Finance
How To Clone An EMV Chip Card
Published: March 6, 2024
Learn how to clone an EMV chip card and protect your finances with our step-by-step guide. Safeguard your financial security today.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The advent of EMV chip cards has revolutionized the way we conduct transactions, offering enhanced security and protection against fraudulent activities. However, with the rise of technology, there has been an increasing concern about the potential for these cards to be cloned, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive financial information. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of EMV chip cards, explore the concept of cloning, and examine the associated risks and legal implications. Additionally, we will provide valuable insights into safeguarding against such illicit activities.
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, it is crucial for consumers to stay informed about the potential vulnerabilities associated with their payment methods. By understanding the complexities of EMV chip card technology and the methods used to clone these cards, individuals can take proactive measures to protect themselves from falling victim to fraudulent activities. Furthermore, gaining insight into the legal ramifications and the steps required to mitigate the risks associated with card cloning is essential for maintaining financial security in an increasingly digital world.
Throughout this article, we will unravel the intricacies of EMV chip card cloning, shedding light on the various techniques employed by fraudsters to compromise the security of these cards. By empowering readers with a comprehensive understanding of this subject, we aim to equip them with the knowledge necessary to safeguard their financial assets and personal information. It is imperative to remain vigilant and proactive in the face of evolving financial threats, and this article serves as a valuable resource for individuals seeking to fortify their defenses against EMV chip card cloning.
Understanding EMV Chip Cards
EMV chip cards, named after the three companies that developed the technology—Europay, Mastercard, and Visa—represent a significant advancement in payment security. Unlike traditional magnetic stripe cards, EMV chip cards store data on an embedded microprocessor chip, providing dynamic authentication for each transaction. This technology effectively combats counterfeit card fraud, as the unique transaction data generated by the chip makes it extremely difficult for fraudsters to replicate the card for unauthorized use.
One of the key features of EMV chip cards is their ability to generate a unique cryptogram for every transaction, ensuring that the data cannot be reused for fraudulent purposes. This dynamic authentication process significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive cardholder information, bolstering the overall security of payment transactions. Furthermore, EMV chip cards are designed to withstand sophisticated hacking attempts, offering a robust defense mechanism against various forms of financial fraud.
Another notable aspect of EMV chip cards is their compatibility with contactless payment methods, allowing users to complete transactions by simply tapping their cards on compatible terminals. This seamless and secure payment process has gained widespread popularity, offering unparalleled convenience without compromising security. Additionally, EMV chip cards are equipped with advanced encryption capabilities, safeguarding cardholder data and minimizing the risk of interception by malicious entities.
As the financial industry continues to embrace the benefits of EMV chip technology, consumers can expect a heightened level of security and protection against fraudulent activities. By leveraging the advanced features of EMV chip cards, individuals can conduct transactions with confidence, knowing that their sensitive financial information is shielded by robust security measures. However, despite the formidable defenses offered by EMV chip cards, it is essential for consumers to remain vigilant and informed about potential threats, including the risk of card cloning and unauthorized access.
Cloning EMV Chip Cards
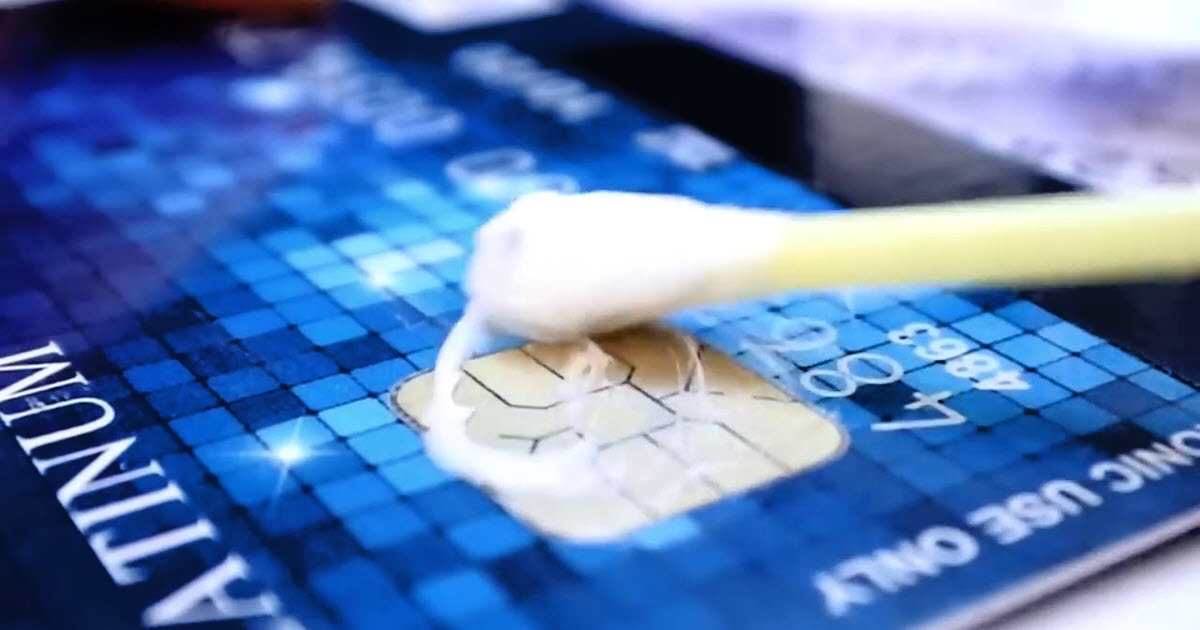
