Finance
How To Perform A Credit Check On A Tenant
Modified: January 10, 2024
Learn how to perform a credit check on a tenant and make informed financial decisions. Discover the best practices and tools for effective tenant screening in the finance industry.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Reasons for Performing a Credit Check on a Tenant
- The Importance of a Credit Check in Tenant Screening
- Legal Considerations for Conducting a Credit Check
- Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Credit Check on a Tenant
- Gathering Tenant Information for a Credit Check
- Understanding Credit Reports and Scores
- Evaluating Credit History and Financial Responsibility
- Assessing Potential Risks and Red Flags
- Additional Screening Methods to Consider
- Conclusion
Introduction
Performing a credit check on a tenant is a crucial step in the rental application process. Whether you are a landlord or a property management company, conducting a credit check allows you to evaluate the financial stability and reliability of potential tenants. It provides valuable insights into their payment history, debt obligations, and overall creditworthiness.
As a landlord, it is in your best interest to lease your property to tenants who are financially responsible and capable of fulfilling their rent obligations. A credit check helps you assess the level of risk involved in renting to a particular individual, minimizing the chances of late or missed payments and potential disputes down the line.
In this article, we will delve into the reasons why conducting a credit check is essential, the legal considerations surrounding the process, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to perform a credit check on a tenant. We will also discuss the key factors to look for in a credit report, highlighting potential red flags and additional screening methods to consider.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to effectively navigate the credit check process and make informed decisions when it comes to choosing tenants for your rental property.
Reasons for Performing a Credit Check on a Tenant
Performing a credit check on a tenant is crucial for several reasons. Let’s explore the key reasons why it is important to gather and analyze a potential tenant’s credit information:
- Evaluate Financial Responsibility: A credit check provides valuable insight into an individual’s financial behavior and responsibility. It allows you to assess how well the applicant manages their finances, including their ability to make timely payments and keep their debt levels under control.
- Determine Creditworthiness: By analyzing a tenant’s credit report, you can gauge their creditworthiness. A good credit score indicates that the tenant has a history of responsible credit management, making them more likely to fulfill their financial obligations, including rent payments.
- Reduce Financial Risks: Renting a property involves financial risks, such as potential loss of rental income due to late or unpaid rent. A credit check allows you to assess the tenant’s likelihood of meeting their financial obligations, reducing the risk of payment issues during the lease term.
- Protect Your Property: Conducting a credit check helps to safeguard your property. By screening potential tenants’ credit history, you can identify any prior eviction records, judgments, or other financial concerns that may put your property at risk.
- Legal Compliance: In some regions, conducting a credit check may be a legal requirement when screening tenants. Ensuring that you comply with relevant laws and regulations is essential to avoid legal complications in the future.
By evaluating a tenant’s financial responsibility, creditworthiness, and potential risks through a credit check, you can make more informed decisions when selecting tenants for your rental property. This helps protect your investment and promotes a positive and financially stable rental experience for both parties involved.
The Importance of a Credit Check in Tenant Screening
When it comes to tenant screening, conducting a credit check is of utmost importance. Here are some key reasons why a credit check is vital in the tenant selection process:
- Financial Reliability: A credit check allows you to gauge the financial reliability of a prospective tenant. By reviewing their credit report, you can determine if they have a history of making payments on time. This information helps you assess their ability to meet their rent obligations consistently.
- Risk Assessment: A credit check provides valuable insights into the financial risks associated with a potential tenant. It allows you to identify any outstanding debts, bankruptcies, or other negative marks on their credit report. This information helps you evaluate the level of risk involved in renting to that individual.
- Past Rental Performance: Conducting a credit check can unveil any eviction or rental-related issues in a prospective tenant’s history. This information helps you determine if the applicant has a track record of meeting their rental obligations, respecting property, and adhering to lease terms.
