Finance
What Is Endowment Insurance?
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about endowment insurance in the finance industry, its benefits, and how it can help secure your financial future.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Endowment Insurance
- Features of Endowment Insurance
- How Endowment Insurance Works
- Types of Endowment Insurance
- Benefits of Endowment Insurance
- Drawbacks of Endowment Insurance
- Factors to Consider before Purchasing Endowment Insurance
- Comparison of Endowment Insurance with Other Insurance Plans
- Conclusion
Introduction
Endowment insurance is a type of life insurance policy that provides both protection and savings benefits to policyholders. It combines the elements of life insurance coverage with a savings component, offering individuals a dual-purpose financial tool. The main objective of endowment insurance is to provide a lump sum payout to the policyholder or their beneficiaries either upon the policy’s maturity or in the event of the insured person’s death.
Endowment insurance policies are designed to offer financial security and peace of mind to individuals and their loved ones. With this type of insurance, individuals can ensure that their beneficiaries are protected financially in the unfortunate event of their premature death. Additionally, endowment insurance serves as a long-term savings vehicle, allowing individuals to accumulate funds over a specified period of time, which can be used for various purposes such as funding education, buying a house, or securing retirement.
Endowment insurance policies are offered by insurance companies and are typically available in various forms to cater to the unique needs and preferences of policyholders. These policies can be customized according to the desired coverage amount, policy term, and premium payments. It is important to note that endowment insurance policies come with certain terms and conditions that individuals need to understand before making a purchase.
In this article, we will delve into the details of endowment insurance, including its definition, features, working mechanism, different types available, as well as the benefits and drawbacks associated with it. We will also discuss the factors individuals should consider before purchasing endowment insurance and how it compares to other insurance plans. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of endowment insurance and be equipped to make an informed decision regarding its suitability for your financial needs.
Definition of Endowment Insurance
Endowment insurance is a type of life insurance policy that offers a combination of protection and savings benefits. It is designed to provide the policyholder with a lump sum payout at a predetermined maturity date or in the event of the insured individual’s death, whichever comes first. This type of insurance policy serves as a financial tool that not only offers coverage for unforeseen circumstances but also helps individuals build savings over time.
Endowment insurance policies have a specific term, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. During this term, policyholders make regular premium payments, which are used to fund the insurance coverage as well as accumulate a cash value within the policy. The cash value grows over time through investments made by the insurance company, such as stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments. At the end of the policy term, the policyholder receives the accumulated cash value as a lump sum payout.
If the policyholder passes away during the term of the policy, the beneficiaries named in the policy will receive the death benefit, which is typically higher than the accumulated cash value. This payout assists the beneficiaries in maintaining their financial stability and meeting expenses in the absence of the policyholder’s income.
Endowment insurance is different from traditional life insurance policies in that it provides both protection and savings components. Unlike term life insurance, which solely offers death benefit protection for a specified period, endowment insurance combines both a savings component and a death benefit. This makes it an attractive option for individuals who want to secure their family’s financial future while also accumulating funds for other financial goals.
It is important to note that endowment insurance policies have a higher cost compared to term life insurance policies with similar coverage amounts. This is because a portion of the premium goes towards building the cash value, as well as covering the insurance risk. Therefore, endowment insurance is suitable for individuals who prioritize both protection and savings, and are willing to pay a higher premium for the additional benefits it provides.
