Finance
How To Calculate The Insurance Premium Formula
Published: November 16, 2023
Learn how to calculate insurance premiums using the formula. Explore the finance aspect of insurance and understand the factors that determine your premium
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Insurance is a crucial aspect of personal finance, providing protection against unexpected events that can have significant financial repercussions. When seeking insurance coverage, understanding how insurance premiums are calculated is essential. The insurance premium refers to the amount an individual or organization pays to an insurance company in exchange for coverage.
Insurance premiums are determined by a variety of factors, including the type of insurance policy, the coverage amounts, and the perceived risk associated with the insured party. Furthermore, insurance companies employ complex formulas and algorithms to calculate premiums, taking into account statistical data, historical claims, and other relevant factors.
In this article, we will explore the key components of insurance premium calculations and how they relate to various insurance policies. Additionally, we will delve into the basic insurance premium formula and provide real-world examples to illustrate its application.
Furthermore, we will discuss the factors that can affect insurance premiums, including personal characteristics, lifestyle choices, and external factors. Finally, we will offer practical tips on how to reduce insurance premiums without compromising coverage.
Whether you are looking for auto insurance, home insurance, health insurance, or any other type of coverage, understanding the insurance premium formula will empower you to make informed decisions and find the best policy to suit your needs and budget.
Understanding Insurance Premiums
Insurance premiums are the amount policyholders pay to their insurance providers in order to obtain coverage. They serve as a function of risk, with higher-risk individuals or entities typically paying higher premiums. Insurance companies use various factors to assess risk and calculate premiums, ensuring that they can adequately cover potential claims while maintaining profitability.
Insurance premiums are crucial because they allow insurance companies to pool resources from policyholders and distribute costs associated with claims. By collecting premiums from a large number of individuals, insurance companies can spread the risk and ensure that there are sufficient funds available to pay out claims.
It’s important to understand that insurance premiums are not arbitrary numbers; they are based on careful analysis of statistical data, historical trends, and actuarial calculations. Insurance companies use these calculations to determine the likelihood of a claim occurring and the potential cost of that claim. This information is then used to assign a corresponding premium.
Insurance premiums can vary significantly depending on the type of insurance policy. For example, auto insurance premiums are influenced by factors such as the driver’s age, driving record, location, and the type of vehicle being insured. On the other hand, health insurance premiums are determined by factors such as age, pre-existing medical conditions, and coverage level.
Understanding the factors that contribute to insurance premium calculations is crucial for individuals seeking insurance coverage. By having a clear understanding of how premiums are determined, policyholders can make informed decisions when shopping for insurance policies, comparing quotes, and assessing the overall value provided by different insurance providers.
Components of Insurance Premium Calculations
Insurance premiums are calculated based on several key components that insurers take into consideration when determining the cost of coverage. These components may vary depending on the type of insurance policy, but there are common factors that are typically taken into account across different insurance types. Let’s explore the main components of insurance premium calculations:
Risk Factors:
Insurance premiums are heavily influenced by risk factors associated with the insured party. These include factors such as age, gender, occupation, health status, driving record, and location. For example, an older individual may be charged a higher premium for life insurance due to an increased likelihood of potential health issues. Similarly, a driver with a history of traffic violations may face higher auto insurance premiums.
Coverage Amount:
The level of coverage desired by the policyholder plays a significant role in premium calculations. The higher the coverage amount, the more the insurance company will need to pay out in the event of a claim. Consequently, higher coverage amounts tend to result in higher premiums.
Deductible:
The deductible is the amount of money the policyholder agrees to pay out-of-pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. Opting for a higher deductible can lower the insurance premium, as it shifts some of the risk and financial burden onto the policyholder.
Claims History:
Insurance companies consider the claims history of the policyholder when calculating premiums. Individuals with a history of filing frequent claims may be considered higher risk and could face higher premiums.
Underwriting and Actuarial Factors:
Insurance companies utilize underwriting practices and actuarial data to assess risk and determine premiums. Underwriting involves evaluating individual characteristics and lifestyle choices, while actuarial factors include statistical data on claims, loss ratios, and expected costs.
It’s important to note that these components interact with one another and can vary in significance depending on the type of insurance policy. Understanding these factors can help policyholders uncover potential ways to lower their premiums and make informed decisions when selecting coverage options.
