Home>Finance>Revenues Have What Effect On The Accounting Equation?


Finance
Revenues Have What Effect On The Accounting Equation?
Published: October 7, 2023
Learn how finance, specifically revenues, impact the accounting equation and influence your company's financial position. Enhance your understanding of finance and accounting principles.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of finance and accounting, where numbers and equations come to life to help us understand the financial health of individuals, businesses, and economies. One fundamental concept in accounting is the accounting equation, which serves as the foundation for financial statements and provides insights into the financial position of an entity. In this article, we will explore the impact of revenues on the accounting equation.
Understanding and interpreting financial data is crucial for decision-making, and the accounting equation lies at the heart of this process. It represents the relationship between a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. The equation is simple yet powerful: assets equal liabilities plus equity. This equation ensures that the books are always balanced and provides a snapshot of the financial health of an entity at any given point in time.
Revenues, often referred to as sales or income, play a significant role in the accounting equation. They represent inflows of economic benefits resulting from the sale of goods, provision of services, or other business activities. Revenues are vital for the growth and profitability of a company, as they directly impact the bottom line.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the definition of revenues and discuss their effects on the accounting equation. Additionally, we will provide an example illustration to help solidify the concepts. So, let’s get started and unlock the secrets of revenues and their impact on the accounting equation!
Understanding the Accounting Equation
Before we explore the effects of revenues on the accounting equation, let’s first establish a clear understanding of the equation itself. As mentioned earlier, the accounting equation is a fundamental principle in accounting that states that assets are equal to liabilities plus equity.
Assets represent the resources owned by a company, such as cash, inventory, buildings, and equipment. Liabilities, on the other hand, are the obligations or debts that a company owes to external parties, such as loans, accounts payable, and accrued expenses. Equity represents the residual interest in the assets of a company after deducting liabilities and represents the ownership interest of the shareholders.
The accounting equation can be visualized as a balancing act, where the left side (assets) and the right side (liabilities plus equity) must always be equal. This equation provides a snapshot of the financial position of a company, helping stakeholders assess the overall health and stability of the entity.
By understanding the accounting equation, we can analyze the impact of various transactions and events on a company’s financial position. Now, let’s dive into the realm of revenues and uncover their role in the accounting equation.
Definition of Revenues
Revenues, also known as sales or income, are a vital component of the accounting equation. They represent the inflow of economic benefits resulting from the sale of goods, provision of services, or other business activities. In simpler terms, revenues are the money a company earns from its core operations.
Revenues can be generated from various sources, including the sale of products to customers, contracts with clients, fees for services rendered, rental income, interest income, and royalties, among others. Regardless of the source, revenues have a significant impact on a company’s financial performance and directly contribute to its overall success.
It is worth noting that revenues are distinct from capital injections or financing activities. Capital injections, such as funds from investors or additional contributions from shareholders, do not constitute revenues. Revenues are specific to the income generated from business operations.
Revenues play a vital role in determining the profitability of a company. By subtracting the costs and expenses associated with generating the revenues from the total revenue earned, we arrive at the net income (or net profit) figure. Net income reflects the company’s bottom line after deducting all related expenses, including operating costs, salaries, taxes, and interest.
Not only do revenues contribute to a company’s profitability, but they also impact its ability to invest in growth initiatives, repay debts, and distribute dividends to shareholders. They are crucial for sustaining and expanding the business. Understanding the dynamics of revenues and their effects on the accounting equation is essential for monitoring the financial performance and sustainability of a company.
Effects of Revenues on the Accounting Equation
Now that we have established the definition of revenues, let’s explore how they impact the accounting equation. Revenues have a direct influence on both the assets and equity sides of the equation.
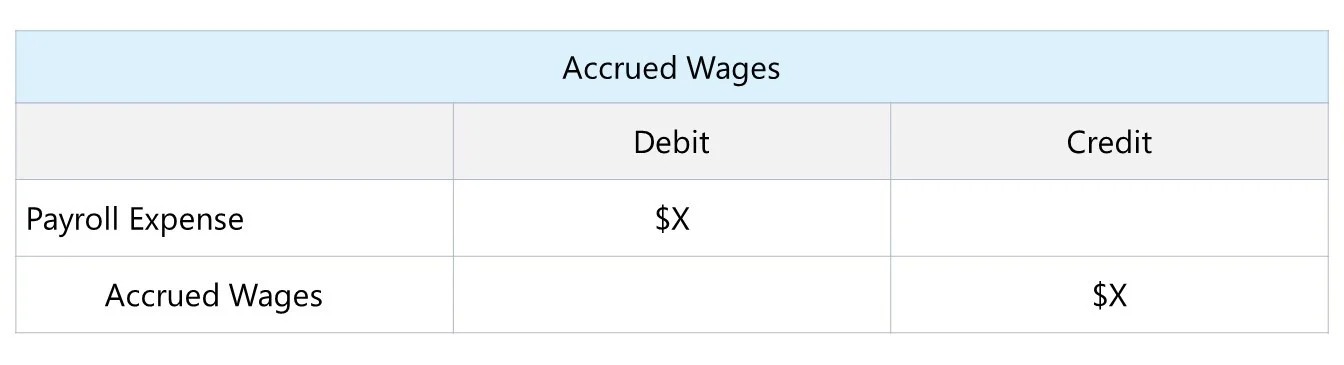
When a company generates revenue, it increases its assets. This increase typically occurs in the form of cash or accounts receivable. Cash is a tangible asset that represents the actual funds received from customers, while accounts receivable is an asset that represents the amount owed to the company by its customers for goods or services provided on credit.