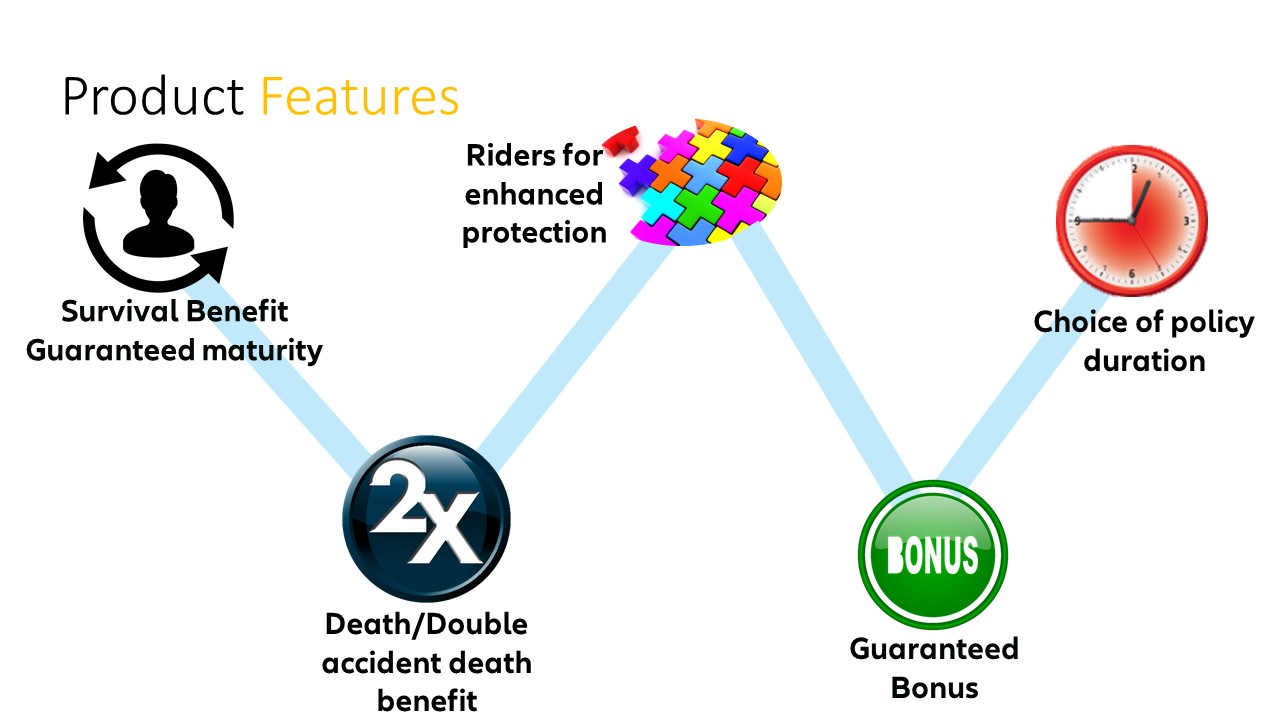
Features of Endowment Insurance
Endowment insurance comes with several distinct features that set it apart from other types of insurance policies. Understanding these features is essential for individuals considering purchasing endowment insurance. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key features:
- Dual-purpose insurance: Endowment insurance provides both life insurance coverage and a savings component. Policyholders can protect their loved ones financially in the event of their premature death, while also accumulating funds over time to meet other financial goals.
- Maturity benefit: Endowment insurance policies have a specific maturity date, usually ranging from 10 to 30 years. At the end of the policy term, the policyholder receives the accumulated cash value as a lump sum payout. This maturity benefit can be used for various purposes such as funding education, starting a business, or enjoying retirement.
- Death benefit: In the unfortunate event of the insured individual’s death during the policy term, endowment insurance provides a death benefit to the beneficiaries named in the policy. The death benefit is typically higher than the accumulated cash value, offering financial protection to the policyholder’s loved ones.
- Guaranteed returns: Endowment insurance policies often come with a guaranteed minimum return on the accumulated cash value. This ensures that the policyholder will receive a certain amount, even if the investments made by the insurance company do not perform as expected.
- Flexibility in premium payments: Endowment insurance policies offer flexibility in premium payments. Policyholders can choose to pay premiums annually, semi-annually, quarterly, or monthly, depending on their financial situation and preferences.
- Policy customization: Insurance companies offer various customization options for endowment insurance policies. Policyholders can select the desired coverage amount, policy term, and premium payment schedule that aligns with their financial goals and circumstances.
- Tax advantages: In many countries, endowment insurance policies offer tax advantages. Policyholders may be eligible for tax deductions on the premium payments or tax-free withdrawals of the accumulated cash value, making endowment insurance an attractive option for individuals seeking tax-efficient savings and investment strategies.
