Finance
How To Calculate Revenue In Accounting
Modified: December 12, 2023
Learn how to calculate revenue in accounting and understand the financial aspect of your business with our helpful finance guides and resources.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of accounting! If you’re new to the field or looking to expand your knowledge, understanding how to calculate revenue is a fundamental concept that you cannot overlook. Revenue is a crucial financial metric that tracks the inflow of money a business generates through its primary operations. It serves as an indicator of a company’s financial performance and helps stakeholders evaluate its profitability.
In accounting, revenue is recognized when a sale or service is rendered, and the customer is obligated to pay. It is an essential component in financial statements such as the income statement and plays a significant role in determining a company’s tax liability. As an SEO expert in finance, I will guide you through the various methods of calculating revenue and shed light on the importance of revenue recognition in accounting.
Understanding how to calculate revenue is essential for businesses of all sizes and industries. Whether you’re a small startup or a multinational corporation, accurately calculating revenue allows you to make informed decisions, set realistic financial goals, and assess your financial health. Whether you’re an auditor, manager, or investor, having a firm grasp of revenue calculations will enable you to evaluate a company’s financial performance, compare it against industry benchmarks, and assess its growth potential.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different methods of calculating revenue, including gross and net revenue calculations. We will delve into the concept of revenue recognition and why it is important in ensuring accurate financial reporting. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of how to calculate revenue in accounting and its significance in assessing business performance.
Why Calculate Revenue in Accounting
Revenue is a key financial metric that plays a crucial role in accounting. It provides vital information about a company’s financial health, profitability, and overall performance. The calculation of revenue serves several essential purposes within the accounting framework:
- Measure of Performance: Revenue is used to assess a company’s financial performance over a specific period. By calculating revenue, businesses can identify if they are generating enough income to cover expenses, invest in growth opportunities, and generate profits.
- Assessing Profitability: Revenue is a fundamental component in determining profitability. By calculating the difference between revenue and expenses, businesses can evaluate if they are making a profit or incurring losses. This information is crucial for making strategic business decisions, attracting investors, and complying with tax regulations.
- Financial Analysis and Comparisons: Revenue calculations enable financial analysis and comparison between companies, industries, and time periods. Investors and analysts use revenue data to evaluate a company’s growth potential, market share, competitive positioning, and overall financial stability. Comparing revenue figures across industry peers and competitors can provide valuable insights into a company’s relative performance.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Calculating revenue is essential for developing accurate budgets and forecasts. By analyzing historical revenue patterns and market trends, businesses can project future revenue streams. This information helps in making strategic decisions, setting realistic financial goals, and allocating resources efficiently.
- Compliance and Taxation: Revenue calculations are crucial for compliance with tax regulations. Governments and tax authorities use revenue data to determine a company’s tax liability. Accurate revenue calculations ensure proper tax reporting and help businesses avoid penalties and legal issues.
Overall, calculating revenue is vital for measuring financial performance, assessing profitability, conducting financial analysis, budgeting, forecasting, and ensuring compliance with tax regulations. By accurately tracking revenue, businesses can make informed decisions, optimize operations, attract investors, and ensure long-term financial success.
Methods of Calculating Revenue
There are several methods that businesses use to calculate revenue, depending on their industry, operations, and specific circumstances. Let’s explore two common approaches: gross revenue calculation and net revenue calculation.
