
Finance
How To Calculate Risk Assessment
Published: January 15, 2024
Learn how to calculate risk assessment in finance with our step-by-step guide. Assess potential risks and make informed financial decisions for your business.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Risk Assessment
- Importance of Risk Assessment
- Factors Considered in Risk Assessment
- Step-by-Step Guide for Risk Assessment
- Identifying Potential Hazards
- Assessing Probability of Occurrence
- Evaluating Potential Consequences
- Determining Risk Levels
- Developing Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Implementing Risk Management Measures
- Reviewing and Monitoring Risk Assessment
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to making informed decisions in the finance world, one crucial aspect that cannot be overlooked is risk assessment. In simple terms, risk assessment is the process of identifying and evaluating potential risks and their impact on financial stability. It involves analyzing various factors to determine the likelihood of risks occurring and their potential consequences.
Whether you are an individual investor, a small business owner, or a financial institution, understanding risk and conducting effective risk assessments is essential to protect your assets and make sound financial decisions. By analyzing potential risks, you can develop strategies to mitigate their impact and minimize financial losses.
Risk assessment plays a vital role in various aspects of finance. It is used in investment analysis, portfolio management, financial planning, and even in securing loans from financial institutions. In today’s unpredictable and ever-changing financial landscape, having a robust risk assessment process is crucial to navigate uncertainties and mitigate potential losses.
While risk assessment may seem complex and intimidating, it follows a systematic approach that anyone, with the right knowledge and tools, can perform. This article will guide you through the process of risk assessment, providing practical steps and insights to help you evaluate and manage risks effectively.
Definition of Risk Assessment
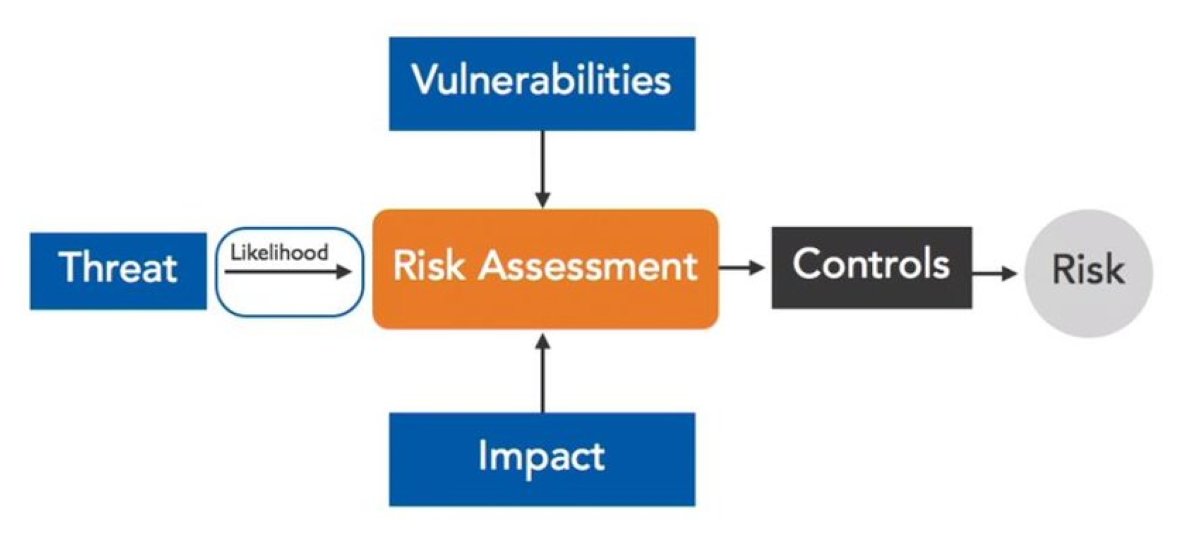
Risk assessment is a systematic and comprehensive process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks that may affect financial stability. It involves assessing the probability of a risk occurring and evaluating its potential impact on the desired outcomes.
In the context of finance, risk assessment helps individuals and organizations understand the potential risks associated with their financial decisions, investments, or business operations. It involves quantifying and qualitatively assessing risks to make informed choices and develop appropriate risk management strategies.
Risk assessment includes identifying potential hazards, analyzing the probability of occurrence, evaluating the magnitude of potential consequences, and determining the overall level of risk. It takes into account both internal and external factors that may influence the likelihood and impact of risks.
By conducting a risk assessment, individuals and organizations can gain a clear understanding of the potential vulnerabilities and threats they may face. This knowledge enables them to take proactive measures to minimize or mitigate the identified risks, enhancing the chances of achieving desired financial goals.
Risk assessment is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process. As financial markets and business environments evolve, new risks emerge, and existing risks may change in nature or magnitude. Regularly reviewing and updating risk assessments is essential to ensure their relevance and effectiveness.