- Financial Stability: A credit check provides a snapshot of an individual’s financial stability. By examining their credit history, you can assess their overall financial well-being, including their ability to manage debts and maintain a healthy credit score. Financially stable tenants are more likely to prioritize rent payments and uphold their lease agreements.
- Protection against Rental Income Loss: By conducting a credit check, you minimize the risk of rental income loss due to late or unpaid rent. A thorough credit analysis helps you identify potential tenants who may struggle to meet their financial commitments, allowing you to make informed decisions regarding lease agreements.
- Legal Compliance: In many jurisdictions, conducting a credit check is a legal requirement for tenant screening. It is important to adhere to local laws and regulations to ensure that you are acting in accordance with fair housing and tenant screening laws.
A credit check provides valuable information that helps you minimize financial risks, select financially responsible tenants, and ensure a smooth and successful rental experience. By utilizing this essential tool in your tenant screening process, you can make informed decisions and protect your property and investment.
Legal Considerations for Conducting a Credit Check
Before conducting a credit check on a tenant, it is crucial to understand and comply with the legal requirements surrounding the process. Here are some important considerations when it comes to the legal aspects of conducting a credit check:
- Fair Housing Laws: It is essential to ensure that your tenant screening practices comply with fair housing laws. These laws protect individuals from discrimination based on factors like race, color, religion, sex, national origin, familial status, and disability. Make sure that you treat all applicants equally and avoid any discriminatory practices during the screening process.
- Consent and Authorization: Before performing a credit check, you must obtain the tenant’s consent and authorization. This typically involves having the applicant sign a separate document specifically granting you permission to access their credit information. Make sure the consent form is clear, easy to understand, and complies with relevant privacy laws.
- Credit Reporting Agencies: When obtaining a credit report, it is important to work with reputable credit reporting agencies that comply with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA). Ensure that you understand the terms and conditions of using the agency’s services and that you have proper authorization to access credit reports for tenant screening purposes.
- Protection of Personal Information: Safeguarding the personal information of applicants is crucial. Ensure that you follow proper data protection and privacy protocols when handling sensitive applicant information. Implement and maintain appropriate security measures to prevent unauthorized access or breach of personal data.
- Adverse Action Procedures: If you decide to reject an applicant based on their credit report, follow the adverse action procedures outlined in the FCRA. This includes providing the applicant with a written notice that includes the name, address, and contact information of the credit reporting agency. The notice should also inform the applicant of their right to obtain a free copy of their credit report and dispute any inaccurate information.
- State and Local Laws: It is crucial to familiarize yourself with state and local laws regarding tenant screening and credit checks. Some jurisdictions may have additional requirements or restrictions on the use of credit reports and other screening practices. Stay informed about the laws in your specific area to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
By being aware of and adhering to the legal considerations surrounding credit checks, you can protect yourself from potential legal issues and ensure a fair and transparent tenant screening process.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Credit Check on a Tenant
Performing a credit check on a tenant involves several steps to ensure a thorough evaluation of their financial history. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
- Obtain Consent: Before initiating a credit check, obtain written consent from the tenant. Provide them with a consent form that outlines the purpose and scope of the credit check and seek their authorization to access their credit information.
- Select a Credit Reporting Agency: Choose a reputable credit reporting agency that complies with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and provides accurate and reliable credit reports. Research and compare different agencies to find the one that best meets your needs.
- Collect Tenant Information: Gather necessary information from the tenant, such as their full name, date of birth, social security number, current address, and previous address(es) if applicable. Ensure that all information provided is accurate and complete.
- Submit Information to the Credit Reporting Agency: Provide the tenant’s information to the credit reporting agency you have selected. This typically involves filling out an online application or submitting the required documents through a secure system or designated channel.
- Review the Credit Report: Once you receive the credit report from the agency, carefully review it to assess the tenant’s credit history, payment patterns, outstanding debts, and any negative marks or red flags. Pay close attention to their credit score and any indications of financial instability.
