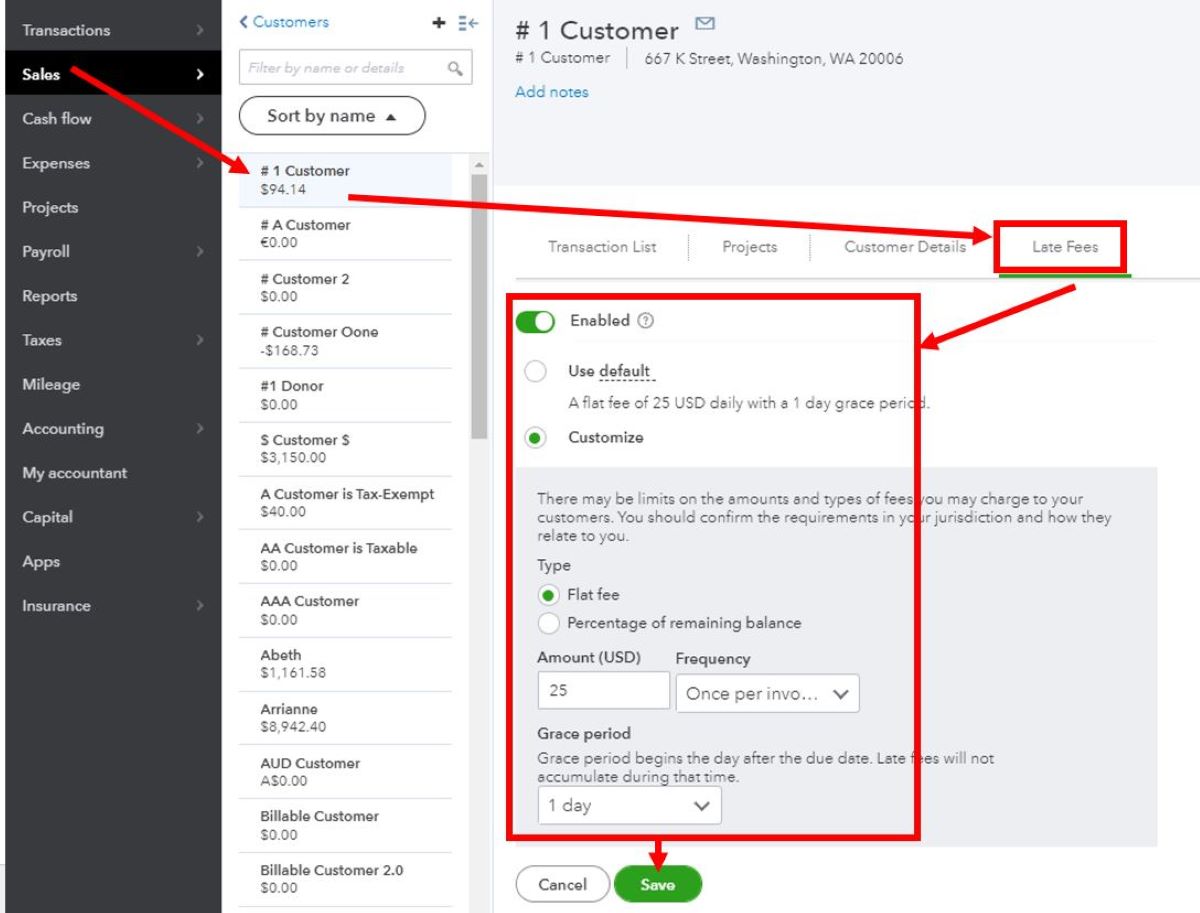
Home>Finance>What Is The Standard Amount Of An Invoice Late Fee


Finance
What Is The Standard Amount Of An Invoice Late Fee
Published: February 23, 2024
Learn about the standard amount for invoice late fees and how it impacts your finances. Understand the importance of setting the right late fee to manage cash flow effectively.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding the Importance of Late Fees in Invoicing
Late payments can significantly impact a company's cash flow and financial stability. When clients fail to settle their invoices promptly, businesses may encounter challenges in meeting their own financial obligations, such as paying employees and suppliers or investing in growth opportunities. To mitigate the adverse effects of delayed payments, many organizations incorporate late fees into their invoicing processes. These fees serve as a form of compensation for the inconvenience and potential financial strain caused by overdue payments.
