
Finance
How Much Is Earned Income Credit 2015
Published: January 7, 2024
Discover how much you can receive from the Earned Income Credit in 2015. Explore the financial benefits and eligibility criteria for this tax credit.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of Earned Income Credit
- Qualifications for Earned Income Credit
- Calculating Earned Income Credit
- Changes to Earned Income Credit for 2015
- Maximum Earned Income Credit Amount for 2015
- Claiming Earned Income Credit on your Tax Return
- Common Mistakes to Avoid when Claiming Earned Income Credit
- Frequently Asked Questions about Earned Income Credit 2015
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of tax credits, where hardworking individuals and families can receive financial assistance from the government. One of the most notable tax credits is the Earned Income Credit (EIC), which is specifically designed to benefit low to moderate-income earners.
The Earned Income Credit is a refundable tax credit, which means that even if you don’t owe any taxes, you may still be eligible to receive a refund. This credit is intended to provide assistance to those who work but have lower incomes, helping to alleviate some financial burden and provide a boost to their overall financial well-being.
Established in 1975, the Earned Income Credit has undergone several changes and updates over the years, with the specific criteria and calculations varying from year to year. In this article, we will focus on the Earned Income Credit for the year 2015 and explore the qualifications, calculations, and maximum credit amount for eligible individuals and families.
By understanding the ins and outs of the Earned Income Credit for 2015, you can make informed decisions, ensure accurate tax filing, and potentially maximize your refund. So, let’s dive into the world of tax credits and explore how the Earned Income Credit can benefit you.
Overview of Earned Income Credit
The Earned Income Credit (EIC) is a tax credit designed to assist low to moderate-income workers by reducing their tax liability and potentially providing them with a refund. It is one of the most valuable credits available to eligible taxpayers and can greatly improve their financial situation.
The EIC is based on the concept of rewarding individuals for their work and encouraging them to pursue employment opportunities. It is calculated using a combination of earned income and adjusted gross income, with the credit amount gradually phasing out as income increases.
The credit is particularly beneficial for families with children as it provides additional support for raising kids. In some cases, families may receive a larger EIC if they have more qualified children.
It’s important to note that the EIC is a refundable credit, meaning that even if an individual’s tax liability is zero, they may still be eligible to receive a refund of the credit amount. This can be a significant financial boost for lower-income individuals and families.
Moreover, the EIC is designed to be inclusive, which means it benefits individuals of all ages – from younger workers starting their careers to older individuals nearing retirement. It helps bridge the income gap and provides assistance to those who are working hard but earning modest incomes.
Claiming the EIC does involve some additional documentation and paperwork. However, the potential benefit of a refund or reduced tax liability makes it well worth the effort for eligible taxpayers.
In the following sections, we will delve into the specific qualifications for the EIC in 2015 and explore how the credit is calculated.
Qualifications for Earned Income Credit
To be eligible for the Earned Income Credit (EIC) in 2015, you must meet certain criteria set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). These qualifications are designed to target individuals and families with lower incomes who are in need of financial assistance. Here are the key requirements to qualify for the EIC in 2015:
- You must have earned income: Earned income refers to income you receive from working, such as wages, salaries, and self-employment income. Investment income and passive income do not count for the purpose of qualifying for the EIC.
- You must have a valid Social Security Number (SSN): To claim the EIC, you, your spouse (if filing jointly), and any qualifying children must have a valid SSN issued by the Social Security Administration.
- Filing status must be single, married filing jointly, or head of household: In order to be eligible for the EIC, you must file your tax return using one of these three filing statuses.
- You must be a U.S. citizen or resident alien for the entire tax year: Nonresident aliens do not qualify for the EIC.
- You cannot be claimed as a dependent on someone else’s tax return: If another person can claim you as a dependent, you are not eligible to claim the EIC.
- Your investment income must not exceed the specified limit: For 2015, the investment income limit is $3,400. If your investment income exceeds this limit, you are not eligible for the EIC.
These are the general qualifications for the Earned Income Credit in 2015. However, it’s important to note that there are additional criteria to determine the specific amount of credit you may be eligible for. These factors include the number of qualifying children you have, your filing status, and your earned income.
Next, we will explore how the Earned Income Credit is calculated based on these qualifications and factors.
