Finance
What Does POS Mean In Banking
Published: October 11, 2023
Discover the meaning of POS in banking and how it relates to finance. Expand your financial knowledge with our comprehensive guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to the world of banking, there are many terms and acronyms that can often be confusing to the average consumer. One such acronym that you may have come across is POS. But what exactly does POS mean in banking? In this article, we will explore the definition of POS and its significance in the banking industry.
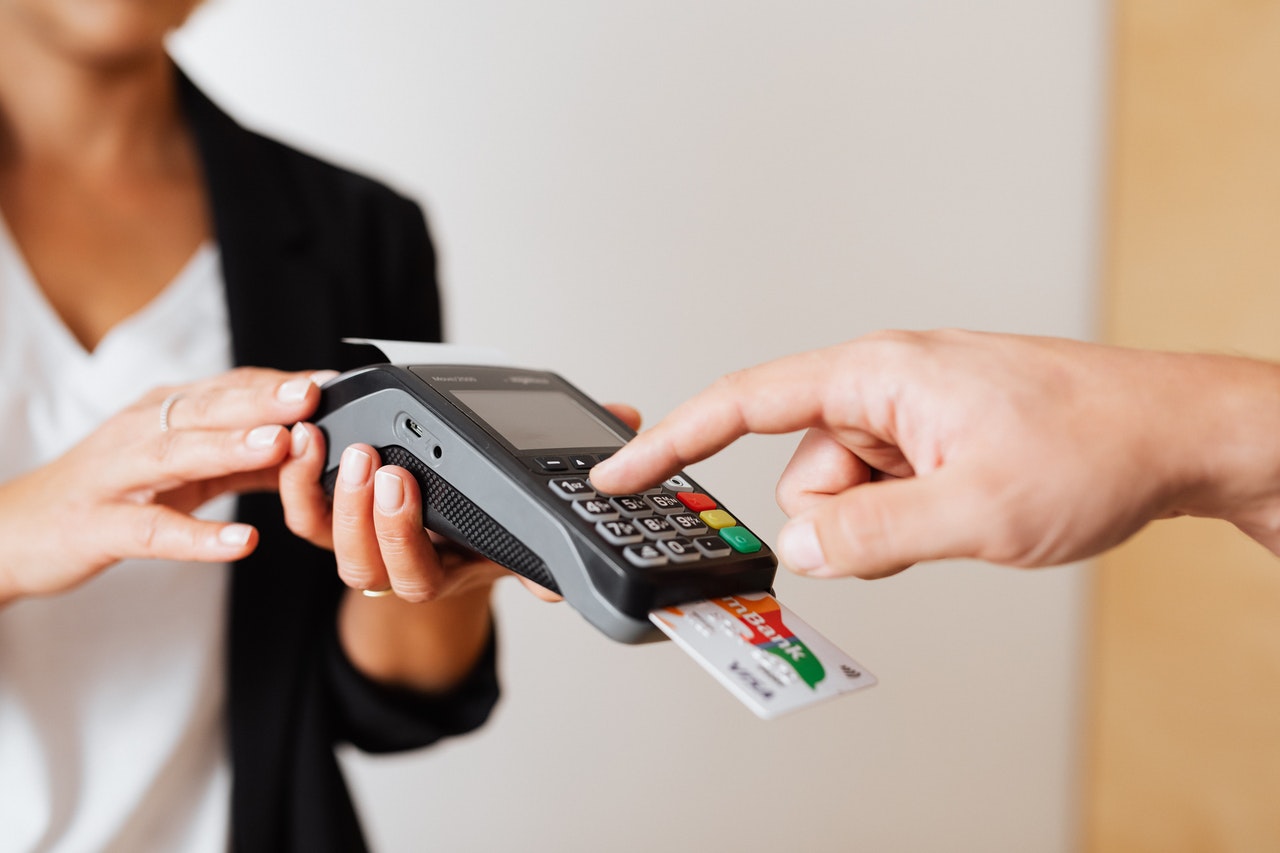
POS stands for Point of Sale, and it refers to the location where a transaction takes place. In the context of banking, POS refers to the use of electronic payment systems to facilitate transactions between a merchant and a consumer. In other words, it is the mechanism through which consumers can make purchases using their debit or credit cards.
