Furthermore, if the $2000 balance incurs interest charges at an annual percentage rate (APR) of, for instance, 18%, the interest accrued over the billing cycle would contribute to the total minimum payment. The inclusion of interest charges in the minimum payment calculation serves to ensure that a portion of the accrued interest is covered, thereby reducing the outstanding balance over time.
Additionally, if the $2000 balance is subject to any fixed fees or penalties, such as late payment fees, these charges would factor into the minimum payment requirement, further influencing the total amount due. It is important for credit cardholders to review their cardholder agreements and disclosures to understand how these fees impact the minimum payment calculation and the overall cost of carrying a balance.
By gaining insight into the potential minimum payment calculation for a $2000 credit card balance, individuals can assess the financial implications of carrying such a balance and make informed decisions regarding their repayment strategy. Understanding the minimum payment requirements is crucial for managing credit card debt effectively and working towards financial stability.
Tips for Managing Credit Card Payments
Effectively managing credit card payments is essential for maintaining financial stability and minimizing the long-term cost of debt. By implementing strategic approaches to handle credit card obligations, individuals can navigate their repayment responsibilities with confidence and control. Here are some valuable tips for managing credit card payments:
- Create a Budget: Establishing a comprehensive budget that prioritizes credit card payments within the overall financial plan is crucial. By allocating funds specifically for credit card repayments, individuals can ensure that the minimum payments are met while working towards reducing the outstanding balances.
- Pay More Than the Minimum: Whenever possible, strive to pay more than the minimum amount due. By making additional payments towards the principal balance, individuals can expedite the reduction of debt and minimize the interest charges accrued over time.
- Monitor Spending Habits: Regularly reviewing credit card statements and tracking spending habits can provide valuable insights into areas where expenses can be reduced. By curbing unnecessary expenditures, individuals can free up funds to allocate towards credit card payments.
- Seek Lower Interest Rates: Explore opportunities to secure lower interest rates, such as transferring balances to credit cards with promotional APR offers or contacting current card issuers to negotiate reduced rates. Lower interest charges can facilitate faster debt repayment.
- Consider Debt Consolidation: For individuals juggling multiple credit card balances, consolidating debts through a personal loan or a balance transfer credit card can streamline repayments and potentially lower overall interest costs.
- Communicate with Creditors: In cases of financial hardship or unexpected challenges, proactive communication with creditors can lead to mutually beneficial arrangements, such as modified payment plans or temporary hardship programs.
- Explore Credit Counseling: Seeking guidance from reputable credit counseling services can provide valuable strategies for managing credit card debt and improving overall financial wellness.
- Avoid New Charges: While focusing on debt repayment, strive to minimize new charges on credit cards to prevent further escalation of balances and ensure that progress is made towards reducing existing debt.
By integrating these tips into their financial approach, individuals can proactively manage their credit card payments, mitigate the impact of high-interest debt, and work towards achieving greater financial freedom and security.
Conclusion
Managing credit card payments, particularly the minimum payment obligations, is a fundamental aspect of maintaining healthy financial habits. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing minimum payments and the implications of carrying credit card balances, individuals can make informed decisions to effectively manage their debt and work towards financial stability.
It is essential for credit cardholders to recognize that while minimum payments offer short-term relief by meeting the immediate payment obligation, they can lead to prolonged debt and increased interest charges over time. By embracing proactive strategies such as paying more than the minimum, monitoring spending habits, and exploring opportunities to secure lower interest rates, individuals can take control of their credit card debt and progress towards debt-free living.
Furthermore, by seeking guidance from reputable credit counseling services and maintaining open communication with creditors, individuals can access valuable resources to support their debt management efforts. The proactive steps outlined in this article empower individuals to navigate their credit card payments with confidence and purpose, ultimately paving the way towards improved financial well-being.
In conclusion, a well-informed and proactive approach to managing credit card payments is pivotal for achieving long-term financial success. By leveraging the insights and strategies shared in this article, individuals can cultivate responsible financial habits, reduce the burden of credit card debt, and embark on a path towards a more secure and prosperous financial future.