Overall, risk assessment serves as a foundation for effective risk management. It helps individuals and organizations to make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and optimize risk-reward trade-offs to achieve long-term financial success.
Importance of Risk Assessment
The importance of risk assessment in finance cannot be overstated. It is a fundamental process that helps individuals and organizations manage uncertainty and protect their financial interests. Here are some key reasons why risk assessment is crucial:
- Identifying and Prioritizing Risks: Risk assessment allows individuals and organizations to identify and prioritize potential risks. By understanding the nature and severity of risks, they can allocate resources and efforts effectively to manage and mitigate these risks.
- Protecting Financial Assets: Through risk assessment, individuals and organizations can safeguard their financial assets from potential threats. By identifying risks early on, they can implement risk management strategies to minimize the impact and potential losses.
- Improving Decision-Making: Risk assessment provides valuable insights that enhance decision-making. By considering potential risks, individuals and organizations can make more informed choices, weighing the potential benefits against the associated risks.
- Enhancing Financial Planning: Risk assessment plays a crucial role in financial planning. By evaluating potential risks, individuals and organizations can incorporate risk mitigation strategies into their financial plans, ensuring long-term financial stability and success.
- Managing Investments: In the world of finance, risk assessment is vital for investment decision-making. It helps investors assess the potential risks and rewards of different investment opportunities, enabling them to make informed investment decisions that align with their risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Securing Business Operations: For businesses, risk assessment is essential for identifying and managing risks that may impact their operations. By understanding potential threats, businesses can implement measures to mitigate the risks and maintain continuity.
- Complying with Regulations: Risk assessment is often required to ensure compliance with regulatory frameworks. Many industries have specific risk management guidelines that organizations must follow. Conducting risk assessments helps organizations meet these requirements and avoid penalties or legal issues.
Overall, risk assessment is a proactive approach to managing risks in finance. It empowers individuals and organizations to identify potential vulnerabilities, make informed decisions, and protect their financial interests. By integrating risk assessment into financial strategies and decision-making processes, individuals and organizations can navigate uncertainties more effectively and increase their chances of achieving long-term financial success.
Factors Considered in Risk Assessment
Risk assessment involves considering various factors that contribute to the likelihood and impact of risks. These factors vary depending on the context and nature of the financial decision or operation being assessed. Here are some common factors considered in risk assessment:
- Probability: Assessing the probability of a risk occurring is a key factor in risk assessment. This involves analyzing historical data, market trends, and other relevant information to determine the likelihood of a risk event taking place.
- Impact: The potential impact of a risk is another critical factor. This includes evaluating the severity of the consequences that may arise if a risk materializes. The impact can be financial, reputational, operational, or legal, among others.
- Timing: The timing of a risk event is also considered in risk assessment. Some risks may have an immediate impact, while others may have a delayed or long-term effect. Understanding the timing helps in developing appropriate risk management strategies.
- External Influences: External factors that may influence risks are taken into account. This includes changes in economic conditions, regulatory environments, technological advancements, and geopolitical events. Accounting for these external influences helps in assessing the potential impact of risks.
- Internal Controls: Evaluating the effectiveness of internal controls is an essential factor in risk assessment. This involves examining the policies, procedures, and systems in place to mitigate risks and protect the organization’s assets and interests.
- Dependencies and Interdependencies: Risks often have dependencies or interdependencies with other factors or events. Assessing these relationships helps in understanding how risks can propagate or amplify through interconnected systems.
- Risk Tolerance: Evaluating the risk tolerance level is crucial in risk assessment. Different individuals and organizations have varying levels of risk appetite. Understanding risk tolerance helps in determining the acceptable level of risk and developing risk management strategies accordingly.
- Historical Data: Historical data and trends are valuable inputs in risk assessment. Analyzing past incidents or patterns helps in identifying potential risks and understanding their characteristics, frequency, and magnitude.
- Expert Judgment: The expertise and insights of subject matter experts play a significant role in risk assessment. Their knowledge and experience contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of risks and their potential impact.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is an integral part of risk assessment. Assessing risks in relation to applicable laws and regulations ensures that the organization operates within the legal framework and avoids potential legal and financial consequences.
By considering these factors, individuals and organizations can gain a holistic view of risks and make informed decisions to manage and mitigate them effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide for Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a systematic process that involves several steps to identify, evaluate, and manage potential risks. While the specific steps may vary depending on the context and complexity of the risk assessment, here is a general guide to conducting a risk assessment:
- Define the Scope: Clearly define the scope of the risk assessment, including the specific financial decision, project, or operation being assessed.
- Identify Potential Hazards: Identify and list potential hazards or risks that may impact the financial objective or operation. This can include internal and external factors, such as market volatility, economic conditions, operational vulnerabilities, or regulatory changes.