The introduction of POS systems in banking has revolutionized the way customers make payments. Instead of relying solely on cash or checks, individuals can now conveniently pay for their purchases using their card, which is swiped or inserted into a card reader at the point of sale.
POS systems have not only simplified the payment process but have also provided various benefits to both consumers and merchants. For consumers, it offers convenience, security, and flexibility, while merchants benefit from faster transactions, reduced cash handling, and improved record-keeping.
It is important to note that POS systems are not limited to physical brick-and-mortar stores. With the advent of e-commerce, online businesses also make use of POS systems to process payments securely and efficiently.
In the next sections, we will delve deeper into the significance of POS in banking, the types of POS transactions, the benefits it offers, the challenges it poses, and the security measures in place to safeguard these transactions.
Definition of POS
POS, which stands for Point of Sale, is a term used to describe the location or moment where a financial transaction occurs between a customer and a merchant. In the context of banking, POS refers to the electronic payment systems used by businesses to accept payments from customers using credit or debit cards.
A POS system typically consists of hardware and software components. The hardware includes a card reader or terminal where the customer’s card is swiped or inserted, a display screen for the merchant to input transaction details, and a receipt printer to provide the customer with a record of the transaction. The software component manages the payment processing, authorization, and record-keeping aspects of the transaction.
While POS systems are commonly associated with physical retail stores, they have evolved to encompass various forms of transactions. Online businesses utilize virtual POS systems, also known as payment gateways, to securely process payments for goods and services over the internet.
With the rapid advancement of technology, POS systems have become more sophisticated and versatile. They now offer integration with inventory management systems, customer relationship management tools, and analytics software, providing businesses with valuable insights into their sales performance and customer behavior.
Furthermore, POS systems have extended beyond traditional card-based payments. They now support alternative payment methods like digital wallets, mobile payments, and even cryptocurrencies. This diversification ensures that businesses can cater to the evolving preferences of their customers, enhancing their overall shopping experience.
In summary, a POS system is a critical component of the banking industry, enabling businesses to accept electronic payments from customers at the point of sale. These systems have transformed the way transactions are conducted, making payments more convenient, secure, and efficient for both consumers and merchants.
POS in Banking
In the banking industry, POS systems play a vital role in facilitating transactions between customers and merchants. These systems enable customers to make payments using their debit or credit cards, providing a seamless and secure payment experience.
POS systems have become an integral part of banking operations, both in physical retail stores and online businesses. They offer an efficient alternative to traditional payment methods such as cash or checks, providing convenience for customers and reducing the risk of carrying large amounts of cash.
For physical retail stores, POS systems allow merchants to process transactions quickly and accurately. Customers simply present their cards, which are then swiped or inserted into the card reader. The system securely authorizes the transaction and deducts the funds from the customer’s account, providing immediate payment to the merchant.
Online businesses, on the other hand, rely on virtual POS systems or payment gateways. These systems securely transmit customers’ card information over the internet, encrypting it to protect against unauthorized access. The payment gateway verifies the transaction and initiates the transfer of funds from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account.
POS systems in banking offer benefits for both customers and merchants. Customers enjoy the convenience of making payments using their preferred payment method, without the hassle of carrying cash or writing checks. They also benefit from the security features of POS systems, such as encryption and fraud detection, which help protect their sensitive card information.
Merchants, on the other hand, benefit from faster and more efficient transactions, reducing wait times for customers and increasing overall productivity. POS systems also automate the tracking and recording of sales, simplifying the process of managing inventory and generating financial reports. This improves operational efficiency and enables merchants to make data-driven decisions to optimize their business.
Overall, POS systems have revolutionized banking by streamlining payment processes and enhancing the customer experience. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further advancements in POS systems, such as contactless payments, mobile wallets, and seamless integration with other banking services.
Types of POS Transactions
POS transactions encompass a variety of payment methods that customers can utilize at the point of sale. Let’s explore some of the most common types of POS transactions:
- Card Present Transactions: This type of POS transaction occurs when a customer physically presents their debit or credit card to the merchant at the point of sale. The card is swiped or inserted into the card reader, and the transaction is processed electronically.
- Card Not Present Transactions: In these transactions, the customer provides their card details to the merchant without physically presenting the card. This can happen in various scenarios, such as online purchases, telephone orders, or mail-order transactions. The merchant enters the customer’s card information manually into the POS system to complete the transaction.