Cloning EMV chip cards involves the illicit replication of card data and security features, allowing fraudsters to create counterfeit cards for unauthorized transactions. While EMV chip technology has significantly reduced the prevalence of card cloning, determined criminals continue to explore methods to circumvent these advanced security measures. One of the primary techniques used to clone EMV chip cards involves skimming, where malicious devices are used to extract card data during legitimate transactions.
Skimming devices, often disguised as legitimate card readers, capture the sensitive information stored on the chip, including the cardholder’s name, card number, and expiration date. Subsequently, this stolen data is used to create counterfeit cards, which can be utilized for unauthorized transactions. Additionally, fraudsters may attempt to intercept the communication between the chip and the terminal, exploiting vulnerabilities to extract critical authentication data and replicate it for fraudulent purposes.
Despite the formidable security features of EMV chip cards, determined criminals continue to explore sophisticated methods to clone these cards, posing a significant threat to consumers and financial institutions. The proliferation of online resources and black-market platforms has facilitated the exchange of illicit techniques and tools, enabling individuals with malicious intent to engage in card cloning activities. As a result, it is imperative for consumers to remain vigilant and adopt proactive measures to safeguard their EMV chip cards against potential cloning attempts.
Risks and Consequences
The proliferation of EMV chip card cloning poses severe risks to consumers, financial institutions, and the broader economy. When an EMV chip card is successfully cloned, the unauthorized party gains access to sensitive financial information, enabling them to conduct fraudulent transactions and potentially compromise the cardholder’s financial security. The consequences of such illicit activities extend beyond financial losses, encompassing reputational damage to the affected individuals and institutions.
For consumers, the risks associated with EMV chip card cloning include unauthorized transactions, potential identity theft, and the compromise of personal financial data. In addition to the financial ramifications, victims of card cloning may experience considerable distress and inconvenience as they navigate the process of reporting and resolving fraudulent activities. Furthermore, the erosion of trust in financial institutions and payment systems can have far-reaching implications, impacting consumer confidence and the overall stability of the financial ecosystem.
Financial institutions face significant challenges in mitigating the risks associated with EMV chip card cloning, including the potential for widespread fraud, regulatory scrutiny, and reputational damage. The detection and resolution of fraudulent activities require substantial resources, and the impact of successful card cloning incidents can undermine the integrity of the payment infrastructure. Moreover, the erosion of consumer trust in payment systems can have detrimental effects on the long-term viability of financial institutions and their ability to foster a secure and resilient financial environment.
From a broader economic perspective, the prevalence of EMV chip card cloning introduces systemic risks that can undermine the stability and integrity of the financial sector. The potential for widespread fraud and the erosion of consumer confidence can disrupt the efficient functioning of payment systems, leading to cascading effects on economic activity and financial stability. As such, addressing the risks and consequences associated with EMV chip card cloning is essential for preserving the trust and reliability of the financial infrastructure.
Legal Implications
The unauthorized cloning of EMV chip cards carries significant legal implications, as it constitutes a form of financial fraud and identity theft. Individuals found guilty of engaging in card cloning activities may face severe legal consequences, including criminal charges, fines, and imprisonment. The legal framework governing financial fraud varies by jurisdiction, but the penalties for EMV chip card cloning are typically stringent to deter illicit activities and protect the integrity of the payment ecosystem.
