Home>Finance>Why Are Interest Rates On Long-Term Loans Higher Than Interest Rates On Short-Term Loans?

Finance
Why Are Interest Rates On Long-Term Loans Higher Than Interest Rates On Short-Term Loans?
Published: November 2, 2023
Discover why interest rates on long-term loans are higher than interest rates on short-term loans and gain insights into the dynamics of finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of interest rates on long-term loans
- Overview of interest rates on short-term loans
- Factors influencing interest rates on long-term loans
- Factors influencing interest rates on short-term loans
- Comparison of interest rates on long-term and short-term loans
- Reasons for higher interest rates on long-term loans
- Conclusion
Introduction
In the world of finance, loans play a crucial role in providing individuals and businesses with the necessary capital to achieve their goals. When considering a loan, one important factor to consider is the interest rate – the percentage of the loan amount that is charged as the cost of borrowing. It is common knowledge that interest rates on long-term loans are often higher than those on short-term loans. But why is this the case? In this article, we will delve into the reasons behind this disparity.
Understanding why interest rates on long-term loans are higher can help borrowers make informed decisions about their financing options and better manage their financial obligations. It is also essential for lenders to assess the risk associated with long-term loans and set interest rates accordingly.
In the following sections, we will provide an overview of interest rates on long-term and short-term loans, explore the factors that influence these rates, compare the two types of loans, and ultimately unveil the reasons for the higher interest rates on long-term loans.
Overview of interest rates on long-term loans
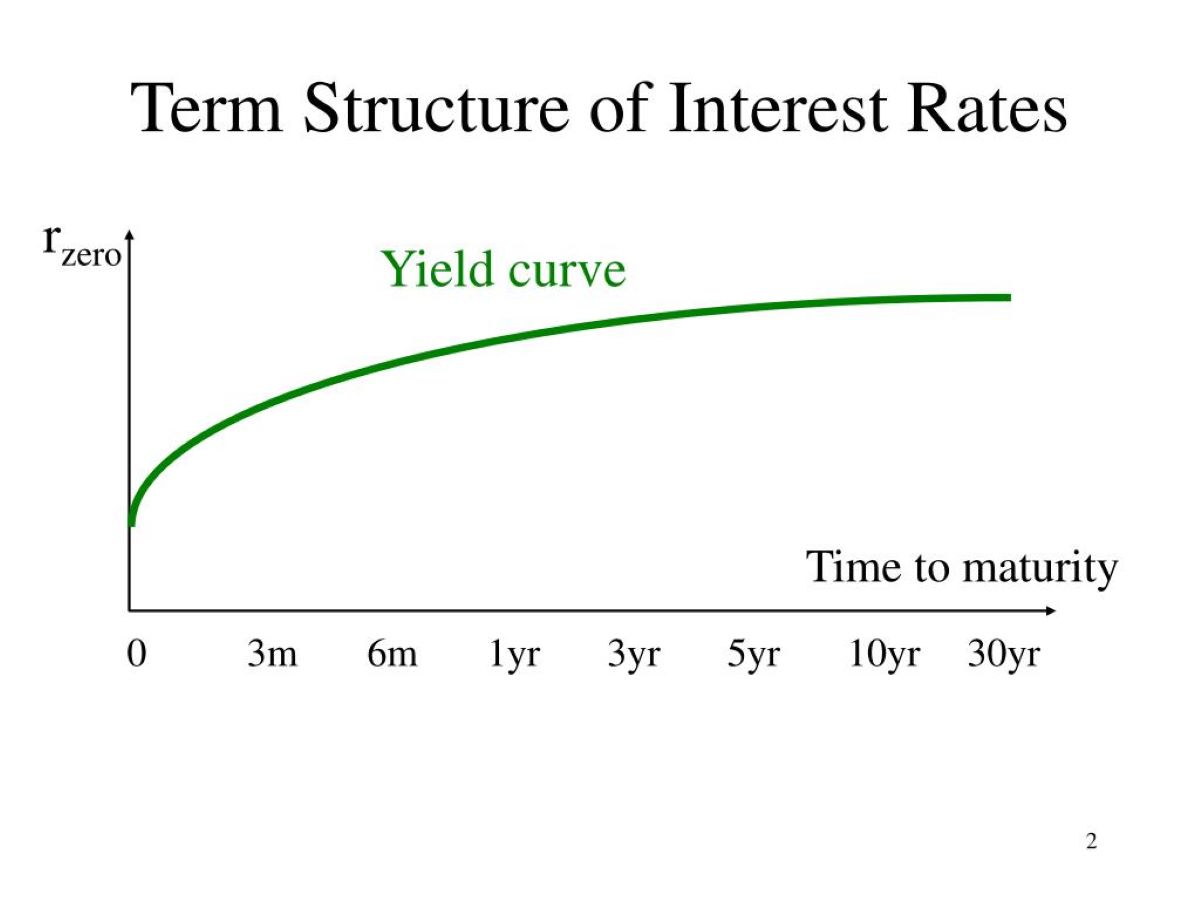
Long-term loans refer to borrowing arrangements that have a repayment term of more than one year. These loans are typically used for significant investments, such as purchasing a home, funding a business expansion, or financing a large project. Due to the extended repayment period, interest rates on long-term loans tend to be higher than those on short-term loans.