- Consider Additional Factors: While the credit report is essential, it should not be the sole determining factor in your decision-making process. Consider other factors, such as employment history, income, references, and rental history, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the tenant’s overall financial stability and reliability.
- Make an Informed Decision: Based on the credit report and other information gathered, evaluate the tenant’s creditworthiness and financial responsibility. Assess the level of risk involved in renting to the applicant and determine whether they meet your criteria for a suitable tenant.
- Notify the Tenant: Once you have made a decision, notify the tenant of your decision in a timely manner. If you decide not to rent to them based on their credit report, follow the adverse action procedures by providing them with a written notice and informing them of their rights to obtain a copy of their credit report and dispute any incorrect information.
Remember to comply with all legal requirements and maintain confidentiality and privacy throughout the credit check process. By following this step-by-step guide, you can effectively perform a credit check on a tenant and make well-informed decisions that minimize financial risks and ensure a positive rental experience.
Gathering Tenant Information for a Credit Check
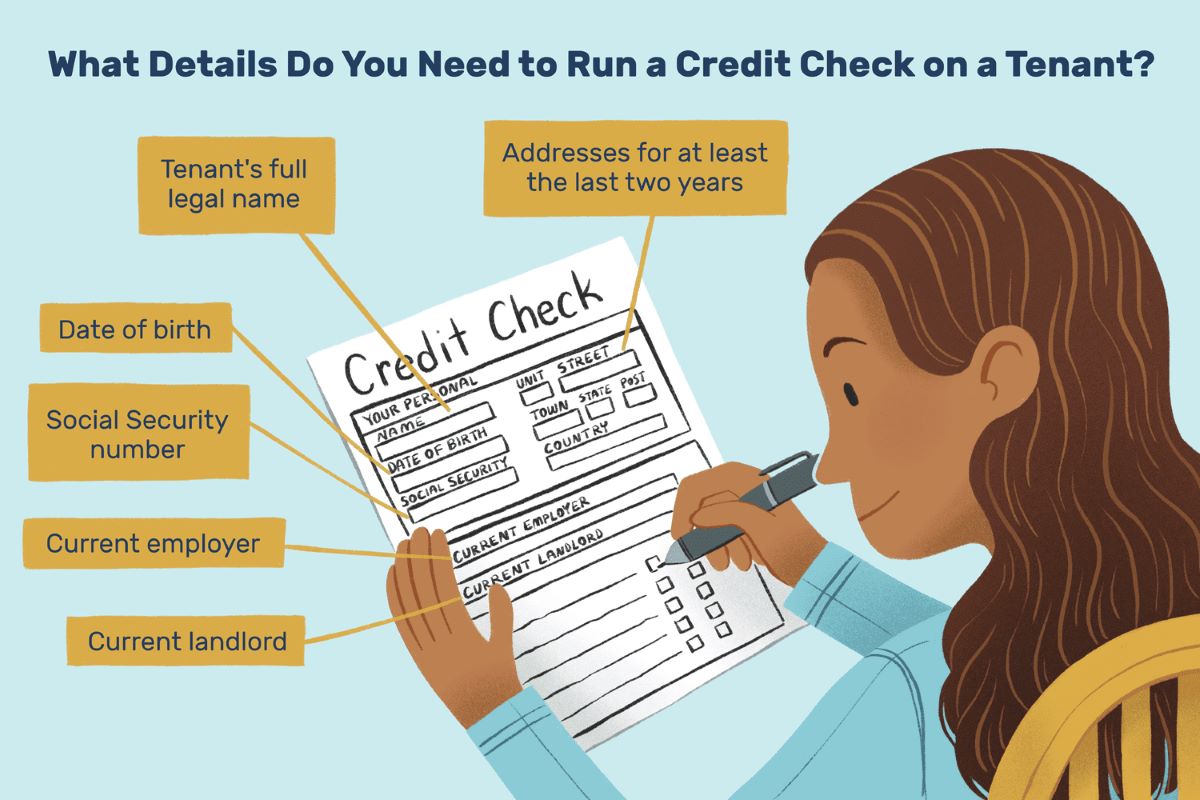
Gathering accurate and comprehensive tenant information is a crucial step in conducting a credit check. Here are the key pieces of information you should collect from the tenant:
- Full Name: Obtain the tenant’s full legal name, including any middle names or initials. This ensures that you have the correct identification details for the credit check.
