Finance
What Is Risk Assessment In IT
Published: January 15, 2024
Learn about the importance of risk assessment in IT for finance sector and how it helps in identifying and managing potential threats and vulnerabilities.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Risk Assessment in IT
- Purpose of Risk Assessment in IT
- Key Components of Risk Assessment in IT
- Steps Involved in Risk Assessment in IT
- Tools and Techniques used in Risk Assessment in IT
- Benefits of Risk Assessment in IT
- Challenges in Conducting Risk Assessment in IT
- Best Practices for Effective Risk Assessment in IT
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of IT risk assessment! In today’s digital age, where businesses rely heavily on technology, the importance of identifying and managing potential risks has never been greater. Risk assessment is a crucial process in the field of Information Technology (IT) that helps organizations identify, evaluate, and prioritize potential risks to their IT systems, infrastructure, and data.
IT risk assessment involves analyzing the potential threats and vulnerabilities that may impact the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of IT assets. This process allows organizations to understand the magnitude of potential risks and make informed decisions on implementing mitigating controls.
The primary objective of risk assessment in IT is to proactively identify and manage risks, minimizing the likelihood of security breaches, data loss, system downtime, and financial loss. By conducting a comprehensive risk assessment, organizations can develop robust strategies to protect their IT systems, maintain compliance with regulations, and safeguard sensitive information.
Risk assessment in IT is a multifaceted process that involves various components and steps. It requires a thorough understanding of the organization’s IT infrastructure, potential vulnerabilities, and potential threats. It also incorporates utilizing tools and techniques to analyze and evaluate risks, as well as determining the appropriate risk treatment plans.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of risk assessment in IT, exploring its definition, purpose, key components, steps involved, tools and techniques used, benefits, challenges, and best practices. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the significance of risk assessment in the realm of information technology.
Definition of Risk Assessment in IT
Risk assessment in IT refers to the systematic process of identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing potential risks that may impact an organization’s IT systems, infrastructure, and data. It involves identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities and analyzing their potential impact on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of IT assets.
A risk assessment in IT aims to uncover the risks associated with various aspects of information technology, including hardware, software, networks, databases, and applications. It involves evaluating the likelihood of a risk occurring and the potential severity of its impact. By assessing risks, organizations can make informed decisions about implementing controls and mitigation strategies to minimize the likelihood and impact of potential incidents.
During the risk assessment process, IT professionals work closely with stakeholders to identify assets, threats, and vulnerabilities. Assets can include sensitive data, hardware, software, and infrastructure. Threats are potential events or actions that can exploit vulnerabilities and harm IT assets, while vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses or loopholes within the IT infrastructure that can be exploited by threats.
Once risks are identified, they are analyzed based on their severity and likelihood. Severity refers to the potential impact of a risk on the organization, such as financial loss or reputational damage. Likelihood refers to the probability of a risk occurring, considering factors such as the current security controls in place and the threat landscape.
Risk assessment in IT is an ongoing process that requires regular review and updates. As the IT landscape evolves and new threats emerge, organizations must continually assess and reassess their IT risks to ensure their security posture remains effective.
By conducting a comprehensive risk assessment in IT, organizations can prioritize and allocate appropriate resources to manage and mitigate potential risks effectively. This enables them to make informed decisions about implementing controls, improving security measures, and preventing or minimizing the impact of security incidents.
Purpose of Risk Assessment in IT
The purpose of risk assessment in IT is to proactively identify and manage potential risks that may impact an organization’s information technology systems, infrastructure, and data. It serves as a critical component of an organization’s overall risk management strategy, helping to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of IT assets.
One of the primary purposes of risk assessment in IT is to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities that could lead to security breaches, data breaches, system downtime, or unauthorized access to critical information. By conducting a thorough risk assessment, organizations can understand the potential impact of these risks and prioritize their resources accordingly.
Another purpose of risk assessment in IT is to evaluate the effectiveness of existing security controls and mitigation strategies. It allows organizations to identify gaps and weaknesses in their current security measures and make informed decisions about implementing additional controls and measures to mitigate the identified risks.
Risk assessment in IT also helps organizations prioritize and allocate resources effectively. By understanding the potential impact and likelihood of various risks, organizations can allocate their budget, personnel, and time to address the highest priority risks. This ensures that limited resources are focused on the areas that pose the greatest threats to the organization.