- Contactless Payments: Contactless payments have gained popularity in recent years, allowing customers to make payments by simply tapping their cards or mobile devices against a contactless-enabled card reader. This method utilizes Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, enabling quick and secure transactions.
- Mobile Wallet Payments: With the rise of smartphones and mobile payment applications, customers can now make payments directly from their mobile devices using digital wallets. These wallets store card information securely and allow users to make payments by scanning a QR code or tapping their phones against a contactless reader.
- EMV Chip Card Transactions: EMV (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) chip cards have become the standard for card-based transactions. Instead of swiping the card, customers insert their chip cards into the card reader. The chip on the card generates a unique code for each transaction, providing enhanced security compared to the magnetic stripe on traditional cards.
- Gift Card Transactions: Gift cards have become increasingly popular as a convenient and versatile gift option. Customers can use POS systems to process transactions involving gift cards, allowing recipients to redeem their cards for goods or services at the point of sale.
These are just a few examples of the different types of POS transactions available in modern banking. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative payment methods in the future, further enhancing the convenience and security of transactions at the point of sale.
Benefits of POS in Banking
The integration of POS systems in the banking industry has brought about a wide range of benefits for both customers and financial institutions. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
- Convenience: POS systems offer customers a seamless and convenient payment experience. With the ability to pay using debit or credit cards, customers no longer need to carry large sums of cash or write checks. It eliminates the need for exact change and simplifies the payment process, making transactions quick and hassle-free.
- Speed and Efficiency: POS systems expedite the payment process, reducing checkout times for customers. Transactions can be authorized and processed within seconds, allowing merchants to serve more customers in less time. This speed and efficiency contribute to a smoother shopping experience, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Accurate Recording and Reporting: POS systems automate the tracking and recording of sales, eliminating the need for manual entry. This enhances accuracy and reduces the risk of human error. It also simplifies the generation of financial reports, providing businesses with valuable insights into their sales performance and customer behavior.
- Improved Cash Flow: For businesses, POS systems offer the advantage of faster access to funds. Instead of waiting for checks to clear or handling cash deposits, funds from POS transactions can be deposited directly into the merchant’s account, improving cash flow and enabling quicker business operations.
- Enhanced Security: POS systems prioritize the security of transactions. They incorporate encryption technology and fraud detection measures, protecting customer data and reducing the risk of unauthorized access or fraudulent activities. By utilizing secure payment gateways, online businesses can provide customers with peace of mind when making card-not-present transactions.
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: The convenience and speed offered by POS systems contribute to improved customer satisfaction. Customers appreciate the ease of payment and the range of payment options available. This positive experience can lead to increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
- Integration and Business Insights: POS systems can be integrated with other business systems such as inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), and accounting software. This integration enables businesses to streamline their operations, manage inventory more efficiently, and gather valuable data on customer preferences and buying patterns.
Overall, the implementation of POS systems in banking has revolutionized the payment process, benefiting both customers and financial institutions. The convenience, speed, accuracy, enhanced security, and integration capabilities of POS systems contribute to a more efficient and satisfying banking experience.
Challenges of POS in Banking
While POS systems bring numerous benefits to the banking industry, they also come with their fair share of challenges. Let’s explore some of the key challenges that arise with the implementation of POS systems:
- High Initial Investment: Implementing a POS system can require a significant upfront investment for businesses. The cost includes not only the hardware and software components but also the training of staff and ongoing maintenance and support costs.
- Technical Issues and Downtime: Like any technology, POS systems can experience technical glitches or downtime, which can disrupt operations and lead to frustration for both customers and merchants. It is crucial for businesses to have robust technical support and backup systems in place to minimize the impact of these issues.
- Data Security Risks: Protecting customer data is of utmost importance in banking. POS systems store sensitive customer information, such as card details, and are vulnerable to security breaches. Financial institutions must implement robust security measures, such as encryption, secure networks, and regular security audits, to reduce the risk of data breaches and comply with relevant regulations.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating POS systems with existing systems and software can be complex and time-consuming. Businesses may face challenges in seamlessly integrating inventory management, CRM, and accounting systems, which can affect the accuracy of data and lead to inconsistencies in reporting.