Late fees are designed to encourage timely payments and discourage clients from extending payment terms beyond the agreed-upon period. By implementing a clear late fee structure, businesses can incentivize clients to prioritize settling their invoices promptly, thereby fostering healthier cash flow management for both parties involved.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of late fees in invoicing, exploring the factors that influence the determination of standard late fee amounts, legal considerations, and best practices for implementing late fees. Whether you are a business owner seeking to optimize your invoicing strategies or a client aiming to better understand the implications of delayed payments, this article will provide valuable insights into the role of late fees in the realm of finance and business operations.
Understanding Late Fees and Their Impact
Late fees are charges imposed on clients or customers who fail to settle their invoices within the specified timeframe. These fees are a critical component of the invoicing process, serving as a deterrent against delayed payments and a means of compensating businesses for the associated inconveniences and financial repercussions.
Late fees play a pivotal role in encouraging timely payments and promoting responsible financial behavior among clients. By clearly outlining the consequences of late payments, businesses can instill a sense of urgency and accountability, thereby reducing the likelihood of extended payment delays. Furthermore, the application of late fees can help businesses maintain a steady cash flow, ensuring that operational expenses and financial obligations are met without undue strain.
From a client's perspective, understanding late fees is essential for fostering positive and mutually beneficial relationships with vendors and service providers. By recognizing the impact of delayed payments on the cash flow and financial stability of businesses, clients can prioritize prompt invoice settlements, thereby contributing to a more seamless and sustainable business ecosystem.
Late fees also serve as a form of compensation for the time and resources expended in following up on overdue payments. By incorporating late fees into their invoicing practices, businesses can mitigate the administrative burden associated with chasing late payments, allowing them to focus on core operations and strategic growth initiatives.
It is important to note that while late fees are a valuable tool for promoting timely payments, they should be implemented judiciously and transparently. Exorbitant or unjustly applied late fees can strain client relationships and tarnish a business's reputation. Therefore, a balanced approach to late fee implementation, coupled with clear communication and flexibility where warranted, is essential for fostering positive and sustainable partnerships with clients.
In the next section, we will explore the factors that businesses should consider when determining the standard amount of late fees, taking into account various financial and operational considerations.
Factors to Consider When Determining Late Fees
Setting the standard amount of late fees requires a thoughtful assessment of several key factors to ensure that the fees are reasonable, fair, and reflective of the impact of late payments on the business. Consider the following elements when determining the appropriate late fee structure:
- Invoice Amount: The size of the invoice plays a crucial role in determining the late fee percentage or flat rate. For larger invoices, a lower percentage may be reasonable to avoid imposing excessively burdensome fees on clients, while smaller invoices may warrant a slightly higher percentage to maintain the deterrent effect.
- Industry Standards: Researching industry-specific practices and standards can provide valuable insights into customary late fee structures. Understanding how other businesses in the same industry approach late fees can help in setting competitive yet reasonable charges.
- Client Relationships: Consider the nature of your relationships with clients. Long-standing, loyal clients may warrant more leniency in late fee application, while new or infrequent clients may be subject to standard late fee terms.
- Impact on Cash Flow: Evaluate the impact of late payments on your business’s cash flow and financial stability. If delayed payments significantly disrupt your operations or financial planning, a slightly higher late fee may be justified to encourage timely settlements.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that your late fee structure complies with local and national regulations. Some jurisdictions impose limitations on the maximum allowable late fees, and non-compliance can lead to legal repercussions.
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can establish a late fee framework that strikes a balance between incentivizing prompt payments and maintaining positive client relationships. It is essential to communicate the late fee structure clearly and transparently to clients, emphasizing its role in promoting responsible payment practices and sustaining the financial health of the business.
In the subsequent section, we will delve into the legal considerations surrounding late fees, providing insights into the regulatory aspects that businesses must navigate when implementing late fee policies.
Legal Considerations for Late Fees
When implementing late fees, businesses must navigate legal considerations to ensure compliance with relevant regulations and statutes. Failure to adhere to legal requirements can result in disputes, financial penalties, and damage to the business’s reputation. Therefore, it is imperative to understand the legal framework surrounding late fees and invoicing practices.
One crucial aspect to consider is the maximum allowable late fee as stipulated by local or national laws. Many jurisdictions impose limitations on the amount or percentage that businesses can charge as late fees. It is essential to research and understand these statutory restrictions to avoid inadvertently imposing excessive or unlawful late fees.