These features make endowment insurance a versatile financial tool that provides individuals with both protection and savings benefits. The dual-purpose nature of endowment insurance appeals to individuals who want to secure their family’s financial future while also accumulating funds for other financial goals. However, it is important to carefully evaluate the terms, costs, and potential returns of endowment insurance before making a decision about purchasing a policy.
How Endowment Insurance Works
Endowment insurance works by combining elements of life insurance coverage and a savings component to provide policyholders with financial protection and the opportunity to accumulate funds over a specified period. Understanding the mechanics of how endowment insurance works is essential for individuals considering this type of policy. Here’s a breakdown of how endowment insurance operates:
- Premium Payments: Policyholders make regular premium payments to the insurance company. The premiums are determined based on factors such as the age and health of the insured individual, the desired coverage amount, and the policy term. A portion of the premium goes towards the insurance coverage, while the rest is allocated towards building the cash value.
- Investment of Funds: The insurance company invests the cash value of the policy in various financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. The goal is to generate returns on these investments, which will contribute to the growth of the cash value over time.
- Accumulation of Cash Value: Over the policy term, the cash value of the endowment insurance policy grows through the investment returns and the additional premiums paid. This cash value serves as a savings component, providing policyholders with a lump sum payout at the end of the policy term.
- Maturity Benefit: At the maturity date of the policy, which is predetermined at the time of purchase, the policyholder receives the accumulated cash value as a lump sum payout. This amount can be used for any purpose the policyholder desires, such as funding education, buying a house, or securing retirement.
- Death Benefit: If the insured individual passes away during the policy term, the beneficiaries named in the policy receive the death benefit. The death benefit is usually higher than the accumulated cash value and provides financial protection to the policyholder’s loved ones.
- Policy Termination: Once the policy reaches maturity and the insured individual receives the lump sum payout, the contract ends. Alternatively, if the policyholder decides to cancel the policy before maturity, they may receive a surrender value, which is the cash value accumulated up until that point, minus any applicable fees or penalties.
It is important to note that the growth of the cash value and the returns generated from the investments are not guaranteed. They are subject to market fluctuations and the performance of the chosen financial instruments. However, many endowment insurance policies come with a guaranteed minimum return, ensuring that the policyholder will receive at least a certain amount even if the investments do not perform as expected.
Overall, endowment insurance offers a comprehensive financial solution by providing both protection and savings benefits. Policyholders can enjoy the peace of mind that comes with life insurance coverage while also building a savings nest egg for their future financial needs.
Types of Endowment Insurance
Endowment insurance policies come in various types to cater to the diverse needs and preferences of individuals. Each type offers different features and benefits, allowing policyholders to select the one that aligns with their financial goals. Let’s explore some of the common types of endowment insurance:
- Traditional Endowment Insurance: This is the most basic type of endowment insurance. It provides a death benefit to the beneficiaries if the insured individual passes away during the policy term and a maturity benefit to the policyholder at the end of the term. The maturity benefit is the accumulated cash value, which can be used for any purpose the policyholder desires.
- Unit-Linked Endowment Insurance: Also known as variable endowment insurance, this type of policy offers investment options to policyholders. The cash value of the policy is invested in a range of investment funds, allowing policyholders to participate in the potential returns of these funds. The death benefit and maturity benefit are linked to the performance of the chosen investment funds.
- Low-Cost Endowment Insurance: This type of policy focuses on providing affordable premiums to policyholders. The coverage amount and potential returns may be lower compared to other types of endowment insurance, but it can be a suitable option for individuals looking for a basic level of protection and savings without high premium costs.
- Unitized With-Profits Endowment Insurance: This type of policy combines the features of unit-linked and with-profits policies. The cash value is invested in a range of investment funds, and policyholders also benefit from the participation in the insurance company’s profits. The returns earned from the investments and the bonuses declared by the insurance company are added to the cash value.
- Endowment Mortgage Insurance: This type of endowment insurance is specifically designed to help individuals pay off their mortgage. The policyholder makes regular premium payments, and upon maturity, the accumulated cash value can be used to repay the mortgage in full. If the insured individual passes away during the policy term, the death benefit can be used to pay off a portion of the outstanding mortgage balance.