Furthermore, risk assessment in IT plays a vital role in compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards. Many regulatory frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), require organizations to conduct regular risk assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities and threats.
Additionally, risk assessment in IT helps organizations make informed decisions regarding risk treatment. Once the risks have been identified and analyzed, organizations can determine the most appropriate risk response strategies, such as risk avoidance, risk mitigation, risk transfer, or risk acceptance.
In summary, the purpose of risk assessment in IT is to proactively identify, evaluate, and manage potential risks in order to protect the organization’s IT systems, infrastructure, and data. It enables organizations to make informed decisions about implementing security controls, allocating resources effectively, maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements, and minimizing the impact of potential security incidents.
Key Components of Risk Assessment in IT
Risk assessment in IT involves several key components that are integral to its successful implementation. These components help organizations thoroughly evaluate potential risks and develop effective strategies to mitigate them. The key components of risk assessment in IT include:
- Asset Identification: The first step in risk assessment is to identify and classify the organization’s IT assets. This includes hardware, software, networks, data centers, and sensitive information. By identifying assets, organizations can understand what needs to be protected and prioritize their risk assessment efforts.
- Threat Assessment: Once assets are identified, the next component is to assess the potential threats that can exploit vulnerabilities and impact the IT systems. Threat assessment involves analyzing internal and external factors, such as malicious attacks, natural disasters, human error, or system failures.
- Vulnerability Analysis: Vulnerability analysis involves identifying weaknesses or loopholes in the IT infrastructure that can be targeted by threats. This can include outdated software, insecure configurations, weak passwords, or lack of encryption.
- Risk Analysis: Risk analysis is the cornerstone of risk assessment in IT. It involves evaluating the potential impact and likelihood of each identified risk. Impact refers to the severity of the consequences if a risk were to occur, such as financial loss or reputational damage. Likelihood refers to the probability of a risk occurring, considering factors such as the current security controls in place and the threat landscape.
- Risk Evaluation: Once risks are analyzed, the next component is to evaluate and prioritize them. This involves comparing risks based on their severity, likelihood, and potential impact on the organization. By evaluating risks, organizations can focus their efforts and resources on managing the most critical risks first.
- Risk Treatment: Risk treatment involves determining the most appropriate response strategy for each identified risk. This can include risk avoidance through implementing preventive measures, risk mitigation by implementing controls and safeguards, risk transfer through insurance or outsourcing, or risk acceptance if the cost of mitigation outweighs the potential impact.
- Documentation: Documentation is a crucial component of risk assessment in IT. It involves recording all the findings, assessments, and decisions made during the risk assessment process. Proper documentation ensures transparency, accountability, and enables future review and updates.
By incorporating these key components, organizations can conduct a comprehensive risk assessment in IT that addresses potential threats and vulnerabilities, evaluates risks, and guides the development of effective risk management strategies. This helps organizations proactively identify and address potential risks, ensuring the protection of their IT systems, infrastructure, and data.
Steps Involved in Risk Assessment in IT
Risk assessment in IT follows a systematic approach that involves several sequential steps. Each step plays a crucial role in identifying, evaluating, and managing potential risks. The steps involved in risk assessment in IT include:
- Establish the Scope: The first step is to define the scope of the risk assessment. This involves identifying the assets, systems, and processes that will be assessed, as well as determining the objectives and desired outcomes of the assessment.
- Identify Assets: Once the scope is established, the next step is to identify the IT assets that need to be protected. This includes hardware, software, networks, databases, and sensitive information. It is important to have a comprehensive understanding of the assets in order to accurately assess the risks they may face.
- Identify Threats: After identifying the assets, the next step is to identify potential threats that could exploit vulnerabilities and impact the IT systems. This can include external threats like hackers and malware, as well as internal threats such as human error or system failures.
- Assess Vulnerabilities: In this step, vulnerabilities within the IT infrastructure are analyzed. This includes identifying weaknesses or loopholes that can be targeted by the identified threats. Vulnerabilities can include outdated software, weak passwords, unpatched systems, or lack of encryption.
- Analyze Risks: Risk analysis involves evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of each identified risk. This step considers the severity of the consequences if a risk were to occur and the likelihood of it happening. The analysis can be qualitative or quantitative, depending on the available data and resources.