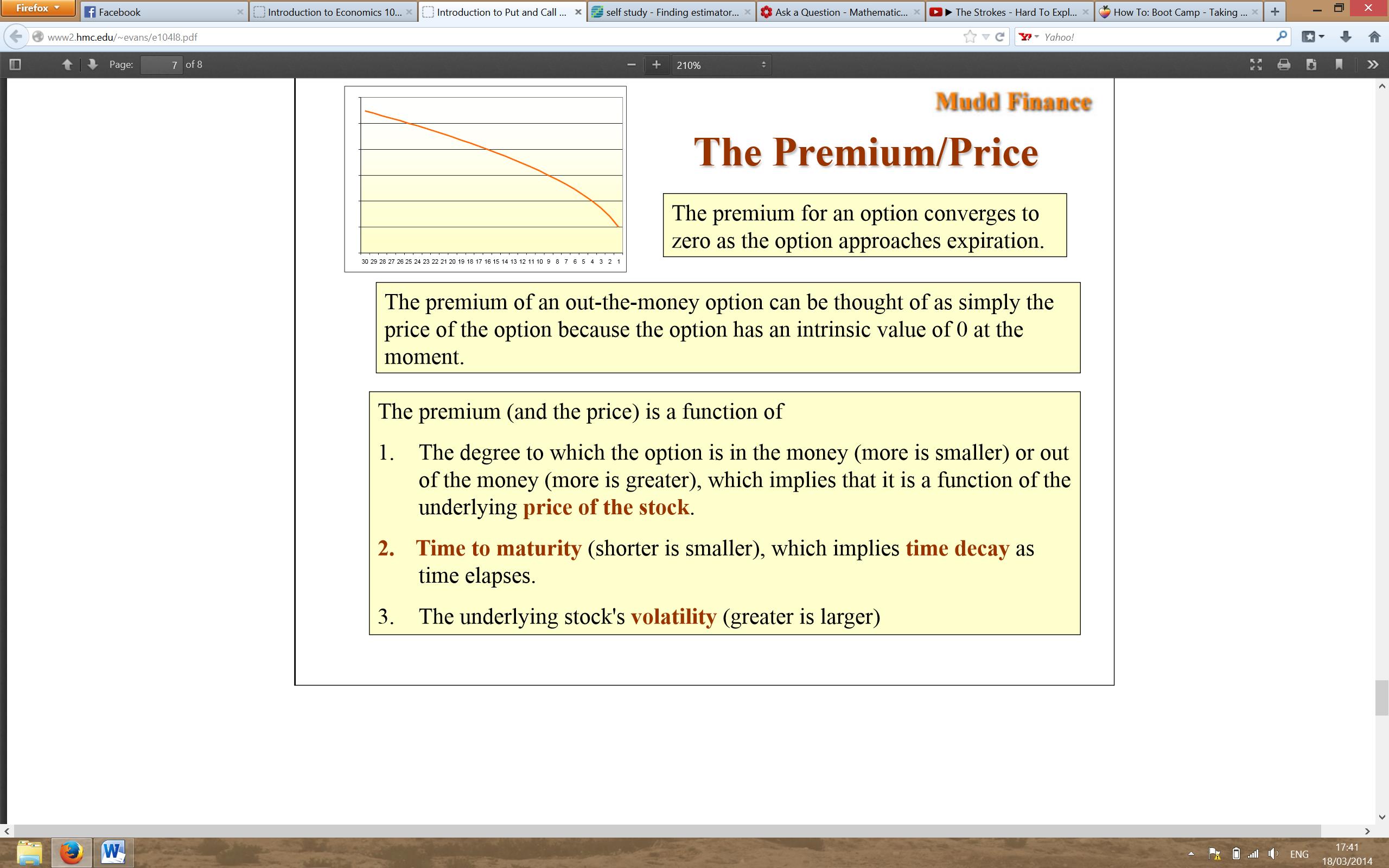
Basic Insurance Premium Formula
The calculation of insurance premiums involves complex mathematical formulas and models to determine the appropriate pricing for coverage. While the specific formulas can vary depending on the type of insurance policy and the insurer’s practices, there is a basic insurance premium formula that serves as a foundation for most calculations. This formula is commonly used as a starting point and can be adjusted based on additional factors specific to each policy.