In many jurisdictions, the act of cloning EMV chip cards is classified as a serious offense, with potential charges including fraud, identity theft, and unauthorized access to sensitive financial data. The legal ramifications of engaging in card cloning activities extend beyond individual perpetrators to encompass entities that facilitate or enable such illicit practices. This includes individuals involved in the distribution of skimming devices, the sale of counterfeit cards, or the provision of illicit services related to card cloning.
Financial institutions and payment service providers are also subject to legal obligations related to EMV chip card security, including the implementation of robust measures to prevent and detect card cloning activities. Failure to fulfill these obligations may result in regulatory sanctions, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Additionally, the legal framework often mandates the collaboration between law enforcement agencies, financial institutions, and regulatory authorities to investigate and prosecute instances of EMV chip card cloning.
It is essential for individuals and organizations to be cognizant of the legal implications associated with EMV chip card cloning, as compliance with the prevailing regulatory framework is imperative for maintaining the integrity of the financial system. By upholding legal standards and actively participating in efforts to combat card cloning, stakeholders can contribute to the preservation of a secure and trustworthy payment environment, safeguarding the interests of consumers and the broader economy.
Protecting Against Cloning
As the threat of EMV chip card cloning persists, it is imperative for consumers and financial institutions to adopt proactive measures to mitigate the risks and bolster the security of payment transactions. One of the fundamental strategies for protecting against cloning involves maintaining heightened awareness and vigilance during card usage. Individuals should scrutinize card readers and terminals for any signs of tampering or unauthorized attachments, as skimming devices are often discreetly installed to capture card data.
Furthermore, the use of contactless payment methods, such as mobile wallets and wearable devices, can offer an additional layer of security by minimizing physical interaction with potentially compromised terminals. Contactless transactions leverage advanced encryption and tokenization technologies to safeguard cardholder data, reducing the risk of interception and unauthorized access. By embracing these secure payment alternatives, consumers can mitigate the vulnerabilities associated with traditional card-present transactions.
Financial institutions play a pivotal role in protecting against EMV chip card cloning by implementing robust fraud detection and prevention mechanisms. This includes real-time monitoring of transactional patterns, the deployment of advanced analytics to detect anomalies, and the continuous enhancement of security protocols to thwart emerging threats. Additionally, the integration of biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, can fortify the security of card-present transactions, offering a reliable means of verifying the cardholder’s identity.
Education and awareness initiatives are essential components of protecting against EMV chip card cloning, empowering consumers with the knowledge and resources to identify and report suspicious activities. Financial institutions and regulatory authorities can collaborate to disseminate information about the latest trends in card cloning and provide guidance on best practices for safeguarding sensitive financial information. By fostering a culture of vigilance and accountability, stakeholders can collectively contribute to the prevention and detection of EMV chip card cloning.
Ultimately, the convergence of technological innovation, consumer awareness, and industry collaboration is pivotal in fortifying the defenses against EMV chip card cloning. By embracing secure payment practices, leveraging advanced authentication methods, and fostering a collective commitment to combat illicit activities, stakeholders can mitigate the risks posed by card cloning and uphold the integrity of the payment ecosystem.
Conclusion
The advent of EMV chip cards has ushered in a new era of payment security, offering robust defenses against fraudulent activities while enhancing the overall integrity of the financial ecosystem. However, the persistent threat of EMV chip card cloning underscores the importance of remaining vigilant and proactive in safeguarding sensitive financial information. As technology continues to evolve, so too do the tactics employed by fraudsters, necessitating a collective commitment to fortify the defenses against illicit activities.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of EMV chip card technology and the methods used to clone these cards, consumers can empower themselves with the knowledge necessary to mitigate the risks and protect their financial assets. Additionally, financial institutions play a pivotal role in combating card cloning by implementing advanced security measures, leveraging innovative authentication methods, and fostering a culture of awareness and vigilance.
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the convergence of technological innovation, consumer education, and industry collaboration is essential for preserving the trust and reliability of payment systems. By embracing secure payment practices, leveraging advanced authentication methods, and fostering a collective commitment to combat illicit activities, stakeholders can collectively contribute to the prevention and detection of EMV chip card cloning.
Ultimately, the preservation of a secure and resilient payment environment requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing technological advancements, regulatory diligence, and consumer empowerment. By aligning these elements, stakeholders can uphold the integrity of the financial infrastructure, safeguard the interests of consumers, and mitigate the risks posed by EMV chip card cloning. As we navigate the dynamic landscape of financial security, it is imperative to remain proactive and adaptable, leveraging the latest innovations and best practices to fortify the defenses against emerging threats.