- Evaluate Risks: Once risks are analyzed, they are evaluated and prioritized. This step involves comparing risks based on their severity, likelihood, and potential impact on the organization. By evaluating risks, organizations can allocate resources effectively and focus on managing the most critical risks first.
- Treat Risks: After evaluating risks, the next step is to determine and implement appropriate risk response strategies. This can include risk avoidance, risk mitigation through controls and safeguards, risk transfer through insurance or outsourcing, or risk acceptance if the cost of mitigation outweighs the potential impact.
- Monitor and Review: Risk assessment is an ongoing process, and regular monitoring and review are essential. This involves continually assessing the effectiveness of implemented controls, identifying any changes in the threat landscape, and updating the risk assessment as needed.
- Document and Communicate: Proper documentation of the risk assessment process is crucial. This includes recording all the findings, assessments, decisions made, and actions taken. Effective communication of the assessment results to relevant stakeholders is also essential to ensure understanding and support for risk management strategies.
By following these steps, organizations can conduct a comprehensive risk assessment in IT, identify potential risks, and develop effective strategies to mitigate them. This systematic approach helps organizations protect their IT systems, infrastructure, and data from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Tools and Techniques used in Risk Assessment in IT
Risk assessment in IT relies on various tools and techniques to assist in the identification, analysis, and evaluation of potential risks. These tools and techniques aid in gathering relevant data, assessing vulnerabilities, and making informed decisions about risk management strategies. Some of the commonly used tools and techniques in risk assessment in IT include:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Vulnerability scanning tools are used to identify and assess vulnerabilities in IT systems. These tools scan the infrastructure to detect potential weaknesses and provide a report highlighting areas that require attention and remediation.
- Penetration Testing: Penetration testing, also known as ethical hacking, simulates real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities and assess system security. Skilled professionals use specialized tools and techniques to exploit weaknesses and gain unauthorized access, allowing organizations to address these vulnerabilities before real attackers can exploit them.