Long-term loans often involve larger loan amounts, which means that lenders are exposed to a higher level of risk. To compensate for this risk, lenders charge higher interest rates. Additionally, the longer repayment term allows borrowers to spread out their repayment over a more extended period, increasing the risk of default or economic uncertainties impacting the loan repayment. Higher interest rates help lenders mitigate this risk.
Furthermore, interest rates on long-term loans are influenced by the overall economic environment and market conditions. When the economy is thriving, and interest rates are low, borrowers may receive more favorable rates on long-term loans. Conversely, during periods of economic uncertainty or high-interest rates, lenders may increase the interest rates on long-term loans to protect themselves from potential defaults or fluctuations in the market.
Another factor that affects interest rates on long-term loans is the borrower’s creditworthiness. Lenders consider a borrower’s credit history, income stability, debt-to-income ratio, and other financial factors when determining the interest rate. Borrowers with a strong credit profile are more likely to secure lower interest rates on long-term loans, while those with a lower credit score may face higher rates due to the perceived risk.
It is important to note that interest rates on long-term loans can vary significantly depending on the lender, the borrower’s financial situation, and the purpose of the loan. Shopping around and comparing offers from different lenders can help borrowers secure the most competitive interest rates on long-term loans.
Overview of interest rates on short-term loans
Short-term loans, as the name suggests, are borrowing arrangements with a repayment term typically ranging from a few weeks to one year. These loans are often used to cover immediate financial needs, such as managing cash flow, paying bills, or handling unexpected expenses. The interest rates on short-term loans are generally lower compared to long-term loans. Here’s an overview of the factors that influence short-term loan interest rates.
One key driver of interest rates on short-term loans is the perceived level of risk. Since short-term loans have a shorter repayment period, lenders view them as less risky compared to long-term loans. The shorter repayment duration greatly reduces the chance of default or unexpected changes in the borrower’s financial situation. As a result, lenders offer lower interest rates to attract borrowers and make short-term loans more appealing.
Market conditions and economic factors also play a significant role in determining interest rates on short-term loans. When interest rates set by central banks are low, it creates a favorable environment for lenders to offer short-term loans at lower rates. Additionally, demand and competition in the lending market can influence interest rates. During times of high demand for short-term loans, lenders may increase interest rates to capitalize on the opportunity.
Borrower creditworthiness is another vital factor affecting the interest rates on short-term loans. Lenders assess the borrower’s credit history, income stability, and other financial factors to determine the level of risk involved. Borrowers with a strong credit profile and a history of timely repayments are likely to secure lower interest rates. On the other hand, borrowers with a lower credit score or a higher level of risk may face higher interest rates on short-term loans, reflecting the perceived likelihood of default.
It’s worth mentioning that certain types of short-term loans, such as payday loans or cash advances, may have higher interest rates compared to traditional short-term loans. These loans are often associated with higher risk due to their quick turnaround and limited qualification criteria. Therefore, borrowers should carefully consider the terms and interest rates associated with such loans before proceeding.
In summary, short-term loans typically carry lower interest rates compared to long-term loans. The shorter repayment period and perceived lower risk make short-term loans an attractive option for borrowers seeking immediate financing. However, it is essential to evaluate the total cost of borrowing, including interest rates and any associated fees, to make informed decisions and ensure affordability.
Factors influencing interest rates on long-term loans
Interest rates on long-term loans are influenced by various factors that lenders take into consideration when determining the cost of borrowing. Understanding these factors can offer valuable insights into why interest rates on long-term loans are higher. Here are some key factors:
1. Economic conditions: The overall state of the economy plays a significant role in determining interest rates on long-term loans. During times of economic growth and stability, interest rates tend to be lower as lenders have more confidence in borrowers’ ability to repay the loans. Conversely, during periods of economic uncertainty or recession, lenders may increase interest rates to account for the higher risk of default.
