Finance
What Are Risk Assessment Tools
Published: January 15, 2024
Learn how risk assessment tools in finance can help businesses manage and mitigate potential risks, ensuring financial stability and success.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of risk assessment tools, where data-driven decisions meet financial intelligence. In today’s rapidly changing business landscape, understanding and managing risks are crucial for the success of any organization. To effectively navigate the complexities of risk management, businesses rely on advanced tools and techniques that provide them with a comprehensive view of potential threats.
Risk assessment tools are powerful resources that enable businesses to identify, analyze, and evaluate potential risks and their potential impact. These tools help businesses in a variety of ways, from making informed investment decisions to mitigating potential losses.
In this article, we will explore the world of risk assessment tools, including the different types available, their benefits, challenges, and best practices for using them effectively. Whether you are a financial analyst, a risk manager, or a business owner, understanding these tools is essential to proactively manage risks and safeguard the financial health of your organization.
So, let’s dive in and discover the world of risk assessment tools!
Overview of Risk Assessment Tools
Risk assessment tools are designed to assist businesses in identifying and evaluating potential risks that may impact their operations. These tools provide a systematic approach to risk management by collecting relevant data, analyzing it, and providing insights and recommendations based on the findings.
At their core, risk assessment tools aim to quantify and assess the likelihood and potential impact of various risks, allowing businesses to prioritize and allocate resources effectively. By understanding the potential risks, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate or minimize their impact, enhancing the overall resilience and sustainability of the business.