- Threat Intelligence: Threat intelligence tools gather and analyze data from various sources to identify emerging threats and trends. These tools provide valuable insights into potential risks by monitoring hacker forums, security blogs, and other sources to stay updated with the latest threat actors and attack techniques.
- Risk Assessment Templates: Risk assessment templates provide a structured approach to conducting risk assessments. These pre-designed templates guide organizations through the process, ensuring that all necessary components and steps are covered. They often include sections to document asset identification, threat assessment, vulnerability analysis, risk analysis, evaluation, and treatment plans.
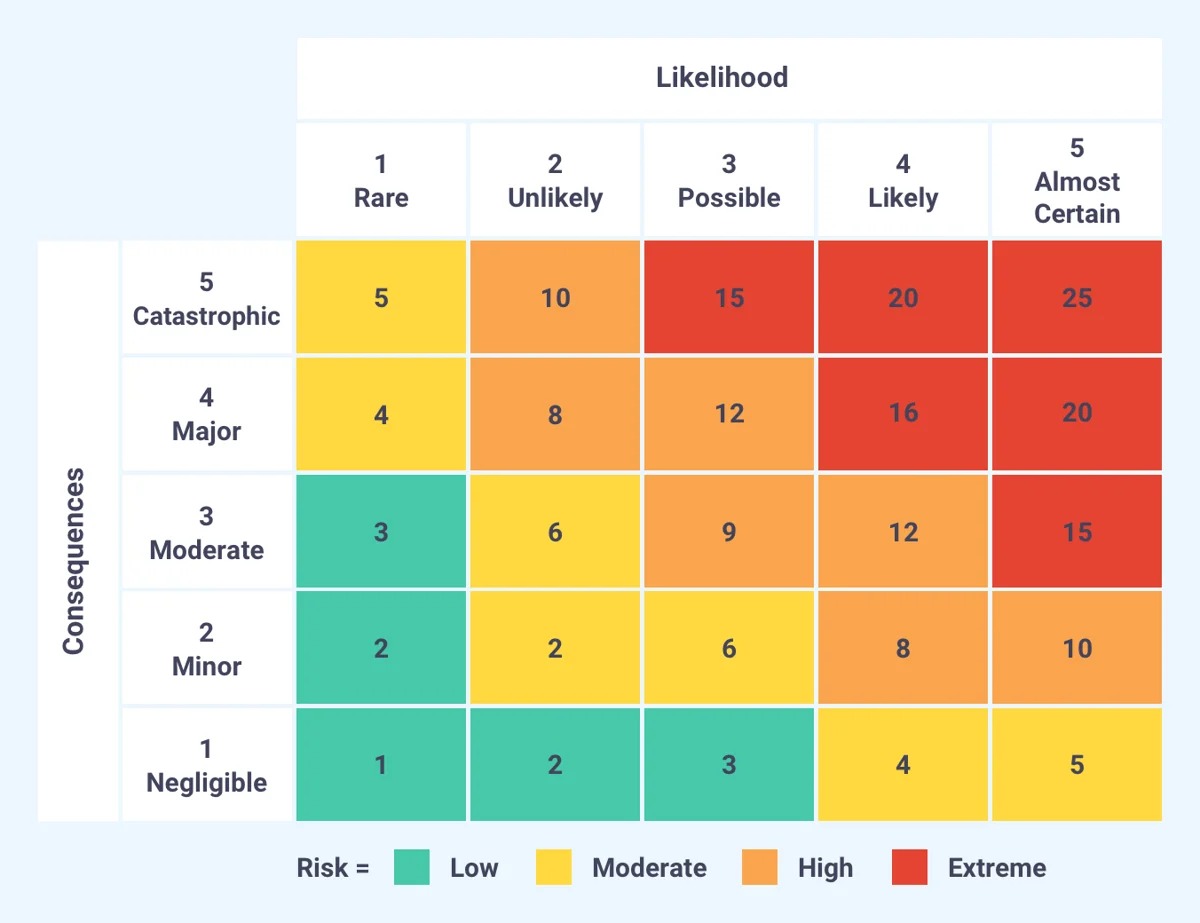
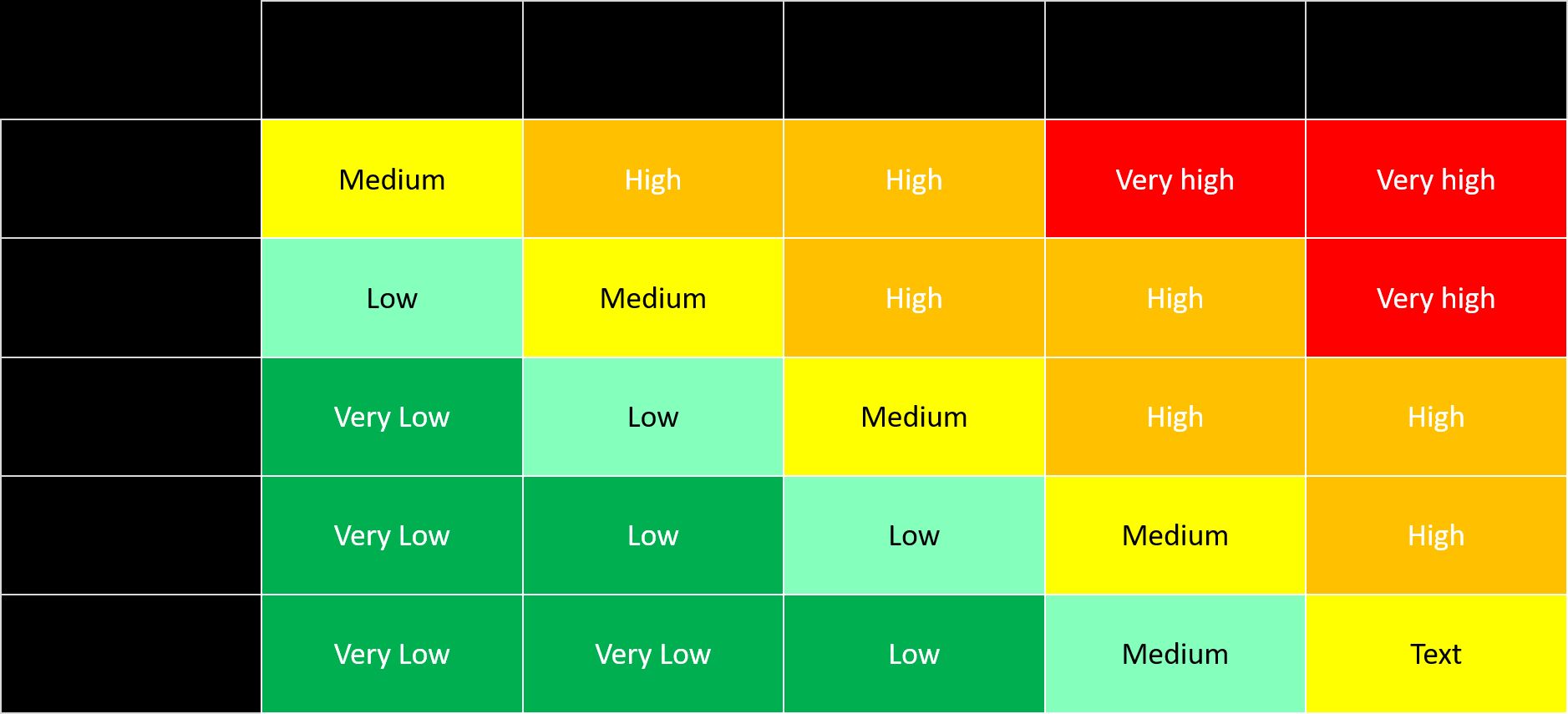
- Risk Matrix: A risk matrix is a visual tool used to evaluate and prioritize risks by considering their likelihood and impact. It categorizes risks into high, medium, or low based on their severity and probability, enabling organizations to allocate resources and prioritize risk response strategies accordingly.
- Business Impact Analysis: A business impact analysis (BIA) is a technique used to identify critical IT systems, processes, and data and evaluate their potential impact on the organization. BIA helps assess the financial, operational, and reputational consequences of specific events, assisting in the prioritization of risk response efforts.
- Data Encryption: Data encryption tools ensure that sensitive information is protected by converting it into an unreadable format. Encryption adds a layer of security to prevent unauthorized access and disclosure of data, reducing the risk of data breaches and theft.
- Firewall and Intrusion Detection Systems: Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) are key tools for network security. Firewalls monitor and control network traffic, filtering out potentially harmful connections, while IDS tools monitor network traffic for unusual or suspicious activity, helping to detect and respond to potential security breaches.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools: SIEM tools collect and analyze logs and events from various systems and devices to identify potential security incidents. These tools provide real-time monitoring, correlation of events, and automated alerting, helping organizations detect and respond to security threats in a timely manner.
These tools and techniques are valuable assets in the risk assessment process, helping organizations identify vulnerabilities, assess risks, and develop effective risk management strategies. It is important to select and utilize the most appropriate tools and techniques based on the organization’s needs, resources, and risk appetite.
