Home>Finance>Why Short-Term Credit Default Swaps Have Higher Premiums


Finance
Why Short-Term Credit Default Swaps Have Higher Premiums
Published: March 4, 2024
Learn why short-term credit default swaps command higher premiums in the finance sector. Understand the factors driving these rates and their impact on the market.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Introduction
Welcome to the intricate world of credit default swaps (CDS), where financial instruments play a pivotal role in managing credit risk. Within this domain, short-term credit default swaps stand out due to their higher premiums, which can perplex even seasoned investors. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of short-term credit default swaps, unraveling the factors contributing to their elevated premiums and shedding light on their significance within the financial landscape.
Understanding the dynamics of short-term credit default swaps is essential for investors, financial analysts, and anyone seeking insights into the intricate workings of the financial markets. By comprehending the factors influencing the premiums associated with short-term CDS, individuals can make informed decisions and navigate the complex terrain of credit risk management more effectively.
Join us on this enlightening journey as we explore the intricacies of short-term credit default swaps, unravel the underlying factors driving their higher premiums, and gain a deeper understanding of their impact on the financial ecosystem.
Understanding Credit Default Swaps
Understanding Credit Default Swaps
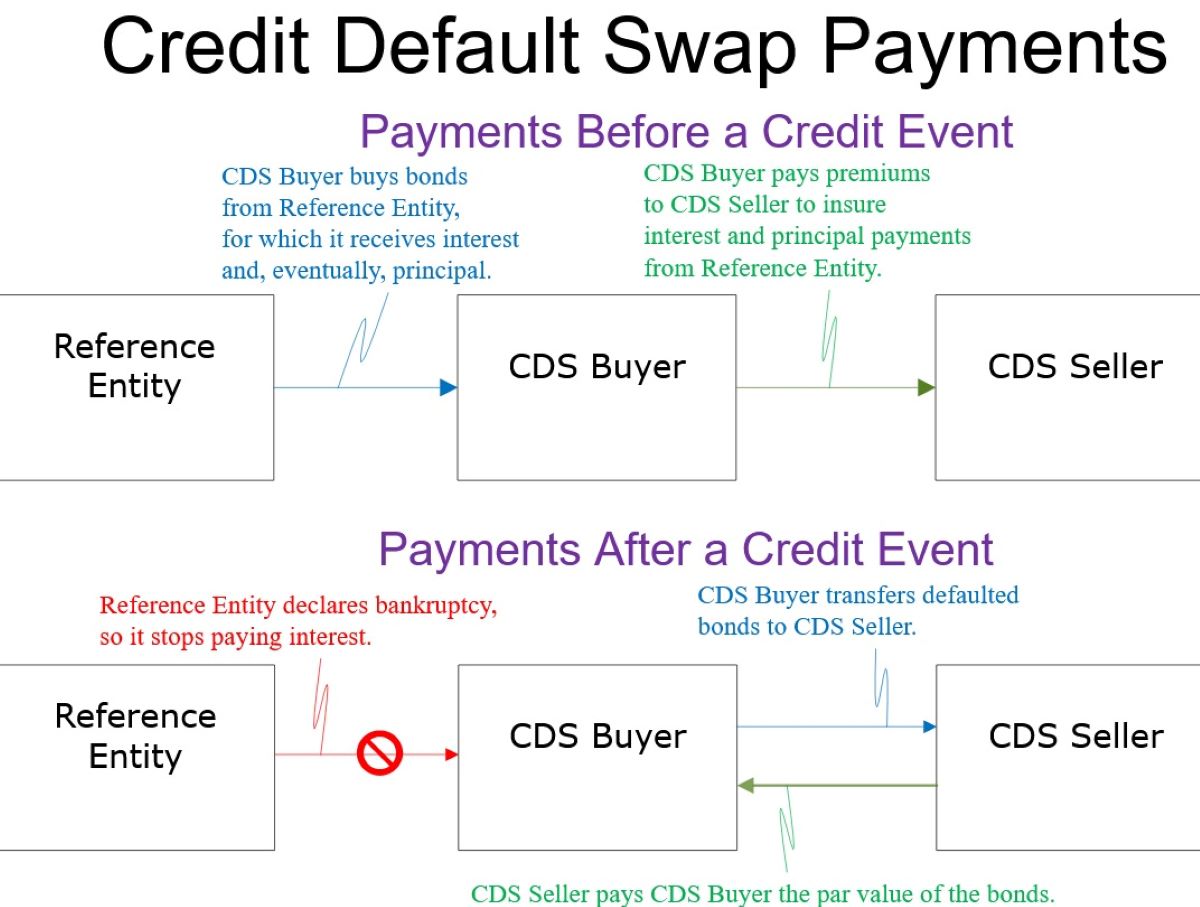
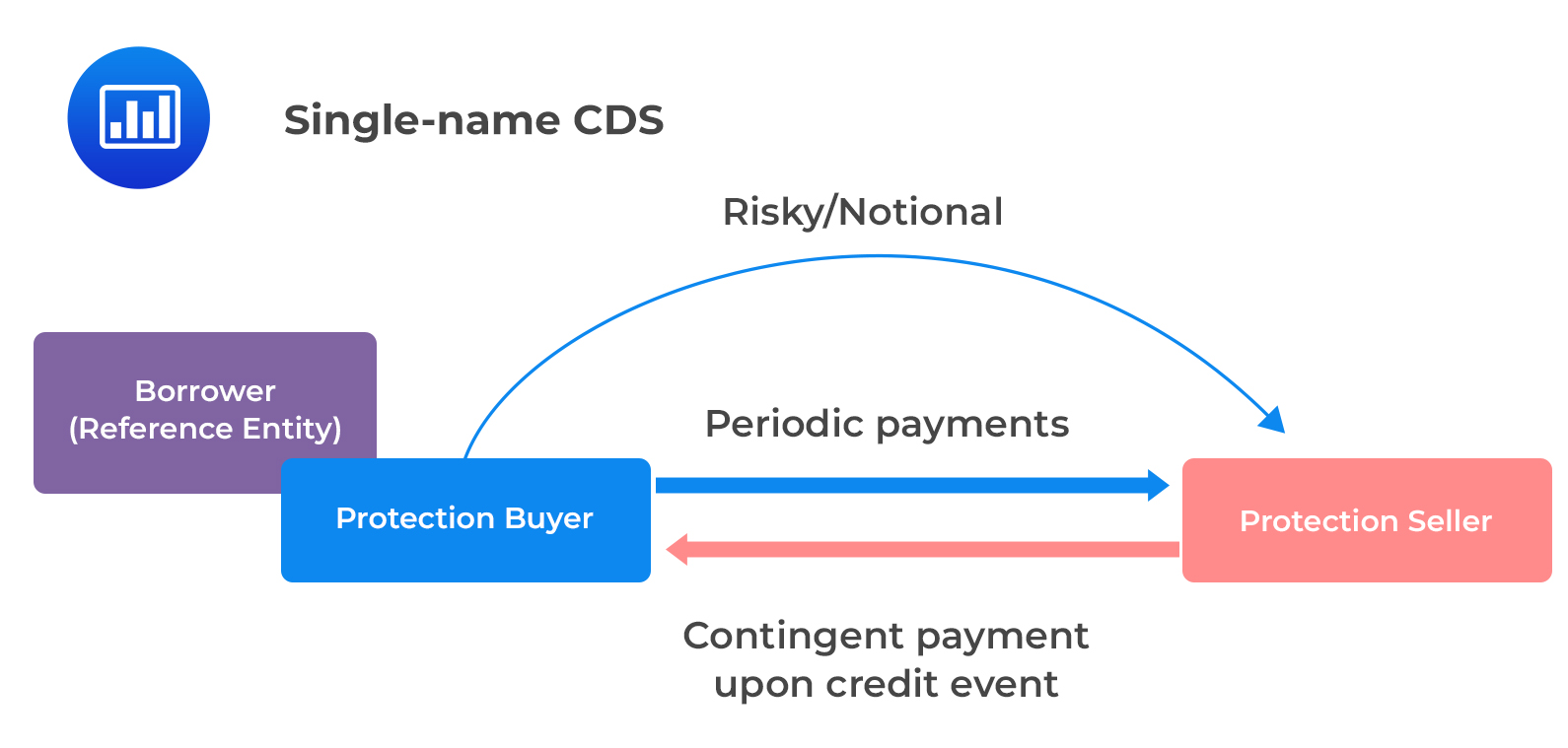
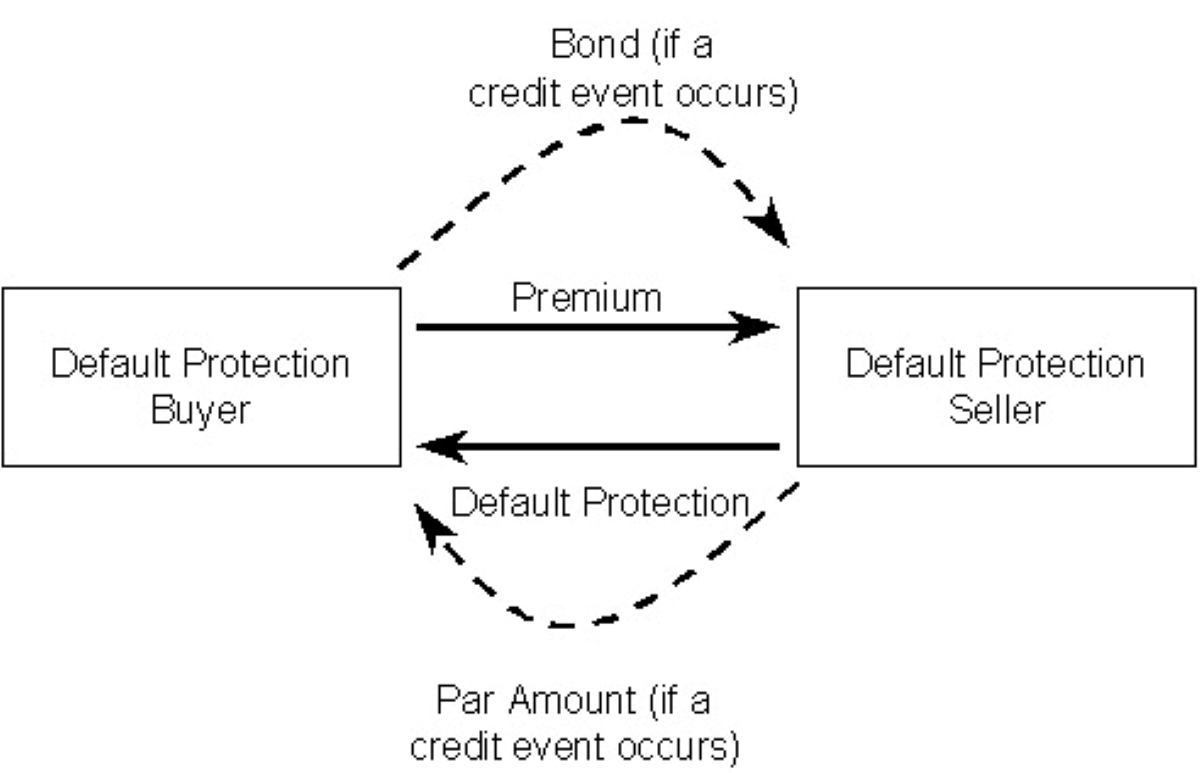
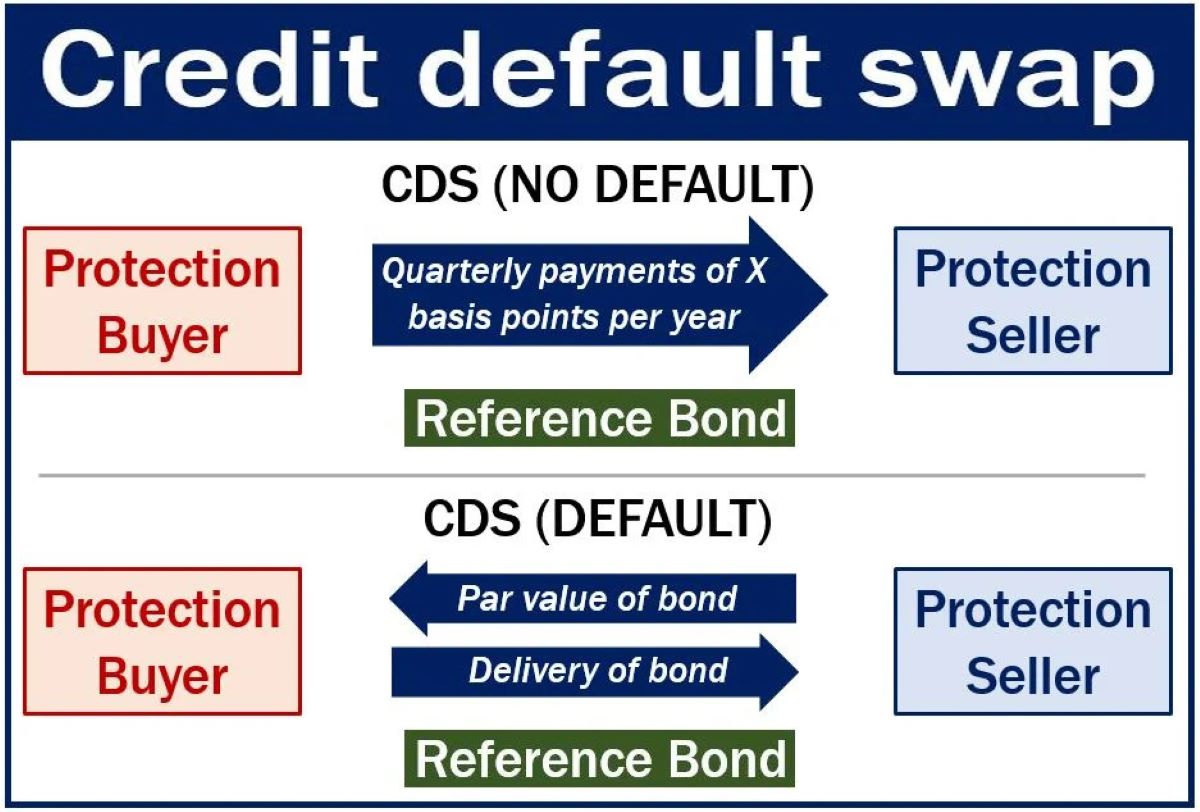
Credit default swaps (CDS) are financial derivatives that enable investors to hedge against the risk of default on debt instruments, such as bonds and loans. These instruments serve as a form of insurance, providing protection to the buyer in the event of a credit event, such as a borrower failing to meet their debt obligations.
When an investor purchases a credit default swap, they are essentially securing a contract that offers compensation in the event of a credit default. In return for this protection, the buyer of the CDS pays a periodic fee, often referred to as the premium, to the seller of the swap. If a credit event occurs, the seller is obligated to compensate the buyer for the loss incurred due to the default.