Risk assessment tools act as a comprehensive framework for risk management, providing a structured approach to identify, assess, and manage risks. They take into account various factors, such as the nature of the business, industry-specific risks, regulatory requirements, and the organization’s risk appetite.
These tools leverage a combination of data analysis, statistical models, and advanced algorithms to assess risks. They can include both quantitative and qualitative methods, depending on the nature of the risk being evaluated. The output from risk assessment tools is often presented in the form of risk ratings, risk scores, or heat maps, allowing businesses to visually understand and prioritize risks.
It’s important to note that risk assessment tools are not one-size-fits-all solutions. They should be tailored to the specific needs and characteristics of each organization. Different industries and sectors may require different tools and methodologies to assess risks effectively. Therefore, businesses should choose risk assessment tools that align with their industry, organizational structure, and risk management objectives.
Overall, risk assessment tools play a critical role in helping businesses proactively manage risks. They provide valuable insights and enable organizations to make informed decisions to protect their financial stability and enhance their long-term success.
Common Types of Risk Assessment Tools
Risk assessment tools come in various forms and utilize different methodologies to evaluate and quantify risks. Here are some common types of risk assessment tools:
- Checklists and Questionnaires: This type of risk assessment tool involves a series of questions or a checklist that helps identify potential risks. It allows businesses to systematically evaluate their processes, operations, and environment to identify any areas of vulnerability.
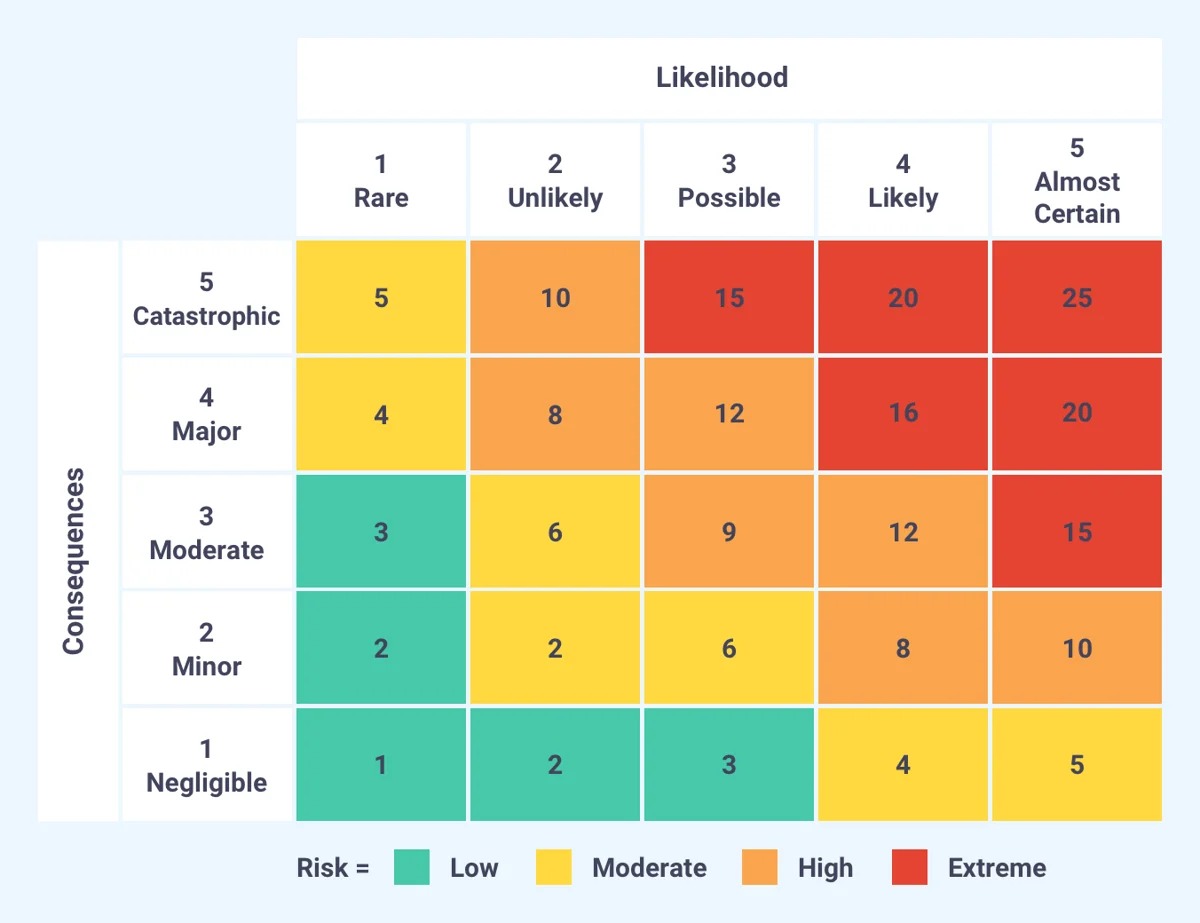
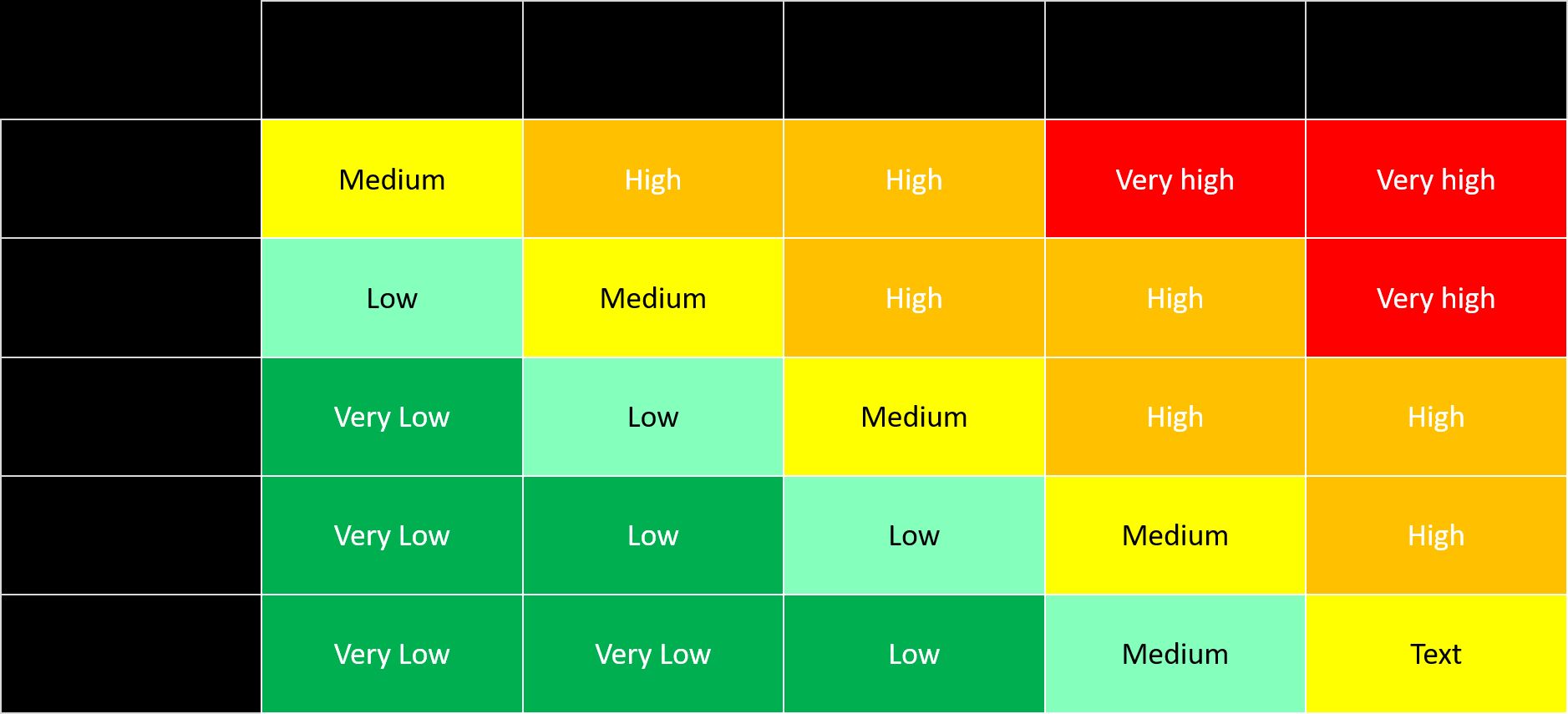
- Probability and Impact Matrix: The probability and impact matrix is a visual tool that helps assess risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. It involves assigning a probability rating and an impact rating to each identified risk, which are then plotted on a matrix to determine the overall risk level.