Benefits of Risk Assessment in IT
Risk assessment in IT offers numerous benefits to organizations, helping them proactively identify, mitigate, and manage potential risks to their information technology systems, infrastructure, and data. Some of the key benefits of conducting risk assessment in IT are:
- Early Identification of Risks: Risk assessment enables organizations to identify potential risks before they turn into significant security incidents. By conducting a thorough assessment, organizations can proactively identify vulnerabilities, threats, and weaknesses in their IT systems, allowing them to implement appropriate controls and measures to mitigate risks in a timely manner.
- Prioritization and Resource Allocation: Risk assessment helps organizations prioritize risks and allocate resources effectively. By evaluating the potential impact and likelihood of risks, organizations can focus their efforts on managing the most critical risks first. This ensures that limited resources are utilized where they are most needed, optimizing risk management strategies.
- Improved Decision-Making: With the insights gained from risk assessment, organizations can make informed decisions about risk treatment strategies. Whether it’s implementing preventative measures, investing in security controls, or transferring risks through insurance, risk assessment provides the necessary information to guide decision-making and develop effective risk management plans.
- Compliance with Regulations and Standards: Many regulatory frameworks and industry standards require organizations to conduct regular risk assessments to ensure compliance. By conducting risk assessments, organizations can identify and address potential vulnerabilities and threats, demonstrating their commitment to data protection and security compliance.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Risk assessment helps organizations identify gaps and weaknesses in their current security measures. By understanding the vulnerabilities and threats, organizations can strengthen their security controls, implement additional safeguards, and improve their overall security posture. This reduces the risk of security breaches, data loss, and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Improved Incident Response: Risk assessment aids organizations in developing incident response plans. By identifying potential risks and their potential impact, organizations can define appropriate response strategies to address and mitigate the risks. This enhances their ability to respond effectively to security incidents, minimizing the impact and facilitating a faster recovery.