- Assess Probability of Occurrence: Evaluate the probability of each identified risk occurring. Use historical data, expert judgment, and other relevant information to determine the likelihood of each risk event.
- Evaluate Potential Consequences: Analyze the potential impact or consequences of each risk event. Consider financial, operational, reputational, and other relevant factors to assess the severity and magnitude of the consequences.
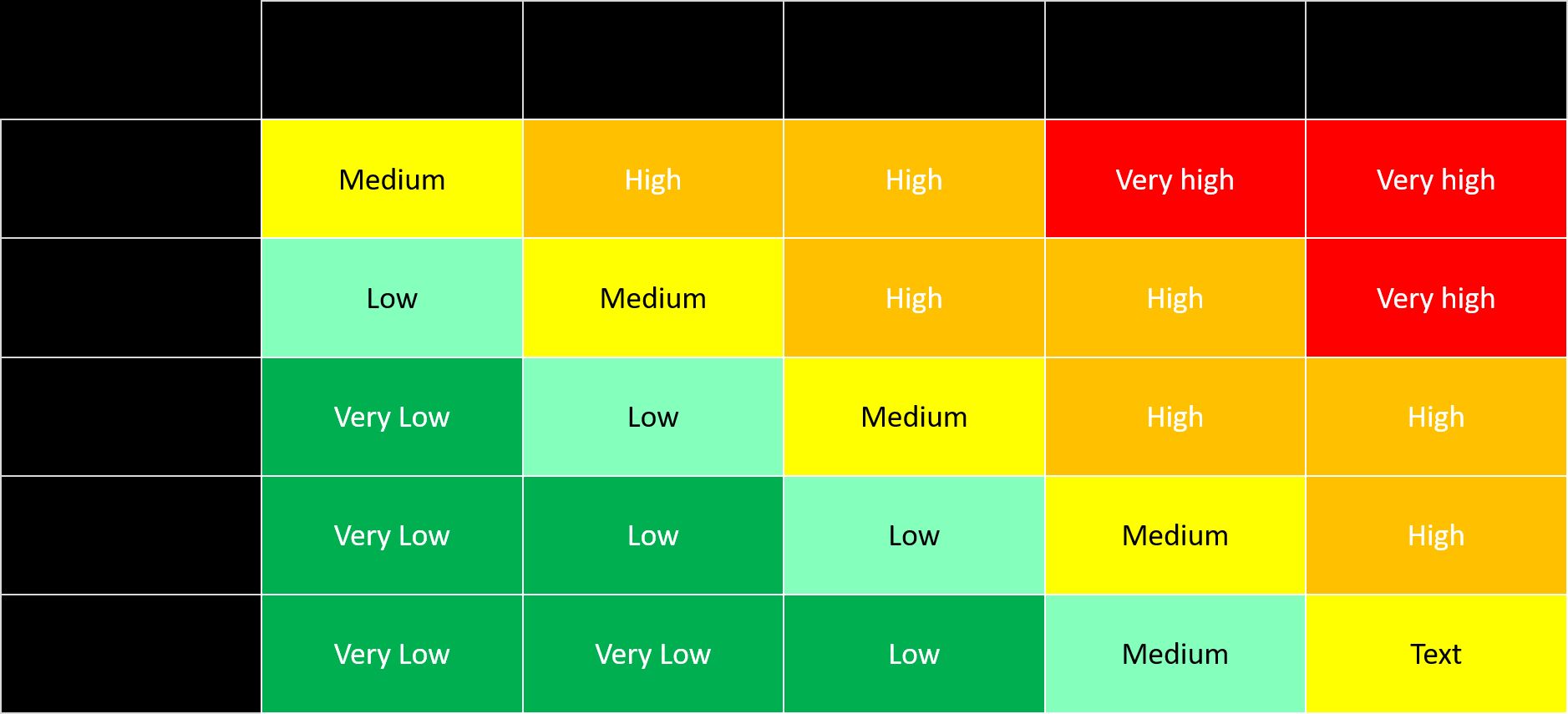
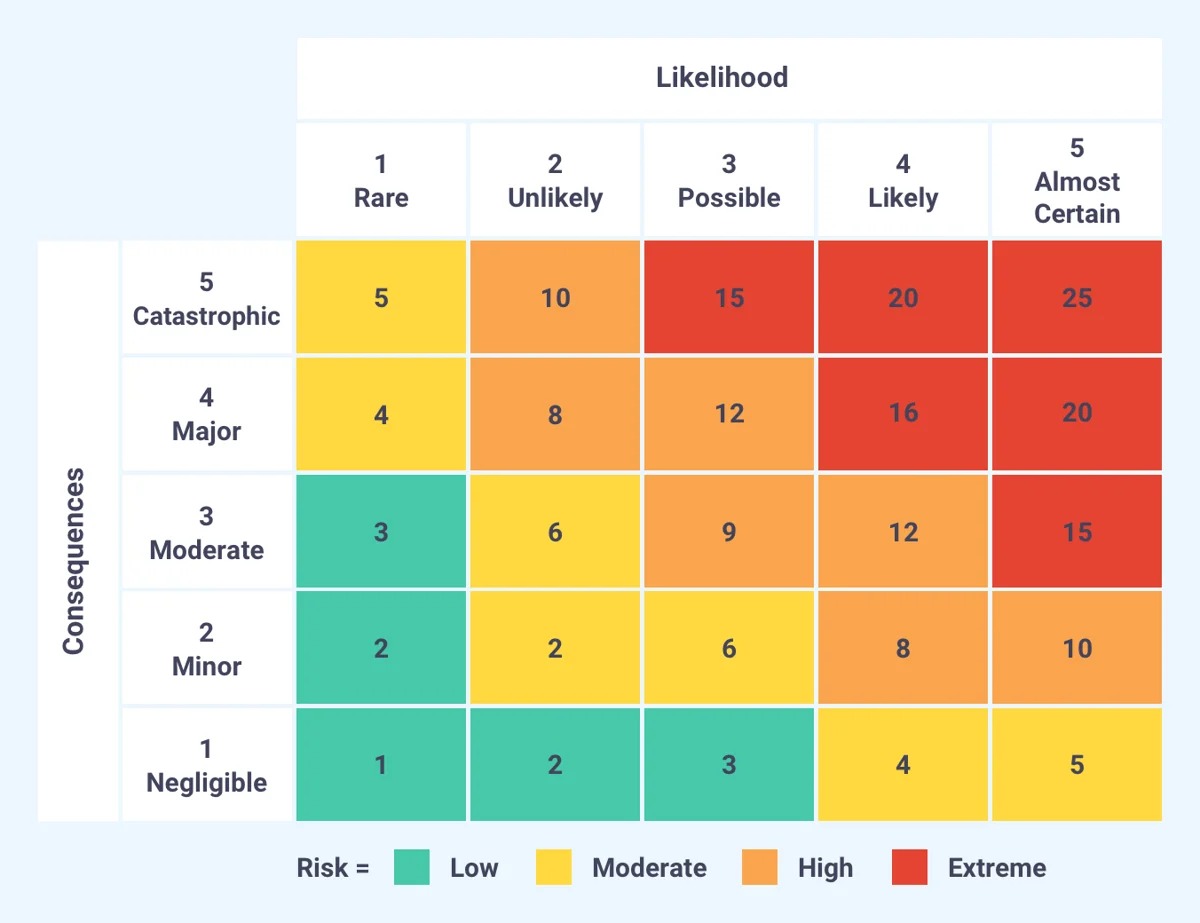
- Determine Risk Levels: Based on the probability and consequences, classify each risk into different risk levels. This can be done using a risk matrix or other quantitative or qualitative methods. Categorize risks as high, medium, or low based on their significance.
- Develop Risk Mitigation Strategies: Once risks are classified, develop strategies to mitigate or manage each risk. This can include preventive measures, risk transfer through insurance, diversification, contingency planning, or establishing internal controls and procedures.
- Implement Risk Management Measures: Put the identified risk management measures into action. Ensure that the necessary resources, systems, and processes are in place to implement and monitor the effectiveness of the risk management strategies.
- Review and Monitor: Regularly review and monitor the effectiveness of the risk assessment and management strategies. Update the assessment as new risks emerge or circumstances change. Continuously monitor the risks to ensure they are adequately managed and controlled.
- Communicate and Document: Effectively communicate the results of the risk assessment to relevant stakeholders. Document the assessment process, findings, and risk management strategies for future reference and compliance purposes.
- Periodically Review: Periodically review and repeat the risk assessment process to align with changing circumstances, industry practices, and emerging risks.
By following this step-by-step guide, individuals and organizations can conduct thorough risk assessments and develop effective risk management strategies to protect their financial interests.
Identifying Potential Hazards
The first step in risk assessment is to identify potential hazards or risks that may impact the financial objective or operation being assessed. This involves identifying both internal and external factors that may pose a threat to the desired outcome. Here are some key steps to help in the identification of potential hazards:
- Thoroughly understand the financial objective or operation: To identify potential hazards, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the specific financial objective or operation that is being assessed. This involves analyzing the purpose, goals, and key aspects of the objective or operation.
- Review historical data and industry trends: Analyze historical data related to similar financial objectives or operations and identify any patterns or recurring issues that may pose risks. Stay updated with industry trends and developments to identify potential emerging risks.
- Consider internal factors: Look within the organization and consider internal factors that may pose risks. This can include operational vulnerabilities, technological limitations, inadequate resources, weak internal controls, or human error.