- Pension Endowment Insurance: Also known as an endowment policy for retirement, this type of policy helps individuals build a retirement fund. The regular premium payments and the investment returns over the policy term contribute to the cash value. At retirement, the accumulated cash value can be converted into an annuity or withdrawn as a lump sum to provide retirement income.
These are just a few examples of the types of endowment insurance available in the market. The specific features, benefits, and terms may vary between insurance companies and jurisdictions. It is important to carefully review and compare different types of endowment insurance policies to select the one that best suits your financial needs and future goals.
Benefits of Endowment Insurance
Endowment insurance offers several benefits that make it an attractive financial tool for individuals seeking both protection and savings. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of endowment insurance:
- Financial Protection: Endowment insurance provides a death benefit to the beneficiaries named in the policy, ensuring that they are financially protected in the event of the insured individual’s untimely demise. This benefit can help cover funeral expenses, outstanding debts, and provide ongoing financial support for loved ones.
- Savings Accumulation: Endowment insurance allows policyholders to accumulate savings over a specific period of time. The regular premium payments and the investment returns generated by the insurance company contribute to the growth of the policy’s cash value. This cash value can be used for a variety of purposes such as funding education, buying a house, or securing retirement.
- Tax Advantages: Many countries offer tax advantages for endowment insurance policies. Policyholders may be eligible for tax deductions on the premium payments or tax-free withdrawals of the accumulated cash value. These tax benefits can enhance the overall returns and make endowment insurance a tax-efficient savings and investment strategy.
- Guaranteed Minimum Return: Endowment insurance policies often come with a guaranteed minimum return on the accumulated cash value. This ensures that the policyholder will receive a certain amount even if the investments made by the insurance company do not perform as expected. This feature provides peace of mind and protects against potential market volatility.
- Flexibility in Premium Payments: Endowment insurance policies offer flexibility in premium payments. Policyholders can choose to pay premiums annually, semi-annually, quarterly, or monthly, depending on their financial situation and preferences. This flexibility allows individuals to manage their premium payments based on their cash flow and budget.
- Protection against Inflation: As endowment insurance usually has a long-term policy term, the death benefit and maturity benefit provided are adjusted for inflation. This means that the payouts received by the beneficiaries or the policyholder at the end of the policy term retain their value in real terms, protecting against the erosive effects of inflation.
- Peace of Mind: With endowment insurance, policyholders can have peace of mind knowing that their loved ones will be financially protected in the event of their premature death. Additionally, the accumulation of savings over time can provide a sense of security and confidence in achieving future financial goals.
These benefits make endowment insurance a well-rounded financial option for individuals looking to secure their family’s financial future while also building savings for other purposes. However, it’s important to carefully evaluate the terms, costs, and potential returns of endowment insurance to ensure it aligns with your specific financial needs and goals.
Drawbacks of Endowment Insurance
While endowment insurance offers several benefits, it also has certain drawbacks that individuals should consider before deciding to purchase a policy. Let’s explore some of the key drawbacks of endowment insurance:
- Higher Premium Costs: Compared to other types of life insurance, endowment insurance tends to have higher premium costs. This is because a portion of the premium payments goes towards building the cash value component of the policy. Individuals considering endowment insurance should carefully evaluate their budget and ensure they can comfortably afford the premiums.
- Lower Investment Returns: The returns on investment for endowment insurance policies may be lower compared to other investment options available in the market. This is because insurance companies prioritize capital preservation and typically invest in low-risk assets. As a result, the potential for higher investment returns is limited, which may not be suitable for individuals seeking maximum growth on their savings.
- Long-Term Commitment: Endowment insurance policies typically have long policy terms, ranging from 10 to 30 years or more. This means that individuals who purchase these policies commit to making regular premium payments over an extended period. It’s important to consider whether a long-term commitment aligns with your financial goals and circumstances.