- Scenario Analysis: Scenario analysis involves assessing risks by considering a range of possible scenarios or events. It allows businesses to understand the potential impact of different scenarios on their operations and financial performance. This tool is particularly useful for identifying risks associated with unpredictable events, such as natural disasters or regulatory changes.
- Hazard Analysis: Hazard analysis focuses on identifying and assessing risks related to workplace safety and health. It involves examining the potential hazards and their potential impact on employees, assets, and the overall business. Hazard analysis is commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and healthcare.
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA): BIA is a tool used to identify and evaluate the potential consequences of a disruption to the business. It assesses the financial, operational, and reputational impacts that may arise from various risks, such as natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or supply chain disruptions.
- Loss Exposure Analysis: This tool focuses on quantifying the potential financial losses that may occur due to specific risks. Loss exposure analysis considers factors such as the value of assets, the probability of the risk occurring, and the financial impact if the risk materializes. It helps businesses prioritize risk mitigation efforts based on potential financial losses.
Each of these risk assessment tools serves a unique purpose and offers different insights into potential risks. Depending on the nature of your business and the specific risks you face, you may utilize one or a combination of these tools to gain a comprehensive understanding of your risk landscape.
Quantitative Risk Assessment Tools
Quantitative risk assessment tools are designed to assess risks using measurable data and mathematical models. These tools utilize statistical analysis and numerical calculations to quantify the likelihood and potential impact of risks. Here are some commonly used quantitative risk assessment tools:
- Monte Carlo Simulation: Monte Carlo simulation is a powerful tool that uses random sampling to model and analyze the impact of uncertainties in a system. It involves running multiple simulations based on different input variables to understand the range of possible outcomes and their associated probabilities. This tool is particularly useful for assessing financial risks, project risks, and investment decisions.
- Event Tree Analysis: Event tree analysis is a tool used to analyze the sequence of events that occur following a specific initiating event. It assesses the likelihood and consequences of different outcomes based on various branches of the event tree. This tool is commonly used in industries such as nuclear power, aerospace, and oil and gas.
- Fault Tree Analysis: Fault tree analysis is a tool used to analyze the causes and consequences of system failures. It involves constructing a graphical representation of events and their logical relationships, leading to a potential system failure. By quantifying the probabilities of individual events, fault tree analysis helps identify critical components or processes that contribute most to system failures.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Sensitivity analysis is a technique used to understand the impact of changes in input variables on the outcomes of a risk assessment. It helps identify the most influential factors and their effect on the overall risk profile. By varying the inputs within specified ranges, sensitivity analysis provides insights into the robustness of risk assessment results.
- Value at Risk (VaR): VaR is a widely used quantitative risk assessment tool in finance to measure and manage market risk. It estimates the maximum potential loss that can occur within a specified confidence level over a given time horizon. VaR considers the historical volatility of asset prices or portfolio values to determine the potential downside risk.
Quantitative risk assessment tools provide a systematic and analytical approach to evaluating risks based on numerical data. These tools offer businesses a quantitative basis for decision-making, allowing for more accurate risk management strategies and resource allocation.
Qualitative Risk Assessment Tools
Qualitative risk assessment tools are used to evaluate risks based on subjective judgments and expert opinions. These tools focus on understanding the characteristics and attributes of risks rather than quantifying them with numerical values. Here are some commonly used qualitative risk assessment tools:
- Risk Matrix: A risk matrix is a visual tool that assesses risks based on two dimensions: likelihood and impact. It involves categorizing risks into different levels of severity based on subjective assessments. The risk matrix helps prioritize risks and determine appropriate risk response strategies.