- Examine external factors: Consider external factors that may pose risks to the financial objective or operation. This can include market volatility, economic conditions, regulatory changes, geopolitical events, or disruptions in the supply chain.
- Engage stakeholders: Involve relevant stakeholders, such as employees, suppliers, customers, or industry experts, to gather their insights and perspectives on potential hazards. They may provide valuable information regarding risks that may not be immediately apparent.
- Brainstorm and conduct risk workshops: Conduct brainstorming sessions or risk workshops with a diverse group of participants to generate a comprehensive list of potential hazards. Encourage open and candid discussions to explore different perspectives and insights.
- Use risk assessment frameworks and checklists: Utilize established risk assessment frameworks or checklists specific to the financial objective or operation being assessed. These frameworks can provide a structured approach to identify potential hazards and ensure they are not overlooked.
- Consider feedback and lessons learned: Incorporate feedback from previous risk assessments or incidents to identify potential hazards that have previously caused issues. Learn from past experiences and apply the lessons learned to future risk assessments.
- Document the identified hazards: Maintain a comprehensive list of all identified potential hazards. Document their nature, characteristics, and any relevant details that will assist in the evaluation and management of the risks.
- Keep the risk assessment updated: Remember that the identification of hazards is an ongoing process. As circumstances change, new risks may emerge, and existing risks may evolve. Regularly review and update the list of potential hazards to ensure the risk assessment remains relevant and effective.
By diligently identifying potential hazards using these steps, individuals and organizations can lay a strong foundation for conducting a comprehensive risk assessment and developing suitable risk management strategies.
Assessing Probability of Occurrence
Assessing the probability of occurrence is a critical step in risk assessment. It involves evaluating the likelihood of each identified risk event happening. Assigning a probability helps in quantifying the level of uncertainty and enables prioritization of risks based on the likelihood of their occurrence. Here are some key considerations when assessing the probability of occurrence:
- Collect and analyze historical data: Review relevant historical data to identify patterns or trends that may indicate the likelihood of similar risks occurring. The analysis of past incidents and their frequency can provide valuable insights into the probability of future occurrences.
- Consider external factors: Take into account external factors that may influence the probability of the risk events. This can include changes in market conditions, economic trends, regulatory environment, or geopolitical factors. The assessment should consider the impact of these factors on the likelihood of the identified risks materializing.
- Assess internal factors: Evaluate internal factors that may affect the likelihood of risk events occurring. This can include the organization’s operations, resources, systems, and processes. Consider the effectiveness of internal controls, risk management measures, and any vulnerabilities that may increase the likelihood of risks.
- Engage subject matter experts: Seek input from subject matter experts who possess domain knowledge and expertise related to the specific risks being assessed. Their insights can help in assessing the probability based on their experience and understanding of the subject matter.
- Use statistical techniques: Utilize statistical techniques, such as probability distributions or regression analysis, where applicable, to quantify the likelihood of risk events occurring. Statistical models can provide a more objective and data-driven assessment of the probability of occurrence.
- Evaluate leading and lagging indicators: Consider leading indicators, such as early warning signs or predictive metrics, that can provide signals about the potential occurrence of risks. Also, evaluate lagging indicators, which are measurable events or incidents that have already occurred, as they can indicate the likelihood of similar events in the future.
- Consider expert judgment: Seek input from individuals with expert knowledge and experience who can provide their professional judgment in assessing the probability of occurrence. Expert judgment can complement data-driven assessments and provide a more comprehensive picture of the likelihood of the identified risks.
- Document the probability assessment: Record the probability assessment for each identified risk event. Use a consistent scale or rating system to ensure clarity and consistency. Document the reasoning and factors considered in the assessment to provide transparency and support the decision-making process.
- Review and update probability assessments: Regularly review and update the probability assessments as new information becomes available or as circumstances change. Revisit and revise the probability estimates in light of any new observations, changes in the environment, or updated data.
By considering these factors and adopting a systematic approach, individuals and organizations can assess the probability of occurrence accurately. This assessment provides a foundation for prioritizing risks and allocating resources effectively in risk management efforts.
Evaluating Potential Consequences
In risk assessment, evaluating the potential consequences is a crucial step to understand the impact that each identified risk event may have on the financial objective or operation. By assessing the potential consequences, individuals and organizations can prioritize risks, allocate resources effectively, and develop appropriate risk mitigation strategies. Here are some key considerations when evaluating potential consequences:
- Financial Impact: Evaluate the potential financial consequences that may arise if a risk event occurs. This includes quantifying potential monetary losses, increased expenses, reduced revenue, or potential legal costs.
- Operational Impact: Assess the potential impact on day-to-day operations and processes. Consider disruptions to supply chain, production delays, loss of productivity, or reputational damage that may occur as a result of the risk event.