- Training and Familiarity: Proper training is essential for both merchants and customers to effectively use POS systems. Staff must be familiar with the system’s features and functionalities to ensure smooth transactions. Some customers might also struggle with adapting to new payment methods or technology, requiring education and support to navigate the process.
- Transaction Fees: Businesses must pay transaction fees for each POS transaction. These fees can vary depending on the payment processor and the volume of transactions. For smaller businesses, the accumulation of these fees can impact profitability.
- Regulatory Compliance: The banking industry is heavily regulated, and businesses must ensure their POS systems comply with relevant laws and regulations. This includes consumer protection laws, data privacy regulations, and payment card industry standards. Non-compliance can result in penalties and reputational damage.
Despite these challenges, it is essential for businesses to adapt and leverage POS systems’ benefits to stay competitive in the evolving banking landscape. By addressing these challenges proactively, financial institutions can mitigate risks and optimize the use of POS systems to enhance customer experiences.
Security Measures for POS in Banking
Ensuring the security of POS systems in the banking industry is crucial to protect sensitive customer information and maintain the integrity of financial transactions. Here are some key security measures implemented to safeguard POS in banking:
- Encryption: Encryption is a fundamental security measure that protects the transmission and storage of sensitive data. POS systems utilize encryption protocols to encrypt cardholder data during transmission from the card reader to the payment processor. This prevents unauthorized parties from intercepting and accessing the data.
- Tokenization: Tokenization is the process of replacing sensitive card information with a unique identifier called a token. When a customer’s card is used in a POS transaction, the POS system generates a token that substitutes the card details. This reduces the risk of exposing actual card information in the event of a data breach.
- Secure Networks: POS systems should be connected to secure networks to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Utilizing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and securing Wi-Fi networks are crucial to protect against malicious attacks that exploit vulnerabilities.
- Regular Updates and Patching: Keeping POS software and firmware up to date is vital for security. Regular updates and patching address vulnerabilities discovered in the software, ensuring that the system remains robust against emerging threats.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implementing two-factor authentication adds an additional layer of security to POS systems. This requires users to provide two different authentication factors, such as a password and a unique code sent to their mobile device, to access the system. It reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Fraud Detection and Monitoring: POS systems incorporate advanced algorithms and machine learning capabilities to detect suspicious activities and identify potential fraud in real-time. Anomalies in transaction patterns, such as unusually large purchases or multiple transactions from different locations, can trigger alerts for further investigation.
- PCI Compliance: Compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is crucial for businesses that handle cardholder data. It outlines best practices for securing POS systems, including network security, access controls, regular testing, and security policy implementation.
- Employee Training: Educating employees on best security practices is essential to maintain the security of POS systems. Training should cover topics such as recognizing phishing attempts, secure password management, and proper handling of customer data, minimizing the risk of internal security breaches.
By implementing these security measures, financial institutions can protect customer data, maintain the integrity of transactions, and build trust with customers. It is an ongoing process that requires constant monitoring, regular security audits, and staying updated with emerging threats to ensure the effectiveness of security measures.
Conclusion
POS systems have revolutionized the banking industry by providing a seamless and secure method for customers to make payments using debit or credit cards. These systems offer a range of benefits, including convenience, speed, accuracy, improved cash flow, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
POS transactions have evolved beyond physical retail stores, with virtual POS systems enabling online businesses to process payments securely. The types of POS transactions have expanded to include contactless payments, mobile wallet payments, EMV chip card transactions, and gift card transactions.
While the implementation of POS systems brings many advantages, it also presents challenges. Initial investment costs, technical issues, data security risks, integration complexities, and training requirements are some of the challenges that businesses and financial institutions must address.
To mitigate these challenges, security measures such as encryption, tokenization, secure networks, regular updates, two-factor authentication, fraud detection, and PCI compliance are implemented. Employee training on security protocols is also crucial to maintaining the integrity of POS systems.
In conclusion, POS systems play a vital role in the banking industry, streamlining payment processes, improving efficiency, and enhancing customer experiences. As technology advances, we can expect continued innovation in POS systems, further enhancing security, expanding payment options, and providing valuable insights for businesses. Implementing and maintaining robust POS systems will remain a priority for financial institutions to provide a secure and seamless payment experience for their customers.