Home>Finance>Hoarding: Definition, How It Works With Commodities, And Examples


Finance
Hoarding: Definition, How It Works With Commodities, And Examples
Published: December 5, 2023
Get a comprehensive understanding of hoarding in finance - its definition, how it operates with commodities, and real-life examples included.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Welcome to the Finance Category: Hoarding
Welcome to the Finance category of our blog! In this post, we will dive into the fascinating world of hoarding, exploring its definition, how it works with commodities, and providing examples to illustrate this phenomenon. So, let’s get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Hoarding refers to the excessive accumulation and retention of items, often driven by a fear of scarcity or a desire for control.
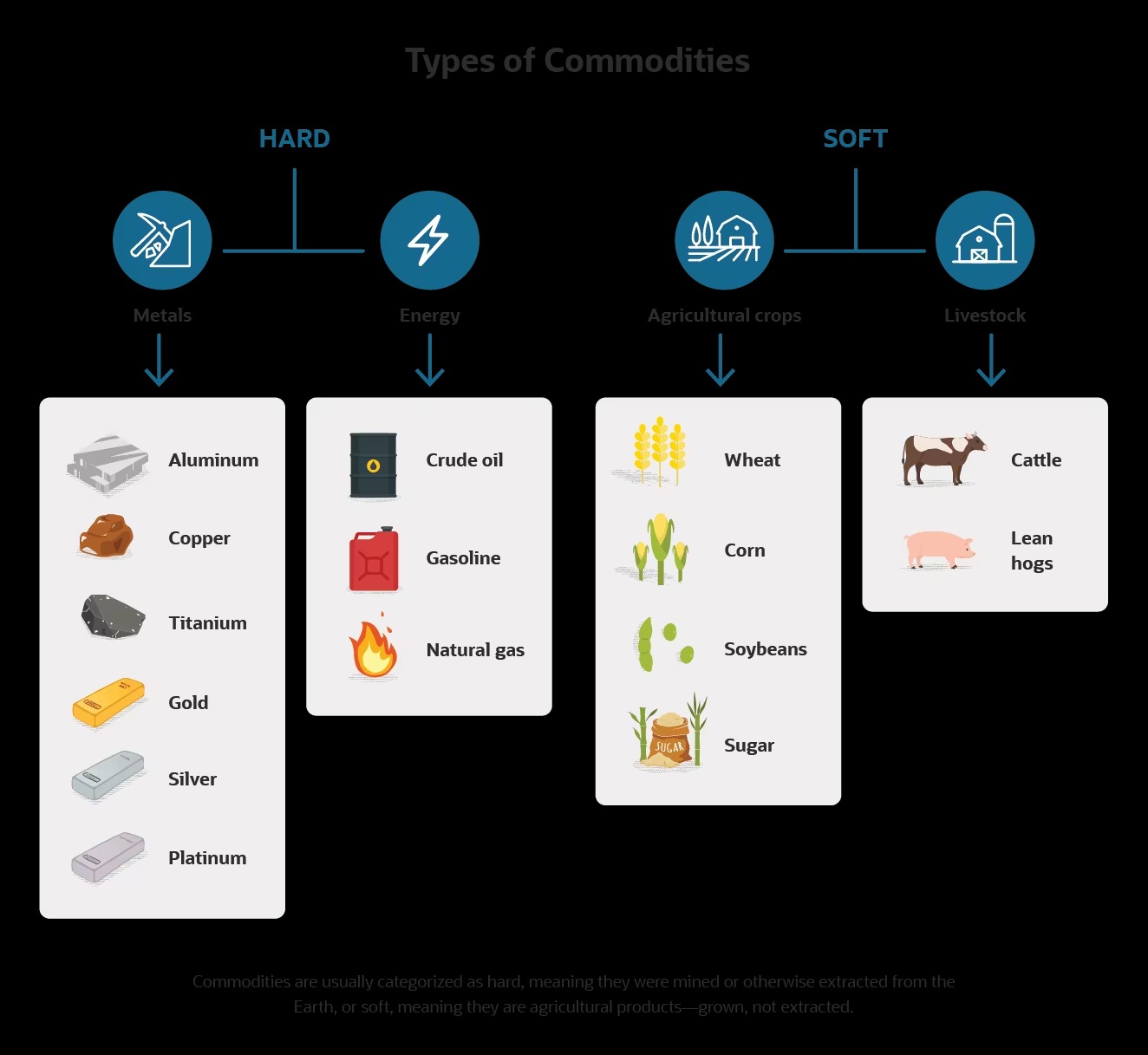
- Commodities such as precious metals, food products, and currencies are commonly hoarded due to their perceived value and potential for future scarcity.
What is Hoarding?
Hoarding, in the context of finance, refers to the behavior of compulsive accumulation and retention of items, often beyond what may be considered useful or necessary. It is driven by various psychological factors, such as a fear of scarcity, a need for control, or an emotional attachment to possessions.
While hoarding is often associated with collecting belongings in one’s home, it can also be observed in the financial realm. In this case, individuals or organizations hoard commodities, such as precious metals, food products, or currencies, with the intention of profiting from their potential future scarcity or value appreciation.
How Hoarding Works with Commodities
When it comes to commodities, hoarding occurs when individuals or entities buy and accumulate large quantities of a particular commodity, creating an artificial shortage in the market. The reduced supply can then drive up the price, enabling the hoarder to sell at a profit in the future.
Here’s how hoarding with commodities typically works:
- Identifying Potential Commodities: Hoarders analyze various commodities to determine their potential for scarcity or appreciation in value. This can be based on factors such as geopolitical events, economic trends, or supply and demand dynamics.
- Accumulating Large Quantities: Once a valuable commodity is identified, hoarders start accumulating large quantities of it over time. This often involves strategic purchasing and storing in secure locations.
- Creating Artificial Scarcity: The hoarded commodity’s limited supply in the market can create an artificial scarcity. This drives up demand, leading to higher prices.
- Selling for Profit: When the hoarder deems the time is right, they sell their accumulated commodity at a higher price, capitalizing on the scarcity they helped create.
Examples of Hoarding
Hoarding in the financial world can take numerous forms. Here are a few examples:
- Precious Metals: Some individuals hoard gold, silver, or other precious metals as a hedge against inflation or economic instability, expecting their value to rise over time.
- Food Products: In times of uncertainty, individuals or institutions may hoard food products, anticipating scarcity or price fluctuations due to potential disruptions in the supply chain.
- Currencies: Hoarding currencies can occur when there are expectations of currency devaluation or instability, motivating individuals or governments to stockpile foreign currencies.
These examples showcase how hoarding can impact various sectors of the financial market, influencing supply, demand, and prices.
Conclusion
Hoarding, in both its physical and financial forms, is a complex phenomenon driven by various psychological and economic factors. Understanding the motivations and implications behind hoarding can provide valuable insights into the workings of financial markets and individual behavior.
We hope you found this exploration of hoarding in the finance world informative. Stay tuned to our Finance category for more engaging and educational content.