- Reputational Impact: Evaluate the potential impact on the organization’s reputation and brand image. Consider the potential loss of trust, customer dissatisfaction, negative publicity, or long-term damage to the organization’s reputation as a consequence of the risk event.
- Legal and Regulatory Consequences: Consider the potential legal and regulatory consequences that may arise from the risk event. Evaluate the potential fines, penalties, lawsuits, or regulatory actions that may be imposed as a result.
- Health and Safety Impact: Assess the potential impact on the health and safety of employees, customers, or the public. Consider the potential physical harm, injuries, or loss of life that may occur if the risk event materializes.
- Environmental Impact: Evaluate the potential impact on the environment. Consider any potential harm to natural resources, pollution, or ecological damage that may result from the risk event.
- Customer and Stakeholder Impact: Assess the potential impact on customers, stakeholders, and business relationships. Consider the potential loss of customers, damage to relationships with stakeholders, or negative impact on investor confidence.
- Timing of Consequences: Consider the timing of the consequences. Evaluate whether the consequences would have an immediate impact or if they would have a delayed or long-term effect on the financial objective or operation.
- Severity and Magnitude: Evaluate the severity and magnitude of the potential consequences. Consider the scale of the impact and the extent to which the consequences would disrupt or hinder the achievement of the financial objective or operation.
- Probability-impact relationship: Consider the relationship between the probability of the risk occurring and the potential consequences. High impact risks with a high probability of occurrence may require immediate attention and prioritization in risk management efforts.
- Document the evaluation: Document the evaluation of the potential consequences for each identified risk event. Record the specific consequences, their potential severity, and any relevant details that will help in the subsequent risk management steps.
- Review and update consequence evaluation: Regularly review and update the consequence evaluation as new information becomes available or as circumstances change. Revisit and revise the assessment of potential consequences to ensure its alignment with evolving risks and objectives.
By carefully evaluating the potential consequences, individuals and organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of the impact that risks may have on the financial objective or operation. This evaluation forms the basis for prioritizing risks and developing effective risk mitigation strategies.
Determining Risk Levels
Determining risk levels is a crucial step in risk assessment that helps individuals and organizations prioritize their efforts and allocate resources appropriately. Assigning risk levels allows for a clear understanding of the magnitude and significance of each identified risk event. By categorizing risks into different levels, stakeholders can focus their attention on the risks that pose the highest potential impact. Here are some key considerations when determining risk levels:
- Probability and Consequences: Consider the evaluated probability of occurrence and the potential consequences of each identified risk event. Combine these factors to determine the overall level of risk. Higher probabilities and more severe consequences generally result in higher risk levels.
- Risk Matrix: Use a risk matrix or similar tool to facilitate the determination of risk levels. A risk matrix is a graphical representation that combines the assessed probability and consequence ratings to categorize risks into different levels, such as high, medium, or low. It provides a visual representation of the risk landscape.
- Suggested Rating Scales: Utilize rating scales for probability and consequences to ensure consistency. For example, probability can be assessed on a scale of 1 to 5, where 5 represents the highest likelihood, and consequences can be assessed on a scale of 1 to 5, where 5 represents the most severe impact. Using consistent rating scales enables accurate comparison and aggregation of risks.
- Consider Risk Tolerance: Take into account the risk tolerance level of the individual or organization conducting the risk assessment. Risk tolerance may vary depending on factors such as industry, financial capacity, and stakeholder preferences. Higher-risk tolerance may result in accepting higher risk levels, while lower-risk tolerance may result in a more conservative approach.
- Expert Judgment: Seek the input of subject matter experts or stakeholders with expertise in the specific risks being assessed. Their knowledge and insights can be valuable in determining risk levels based on their experience and understanding of the consequences and probabilities involved.
- Nature of the Financial Objective or Operation: Consider the nature and criticality of the financial objective or operation being assessed. Some objectives or operations may have a higher sensitivity to certain risks, warranting a higher risk level, while others may be more resilient or have stronger risk mitigation measures in place.
- Communicate and Document: Clearly communicate and document the determined risk levels for each identified risk event. Provide a clear rationale for why each risk is categorized as high, medium, or low. This supports transparency, decision-making, and future reference.
- Regular Review and Update: Regularly review and update the determined risk levels as new information becomes available or as circumstances change. Reassess risks periodically to ensure that the risk levels accurately reflect the evolving risk landscape and the changing dynamics of the financial objective or operation.
Determining risk levels enables prioritization and provides guidance for subsequent risk management efforts. By categorizing risks based on their levels, individuals and organizations can allocate resources and focus their attention on addressing the most critical and impactful risks.