- Better Business Continuity: Risk assessment helps organizations assess the potential impact of risks on business operations and continuity. By understanding the potential risks and their consequences, organizations can develop robust business continuity plans to ensure timely recovery and minimize downtime in the event of a security incident.
- Protection of Reputation: A security incident can damage an organization’s reputation and erode customer trust. Risk assessment helps organizations identify and mitigate risks that could potentially harm their reputation. By implementing proactive measures, organizations can maintain a strong security posture and demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive information, enhancing their reputation in the eyes of customers, partners, and stakeholders.
Overall, risk assessment in IT provides significant advantages for organizations, including early risk identification, efficient resource allocation, informed decision-making, compliance, enhanced security measures, improved incident response, business continuity planning, and reputation protection. By conducting regular risk assessments, organizations can better protect their IT systems, infrastructure, and data, safeguarding their operations and supporting business growth.
Challenges in Conducting Risk Assessment in IT
Conducting risk assessment in IT can present various challenges that organizations need to address to ensure the effectiveness of the process. Understanding and mitigating these challenges is crucial for a successful risk assessment. Some of the major challenges in conducting risk assessment in IT include:
- Lack of Data: Obtaining accurate and reliable data can be challenging for risk assessment. Availability of relevant historical data, threat intelligence, and vulnerability information is required to assess risks effectively. However, organizations may face difficulties in collecting and analyzing sufficient data, especially in emerging or evolving threat landscapes.
- Complexity of IT Systems: Modern IT systems can be complex, incorporating numerous interconnected components and technologies. Assessing risks in such intricate environments can be challenging, as it requires a comprehensive understanding of the system’s architecture, dependencies, and potential vulnerabilities across different layers, including hardware, software, networks, and databases.
- Rapid Technological Advancements: The rapid pace of technological advancements poses a challenge for risk assessment. New technologies, such as cloud computing, Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence, introduce new risks and vulnerabilities that organizations must consider. Staying updated with these advancements and their associated risks requires a continuous learning and adaptation process.
- Dynamic Threat Landscape: The threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats and attack vectors emerging regularly. Organizations face the challenge of staying ahead of these dynamic threats and anticipating potential risks that may arise. This requires continuous monitoring, threat intelligence gathering, and adapting risk assessment approaches to address evolving threats.
- Resource Constraints: Conducting thorough risk assessments requires adequate resources, including skilled personnel, tools, and time. However, many organizations face resource constraints, making it challenging to allocate sufficient resources for risk assessment activities. Limited budgets, shortage of cybersecurity experts, and other operational priorities can hinder the effectiveness of risk assessment efforts.
- Complexity of Risk Analysis: Analyzing risks involves considering multiple factors, such as the likelihood of occurrence and potential impact. Quantitative assessment often requires statistical analysis and modeling, which can be complex and time-consuming. Additionally, qualitative assessment relies on expert judgment and can be subjective, making it challenging to achieve standardization and consistency in risk analysis.
- Organizational Culture and Awareness: Risk assessment requires a culture of security awareness and proactive risk management at all levels of the organization. Resistance to change, lack of awareness, or a reactive approach to risk management can impede the effectiveness of risk assessment efforts. Organizations need to foster a culture that recognizes the importance of risk assessment and encourages participation and collaboration.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements adds complexity to risk assessment. Organizations must navigate through various compliance frameworks, such as GDPR, PCI DSS, or HIPAA, which have specific requirements for risk assessment. Ensuring compliance while conducting risk assessments can be challenging and time-consuming, especially for organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions.
Addressing these challenges requires organizations to have a strategic approach to risk assessment, leverage appropriate tools and technologies, invest in skilled personnel, and prioritize risk management as an ongoing process. By recognizing these challenges and implementing effective strategies, organizations can overcome barriers and conduct thorough risk assessments that support their overall information security and risk management objectives.
