Finance
Endowment Loan Definition
Published: November 18, 2023
Learn the meaning of an endowment loan in the world of finance. Explore how this unique financial instrument can help you achieve your long-term financial goals.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Endowment Loan: A Complete Guide
Finance plays a crucial role in our lives, allowing us to meet our goals and aspirations. One financial tool that you may have come across is an endowment loan. But what is an endowment loan, and how does it work? In this comprehensive guide, we will dive into the world of endowment loans and help you understand how they can be utilized to achieve your financial goals.
Key Takeaways:
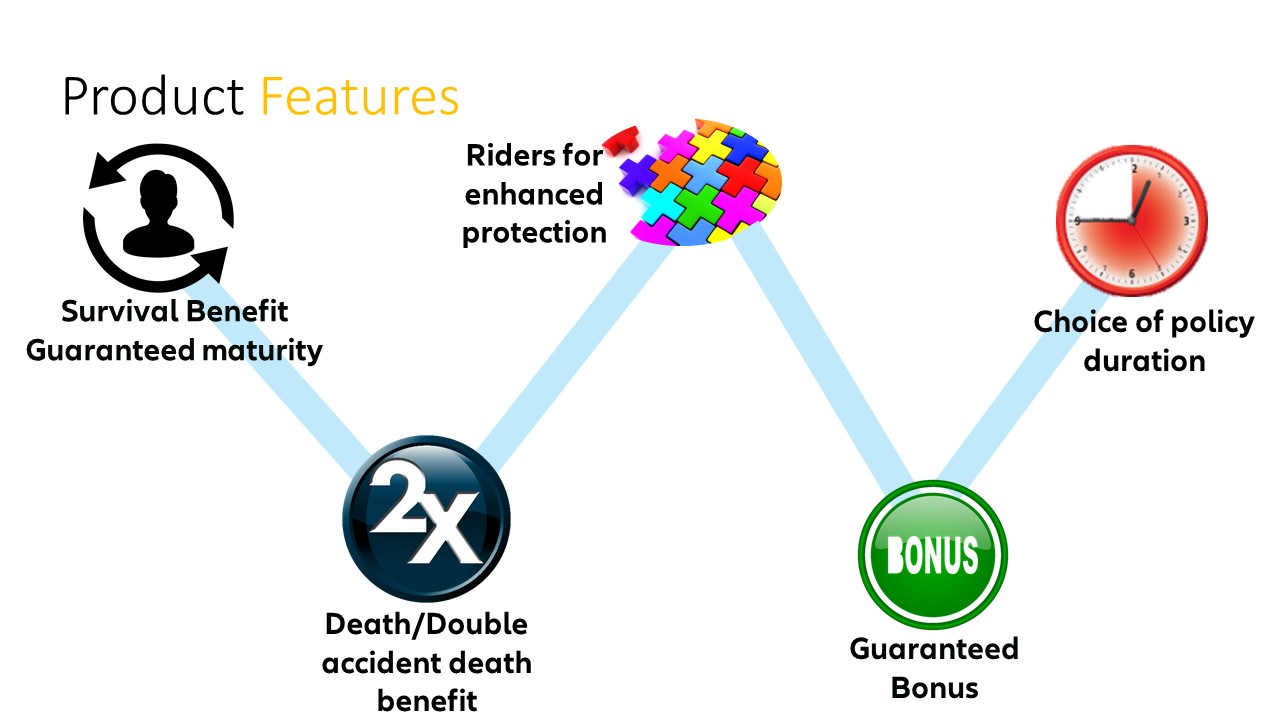
- An endowment loan is a type of borrowing in which the borrower pledges an endowment policy as collateral.
- Endowment loans offer the potential for both loan value and accumulated policy benefits.
What is an Endowment Loan?
An endowment loan, also known as an endowment policy loan, is a type of borrowing in which the borrower pledges an endowment policy as collateral. An endowment policy is essentially a life insurance policy that comes with an investment component. The borrower can use the endowment policy as security for obtaining a loan from a financial institution.
Endowment loans offer borrowers the potential for both the loan value and accumulated policy benefits. This means that the borrower not only obtains the desired loan amount but also retains the potential to benefit from the investment returns of the endowment policy, such as bonuses or dividends.
How Does an Endowment Loan Work?
The process of obtaining an endowment loan involves a few steps:
- Evaluation of the endowment policy: The financial institution evaluates the endowment policy to determine its current surrender value, which is the amount that can be borrowed against the policy.
- Pledging the endowment policy: Once the surrender value is determined, the borrower pledges the endowment policy as collateral for the loan.
- Loan approval: If the financial institution is satisfied with the collateral and the borrower’s creditworthiness, the loan is approved, and the funds are disbursed.
- Loan repayment: The borrower repays the loan over a predetermined period, typically through installments that include both principal and interest.
- Policy benefits: Throughout the loan tenure, the borrower continues to receive the policy benefits, such as bonuses or dividends, unless stated otherwise in the loan agreement.
Advantages of Endowment Loans:
Endowment loans come with several advantages that make them an attractive option for borrowers:
- Access to funds: By pledging an endowment policy, borrowers can access funds that they can utilize for various purposes, such as education, home improvements, or debt consolidation.
- Potential returns: With an endowment loan, borrowers retain the potential for policy benefits, which may include investment returns or bonuses accumulated in the policy.
- Lower interest rates: Since the endowment policy serves as collateral, financial institutions often offer comparatively lower interest rates on endowment loans.
- Flexible repayment options: Borrowers can choose repayment terms that suit their financial situation, including the loan amount, interest rate, and repayment duration.
The Risks to Consider:
While endowment loans offer benefits, it is important to consider the associated risks as well:
- Limited policy benefits: Borrowers should note that during the loan tenure, the policy benefits may be impacted by the loan amount and interest payments.
- Potential loss of policy: In case of default on loan repayments, the financial institution may exercise their right to surrender the endowment policy, leading to a loss of not only the policy benefits but also the investment component.
- Interest and charges: Borrowers need to consider the interest charges and fees associated with endowment loans, as they can impact the overall cost of borrowing.
In Conclusion:
An endowment loan can be a valuable financial tool for those looking to borrow against their endowment policies. It provides borrowers with access to funds while retaining the potential for policy benefits. However, borrowers need to carefully evaluate the risks and costs associated with endowment loans before making a decision. If you have an endowment policy and are in need of funds, exploring an endowment loan could be a wise consideration.