Finance
How To Disable An EMV Chip
Published: March 6, 2024
Learn how to disable an EMV chip to protect your finances and prevent unauthorized transactions. Follow our step-by-step guide to safeguard your financial security.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the digital age, where cashless transactions have become the norm. With the widespread adoption of credit and debit cards, the technology behind these financial tools has evolved to provide enhanced security and convenience. One of the most significant advancements in this realm is the introduction of EMV chips, which have revolutionized the way we make in-person transactions.
However, there are instances where individuals may consider disabling their EMV chips for various reasons. Whether it’s due to a preference for alternative payment methods or specific circumstances, understanding the process of disabling an EMV chip can be valuable knowledge.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of EMV chips, explore the reasons why one might want to disable them, and discuss the methods available for accomplishing this task. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of the considerations involved in disabling an EMV chip and the potential implications of doing so.
What is an EMV Chip?
The EMV chip, named after its original developers Europay, Mastercard, and Visa, is a small, metallic square embedded in credit and debit cards. This technology represents a significant upgrade from traditional magnetic stripe cards, offering advanced security features and reducing the risk of fraud during in-person transactions.
Unlike magnetic stripe cards, which store static data that can be easily replicated, EMV chips generate dynamic data for each transaction, making it extremely difficult for fraudsters to clone or counterfeit the card. This dynamic authentication process, known as EMV technology, has significantly enhanced the security of card-present transactions, providing peace of mind to both cardholders and merchants.
EMV chips are equipped with microprocessors that enable them to interact with EMV-compliant payment terminals, creating a unique transaction code for each purchase. This technology, often referred to as “chip and PIN” or “chip and signature,” has become the global standard for card-present transactions, offering a more secure alternative to traditional magnetic stripe cards.
Furthermore, EMV chips can store a wealth of information, including cardholder data, account details, and cryptographic keys, all of which contribute to the robust security measures implemented within the chip. As a result, the adoption of EMV technology has significantly reduced instances of counterfeit card fraud and unauthorized transactions, bolstering consumer confidence in the safety of electronic payments.
Overall, the EMV chip represents a pivotal advancement in payment card technology, prioritizing security and fraud prevention in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
Reasons for Disabling an EMV Chip
While EMV chips offer robust security and protection against fraudulent activities, there are specific scenarios where individuals may contemplate disabling the chip functionality on their payment cards. Understanding the reasons behind this consideration is essential for gaining insight into the diverse needs and preferences of cardholders.
- Compatibility: In some regions or with certain merchants, EMV chip technology may not be universally accepted or compatible with the available payment infrastructure. As a result, individuals may opt to disable the chip to facilitate smoother transactions using the magnetic stripe or alternative methods.
- Preference for Contactless Payments: With the increasing popularity of contactless payment methods, some individuals may prefer to use this feature exclusively, bypassing the EMV chip functionality altogether. Disabling the chip allows for seamless utilization of contactless payment options, aligning with the user’s preferences and convenience.
- Card Testing and Development: In the realm of card testing, development, and research, disabling the EMV chip can provide a controlled environment for analyzing and experimenting with card functionalities, security protocols, and transaction processes. This practice is instrumental in the continuous improvement and innovation of payment card technologies.
- Legacy Systems and Equipment: In certain situations, legacy payment systems or equipment may not support EMV chip transactions, compelling individuals to disable the chip to ensure compatibility and uninterrupted usage of their payment cards.
It is important to note that the decision to disable an EMV chip should be approached with careful consideration, as it directly impacts the security and authentication mechanisms embedded within the card. While these reasons shed light on the circumstances where disabling the chip may be warranted, individuals should assess the implications and weigh the associated risks before proceeding with this action.
Methods to Disable an EMV Chip
Disabling an EMV chip involves altering the functionality of the chip within a payment card, a process that requires careful consideration and adherence to specific methods. While this action should be approached with caution due to its potential impact on security and transaction processes, there are several approaches to accomplishing this task.