Calculating Earned Income Credit
Calculating the Earned Income Credit (EIC) can be a bit complex, as it involves several factors and formulas. However, the IRS provides worksheets and online resources to assist taxpayers in determining their eligibility and calculating their credit amount accurately.
The EIC is calculated based on your earned income, filing status, and the number of qualifying children you have. The credit amount gradually increases as your earned income increases, reaching a maximum point, and then phases out as your income exceeds certain thresholds.
In order to determine your eligibility and calculate your EIC, you need to follow these steps:
- Determine your eligibility: First, ensure that you meet all the qualifications for the EIC, such as having earned income, a valid Social Security Number, and the correct filing status.
- Determine the number of qualifying children: If you have children, you must determine the number of qualifying children you have. This includes children who meet the age, relationship, and residency requirements set by the IRS.
- Calculate your earned income: Add up all the income you earned from working, including wages, salaries, and self-employment income. Exclude any income that does not qualify as earned income, such as investment income or passive income.
- Use the EIC table or worksheet: The IRS provides an EIC table or an interactive online worksheet to calculate your credit amount based on your filing status, earned income, and number of qualifying children. This table or worksheet will determine the maximum credit amount you are eligible for.
- Phase-out calculations: If your income exceeds the specified thresholds, the EIC amount will gradually decrease until it phases out completely. The IRS provides detailed instructions and worksheets to calculate the phase-out amounts accurately.
It’s important to note that the EIC calculations can be complex, especially if you have multiple qualifying children or if your income is close to the phase-out thresholds. In such cases, it’s advisable to seek assistance or consult a tax professional to ensure accurate calculations and maximize your eligible credit amount.
Now that we have covered the basics of calculating the Earned Income Credit, let’s move on to discuss the changes made to the EIC for the year 2015.
Changes to Earned Income Credit for 2015
Each year, the IRS makes adjustments and updates to various tax credits, including the Earned Income Credit (EIC). These changes are implemented to account for inflation, tax law revisions, and other factors that may affect eligibility and credit amounts.
For the year 2015, there were a few notable changes to the EIC that taxpayers should be aware of:
- Increased maximum credit amounts: The maximum credit amount for the EIC increased slightly in 2015. These increases were aimed at providing additional support to eligible individuals and families. The specific maximum credit amounts for 2015 depend on the filing status and the number of qualifying children a taxpayer has.
- Modified income thresholds: The income thresholds for determining eligibility and calculating the credit amount were adjusted for inflation in 2015. This means that taxpayers with higher incomes may still be eligible for a reduced credit amount compared to previous years.
- Changes in qualifying child rules: The rules for determining if a child qualifies for the EIC were modified in 2015. These changes include stricter requirements for residency, age, and relationship to the taxpayer. It’s important to carefully review the guidelines to ensure that your child meets all the necessary criteria.
- Enhanced reporting requirements: In an effort to reduce fraud and improve compliance, the IRS introduced stricter reporting requirements for taxpayers claiming the EIC. This includes providing additional documentation to verify the eligibility of qualifying children and their relationship to the taxpayer.
It’s crucial to stay updated on these changes and any future amendments to the EIC guidelines. Failing to adhere to the updated requirements could result in errors on your tax return or potential penalties from the IRS.
Understanding the changes implemented for the year 2015 is essential when preparing your tax return and claiming the EIC. Consult the IRS publications and resources available to ensure that you meet all the updated requirements and accurately calculate your eligible credit amount.
In the next section, we will discuss the maximum EIC amount for the year 2015, which is the highest credit amount that taxpayers can receive.