Additionally, businesses should clearly outline their late fee policies in their contracts, terms of service, or invoicing documents. Transparent communication of late fee terms ensures that clients are aware of the consequences of delayed payments and prevents misunderstandings or disputes. Providing clients with a clear overview of late fee calculations and the escalation of charges for prolonged delinquency can help manage expectations and foster a sense of fairness in the fee application process.
Furthermore, businesses should be mindful of any consumer protection laws that govern late fees, particularly in consumer-facing industries. These regulations may include provisions for grace periods, mandatory notifications, and restrictions on compounding late fees. Adhering to these guidelines is essential for upholding ethical invoicing practices and safeguarding the business’s reputation.
It is advisable for businesses to seek legal counsel or consult industry-specific resources to ensure full compliance with applicable laws and regulations. By proactively addressing legal considerations and integrating them into their invoicing processes, businesses can mitigate the risk of legal disputes and foster trust and confidence among their clients.
In the subsequent section, we will explore best practices for implementing late fees, encompassing strategies for transparent communication and effective fee management.
Best Practices for Implementing Late Fees
Implementing late fees in a fair, transparent, and strategic manner is essential for fostering positive client relationships and optimizing cash flow management. By adhering to best practices in late fee implementation, businesses can effectively incentivize timely payments while maintaining a reputation for fairness and professionalism.
Clear Communication: Transparently communicate late fee policies to clients through contracts, terms of service, or invoicing documents. Clearly outline the calculation method, the grace period (if applicable), and the escalation of charges for prolonged delinquency. Providing clients with a comprehensive overview of late fee terms helps manage expectations and reduces the likelihood of disputes.
Flexibility and Understanding: While it is crucial to enforce timely payments, businesses should also demonstrate flexibility and understanding in certain circumstances. Establishing a reasonable grace period and considering extenuating circumstances can contribute to a more amicable and cooperative client-business relationship.
Automated Reminders: Implement automated reminders for upcoming and overdue payments. Leveraging invoicing software or customer relationship management (CRM) systems to send gentle yet firm reminders can prompt clients to settle their invoices before late fees accrue.
Professional Courtesy: When applying late fees, maintain a professional and courteous approach. Personalized communication and a willingness to discuss payment challenges can mitigate potential friction and preserve the client-business rapport.
Regular Review and Adjustment: Periodically review the effectiveness of late fee policies and consider adjusting the fee structure if necessary. As business dynamics evolve, reassessing the appropriateness of late fees ensures that they remain aligned with the organization’s financial objectives and industry standards.
Compliance and Ethical Practices: Uphold compliance with legal regulations and ethical invoicing practices. Educate staff members involved in the invoicing process about the legal framework governing late fees to prevent inadvertent violations and maintain the business’s integrity.
By incorporating these best practices into their late fee implementation strategies, businesses can strike a harmonious balance between promoting timely payments and nurturing positive client relationships. In the subsequent section, we will summarize the key insights and considerations pertaining to late fees, providing a comprehensive overview of their significance in the realm of finance and business operations.
Conclusion
Late fees play a pivotal role in incentivizing timely payments, mitigating the impact of delayed invoicing, and fostering healthy financial practices in the realm of business transactions. By understanding the importance of late fees and implementing them judiciously, businesses can navigate the complexities of invoicing while maintaining positive client relationships.
When determining the standard amount of late fees, businesses must consider various factors, including the invoice amount, industry standards, client relationships, impact on cash flow, and regulatory compliance. Striking a balance between incentivizing prompt payments and demonstrating understanding toward clients’ circumstances is essential for cultivating a fair and effective late fee structure.
Legal considerations surrounding late fees necessitate thorough awareness of local and national regulations, transparent communication of late fee policies, and adherence to consumer protection laws. By integrating legal compliance into their invoicing practices, businesses can mitigate the risk of disputes and uphold ethical standards in fee management.
Implementing best practices, such as clear communication, flexibility, automated reminders, professional courtesy, and regular review of fee structures, empowers businesses to optimize their late fee strategies while preserving professionalism and client goodwill. Striving for compliance and ethical invoicing practices further reinforces the integrity and trustworthiness of the business.
In conclusion, late fees serve as a multifaceted tool in the invoicing landscape, promoting financial responsibility, sustaining cash flow stability, and nurturing collaborative client-business relationships. By embracing a holistic approach to late fee implementation, businesses can navigate the complexities of invoicing with confidence, ensuring that the impact of delayed payments is mitigated while fostering a culture of financial diligence and mutual respect.