Developing Risk Mitigation Strategies
Once the risks have been identified and their levels determined, the next step in the risk assessment process is developing risk mitigation strategies. Risk mitigation involves implementing measures and strategies to reduce the likelihood or impact of the identified risks. The goal is to minimize the potential negative consequences and enhance the resilience of the financial objective or operation. Here are some key steps to develop effective risk mitigation strategies:
- Understand the risks: Gain a thorough understanding of each identified risk, including its nature, causes, and potential consequences. This understanding is essential in devising appropriate mitigation strategies.
- Evaluate existing controls: Review existing control measures and risk management practices already in place. Assess their effectiveness in mitigating the identified risks and identify any gaps or areas for improvement.
- Preventive measures: Identify and implement preventive measures that can reduce the probability of the risk occurring. This can include implementing robust internal controls, improving operational processes, enhancing security measures, or conducting regular training and awareness programs.
- Risk transfer options: Consider risk transfer options such as insurance, contracts, or outsourcing. Transferring a portion of the risk to a third party can help reduce the financial impact and provide a safety net in case the risk event occurs.
- Diversification: Explore strategies to diversify and spread out risks. This can include diversifying investment portfolios, establishing multiple revenue streams, or creating redundancy in critical systems or processes.
- Contingency planning: Develop contingency plans or alternative courses of action to mitigate the impact of the risk event if it materializes. Anticipate and prepare for potential scenarios by identifying trigger points, response protocols, and recovery strategies.
- Establish response and recovery mechanisms: Create response and recovery mechanisms that outline step-by-step procedures to be followed in case of a risk event. Clearly define roles, responsibilities, and communication channels to ensure a coordinated and effective response.
- Continuous monitoring: Implement systems and processes for continuous monitoring of risks. Regularly assess the effectiveness of risk mitigation measures and make adjustments as necessary. Stay vigilant and proactive in identifying emerging risks and adapting strategies accordingly.
- Evaluate cost-benefit trade-offs: Consider the cost and feasibility of implementing risk mitigation strategies compared to the potential impact of the risks. Assess the cost-benefit trade-offs to ensure that the chosen strategies are cost-effective and aligned with the financial objectives and resources available.
- Document and communicate: Document the selected risk mitigation strategies, including the rationale behind each strategy and the expected outcomes. Clearly communicate the strategies to relevant stakeholders to ensure alignment, understanding, and support.
- Regularly review and update: Regularly review and update the risk mitigation strategies as needed. Reassess the effectiveness of the strategies and adapt to changes in the risk landscape, industry practices, or the financial objective or operation itself.
Developing risk mitigation strategies is crucial to proactively address identified risks and minimize their potential impact. By following these steps, individuals and organizations can enhance their ability to effectively manage and mitigate risks, ensuring the continuity and success of their financial objectives or operations.
Implementing Risk Management Measures
Implementing risk management measures is a crucial step in the risk assessment process. This step involves putting into action the selected risk mitigation strategies and measures that were developed in the previous stage. By implementing effective risk management measures, individuals and organizations can reduce the likelihood and impact of identified risks. Here are some key steps to successfully implement risk management measures:
- Create an implementation plan: Develop a detailed implementation plan that outlines the actions, timelines, and responsibilities needed to execute the risk management measures effectively. This plan should provide a clear roadmap for the implementation process.
- Allocate the necessary resources: Ensure that the required resources, including financial resources, personnel, technology, and infrastructure, are allocated to support the implementation of the risk management measures. Adequate resources are essential for successful execution.
- Communicate the plan: Clearly communicate the implementation plan to all relevant stakeholders involved in the risk management process. Provide clear instructions, expectations, and timelines to ensure everyone is aligned and working towards the same goals.
- Train and educate: Provide training and education to employees or individuals involved in the implementation of risk management measures. This ensures that they have the necessary knowledge and skills to carry out the required tasks effectively.
- Establish monitoring mechanisms: Set up monitoring mechanisms to track the progress and effectiveness of the implemented risk management measures. Regularly review and assess their performance to ensure they are achieving the desired outcomes.
- Address barriers and challenges: Identify any potential obstacles or challenges that may hinder the effective implementation of the risk management measures. Develop strategies to overcome these barriers and address any concerns or resistance from stakeholders.
- Integrate risk management into daily operations: Embed risk management practices into the day-to-day operations of the organization or individual. Integrate risk considerations into decision-making processes, standard operating procedures, and performance evaluations.
- Document actions and results: Keep clear and comprehensive documentation of the actions taken during the implementation process, as well as the results achieved. This helps in evaluating the effectiveness of the risk management measures and provides a historical reference for future assessments.
- Ensure ongoing compliance: Continuously monitor and ensure ongoing compliance with the implemented risk management measures. Regularly review and update policies, procedures, and controls to adapt to changing risks and evolving best practices.
- Promote a risk-aware culture: Foster a culture of risk awareness and accountability throughout the organization or individual. Encourage open communication, reporting of potential risks or issues, and a proactive approach to risk management at all levels.