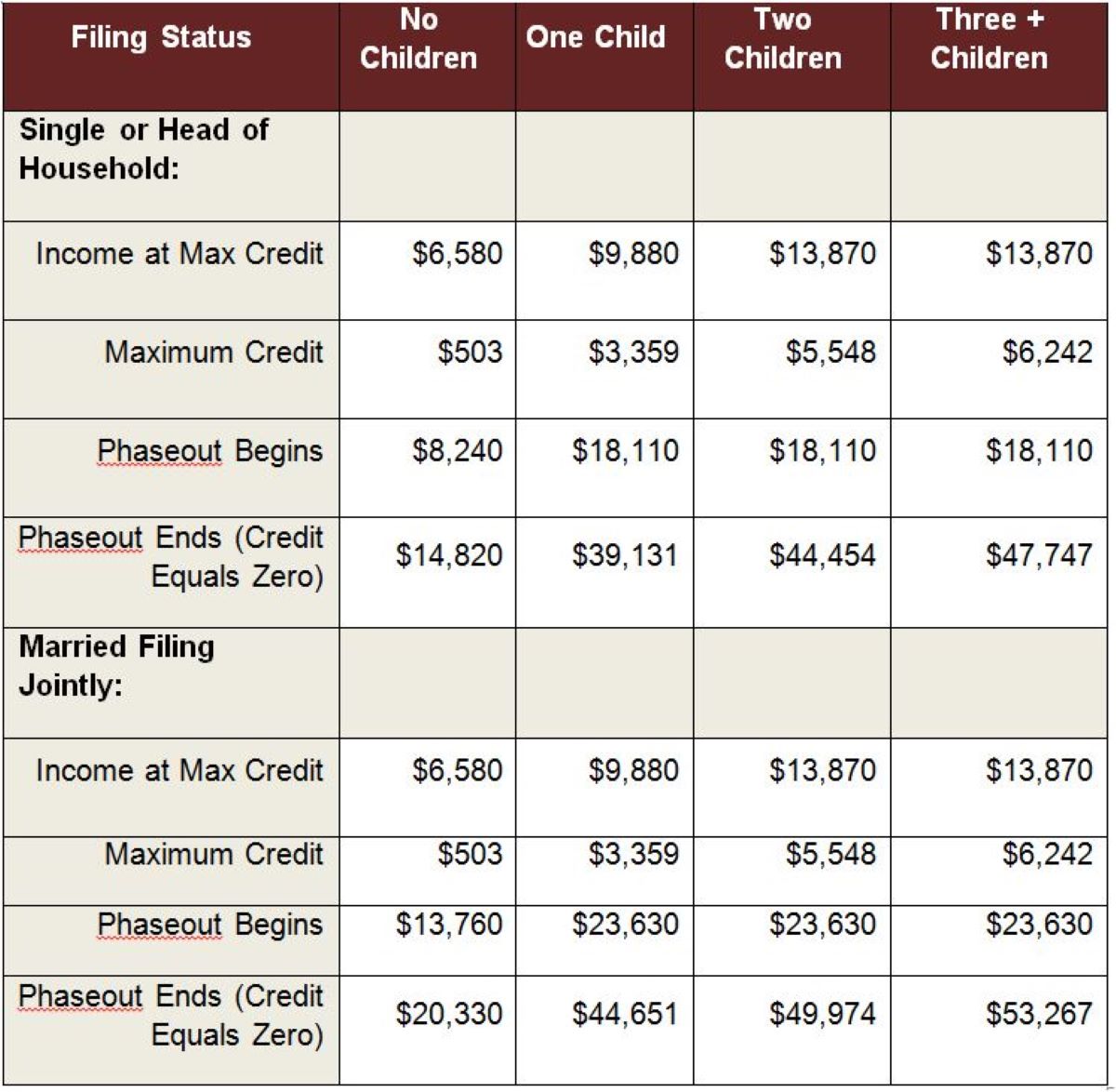
Maximum Earned Income Credit Amount for 2015
The maximum amount of the Earned Income Credit (EIC) for 2015 depends on several factors, including filing status, earned income, and the number of qualifying children. The EIC is a progressive credit, meaning that as your income increases, the credit amount gradually phases out.
For tax year 2015, the maximum EIC amounts are as follows:
- Filing as Single or Head of Household with no qualifying children:
- Income below $14,820: Maximum credit of $503
- Income between $14,820 and $19,790: Credit amount gradually decreases
- Income above $19,790: No credit
- Filing as Single or Head of Household with one qualifying child:
- Income below $39,131: Maximum credit of $3,359
- Income between $39,131 and $44,651: Credit amount gradually decreases
- Income above $44,651: No credit
- Filing as Single or Head of Household with two qualifying children:
- Income below $44,454: Maximum credit of $5,548
- Income between $44,454 and $49,974: Credit amount gradually decreases
- Income above $49,974: No credit
- Filing as Single or Head of Household with three or more qualifying children:
- Income below $47,747: Maximum credit of $6,242
- Income between $47,747 and $53,267: Credit amount gradually decreases
- Income above $53,267: No credit
- Filing as Married Filing Jointly with no qualifying children:
- Income below $20,330: Maximum credit of $503
- Income between $20,330 and $25,300: Credit amount gradually decreases
- Income above $25,300: No credit
These maximum credit amounts were set to ensure that the EIC provides the most significant benefit to low-income individuals and families. It’s important to note that the specific credit amounts may vary depending on your individual circumstances. The IRS provides worksheets and resources to help taxpayers determine their eligible credit amount based on their income and filing status.