Best Practices for Effective Risk Assessment in IT
To ensure the effectiveness of risk assessment in IT and maximize its benefits, organizations should follow certain best practices. By adopting these practices, organizations can enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and comprehensiveness of their risk assessment processes. Some of the best practices for effective risk assessment in IT include:
- Establish Clear Objectives: Define clear objectives and scope for the risk assessment. Identify the specific goals, timelines, and desired outcomes of the assessment to ensure that it aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives and risk management priorities.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage stakeholders from different areas of the organization, including IT, security, legal, compliance, and business units. Collaboration and input from various perspectives ensure a comprehensive understanding of risks and improved decision-making during the risk assessment process.
- Develop a Risk Assessment Framework: Establish a risk assessment framework that outlines the methodology, processes, and criteria for assessing and evaluating risks. This framework should be tailored to the organization’s specific needs and enable a consistent and structured approach to risk assessment.
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Risk assessment should be an ongoing process rather than a one-time event. Regularly review and update risk assessments to account for changes in the threat landscape, technology, and organizational environment. This helps organizations maintain an accurate understanding of their risks and adapt their risk management strategies accordingly.
- Combine Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches: Use a combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches to assess risks. Qualitative methods, such as expert judgment and risk rating scales, provide insights into the likelihood and impact of risks. Quantitative methods, such as data analysis and modeling, offer a more objective assessment based on available data, improving the accuracy of risk assessment results.
- Utilize Relevant Data Sources: Gather and analyze reliable data from internal and external sources to support risk assessment. This can include historical incident data, threat intelligence, vulnerability reports, and industry benchmarks. Accurate and up-to-date data enhances the accuracy and validity of risk assessment outcomes.
- Consider Emerging Threats: Stay vigilant about emerging threats and evolving technologies that may introduce new risks. Continuously monitor the threat landscape, keep abreast of the latest cybersecurity trends, and incorporate emerging threats into risk assessments. This ensures that the organization is prepared to address new and emerging risks proactively.
- Document and Communicate Findings: Thoroughly document the risk assessment process, including the identified risks, analysis, and risk treatment decisions. Clear documentation ensures transparency, enables knowledge sharing, and facilitates future reviews and updates. Communicate the assessment findings and recommendations to relevant stakeholders, fostering a shared understanding of risks and risk management strategies.
- Integrate Risk Assessment into Overall Risk Management: Integrate risk assessment into the organization’s overall risk management framework. Link risk assessment results to risk treatment plans, business continuity strategies, incident response procedures, and ongoing monitoring and review processes. This ensures that risk assessment is a seamless and integrated part of the organization’s risk management practices.
- Regularly Review and Update Controls: Continuously assess the effectiveness of implemented controls and mitigation strategies. Regularly review and update control measures to address new vulnerabilities and emerging risks. This ensures that the organization’s risk mitigation efforts remain relevant and effective in light of evolving threats and changes in the IT environment.
By following these best practices, organizations can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of their risk assessment in IT. These practices enable organizations to identify, assess, and manage risks in a structured and proactive manner, ultimately helping them protect their IT systems, infrastructure, and data from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Risk assessment in IT is a critical process for organizations to proactively identify, evaluate, and manage potential risks to their information technology systems, infrastructure, and data. By conducting thorough risk assessments, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their IT risks and develop effective strategies to mitigate them.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various aspects of risk assessment in IT, including its definition, purpose, key components, steps involved, tools and techniques used, benefits, challenges, and best practices. We have seen that risk assessment helps organizations identify vulnerabilities, assess threats, prioritize risks, and allocate resources effectively.
Effective risk assessment in IT offers numerous benefits, such as early identification of risks, improved decision-making, compliance with regulations, enhanced security measures, and protection of reputation. It enables organizations to better protect their IT systems, infrastructure, and data, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical assets.
However, conducting risk assessments in IT does come with challenges. These challenges include the lack of data, complexity of IT systems, rapid technological advancements, dynamic threat landscapes, resource constraints, complexity of risk analysis, organizational culture, and regulatory compliance. Organizations must address these challenges by adopting best practices for risk assessment to maximize the benefits and overcome potential barriers.
In conclusion, risk assessment in IT is an essential process in today’s digital landscape. It empowers organizations to identify, assess, and manage risks effectively, ensuring the protection of their IT assets and supporting business continuity. By incorporating best practices, organizations can enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and comprehensiveness of their risk assessment processes, enabling them to make informed decisions and navigate the ever-evolving threat landscape.