Gross Revenue Calculation
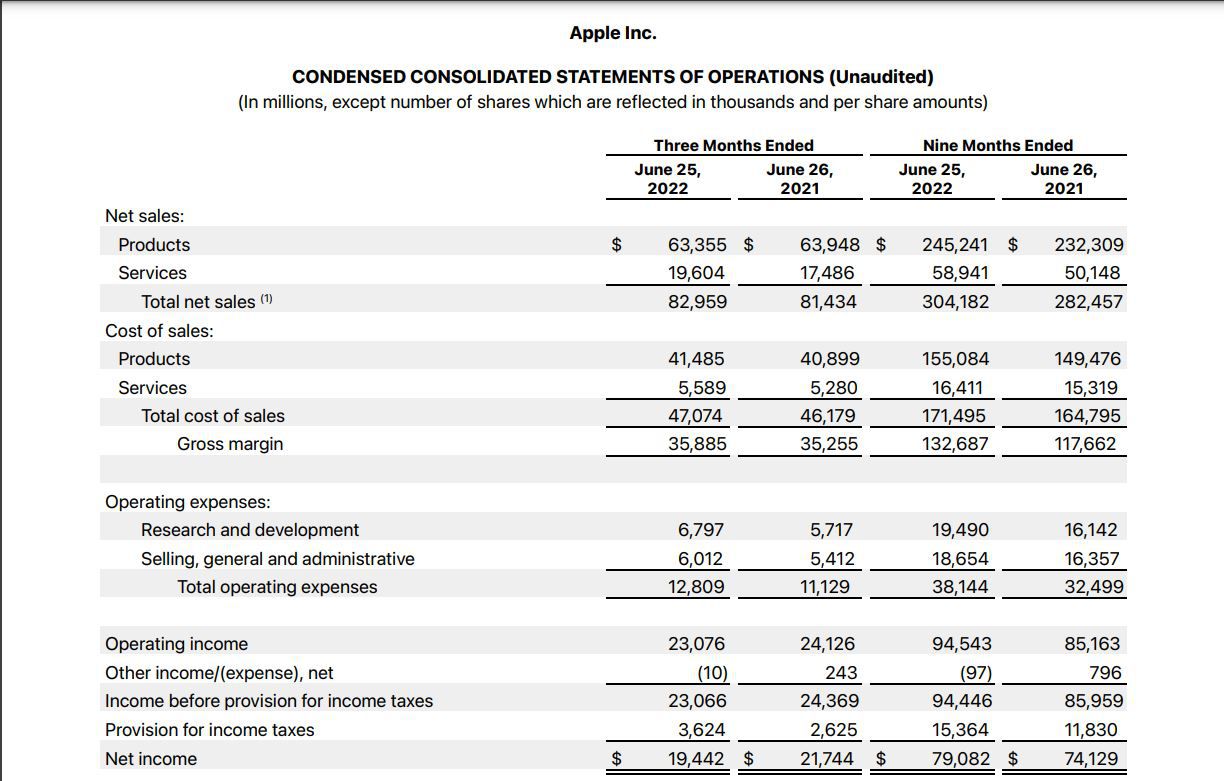
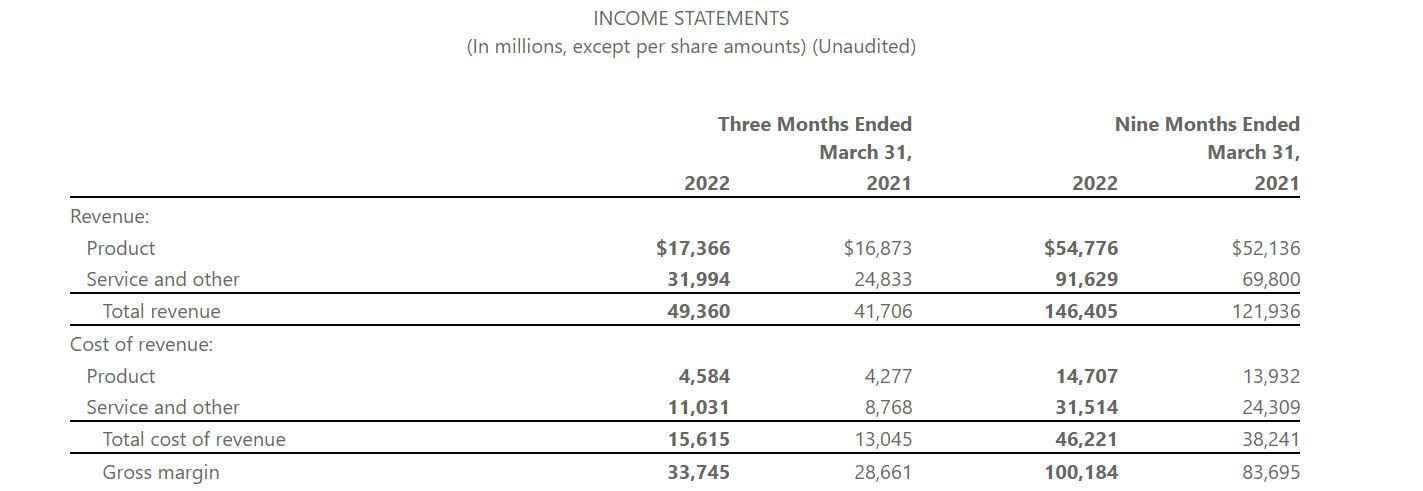
Gross revenue is the total revenue generated by a business from its primary activities without subtracting any expenses or deductions. It represents the total inflow of money before any cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, or taxes are taken into account. Gross revenue is a valuable metric for assessing the overall scale of a business’s operations. It is calculated by multiplying the number of units sold by the price per unit or by adding up the total value of products or services rendered during a specific period.