- Penalties for Early Termination: If you decide to cancel or surrender an endowment insurance policy before the maturity date, you may incur penalties or face a reduced surrender value. Insurance companies charge these penalties to compensate for the loss of premiums and expenses associated with administering the policy. Early termination can result in a significant loss of funds.
- Market Volatility Exposure: Although endowment insurance policies come with a guaranteed minimum return, the actual returns on the cash value are subject to market fluctuations. If the investments made by the insurance company perform poorly, the returns generated may be lower than expected. This exposes policyholders to some level of market risk.
- Limited Liquidity: The cash value accumulated in an endowment insurance policy is not readily accessible. Typically, policyholders can only access the cash value upon the policy’s maturity or through a policy loan, which may incur additional interest charges. This limited liquidity may restrict your ability to use the funds for immediate financial needs.
- Opportunity for Better Investment Options: Some individuals may find that they can achieve higher investment returns by pursuing alternative investment options rather than investing in an endowment insurance policy. Depending on your risk tolerance and investment objectives, exploring other investment vehicles such as stocks, real estate, or mutual funds may offer better growth potential.
It’s essential to carefully weigh these drawbacks against the benefits of endowment insurance before making a decision. Consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and overall financial situation to determine whether endowment insurance aligns with your needs and objectives.
Factors to Consider before Purchasing Endowment Insurance
Before purchasing endowment insurance, it’s important to carefully consider various factors to ensure that it aligns with your financial goals and circumstances. Making an informed decision requires evaluating the following key factors:
- Financial Goals: Determine your financial goals and objectives. Consider whether you need a combination of life insurance coverage and savings accumulation, or if you have other investment options that can better meet your needs.
- Budget and Affordability: Evaluate your budget and ensure that you can comfortably afford the premium payments associated with endowment insurance. Assess the impact of premium costs on your overall financial situation and consider whether they align with your monthly cash flow.
- Risk Tolerance: Understand your risk tolerance and investment preferences. Endowment insurance policies typically prioritize capital preservation over high investment returns. If you are comfortable taking on more investment risk, you may want to explore other investment options that offer potentially higher returns.
- Policy Duration: Consider the duration of the policy term. Endowment insurance policies often have long-term commitments ranging from 10 to 30 years or more. Ensure that the policy duration aligns with your financial goals and the timeframe in which you anticipate needing the accumulated funds.
- Liquidity: Assess your need for liquidity. Endowment insurance policies have limited liquidity, and accessing the accumulated cash value may require waiting until the maturity date or taking out a policy loan, which may incur additional costs. Consider whether you have other sources of liquid funds for emergencies or unforeseen expenses.
- Tax Implications: Understand the tax implications of endowment insurance in your jurisdiction. In some countries, premium payments may be tax-deductible, or withdrawals of the accumulated cash value may be tax-free. Consult with a tax advisor to fully comprehend the potential tax benefits and implications of an endowment insurance policy.
- Insurance Company Reputation: Research and evaluate the reputation and financial stability of the insurance company offering the endowment insurance policy. Consider factors such as the company’s financial strength ratings, customer reviews, and claims settlement track record. Choose a reputable and trustworthy insurer to ensure the security of your investment.
- Policy Flexibility: Examine the flexibility offered by the endowment insurance policy. Consider whether the policy allows for adjustments to the coverage amount, premium payment frequency, or the ability to add or remove riders to customize the policy to your changing needs over time.
- Professional Advice: Seek advice from a qualified financial advisor or insurance professional who can provide personalized guidance based on your unique financial situation and goals. They can help assess whether endowment insurance is the right choice for you and recommend suitable policy options.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision about whether endowment insurance aligns with your financial needs and objectives. Take the time to conduct thorough research, review policy details, and seek professional advice to choose the most appropriate endowment insurance policy for your specific circumstances.
Comparison of Endowment Insurance with Other Insurance Plans
When considering endowment insurance, it’s important to compare it with other types of insurance plans to determine which option best suits your needs. Here, we will compare endowment insurance with term life insurance and whole life insurance, two commonly considered alternatives:
- Endowment Insurance vs. Term Life Insurance: Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. It offers a death benefit to the beneficiaries if the insured individual passes away during the policy term, but does not build cash value. Unlike endowment insurance, term life insurance is purely protection-oriented and does not provide savings accumulation. Term life insurance premiums are typically lower compared to endowment insurance, making it an affordable option for those primarily concerned with providing financial security for their loved ones.