It’s important to note that credit default swaps can be either standardized or customized. Standardized CDS are typically linked to widely traded debt instruments and adhere to predetermined terms and conditions. On the other hand, customized CDS are tailored to specific debt obligations, offering greater flexibility but requiring negotiation of terms between the parties involved.
These financial instruments play a crucial role in the management of credit risk, allowing investors to mitigate potential losses resulting from defaults. By understanding the mechanics of credit default swaps, market participants can effectively navigate the complexities of credit risk management and make informed decisions regarding their investment strategies.
Factors Affecting Short-Term Credit Default Swaps
Factors Affecting Short-Term Credit Default Swaps
Several key factors influence the premiums associated with short-term credit default swaps, reflecting the unique characteristics of these financial instruments. Understanding these factors is essential for investors and market participants seeking to comprehend the dynamics of short-term CDS and their impact on credit risk management.
-
Duration of Coverage: The duration of the protection offered by a short-term credit default swap significantly impacts its premium. Shorter durations often command higher premiums, as they provide coverage against credit events over a limited timeframe. This reflects the heightened risk associated with shorter-term obligations and the potential for rapid changes in creditworthiness.
-
Market Volatility: Fluctuations in market conditions and increased volatility can lead to higher premiums for short-term credit default swaps. Elevated uncertainty and rapid shifts in credit risk perceptions can prompt sellers to demand higher compensation for providing protection, driving up the cost of these derivatives.
-
Creditworthiness of the Reference Entity: The credit quality of the entity referenced in the CDS contract plays a pivotal role in determining the premium. Weaker creditworthiness and heightened default risk of the underlying entity can result in higher premiums for short-term CDS, reflecting the increased likelihood of a credit event occurring within a shorter timeframe.