- Expert Interviews: Expert interviews involve consulting subject matter experts within the organization or industry to gather insights and opinions about potential risks. These interviews provide qualitative information about risks, their likelihood, and potential impacts. Expert interviews help capture tacit knowledge and perspectives that may not be captured by other tools.
- Delphi Technique: The Delphi technique is a structured approach that involves collecting opinions and judgments from a panel of experts anonymously. Through a series of iterative rounds, the panel members review and refine their responses based on the feedback from other experts. The Delphi technique helps achieve consensus and reduce bias in risk assessments.
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is a tool commonly used to assess risks in a strategic context. It involves evaluating the internal strengths and weaknesses of the organization, as well as the external opportunities and threats it faces. SWOT analysis helps identify risks associated with market dynamics, competitive landscape, and internal capabilities.
- Causal Analysis: Causal analysis, also known as root cause analysis, focuses on identifying the underlying causes and contributing factors of risks. This qualitative tool helps uncover the reasons behind risks and provides insights into potential mitigation strategies. Causal analysis is particularly useful for identifying risks resulting from human errors or system failures.
Qualitative risk assessment tools offer a more subjective and nuanced understanding of risks. They are particularly valuable when dealing with complex and ambiguous risks that cannot be easily quantified. These tools leverage the expertise and judgment of individuals to assess risks and provide qualitative insights for risk management decision-making.
Benefits of Using Risk Assessment Tools
Utilizing risk assessment tools offers numerous benefits for businesses in effectively managing risks and making informed decisions. Here are some key benefits of using risk assessment tools:
- Identification of Potential Risks: Risk assessment tools help businesses identify potential risks that may otherwise go unnoticed. By systematically evaluating different aspects of the organization’s operations, processes, and environment, these tools uncover vulnerabilities and areas of potential concern.
- Quantification of Risks: Risk assessment tools, particularly quantitative ones, provide a means to quantify risks in terms of their likelihood and potential impact. This allows businesses to prioritize and allocate resources based on the level of risk, ensuring that limited resources are directed towards managing high-impact risks.
- Informed Decision-Making: With risk assessment tools, businesses can make informed decisions by considering the potential risks and their associated consequences. By understanding the potential impacts of different courses of action, organizations can select the best options and develop appropriate risk management strategies.
- Financial Protection: Risk assessment tools help businesses protect their financial interests by identifying and mitigating potential risks that may result in financial losses. By proactively managing risks, organizations can avoid or minimize the financial impact of adverse events, ensuring the long-term financial stability and sustainability of the business.
- Enhanced Resilience and Adaptability: Through the use of risk assessment tools, businesses can enhance their resilience and adaptability to changing circumstances. By identifying potential risks, organizations can develop contingency plans and strategies to effectively respond to unexpected events, ensuring business continuity and mitigating potential disruptions.
- Improved Communication and Stakeholder Confidence: Risk assessment tools provide a clear and structured framework for communicating risks to stakeholders. By presenting risks in a visual and understandable format, businesses can enhance stakeholder confidence and transparency. This is especially important for investors, lenders, regulators, and other external parties who rely on accurate risk information to make decisions.
Overall, utilizing risk assessment tools brings numerous benefits to businesses, enabling them to proactively manage risks, make informed decisions, protect their financial interests, and enhance their overall resilience and adaptability in a rapidly changing business environment.
Challenges and Limitations of Risk Assessment Tools
While risk assessment tools provide valuable insights, they also come with certain challenges and limitations that businesses should be aware of. Here are some common challenges and limitations associated with risk assessment tools:
- Data Limitations: Risk assessment tools heavily rely on data for accurate analysis. However, data availability, quality, and completeness can be a challenge. Inaccurate or incomplete data may lead to biased risk assessments and inaccurate predictions. Obtaining relevant and reliable data can be a significant challenge, especially for emerging or rapidly changing risks.
- Uncertainty and Assumptions: Risk assessment tools often require assumptions and simplifications due to the uncertainty associated with future events. The accuracy of the risk assessment heavily depends on the validity of these assumptions. Any deviation from the assumed conditions may have a significant impact on the accuracy of the risk assessment results.
- Complexity and Expertise: Some risk assessment tools, particularly quantitative ones, can be complex and require a certain level of expertise to understand and implement. These tools may involve statistical models, mathematical calculations, and advanced algorithms that require experienced analysts to ensure accurate interpretation and meaningful results.