- Date of Birth: Request the tenant’s date of birth to confirm their age and verify their identity. This information is necessary for accurate identification and reporting purposes.
- Social Security Number (SSN): Ask the tenant for their Social Security Number. The SSN is crucial for accessing credit reports, as it serves as a unique identifier for individuals in the United States.
- Current Address: Collect the tenant’s current residential address, including the street name, city, state, and ZIP code. This information helps verify their current living situation and ensures accurate reporting.
- Previous Addresses: Inquire about the tenant’s previous addresses for the past few years, typically between two to five years. Obtaining this information allows you to gather a more comprehensive view of their rental history and credit patterns.
- Employment Details: Request information about the tenant’s current employment, including the employer’s name, job title, and contact information. This helps validate their income and employment stability, which can be an important factor in assessing their creditworthiness.
- Income Verification: Ask the tenant to provide proof of income, such as recent pay stubs, employment contracts, or tax returns. Verifying their income helps determine if they have the financial means to meet their rent obligations.
- References: Request references from the tenant, such as previous landlords or professional contacts. Contacting these references can provide valuable insights into the tenant’s rental history, behavior, and financial reliability.
When gathering tenant information, it is essential to handle it with care and ensure the privacy and security of sensitive data. Inform the tenant about how their information will be used, stored, and protected, in compliance with applicable data protection and privacy laws.
By collecting comprehensive tenant information, you can conduct a thorough credit check that provides a more accurate assessment of their financial history, creditworthiness, and overall suitability as a tenant.
Understanding Credit Reports and Scores
When performing a credit check on a tenant, it is essential to understand the components of a credit report and how credit scores are determined. Here is a breakdown of what you need to know:
Credit Report: A credit report is a detailed record of an individual’s credit history. It includes information from various sources, such as credit card companies, banks, lenders, and collection agencies. The report typically includes:
- Personal Information: This section includes the tenant’s personal details, such as their name, address, date of birth, and social security number. Verify that this information matches what the tenant provided.
- Accounts: The accounts section lists the individual’s credit accounts, such as credit cards, loans, mortgages, and other lines of credit. It includes information on the account balance, payment history, credit limit, and account status.
- Payment History: This section displays the tenant’s payment history for each credit account. It shows whether payments were made on time, late, or if any payments were missed entirely.
- Credit Inquiries: The credit inquiries section lists inquiries made by potential lenders or creditors when the tenant applied for credit. It helps you determine if the tenant has recently applied for multiple lines of credit, which may indicate increased financial strain.
- Public Records: This section includes any public records related to the tenant’s credit, such as bankruptcies, tax liens, or court judgments. Public records may indicate financial instability and may be a cause for concern.