The formula for calculating gross revenue is as follows:
Gross Revenue = Price per Unit x Number of Units Sold
For example, if a software company sells 500 licenses of their software for $50 each, the gross revenue would be calculated as:
Gross Revenue = $50 x 500 = $25,000
Net Revenue Calculation
Net revenue, also known as net sales or net income, is the revenue generated by a business after deducting expenses and allowances such as returns, discounts, and rebates. It reflects the amount of money that a company retains after accounting for the direct costs of delivering its products or services and any applicable expenses. Net revenue provides a clearer picture of a company’s profitability and financial performance.
The formula for calculating net revenue is as follows:
Net Revenue = Gross Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses
For example, let’s say a retail store had a gross revenue of $100,000. After deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS) of $40,000 and operating expenses of $20,000, the net revenue would be:
Net Revenue = $100,000 – $40,000 – $20,000 = $40,000
It’s important to note that there may be additional factors to consider when calculating net revenue, such as taxes, interest, and non-operating income or expenses. However, the basic formula mentioned above provides a solid foundation for determining net revenue.
By utilizing these methods of calculating revenue, businesses can evaluate their financial performance, set realistic goals, and make informed decisions to drive growth and profitability.
Gross Revenue Calculation
Gross revenue is a key metric that helps businesses assess the total revenue generated from their primary activities without any deductions. Calculating gross revenue provides valuable insights into the scale and magnitude of a company’s operations. Here’s how gross revenue is calculated:
- Price per Unit: Determine the price at which each unit of a product or service is sold. For example, if a company sells widgets for $10 each, the price per unit is $10.
- Number of Units Sold: Determine the total number of units sold during a specific period. This can be determined by tracking sales transactions or analyzing sales records. For example, if the company sold 500 widgets, the number of units sold is 500.
- Gross Revenue Calculation: Multiply the price per unit by the number of units sold to calculate the gross revenue. For example, if the price per unit is $10 and 500 units were sold, the gross revenue would be $10 x 500 = $5,000.
Gross revenue represents the total inflow of money generated from sales or services rendered before accounting for any expenses or deductions. It provides a clear indication of the overall scale and scope of a company’s operations. By tracking gross revenue, businesses can evaluate their sales performance, identify trends, and compare their revenue against industry benchmarks.
It’s important to note that gross revenue does not provide a complete picture of a company’s financial health, as it does not consider the cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, or taxes. However, it serves as a starting point for analyzing a company’s revenue generation capabilities.
Calculating gross revenue is particularly useful for businesses in industries such as retail, manufacturing, and services, where sales volume and pricing play significant roles. By monitoring gross revenue over time, businesses can identify patterns, adjust pricing strategies, and evaluate the effectiveness of marketing and sales efforts.
While gross revenue is an important metric, it is equally crucial to analyze other financial aspects, such as net revenue and profitability, to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial performance. Gross revenue is just one piece of the puzzle that, when combined with other financial metrics, provides a holistic view of a company’s revenue generation and overall financial health.
Net Revenue Calculation
Net revenue, also referred to as net sales or net income, provides a more accurate representation of a company’s financial performance by accounting for deductions and expenses. Calculating net revenue is essential for evaluating profitability and determining the amount of money a company retains after deducting costs. Here’s how net revenue is calculated:
- Gross Revenue: Begin by determining the gross revenue, which is the total revenue generated from sales or services rendered without any deductions.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Identify the direct costs associated with producing or delivering the products or services. This can include expenses such as raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead.
- Operating Expenses: Consider the indirect expenses incurred in running the business, such as marketing costs, rent, salaries, utilities, and administrative expenses.
- Net Revenue Calculation: Subtract the COGS and operating expenses from the gross revenue to calculate the net revenue. The formula is as follows: Net Revenue = Gross Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses.
Net revenue provides a more accurate representation of a company’s profitability as it factors in the costs directly associated with generating revenue. By deducting the COGS and operating expenses, businesses can assess their ability to generate profits from their core operations.
It’s worth noting that net revenue calculation may involve additional considerations. For instance, certain expenses like taxes, interest payments, and non-operating income or expenses may affect the final net revenue figure. However, for the primary calculation, subtracting the COGS and operating expenses from the gross revenue provides a solid foundation.