The basic insurance premium formula can be expressed as:
Premium = (Risk Factor + Administrative Costs) * Coverage Amount + (Claims History Factor – Deductible Credit) + Underwriting/Actuarial Factor
Let’s break down each component of this formula:
- Risk Factor: This represents the level of risk associated with the insured party. It takes into account demographic factors, such as age and gender, as well as occupation, health status, and other relevant characteristics. The higher the perceived risk, the higher the risk factor, and thus, the higher the premium.
- Administrative Costs: Insurance companies incur administrative costs to process applications, manage policies, and handle claims. These costs are typically included in the premium calculation to cover the insurer’s operational expenses.
- Coverage Amount: The desired coverage amount dictates the level of protection the policyholder wants. As the coverage amount increases, so does the potential payout by the insurance company in the event of a claim, resulting in a higher premium.
- Claims History Factor: Insurers analyze the claims history of the policyholder to assess the likelihood of future claims. A history of frequent claims may indicate a higher risk of future claims, leading to an increase in the premium.
- Deductible Credit: The deductible represents the amount the policyholder agrees to pay out-of-pocket before the insurance coverage applies. Opting for a higher deductible can lead to a reduced premium, as the policyholder assumes a greater portion of the risk.
- Underwriting/Actuarial Factor: Insurance companies utilize underwriting practices and actuarial data to analyze risk and determine appropriate premiums. These factors encompass statistical data on claims, loss ratios, and expected costs to ensure the financial stability of the insurance company.
It’s important to note that this basic formula may be adjusted or supplemented by additional factors specific to each insurance policy. The complexity of premium calculations highlights the importance of obtaining quotes from multiple insurers to compare prices and coverage options effectively.
Example Calculation
Let’s walk through an example to illustrate how the basic insurance premium formula works in practice. Suppose we are calculating the premium for a home insurance policy for a property valued at $300,000. Here is the breakdown:
Risk Factor: The insured party is a homeowner in an area with a low crime rate and a history of minimal natural disasters. The risk factor is determined to be low.
Administrative Costs: The insurance company estimates administrative costs to be $100 per year.
Coverage Amount: The property owner desires coverage for the full value of $300,000.
Claims History Factor: The homeowner has not previously filed any insurance claims, indicating a clean claims history.
Deductible Credit: The homeowner opts for a deductible of $1,000, providing a credit towards the premium.
Underwriting/Actuarial Factor: The insurance company’s actuarial data suggests an underwriting factor of 1.2 for this type of property.
To calculate the premium, we can plug these values into the basic insurance premium formula:
Premium = (Risk Factor + Administrative Costs) * Coverage Amount + (Claims History Factor – Deductible Credit) + Underwriting/Actuarial Factor
Premium = (Low Risk + $100) * $300,000 + (Clean History – $1,000) + 1.2
In this hypothetical scenario, let’s assume the low risk factor is assigned a value of 0.8 and the clean claims history factor is assigned a value of 0.9.
Premium = (0.8 + $100) * $300,000 + (0.9 – $1,000) + 1.2
Premium = ($100.8) * $300,000 + ($-99.1) + 1.2
Premium = $30,240 + ($-99.1) + 1.2
Premium = $30,141.1
Therefore, the calculated premium for the home insurance policy in this example is $30,141.1 per year.
It is important to note that this is a simplified example, and actual insurance premiums may involve more complex calculations and additional factors specific to each policy and insurance provider.
Factors Affecting Insurance Premiums
Insurance premiums are influenced by a variety of factors that insurance companies consider when calculating the cost of coverage. These factors help insurers assess the risk associated with each policyholder and determine the appropriate premium. Here are some key factors that can affect insurance premiums:
Age and Gender:
Age and gender are important factors considered in insurance premium calculations. For example, younger individuals may face higher auto insurance premiums due to their relative lack of driving experience. Similarly, certain health insurance policies may charge higher premiums for older individuals who are considered to have a higher risk of developing health issues.
Occupation:
Some insurance policies take into account the type of occupation the policyholder has. Certain occupations, such as those in high-risk industries like construction or aviation, may result in higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of accidents or injuries.