- Endowment Insurance vs. Whole Life Insurance: Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers lifelong coverage. It provides both a death benefit and a cash value component. The cash value grows slowly over time, and policyholders can access it through withdrawals or policy loans. Whole life insurance premiums are typically higher than those of endowment insurance, but they offer more flexibility and potential for higher investment returns. Unlike endowment insurance, whole life insurance serves as a long-term savings and investment tool with the potential to accumulate significant cash value over time.
When comparing these insurance plans, here are some key factors to consider:
- Protection vs. Savings: Assess whether you prioritize life insurance coverage or the accumulation of savings. Endowment insurance offers a combination of both, making it suitable for individuals seeking protection as well as savings accumulation. Term life insurance primarily focuses on protection, while whole life insurance emphasizes both protection and savings.
- Premium Costs: Compare the premium costs associated with each type of insurance. Term life insurance generally has the lowest premiums, followed by endowment insurance and then whole life insurance. Choose a plan with premium payments that fit within your budget.
- Policy Flexibility: Consider the flexibility offered by each insurance plan. Endowment insurance policies often offer limited flexibility, while whole life insurance policies may allow for adjustments to coverage amounts, premium payments, and the ability to access the cash value.
- Policy Term: Evaluate the policy term that best suits your needs. Endowment insurance has a specific maturity date, while whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage. Term life insurance allows you to match the policy term with specific financial obligations, such as mortgage payment periods or a child’s college education.
- Investment Opportunities: Consider the investment opportunities and potential returns offered by each plan. Endowment insurance typically offers conservative investment options with moderate returns. Whole life insurance policies may provide more investment options and potentially higher returns. Term life insurance does not have an investment component.
- Tax Considerations: Evaluate the tax implications of each plan. Endowment insurance and whole life insurance may offer tax advantages, such as tax deductions on premium payments or tax-free withdrawals, depending on your jurisdiction. Check with a tax advisor or insurance professional to understand the specific tax benefits associated with each policy.
Ultimately, the choice between endowment insurance, term life insurance, or whole life insurance depends on your unique financial goals, risk tolerance, and budget. Consider your preferences and consult with a financial advisor or insurance professional to ensure you select the insurance plan that best aligns with your needs and objectives.
Conclusion
Endowment insurance is a comprehensive financial tool that provides both protection and savings benefits to policyholders. It offers a combination of life insurance coverage and the opportunity to build cash value over a specified period. Endowment insurance is designed to provide financial security for individuals and their loved ones, while also offering a savings component that can be used for various purposes such as education expenses, retirement planning, or funding major life events.
In this article, we explored the definition of endowment insurance and its key features, including the maturity benefit, death benefit, and guaranteed returns. We discussed different types of endowment insurance available, such as traditional, unit-linked, and endowment mortgage insurance. We also highlighted the benefits of endowment insurance, including financial protection, savings accumulation, tax advantages, and guaranteed minimum returns.
However, it’s important to consider the drawbacks of endowment insurance, such as higher premium costs, lower investment returns compared to other options, and limited liquidity. We also discussed the factors that individuals should consider before purchasing endowment insurance, such as financial goals, budget, risk tolerance, and policy flexibility. Additionally, we compared endowment insurance with term life insurance and whole life insurance, highlighting the differences between these insurance plans.
To make an informed decision about endowment insurance, it is recommended to carefully evaluate your financial goals, budget, risk tolerance, and other specific needs. Seek the advice of a qualified financial advisor or insurance professional who can guide you through the process and help you choose the most appropriate policy.
In conclusion, endowment insurance can be a valuable financial tool for individuals seeking both protection and savings. By understanding its features, benefits, and considerations, you can determine whether endowment insurance aligns with your financial objectives and provides the level of coverage, savings, and financial security you desire.