Claiming the maximum credit amount can be a significant financial boost for eligible individuals and can help improve their overall financial stability. However, it’s crucial to accurately calculate your credit amount to avoid any errors or potential penalties.
In the next section, we will discuss how to claim the Earned Income Credit on your tax return.
Claiming Earned Income Credit on your Tax Return
Claiming the Earned Income Credit (EIC) on your tax return is relatively straightforward, but it does require careful attention to detail and accurate reporting. Here are the steps to follow when claiming the EIC:
- Determine your eligibility: Before claiming the EIC, ensure that you meet all the qualifications, such as having earned income, a valid Social Security Number, and the correct filing status.
- Gather the necessary documentation: To claim the EIC, you will need to provide specific information, such as proof of earned income, documentation for qualifying children, and other supporting documents as required. Be sure to gather all the necessary paperwork before filing your tax return.
- Fill out the appropriate tax forms: When preparing your tax return, you will need to fill out the appropriate tax forms to claim the EIC, such as Form 1040 or Form 1040A. These forms have specific sections dedicated to reporting the EIC.
- Calculate your credit amount: Use the EIC tables or worksheets provided by the IRS to calculate your eligible credit amount based on your filing status, earned income, and number of qualifying children. Ensure that you accurately input the information to determine the correct credit amount.
- Enter the credit amount on your tax return: Once you have calculated your EIC, enter the credit amount on the appropriate line of your tax return. Double-check the entered amount to avoid any errors.
- Submit your tax return: After completing all the necessary steps, review your tax return for accuracy and submit it to the IRS. Make sure to keep a copy of your tax return and any supporting documents for your records.
It’s important to note that claiming the EIC may involve additional requirements, such as providing additional documentation to verify the eligibility of qualifying children or certain income sources. It’s advisable to carefully review the IRS guidelines and publications to ensure compliance with all the necessary procedures.
If you are uncertain or have any questions about claiming the EIC, consider seeking assistance from a tax professional. They can provide guidance and ensure that you accurately report your EIC, maximizing your eligible credit amount and avoiding any potential errors or penalties.
In the next section, we will address common mistakes to avoid when claiming the Earned Income Credit.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Claiming Earned Income Credit
Claiming the Earned Income Credit (EIC) can be a valuable opportunity to reduce your tax liability or even receive a refund. However, there are several common mistakes that taxpayers should be aware of to ensure the accurate and successful claiming of the EIC. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Incorrectly reporting earned income: It’s essential to accurately report your earned income when claiming the EIC. This includes wages, salaries, self-employment income, and any other income that qualifies as earned income. Double-check your income sources and ensure all necessary income is included.
- Failing to meet the qualifying child criteria: If you are claiming the EIC based on having qualifying children, it’s important to meet all the criteria set by the IRS. This includes meeting age, relationship, residency, and support tests. Review the rules carefully and provide accurate documentation for each qualifying child.
- Not filing with the appropriate filing status: The EIC eligibility and credit amount vary based on filing status. Make sure you file your tax return with the correct filing status – single, married filing jointly, or head of household – to ensure you receive the correct credit amount.
- Overlooking income phase-out limits: The EIC gradually phases out as income increases. Be aware of the income thresholds and carefully calculate your credit amount based on your income level. Failing to account for the phase-out can result in overestimating the credit or claiming more than you are eligible for.
- Failure to provide accurate documentation: The IRS may request additional documentation to verify your eligibility for the EIC, such as birth certificates, Social Security Numbers, or proof of residency for qualifying children. Failing to provide accurate and complete documentation can result in delayed refunds or disqualification from claiming the EIC.