2. Inflation: Inflation can impact interest rates on long-term loans. When inflation is high, lenders will often charge higher interest rates to compensate for the loss of purchasing power over time. This is known as the inflation premium, which helps to protect the lender’s return on investment.
3. Risk assessment: Lenders assess the risk associated with long-term loans before determining the interest rate. Factors such as the borrower’s credit history, income stability, debt-to-income ratio, and collateral offered all play a role in assessing the risk. Higher perceived risk may result in higher interest rates to compensate for the potential default or non-payment of the loan.
4. Loan term: The length of the loan term itself can impact interest rates. Longer-term loans carry higher interest rates since the lender’s money is tied up for a more extended period. This exposes the lender to a higher level of risk, and they may require higher compensation in the form of interest payments.
5. Market conditions: The general market conditions, including supply and demand dynamics and interest rates set by central banks, can also influence interest rates on long-term loans. If lenders anticipate a higher demand for long-term loans, they may increase interest rates to manage their risk or to take advantage of the market opportunity.
6. Lender policies and costs: Each lender has its own policies and costs associated with providing long-term loans. These can include administrative costs, operational expenses, and profit margins. These factors are taken into account when determining the interest rates on long-term loans.
By considering these factors, borrowers can better understand why interest rates on long-term loans may be higher. It is important to shop around and compare loan offers from different lenders to find the most competitive rates based on individual financial circumstances and needs.
Factors influencing interest rates on short-term loans
Interest rates on short-term loans are influenced by several factors that lenders take into consideration when determining the cost of borrowing. Understanding these factors can provide valuable insights into why interest rates on short-term loans vary. Here are some key factors influencing interest rates on short-term loans:
1. Economic conditions: The state of the economy has a significant impact on interest rates for short-term loans. During periods of economic stability or growth, lenders may offer lower interest rates on short-term loans to attract borrowers. Conversely, during economic downturns or periods of uncertainty, lenders may increase interest rates to mitigate the higher risk associated with lending.
2. Risk assessment: Lenders assess the risk of default when determining the interest rates on short-term loans. Factors such as the borrower’s credit history, income stability, and debt-to-income ratio are considered. Borrowers with a higher risk of default are likely to be charged higher interest rates to compensate for the increased risk undertaken by the lender.
3. Market conditions: The demand and supply dynamics of the lending market can influence interest rates on short-term loans. If the demand for short-term loans is high, lenders may increase interest rates to capitalize on the opportunity and balance the risk. Conversely, if the demand is low, lenders may lower interest rates to attract borrowers.
4. Central bank policies: The policies and interventions of central banks can impact interest rates on short-term loans. Central banks regulate the monetary supply and set benchmark interest rates. Changes in these rates can indirectly affect the interest rates offered by lenders on short-term loans.
5. Loan amount and duration: Short-term loans typically involve smaller loan amounts and shorter repayment periods. Lenders may offer lower interest rates for shorter loan durations due to the reduced risk of default and the faster recovery of the principal. However, the interest rate may vary depending on the specific terms of the loan.
6. Lender costs and profitability: Lenders incur operational costs, administrative expenses, and bear the opportunity cost of lending. These costs and the desired profit margin factor into the interest rates charged on short-term loans. Lenders need to ensure that the interest rates cover their costs and generate a reasonable return on their investment.
By considering these factors, borrowers can better understand the reasons for the variation in interest rates on short-term loans. It is essential to compare loan offers from different lenders to find the most competitive rates based on individual financial needs and circumstances.
Comparison of interest rates on long-term and short-term loans
When comparing interest rates on long-term and short-term loans, it is important to consider the differences in loan duration, risk factors, and market dynamics. Here are some key points to consider when comparing the interest rates on these two types of loans:
Loan Duration: One of the most significant differences between long-term and short-term loans is the duration of repayment. Long-term loans have a repayment period exceeding one year, while short-term loans typically have a repayment period of a few weeks to one year. Due to the extended repayment period, long-term loans often have higher interest rates compared to short-term loans.
Risk Factors: Long-term loans generally carry higher risk compared to short-term loans. The longer repayment period increases the likelihood of economic uncertainties, changes in the borrower’s financial situation, or other unforeseen events that may impact the repayment. Higher interest rates on long-term loans help lenders mitigate this risk. Short-term loans, on the other hand, have a shorter repayment period, reducing the risk of default. Consequently, the interest rates on short-term loans are typically lower.