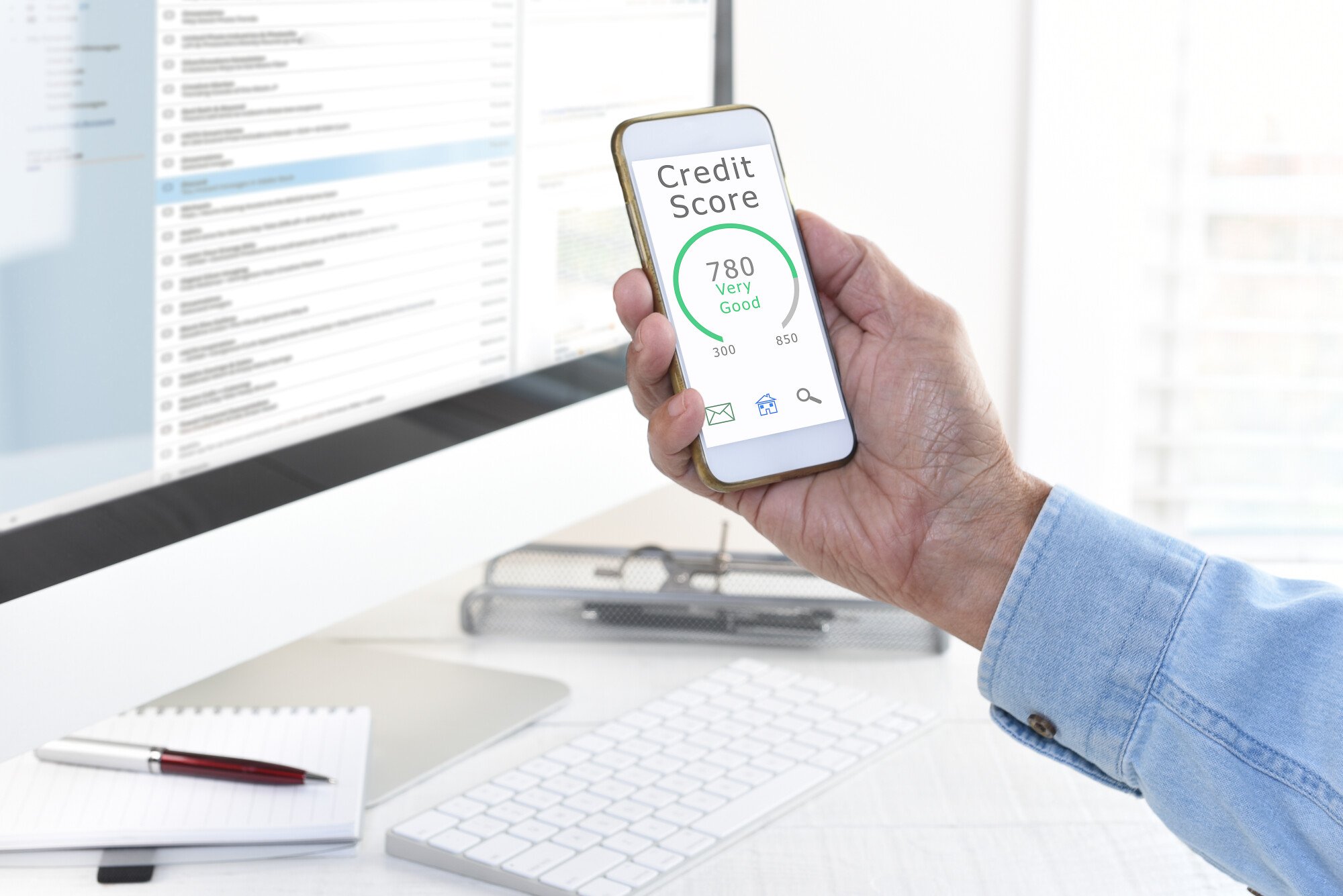
Credit Score: A credit score is a numerical representation of an individual’s creditworthiness. It is calculated based on the information in the credit report and helps lenders assess the likelihood of a borrower repaying their debts. Credit scores typically range from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating better creditworthiness. Factors that influence credit scores include:
- Payment History: The tenant’s history of making timely payments has a significant impact on their credit score. Consistent on-time payments positively influence the score, while late or missed payments can lower it.
- Amounts Owed: The amount of debt the tenant carries relative to their credit limits, known as credit utilization, affects the credit score. Higher credit utilization ratios may indicate financial strain and can negatively impact the score.
- Length of Credit History: The length of time the tenant has held credit accounts impacts their credit score. A longer credit history generally results in a higher score, as it provides more data for evaluating creditworthiness.
- Credit Mix: Lenders consider the types of credit accounts the tenant holds, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages. A diverse mix of credit types can positively influence the credit score.