Calculating net revenue is crucial for understanding a company’s financial performance and assessing its profitability. A higher net revenue signifies stronger revenue generation capabilities and better financial health. It helps businesses make strategic decisions, allocate resources effectively, and plan for future growth and expansion. Additionally, net revenue is a key component in financial statements, such as the income statement, and provides crucial information for investors, lenders, and potential stakeholders.
By monitoring net revenue over time, businesses can evaluate the impact of cost management initiatives, pricing strategies, and efficiency improvements on their bottom line. It also enables comparisons against industry benchmarks and helps identify areas for improvement within the business.
While net revenue is an essential metric, it should be considered alongside other financial indicators, such as gross revenue, gross profit margin, and net profit margin, for a comprehensive assessment of a company’s financial performance.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue recognition is an accounting principle that outlines when and how revenue should be recognized in a company’s financial statements. It provides guidelines for determining the timing and amount of revenue to be recorded, ensuring accurate and transparent financial reporting. Proper revenue recognition is crucial for compliance with accounting standards and enables stakeholders to make informed decisions. Here’s an overview of revenue recognition and its significance:
Timing of Revenue Recognition: Revenue should be recognized when it is earned and realizable. This typically occurs when goods are delivered or services are rendered, and the company has the right to receive payment. The key principle is that revenue should be recognized when the transaction is complete and all performance obligations have been fulfilled.
Criteria for Recognizing Revenue: According to accounting standards, revenue should be recognized when specific criteria are met, including:
- Identifiability of the Transaction: The transaction and the resulting revenue should be clearly identifiable and measurable.
- Transfer of Control: The customer should have control over the goods or services received.
- Fixed or Determinable Price: The price of the goods or services should be fixed or easily determinable at the time of the transaction.
- Collectibility: It must be probable that the company will collect the payment for the goods or services provided.
Methods of Revenue Recognition: Different methods may be used to recognize revenue, depending on the nature of the transaction and the applicable accounting standards. Common methods include:
- Completed Contract Method: Revenue is recognized once the contract is fully completed and all obligations are fulfilled.
- Percentage of Completion Method: Revenue is recognized proportionally as the company completes the performance obligations specified in the contract.
- Point of Sale Method: Revenue is recognized at the point of sale when ownership and control of the goods transfer to the customer.
Importance of Revenue Recognition: Revenue recognition is critical for accurate financial reporting and decision-making. It ensures that revenue is recorded in the appropriate period, matching it with the associated expenses incurred in generating that revenue. Proper revenue recognition enables stakeholders to assess a company’s financial performance, profitability, and cash flow. It also provides transparency and comparability in financial statements, facilitating meaningful analysis and evaluation.
Non-compliance with proper revenue recognition guidelines can lead to misleading financial statements, misrepresentation of a company’s financial health, and potential legal and regulatory consequences. Ensuring accurate revenue recognition is vital for maintaining the trust of investors, creditors, and other stakeholders.
Overall, revenue recognition is a fundamental principle in accounting that governs when and how revenue should be recorded. By following the appropriate guidelines and methods, businesses can achieve consistent and transparent financial reporting, enabling stakeholders to make well-informed decisions about the company’s financial performance and future prospects.
Conclusion
Calculating revenue is a critical aspect of accounting that provides valuable insights into a company’s financial performance, profitability, and overall health. Understanding how to calculate revenue allows businesses to make informed decisions, set realistic financial goals, and assess their growth potential. It serves as a measure of performance, enables financial analysis and comparisons, helps with budgeting and forecasting, and ensures compliance with tax regulations.
There are various methods of calculating revenue, with two common approaches being gross revenue calculation and net revenue calculation. Gross revenue represents the total revenue generated from primary activities without deducting any expenses, while net revenue takes into account deductions such as the cost of goods sold and operating expenses. Both methods have their significance in assessing a company’s revenue generation capabilities and profitability.
Additionally, revenue recognition is a crucial accounting principle that outlines when and how revenue should be recognized in financial statements. Proper revenue recognition ensures accurate and transparent financial reporting, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions. Following the criteria for revenue recognition and using appropriate methods ensure that revenue is recorded in the appropriate period, matching it with associated expenses and facilitating meaningful analysis.
In conclusion, understanding how to calculate revenue and properly recognize it in accounting is essential for businesses of all sizes and industries. It allows for accurate financial reporting, assessment of profitability, and informed decision-making. By incorporating revenue calculations and recognition practices into business operations, companies can optimize their financial performance, attract investors, and ensure long-term success.