- Ignorance of IRS guidelines and updates: The IRS regularly updates guidelines and requirements for the EIC. It’s crucial to stay informed about any changes, adjustments, or new documentation requirements to ensure compliance and accuracy when claiming the credit.
To avoid these mistakes, take the time to review the IRS guidelines, publications, and resources related to the EIC. Consider utilizing tax software or consulting a tax professional who can help guide you through the process and ensure accurate reporting.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can properly claim the EIC and maximize your eligible credit amount without encountering any penalties or complications. In the next section, we will address frequently asked questions about the Earned Income Credit for 2015.
Frequently Asked Questions about Earned Income Credit 2015
As the Earned Income Credit (EIC) can sometimes be complex and confusing, it’s common for taxpayers to have questions regarding its eligibility, calculations, and other related aspects. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about the EIC for the year 2015:
- Q: Who is eligible for the Earned Income Credit?
A: The EIC is available to low to moderate-income individuals and families who have earned income from working. The specific eligibility requirements include having a valid Social Security Number, meeting the income thresholds, and filing under the appropriate filing status. - Q: How is the Earned Income Credit calculated?
A: The EIC is calculated based on factors such as earned income, filing status, and the number of qualifying children. The credit amount gradually increases with earned income and the number of qualifying children until reaching a maximum point. It then phases out as income exceeds certain thresholds. - Q: Can I claim the Earned Income Credit if I am self-employed?
A: Yes, self-employed individuals can still claim the EIC. It’s essential to accurately report your self-employment income and meet all the eligibility criteria. Keeping detailed records of your business activities and income will help in determining your eligible credit amount. - Q: Is the Earned Income Credit refundable?
A: Yes, the EIC is a refundable tax credit. This means that even if you have no tax liability, you may still be eligible to receive a refund of the credit amount. It can be a significant financial boost for individuals and families with lower incomes. - Q: What documentation do I need to claim the Earned Income Credit?
A: To claim the EIC, you may need to provide documentation such as W-2 forms, proof of earned income, Social Security Numbers for yourself and your qualifying children, and any other required supporting documents. It’s important to keep accurate records and save all necessary documents for your tax filing. - Q: Can I claim the EIC if I am claimed as a dependent on someone else’s tax return?
A: No, if you can be claimed as a dependent on someone else’s tax return, you are not eligible to claim the EIC. The EIC is generally reserved for individuals who are not dependents of someone else.
If you have further questions about the Earned Income Credit for the year 2015, consult the IRS publications and resources for additional information. Additionally, consider seeking assistance from a tax professional who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific circumstances.
Now that we have covered the frequently asked questions, let’s conclude our discussion on the Earned Income Credit for 2015.
Conclusion
The Earned Income Credit (EIC) is a valuable tax credit designed to provide financial assistance to low to moderate-income individuals and families. By understanding the qualifications, calculations, and maximum credit amounts for the year 2015, taxpayers can make informed decisions and maximize their eligible credit amount.
Throughout this article, we have covered the key aspects of the 2015 Earned Income Credit, including an overview of the credit, the qualifying criteria, calculations, changes for the year, and common mistakes to avoid. We have also addressed frequently asked questions to provide clarity on various aspects of the EIC.
It’s important to remember that claiming the EIC requires accurate reporting, proper documentation, and adherence to the IRS guidelines. Staying updated on any changes and seeking help from tax professionals can ensure a smooth claiming process and accurate results.
The Earned Income Credit can provide significant financial assistance, reduce tax liability, and even result in a refund. It is a crucial tool that helps support hardworking individuals and families, ensuring that they can make ends meet and improve their overall financial well-being.
As tax laws and regulations evolve, it’s essential to stay informed and updated on any changes to the Earned Income Credit. By doing so, you can harness the full benefits of this credit and ensure compliance with all requirements.
Remember, the Earned Income Credit is just one of the many ways the government provides support to individuals and families. By taking advantage of available credits and deductions, you can make the most of your hard-earned money and improve your financial outlook.
As you navigate the world of tax credits and deductions, always consult reliable sources, seek professional advice when needed, and maintain accurate records to ensure a seamless tax filing experience.
With a clear understanding of the Earned Income Credit, you can confidently approach your tax return and potentially receive the financial assistance that will make a difference in your life and the lives of your loved ones.