- New Credit: Opening multiple new credit accounts within a short period can negatively impact the credit score. It may suggest a higher risk of financial instability or a need for additional credit.
Understanding credit reports and scores enables you to interpret the information accurately and evaluate a tenant’s creditworthiness effectively. This knowledge helps you make informed decisions during the tenant screening process.
Evaluating Credit History and Financial Responsibility
When performing a credit check on a tenant, it is essential to evaluate their credit history and financial responsibility. Here are key factors to consider in assessing a tenant’s creditworthiness:
- Payment History: Review the tenant’s payment history to determine if they have a consistent record of making on-time payments. Late or missed payments may indicate a pattern of financial irresponsibility and could pose a risk of late rent payments.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: Evaluate the tenant’s debt-to-income ratio, which compares their monthly debt payments to their monthly income. A high debt-to-income ratio may suggest that the tenant is stretched financially and could face challenges in meeting their rent obligations.
- Credit Utilization: Assess how much of their available credit the tenant is currently utilizing. High credit utilization, where they are close to maxing out their credit limits, may indicate a reliance on credit and potential financial strain.
- Derogatory Marks: Look for any derogatory marks on the tenant’s credit report, such as bankruptcies, foreclosures, or late payments. These marks may indicate financial instability and could raise concerns about their ability to meet rent obligations.
- Length of Credit History: Consider the length of the tenant’s credit history. A longer credit history provides more information about their financial behavior and can be indicative of their ability to manage credit responsibilities over an extended period.
- Credit Inquiries: Be mindful of the number of credit inquiries on the tenant’s credit report. Multiple recent inquiries may suggest that the tenant is actively seeking credit and could be an indicator of potential financial challenges.
- Public Records: Pay attention to any public records on the tenant’s credit report, such as bankruptcies or tax liens. These records may indicate financial difficulties and could impact their ability to meet rent obligations.
- Stability and Consistency: Look for indications of stability and consistency in the tenant’s credit history. A long history of steady employment and residence can demonstrate financial stability and reliable income sources.