- Subjectivity and Bias: Qualitative risk assessment tools are inherently subjective and rely on human judgment. This subjectivity introduces the potential for bias in the assessment, as different individuals may interpret risks differently. There is a risk of overestimating or underestimating risks due to bias or inadequate expertise, which may lead to ineffective risk management strategies.
- Dynamic Nature of Risks: Risks are dynamic and continuously evolving. Risk assessment tools may not always capture the real-time changes in the risk landscape. It is essential for businesses to regularly review and update their risk assessments to account for new risks, changes in risk profiles, and emerging threats.
- Interdependencies and Systemic Risks: Risk assessment tools often focus on individual risks and may not adequately consider interdependencies and systemic risks. Certain risks may be interconnected and have a cascading effect on multiple aspects of the business. Failure to identify and assess these interdependencies can result in incomplete risk assessments.
Despite these challenges and limitations, risk assessment tools remain valuable resources for businesses in managing risks. It is important to approach the use of these tools with a critical mindset, understanding their limitations and using them in conjunction with other risk management practices to enhance overall risk awareness and decision-making.
Best Practices for Using Risk Assessment Tools
Effectively utilizing risk assessment tools requires a thorough understanding of their capabilities and limitations. Here are some best practices to consider when using risk assessment tools:
- Define Clear Objectives: Before using any risk assessment tool, clearly define the objectives and scope of the assessment. Understand what you aim to achieve and what risks you want to assess. This will help you select the most appropriate tool and focus your efforts on the most relevant risks.
- Ensure Data Quality: Pay careful attention to the quality and reliability of the data used in the risk assessment process. Ensure the data is accurate, up-to-date, and relevant to the risks being assessed. Validate and verify data sources to enhance the credibility of the risk assessment results.
- Combine Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches: Consider using a combination of quantitative and qualitative risk assessment tools to gain a comprehensive understanding of the risks. Quantitative tools provide numerical analysis while qualitative tools offer valuable insights and expert opinions. Together, they provide a more holistic view of the risk landscape.
- Involve Multiple Stakeholders: Engage various stakeholders throughout the risk assessment process. This includes subject matter experts, management, employees, and external stakeholders. Different perspectives and expertise ensure a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of risks.
- Regularly Review and Update: Risk assessments should not be treated as one-time exercises. Regularly review and update the risk assessment to keep it relevant and aligned with the changing organizational and industry landscapes. New risks may emerge, and existing risks may evolve, requiring ongoing monitoring and evaluation.
- Consider Scenario Planning: In addition to assessing individual risks, consider utilizing scenario planning. This involves analyzing potential future scenarios and their associated risks. By exploring different what-if scenarios, you can anticipate and prepare for potential risks and develop contingency plans accordingly.
- Communicate Risks Effectively: Use clear and concise language to communicate the results and findings of the risk assessment. Tailor the communication to different stakeholders, ensuring that the information is easily understandable and actionable. Visual representations such as charts, graphs, or heat maps can be helpful in conveying complex information.
- Integrate Risk Management into Decision-Making: Use risk assessment tools as a tool to inform decision-making processes. Consider the risk assessments when making strategic, operational, and investment decisions. Integrate risk management practices into the organization’s culture, ensuring risks are considered at all levels of decision-making.
By following these best practices, businesses can maximize the value and effectiveness of risk assessment tools in identifying, evaluating, and managing risks proactively.
Conclusion
Risk assessment tools are indispensable resources for businesses seeking to manage and mitigate the potential risks they face. These tools provide a structured and systematic approach to identify, assess, and prioritize risks. By utilizing both quantitative and qualitative methodologies, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of the risk landscape and make informed decisions to protect their financial well-being.
While risk assessment tools offer numerous benefits, they also come with challenges and limitations. Data limitations, subjective judgments, and the dynamic nature of risks can pose obstacles to the accuracy and effectiveness of these tools. However, by following best practices such as defining clear objectives, ensuring data quality, and involving multiple stakeholders, businesses can overcome these challenges and leverage risk assessment tools to their advantage.
It is important to note that risk assessment should be an ongoing process rather than a one-time exercise. Regularly reviewing and updating risk assessments ensures that organizations stay attuned to evolving risks and can adapt their strategies accordingly. By integrating risk management practices into decision-making processes and effectively communicating risks to stakeholders, businesses can foster resilience, adaptability, and informed decision-making in the face of uncertainty.
Ultimately, risk assessment tools serve as invaluable tools in the arsenal of businesses striving to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape. By embracing these tools, organizations can build a strong foundation for proactive risk management and safeguard their long-term success.