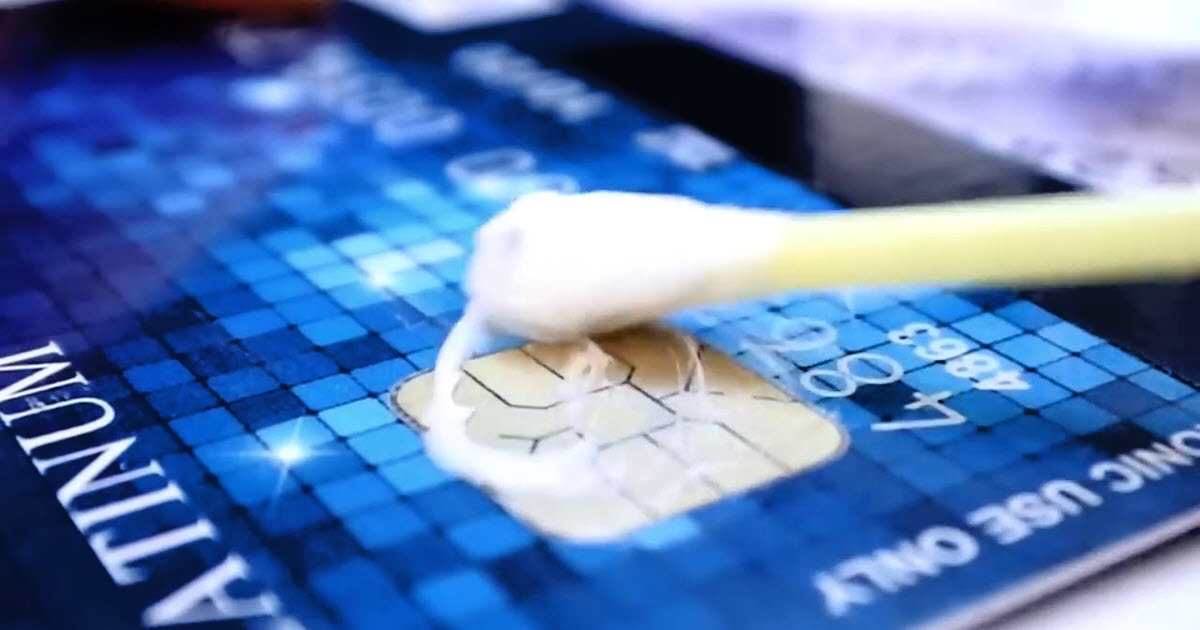
- Physical Modification: One method of disabling an EMV chip involves physically altering the card to render the chip inoperable. This may include drilling a hole through the chip or using heat to deactivate its functionality. However, it is crucial to recognize that such modifications may damage the card and could potentially violate terms of use set by the card issuer.
- Blocking the Chip’s Contacts: By strategically applying tape or a specialized material over the chip’s contacts, individuals can obstruct the electrical connection, effectively preventing the chip from engaging with EMV-compliant terminals. While this method is non-invasive and reversible, it may still raise concerns regarding the card’s integrity and compliance with usage guidelines.
- Seeking Issuer Assistance: Some card issuers may offer the option to disable the EMV chip through official channels, allowing cardholders to request this modification in accordance with their preferences or specific requirements. This approach ensures compliance with the issuer’s policies and may provide a more secure and authorized method of disabling the chip.
It is imperative to emphasize that disabling an EMV chip should be approached with caution, as it may impact the card’s security features and compliance with industry standards. Individuals contemplating this action should carefully assess the potential implications and consider consulting with their card issuer or financial institution to explore authorized avenues for addressing their specific needs.
Conclusion
As we navigate the intricacies of modern payment technologies, the presence of EMV chips in credit and debit cards represents a pivotal advancement in safeguarding transactions and mitigating fraudulent activities. However, the decision to disable an EMV chip warrants thoughtful consideration, as it involves altering the security mechanisms embedded within the card and may impact its compatibility with payment terminals and systems.
Understanding the reasons behind disabling an EMV chip, such as regional compatibility, preference for contactless payments, and specialized testing and development needs, underscores the diverse circumstances that may prompt individuals to explore this option. It is crucial to recognize that while certain methods exist for disabling the chip, such actions should be approached with caution and adherence to issuer guidelines to ensure the integrity and security of the payment card.
Ultimately, the decision to disable an EMV chip should be driven by a thorough assessment of individual needs, compliance with usage regulations, and consideration of potential impacts on transaction security and convenience. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about the intricacies of payment technologies empowers individuals to make informed decisions aligned with their preferences and requirements.
By balancing the advantages of EMV chip technology with the considerations surrounding its potential disablement, individuals can navigate the realm of cashless transactions with confidence and clarity, leveraging the security features and flexibility offered by modern payment cards.