Market Dynamics: The market conditions and demand for different loan types can influence interest rates. Long-term loans often involve larger loan amounts and are used for significant investments, such as buying a home or financing a business. Lenders may charge higher interest rates to compensate for the larger loan size and higher risk. Short-term loans, on the other hand, cater to immediate financial needs and are often in high demand. Lenders may offer lower interest rates on short-term loans to attract borrowers.
Economic Factors: Interest rates on both long-term and short-term loans are influenced by the overall economic environment. During times of economic growth and stability, interest rates tend to be lower as lenders have more confidence in borrowers’ ability to repay the loan. Conversely, during economic downturns or periods of uncertainty, lenders may increase interest rates on both long-term and short-term loans to manage the higher risk associated with lending.
It is important for borrowers to carefully consider their financial needs and circumstances when deciding between long-term and short-term loans. While short-term loans may offer lower interest rates, they may not be suitable for larger, long-term financial commitments. Conversely, long-term loans may have higher interest rates, but they provide the necessary capital to fund significant investments. Ultimately, borrowers should analyze their repayment capabilities, evaluate the loan terms, and seek professional advice if needed to make an informed decision.
Reasons for higher interest rates on long-term loans
Long-term loans often come with higher interest rates compared to short-term loans. Several factors contribute to this disparity, and understanding these reasons can help borrowers make informed decisions. Here are some key reasons for the higher interest rates on long-term loans:
1. Increased Risk: The longer repayment period of long-term loans exposes lenders to a higher level of risk compared to short-term loans. Economic conditions and borrowers’ financial circumstances can change significantly over an extended period, increasing the risk of default or non-payment. To compensate for this greater risk, lenders charge higher interest rates on long-term loans.
2. Inflationary Expectations: Lenders consider the impact of inflation when setting interest rates on long-term loans. Over time, inflation erodes the purchasing power of money. To protect against this loss, lenders incorporate an inflation premium into long-term loan interest rates. This premium helps maintain the lender’s expected return on investment over the loan term.
3. Opportunity Cost: Lenders have alternative uses for their funds, such as investing in other assets or extending short-term loans. By tying up their capital in long-term loans, lenders forgo these other opportunities for a more extended period. To compensate for this opportunity cost, lenders charge higher interest rates on long-term loans.
4. Market Volatility: Over a long period, market conditions can become more volatile and unpredictable. Lenders need to factor in this uncertainty when determining interest rates on long-term loans. Increased market volatility can pose risks to the lender’s profitability and repayment, leading to higher interest rates to mitigate these risks.
5. Administrative and Operational Costs: Long-term loans often involve more complex administrative and operational processes compared to short-term loans. Lenders incur additional costs in managing and tracking these loans over an extended period. These costs, including loan origination fees, underwriting expenses, and administrative overheads, contribute to the higher interest rates on long-term loans.
6. Additional Features and Flexibility: Long-term loans may offer additional features and flexibility, such as the ability to prepay or refinance the loan. These features come at a cost to the lender, as they can impact their revenue and interest income. To account for these added benefits, lenders may charge higher interest rates on long-term loans compared to their short-term counterparts.
It’s important to note that while interest rates on long-term loans may be higher, they may still be a suitable financing option for borrowers who require substantial funds for significant investments or projects. Borrowers should weigh the benefits of the loan against the cost of borrowing and carefully assess their financial situation before committing to a long-term loan.
Conclusion
In summary, the disparity in interest rates between long-term and short-term loans can be attributed to various factors. Long-term loans generally carry higher interest rates due to the increased risk associated with the longer repayment period, inflationary expectations, and the opportunity cost for lenders. Market conditions, borrower creditworthiness, and lender costs also play a role in determining interest rates.
On the other hand, short-term loans typically come with lower interest rates due to their shorter repayment period, lower risk of default, and market dynamics. Economic conditions, borrower risk assessment, and lender profitability also influence interest rates on short-term loans.
It’s crucial for borrowers to carefully consider their financial needs, repayment capabilities, and the associated costs when deciding between long-term and short-term loans. While long-term loans may have higher interest rates, they provide access to larger amounts of capital for significant investments. Short-term loans, with their lower interest rates, are more suitable for immediate financial needs and smaller loan amounts.
By comparing loan offers from different lenders, evaluating the terms and conditions, and understanding the reasons for the disparity in interest rates, borrowers can make informed decisions about the most suitable loan option for their specific financial circumstances.
In conclusion, whether opting for a long-term or short-term loan, borrowers should carefully assess their financial goals, budget, and ability to repay the loan to ensure they make a well-informed choice that aligns with their long-term financial well-being.