- Patterns and Trends: Analyze patterns and trends within the tenant’s credit history. Are there recurring patterns of late payments or increasing debts? Identifying such patterns can provide valuable insights into their financial management habits.
While evaluating a tenant’s credit history and financial responsibility, it is important to consider these factors in context and weigh them against other information obtained during the tenant screening process, such as employment and rental history. This comprehensive evaluation enables you to make an informed decision about whether the tenant is likely to fulfill their rent obligations and be a responsible tenant.
Assessing Potential Risks and Red Flags
When conducting a credit check on a tenant, it is crucial to be vigilant in assessing potential risks and red flags that may indicate financial instability or pose concerns for the rental property. Here are some key areas to consider:
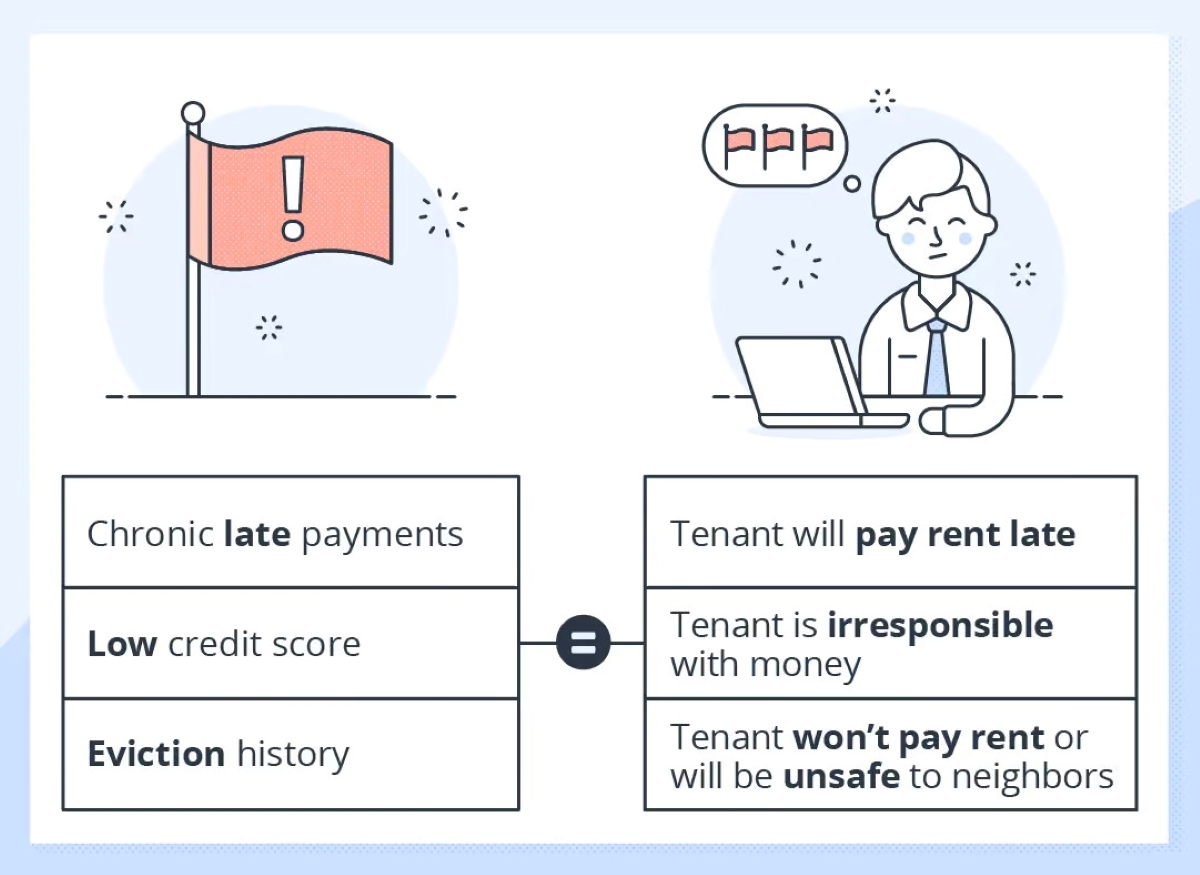
- Significant Debt: Take note of excessive debt levels that may strain the tenant’s ability to pay rent consistently. Excessive credit card balances, outstanding loans, or high monthly debt payments could indicate financial stress and increase the risk of late or missed rent payments.
- History of Late Payments: Look for patterns of late or missed payments in the tenant’s credit history. Frequent late payments may suggest a lack of financial discipline or an inability to manage obligations on time, potentially translating into late rent payments.
- Recent Financial Issues: Pay attention to recent financial challenges or significant negative events, such as bankruptcies, foreclosures, or judgments. These issues may indicate ongoing financial difficulties that could impact the tenant’s ability to meet financial obligations, including rent.
- Unstable Employment: Assess the stability of the tenant’s employment history. Frequent job changes or a track record of unemployment may raise concerns about consistent income and the tenant’s ability to afford rent payments over the long term.
- Poor Credit Score: Evaluate the tenant’s credit score as an overall measure of their creditworthiness. A low credit score may indicate a history of financial mismanagement, increasing the risk of potential payment issues and property damage.
- Eviction or Rental History Issues: Review the tenant’s rental history, including any prior evictions or rental-related problems. While a credit check may not show evictions directly, it can reveal any negative marks related to rental payments or judgments that could indicate a history of problematic tenancies.
- Inconsistent Information: Be cautious if you encounter inconsistencies in the information provided by the tenant. Inaccurate or misleading information can raise suspicions about their credibility, financial stability, or suitability as a tenant. Verify any discrepancies before making a decision.