- Regularly evaluate and improve: Continually evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented risk management measures and seek opportunities for improvement. Solicit feedback from stakeholders and conduct periodic reviews to ensure that the measures remain relevant and responsive to changing risks.
By following these steps, individuals and organizations can successfully implement risk management measures to mitigate the identified risks. Effective implementation is crucial for achieving the intended risk reduction and ensuring the long-term success and resilience of the financial objectives or operations.
Reviewing and Monitoring Risk Assessment
The process of risk assessment does not end once risk management measures are implemented. It is essential to regularly review and monitor the risk assessment to ensure its ongoing effectiveness and relevance. Continuous review and monitoring help identify emerging risks, assess the performance of risk mitigation strategies, and make any necessary adjustments. Here are some key steps for reviewing and monitoring risk assessment:
- Establish review intervals: Define a schedule for regular reviews of the risk assessment. The frequency of reviews may vary depending on the nature of the financial objective or operation, industry trends, and regulatory requirements. Common review intervals range from quarterly to annually.
- Evaluate changes in the risk landscape: Assess the external environment and internal factors that may impact the risk landscape. Consider changes in market conditions, economic trends, regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, or organizational dynamics. Identify any new risks or changes in the likelihood and consequences of existing risks.
- Monitor risk indicators: Track key risk indicators (KRIs) that provide early warning signals of potential risk events. Establish monitoring mechanisms to capture relevant data and analyze deviations from established thresholds. Regularly review and analyze KRIs to identify potential risks and trigger appropriate risk mitigation actions.
- Engage stakeholders: Seek input and feedback from relevant stakeholders during the review process. This can include employees, subject matter experts, customers, suppliers, and regulatory authorities. Their perspectives and insights can provide valuable information for assessing the effectiveness of risk mitigation measures.
- Assess the performance of risk mitigation strategies: Evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented risk management measures in reducing the likelihood and impact of identified risks. Assess whether the strategies are achieving the desired outcomes and whether any adjustments or enhancements are necessary.
- Revisit risk levels: Reassess the determined risk levels to ensure that they reflect the current risk landscape accurately. Evaluate whether any changes in the probability or consequences of risks warrant a revision of risk levels. Adjust risk levels as needed to accurately prioritize risks.
- Update risk documentation: Regularly update the risk assessment documentation to reflect any changes in the risk landscape, risk levels, or risk mitigation strategies. Document the review findings, any adjustments made, and the rationale behind them. Maintain a historical record of the risk assessment process.
- Communicate review results: Share the results of the risk assessment review with relevant stakeholders. Clearly communicate any changes, adjustments, or areas that need attention. Promote transparency and understanding of the risks and risk management efforts within the organization or among stakeholders.
- Iterate risk management measures: Continuously improve and iterate on risk management measures based on the findings of the review process. Implement any necessary adjustments, updates, or enhancements to ensure that the risk mitigation strategies remain effective and aligned with the evolving risk landscape.
- Stay informed: Stay updated on industry trends, best practices, and emerging risks. Attend industry conferences, participate in professional networks, and engage in continuous learning to ensure that the risk assessment remains current and aligned with industry standards.
By regularly reviewing and monitoring the risk assessment, individuals and organizations can adapt to changing circumstances, address emerging risks, and improve the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies. Continuous monitoring ensures that the risk assessment remains a proactive and dynamic process, promoting sustainable financial decision-making and operational resilience.
Conclusion
Risk assessment is a fundamental process in the world of finance that enables individuals and organizations to make informed decisions, protect their financial interests, and navigate uncertainties. By systematically identifying, evaluating, and managing potential risks, individuals and organizations can minimize financial losses, optimize risk-reward trade-offs, and enhance their long-term financial stability and success.
Throughout the risk assessment process, several key steps are essential for a comprehensive and effective assessment. From identifying potential hazards and assessing the probability of occurrence to evaluating potential consequences and determining risk levels, each step contributes to a holistic understanding of the risks involved.
Developing risk mitigation strategies and implementing effective risk management measures are critical to reducing the likelihood and impact of identified risks. By implementing preventive measures, transferring risks, diversifying portfolios, and establishing contingency plans, individuals and organizations can enhance their resilience and minimize potential losses.
Regularly reviewing and monitoring the risk assessment is essential for maintaining its relevance and effectiveness. By continuously evaluating the risk landscape, monitoring risk indicators, assessing the performance of risk mitigation strategies, and making necessary adjustments, individuals and organizations can stay ahead of emerging risks and changing circumstances.
In conclusion, risk assessment is an indispensable process that underscores the importance of proactive risk management in the world of finance. By practicing thorough risk assessment, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions, protect their financial well-being, and increase the chances of achieving their long-term financial objectives.