On the equity side of the equation, revenues affect retained earnings. Retained earnings are a component of equity and represent the accumulated profits of a company that have not been distributed as dividends to shareholders. When revenues are earned, they contribute to the increase in retained earnings, reflecting the company’s profitability.
Therefore, the impact of revenues on the accounting equation can be summarized as follows:
- Assets: Revenues increase the value of assets, primarily in the form of cash or accounts receivable.
- Equity: Revenues contribute to the increase in retained earnings, reflecting the profitability of the company.
It is important to note that as revenues impact both sides of the equation, they maintain the balance between the two sides. This ensures that the accounting equation remains in equilibrium.
Next, let’s walk through an example illustration to better understand how revenues affect the accounting equation.
Example Illustration
To illustrate the effects of revenues on the accounting equation, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario involving a retail company.
ABC Retail is a clothing store that sells various apparel and accessories. In a given month, ABC Retail generates $50,000 in total revenues from the sale of its products. The breakdown of these revenues is as follows:
- $40,000 from cash sales
- $10,000 from credit sales
First, let’s look at the impact of revenues on the asset side of the accounting equation. The $40,000 from cash sales would increase the company’s cash balance in its assets. Additionally, the $10,000 from credit sales would result in an increase in accounts receivable, as this represents the amount owed to the company by its customers who made purchases on credit.
On the equity side of the equation, the $50,000 in total revenues would contribute to an increase in retained earnings. Retained earnings capture the cumulative profits of the company, and the revenue generated reflects the profitability of ABC Retail.
Therefore, after considering the effects of revenues, the accounting equation for ABC Retail would be as follows:
- Assets: Cash + Accounts Receivable + Other Assets
- Liabilities: Accounts Payable + Other Liabilities
- Equity: Capital + Retained Earnings
As we can see, the increase in cash and accounts receivable on the asset side is balanced by the increase in retained earnings on the equity side, ensuring the equation remains in balance.
This example serves as a basic illustration of how revenues affect the accounting equation. In real-world scenarios, the equation can become more complex due to additional factors and transactions.
Now that we have examined the impact of revenues on the accounting equation, let’s explore some other factors that can influence this equation.
Factors Affecting the Accounting Equation
While revenues have a significant impact on the accounting equation, it is essential to recognize that there are other factors that can influence the equation as well. These factors include transactions, events, and changes in business operations that can affect the assets, liabilities, and equity of a company.
Here are some key factors that can impact the accounting equation:
- Expenses: Expenses represent the costs incurred by a company in its day-to-day operations, such as rent, salaries, utilities, and inventory purchases. Expenses reduce the net income of a company and, in turn, decrease retained earnings and owner’s equity.
- Liabilities: Changes in liabilities, such as taking on new loans or paying off existing debts, can directly affect the accounting equation. An increase in liabilities would increase the right side of the equation (liabilities plus equity), while a decrease in liabilities would decrease the right side.
- Owner’s Investment/Withdrawal: If the owner contributes additional funds to the business, it would increase the equity side of the equation. Conversely, if the owner withdraws funds from the business, it would decrease the equity side.
- Purchases and Sales of Assets: Acquiring or disposing of assets, such as property, equipment, or investments, can impact the equation. Purchasing assets would increase the asset side, while selling assets would decrease the asset side.
- Income or Loss: Apart from revenues, a company’s income or loss from sources other than its primary operations can impact the equation. This includes income or loss from investments, interest income, or extraordinary events.
These factors, along with revenues, work together to determine the financial position of a company. It is essential for accountants, financial analysts, and stakeholders to consider these factors when analyzing the accounting equation and assessing the overall health of a business.
Now that we have explored the various factors affecting the accounting equation, let’s summarize the key points before concluding our discussion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, revenues have a significant impact on the accounting equation, which serves as the foundation for financial reporting and analysis. Revenues, representing the income generated from business operations, directly affect both the asset and equity sides of the equation.
On the asset side, revenues increase the value of assets, usually in the form of cash or accounts receivable. Cash represents the actual funds received from customers, while accounts receivable reflects the amount owed to the company by customers who made purchases on credit. These increases in assets contribute to the financial strength of the company.
On the equity side, revenues contribute to the increase in retained earnings, reflecting the profitability of the company. Retained earnings represent the cumulative profits of the company that have not been distributed as dividends to shareholders. Higher revenues lead to higher retained earnings, which, in turn, can support future growth and business expansion.
It is important to note that while revenues play a crucial role in the accounting equation, other factors also influence its balance. Expenses, liabilities, owner’s investment/withdrawal, purchases and sales of assets, and income or loss from various sources can impact the equation and provide a more comprehensive financial picture.
Understanding the effects of revenues and other factors on the accounting equation is essential for financial decision-making, planning, and evaluating the financial position of a company. It allows stakeholders to assess the profitability, liquidity, and overall health of the business.
By analyzing the accounting equation and considering all the relevant factors, businesses can make informed decisions, investors can evaluate investment opportunities, and creditors can assess creditworthiness. It is a valuable tool in the world of finance and accounting that contributes to the efficient functioning of the global economy.
So remember, revenues, along with other factors, shape and impact the accounting equation, providing insights into the financial position and performance of a company.