- Excessive Credit Inquiries: Take note if the tenant has numerous recent credit inquiries on their report. Multiple inquiries could suggest they are actively seeking credit and potentially overextending themselves financially, posing a risk to timely rent payments.
- Failure to Provide Required Documents: If the tenant fails to provide necessary documentation, such as proof of income or references, it could indicate a lack of cooperation or potential issues they may be trying to conceal. Delays or evasiveness in providing requested information should be viewed with caution.
Assessing potential risks and red flags helps you make informed decisions regarding tenant suitability and minimizes the likelihood of facing rental payment issues or tenant-related problems. Always consider these factors in conjunction with other information gathered during the screening process to gain a comprehensive understanding of the tenant’s financial stability and responsibility.
Additional Screening Methods to Consider
While a credit check provides valuable insights into a tenant’s financial history, there are additional screening methods you can consider to gain a more comprehensive understanding of potential tenants. Here are some methods that can help you make informed decisions:
- Background Checks: Conducting a background check allows you to identify any criminal history or legal issues that may pose a risk to the property or other tenants. This may include searching for past convictions, verifying identity, and checking for sex offender records.
- Employment Verification: Contact the tenant’s employer to verify their employment status, income, and job stability. This can help you assess their ability to meet rent obligations and gauge their overall financial stability.
- Previous Landlord References: Reach out to previous landlords to inquire about the tenant’s rental history. This can provide valuable insight into their conduct as a tenant, including their ability to pay rent on time, maintain the property, and adhere to lease agreements.
- Income Verification: Request documentation to verify the tenant’s income such as pay stubs, tax returns, or employment contracts. Verifying their income helps determine if they have the financial means to afford the rental property.
- Reference Checks: In addition to contacting previous landlords, consider reaching out to personal references provided by the tenant. These references can offer insights into the tenant’s character, reliability, and ability to fulfill their obligations.
- Interviews: Conducting an interview with the tenant allows you to ask specific questions about their rental history, income, and other relevant information. This provides an opportunity to assess their communication skills, professionalism, and suitability as a tenant.
- Online Research and Social Media: Perform online research and search social media profiles to gather additional information about the tenant. This can provide insights into their lifestyle, behavior, and overall character. Use caution and ensure compliance with applicable privacy laws.
- Co-Signer or Guarantor: Consider requesting a co-signer or guarantor if you have concerns about a tenant’s financial history or creditworthiness. A co-signer or guarantor is legally responsible for meeting rent obligations in the event that the tenant fails to do so.
Remember to comply with all relevant laws and regulations when utilizing these additional screening methods. Each method provides an opportunity to gather different perspectives on the tenant, helping you evaluate their suitability and make well-informed decisions.
Conclusion
Performing a credit check on a tenant is a critical step in the rental application process. By evaluating a tenant’s credit history and financial responsibility, you can make informed decisions that minimize financial risks and ensure a positive rental experience.
Throughout this article, we have explored the reasons for conducting a credit check, the importance of credit checks in tenant screening, and the legal considerations surrounding the process. We also provided a step-by-step guide to performing a credit check on a tenant, emphasizing the significance of gathering comprehensive tenant information and understanding credit reports and scores.
We discussed evaluating credit history and financial responsibility, assessing potential risks and red flags, and highlighted additional screening methods to consider. By integrating these various screening methods, including background checks, reference checks, and employment verification, you can gain a comprehensive view of the tenant’s suitability.
Remember to always comply with fair housing laws, obtain proper consent and authorization, and handle tenant information with confidentiality and security. It is also crucial to stay updated on local laws and regulations regarding tenant screening to ensure compliance.
By conducting a thorough credit check and employing additional screening methods, you can minimize risks, select financially responsible tenants, and promote a positive and successful rental experience for both parties involved.
Ultimately, the goal of a credit check is to protect your investment and ensure the financial stability of your rental property. By making informed decisions and selecting reliable tenants, you can create a mutually beneficial renting relationship that fosters trust and security.