-
Market Sentiment and Perception: The overall market sentiment and perception of credit risk can significantly impact the premiums of short-term credit default swaps. Negative market sentiment and heightened concerns regarding creditworthiness can drive up the cost of protection, as investors seek to safeguard against potential defaults in the short term.
-
Liquidity and Demand: The liquidity of the CDS market and the demand for short-term protection also influence premiums. Limited liquidity and heightened demand for short-term CDS can exert upward pressure on premiums, reflecting the supply-demand dynamics within the market.
By considering these factors, investors can gain valuable insights into the determinants of short-term credit default swap premiums, enabling them to assess the cost of mitigating credit risk over shorter timeframes and make informed decisions regarding risk management strategies.
Higher Premiums for Short-Term Credit Default Swaps
Higher Premiums for Short-Term Credit Default Swaps
Short-term credit default swaps often command higher premiums compared to their longer-term counterparts, reflecting distinct market dynamics and risk considerations. Several factors contribute to the elevated premiums associated with short-term CDS, shedding light on the unique characteristics of these financial instruments.
-
Rapid Changes in Creditworthiness: Short-term credit default swaps offer protection against credit events over a limited timeframe, exposing investors to the rapid changes in creditworthiness that can occur within a short duration. The heightened uncertainty and potential for swift shifts in risk perceptions contribute to the higher premiums demanded for short-term CDS, reflecting the dynamic nature of credit risk over shorter horizons.
-
Increased Default Risk: The compressed timeline of short-term credit default swaps amplifies the impact of default risk, leading to higher premiums. With a shorter window of protection, the likelihood of a credit event occurring within the specified timeframe is inherently higher, prompting sellers to demand increased compensation for assuming this concentrated risk.
-
Market Volatility and Uncertainty: Short-term CDS are susceptible to heightened market volatility and uncertainty, which can drive up their premiums. The rapid fluctuations in credit risk perceptions and market conditions within shorter timeframes contribute to the elevated cost of short-term protection, as sellers factor in the amplified risk exposure associated with these derivatives.
-
Flexibility and Liquidity Considerations: The flexibility and liquidity offered by short-term credit default swaps also contribute to their higher premiums. Investors seeking short-term protection may be willing to pay a premium for the flexibility to adjust their risk management strategies more frequently, while the relatively limited liquidity of short-term CDS can exert upward pressure on their premiums.
By comprehending the factors driving the higher premiums for short-term credit default swaps, market participants can gain a deeper understanding of the cost associated with mitigating credit risk over shorter durations. This insight enables investors to make informed decisions regarding the selection of CDS contracts that align with their risk management objectives and market outlook.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Short-term credit default swaps, characterized by their higher premiums, offer valuable insights into the nuanced realm of credit risk management and financial derivatives. As we conclude our exploration of these instruments, it becomes evident that the elevated premiums for short-term CDS stem from a confluence of factors, including the compressed timeline of protection, increased default risk, market volatility, and liquidity considerations.
Understanding the dynamics of short-term credit default swaps is essential for investors and financial professionals, enabling them to navigate the complexities of credit risk management and make informed decisions regarding risk mitigation strategies. By comprehending the factors influencing the premiums of short-term CDS, market participants can effectively assess the cost of safeguarding against credit events over shorter timeframes and tailor their risk management approaches accordingly.
Furthermore, the unique characteristics of short-term credit default swaps underscore the dynamic nature of credit risk within the financial markets, highlighting the importance of adaptability and proactive risk management. Investors and analysts can leverage this understanding to refine their risk management frameworks and align their investment strategies with prevailing market conditions and credit risk dynamics.
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the significance of short-term credit default swaps and their higher premiums serves as a testament to the intricate interplay of risk, time horizons, and market dynamics. By embracing a comprehensive understanding of these instruments, market participants can navigate the ever-changing terrain of credit risk with confidence, leveraging the insights gleaned from the complexities of short-term CDS to bolster their risk management capabilities and make informed investment decisions.
In essence, the higher premiums associated with short-term credit default swaps encapsulate the multifaceted nature of credit risk and the evolving dynamics of the financial markets, offering a compelling lens through which to examine the interwoven complexities of risk, time, and market sentiment.