Health Status:
Health insurance premiums are influenced by the health status of the insured individual. Those with pre-existing medical conditions or a history of health issues may face higher premiums as they are more likely to require medical treatment.
Lifestyle Choices:
Lifestyle choices can impact insurance premiums as well. For example, smokers often face higher health and life insurance premiums due to the increased risk of health-related issues, including respiratory problems and certain types of cancer.
Location:
The geographical location of the insured party can affect insurance premiums. Areas with higher crime rates, higher traffic congestion, or higher instances of natural disasters may have higher auto or property insurance premiums due to the increased risk of theft, accidents, or property damage.
Driving Record:
When it comes to auto insurance, a person’s driving record plays a significant role in determining premiums. Those with a history of accidents or traffic violations may face higher insurance costs as they are considered a higher-risk driver.
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples of the many factors that can influence insurance premiums. Each insurance policy and provider may have additional specific factors that they consider in their premium calculations. Understanding how these factors affect premiums can help individuals make informed decisions when comparing insurance quotes and seeking coverage.
Tips for Lowering Insurance Premiums
Insurance premiums can often be a significant expense in a person’s budget, and finding ways to lower them without compromising coverage is a top priority for many individuals. While insurance premiums are determined by various factors, there are several strategies that can help reduce insurance costs. Here are some tips for lowering insurance premiums:
Shop Around:
One of the most effective ways to lower insurance premiums is to shop around and compare quotes from multiple insurance providers. Different insurers may offer different rates, discounts, and coverage options, so it’s essential to research and get quotes from several companies before making a decision.
Bundle Policies:
Consider bundling multiple insurance policies with the same insurer. Many insurance companies offer multi-policy discounts for combining auto, home, and other types of insurance coverage. Bundling policies can lead to significant savings on premiums.
Opt for Higher Deductibles:
Choosing a higher deductible can lower insurance premiums. By assuming a greater portion of the risk and agreeing to pay a higher amount out-of-pocket before insurance coverage applies, policyholders can enjoy reduced premiums.
Maintain a Good Credit Score:
Insurance companies often consider credit scores when determining premiums. Maintaining a good credit score demonstrates financial responsibility and can result in lower insurance rates. Pay bills on time, manage debt effectively, and regularly review credit reports to ensure accuracy.
Practice Safe Behavior and Maintain a Good Record:
Safe behavior, whether it’s driving responsibly, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, or prioritizing safety measures in your home, can help lower insurance premiums. Avoid accidents, traffic violations, and claims to maintain a clean record, which insurers often reward with lower rates.
Take Advantage of Discounts:
Insurance providers offer a variety of discounts that policyholders can take advantage of to lower premiums. These may include discounts for having a safe driving record, being a non-smoker, installing safety features in your home or vehicle, or being a member of certain professional organizations. Inquire about available discounts and ensure that you are taking advantage of all the savings opportunities.
Consider Usage-Based Insurance:
For certain types of insurance, such as auto insurance, usage-based insurance programs are becoming increasingly popular. These programs use technology to monitor driving habits and offer discounts or rewards for safe driving behavior. If you are a responsible and low-risk driver, a usage-based insurance program may result in lower premiums.
It’s important to note that while these strategies can help lower insurance premiums, it’s crucial to maintain adequate coverage and understand the potential impact of making changes to your policy. Consult with insurance professionals to ensure that you are making informed decisions tailored to your specific needs.
Conclusion
Understanding how insurance premiums are calculated and the factors that influence them is essential for anyone seeking insurance coverage. Insurance premiums play a crucial role in determining the cost of coverage and ensuring that insurance companies can adequately cover potential claims.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various components of insurance premium calculations and discussed the basic insurance premium formula. We have also delved into real-world examples to illustrate how premiums can be calculated for different insurance policies.
Additionally, we have highlighted the factors that can affect insurance premiums, including age, gender, occupation, health status, location, and claims history. By understanding these factors, individuals can make informed decisions when comparing insurance quotes and seeking coverage that aligns with their needs and budget.
Moreover, we have provided useful tips for lowering insurance premiums, such as shopping around for the best rates, bundling policies, opting for higher deductibles, maintaining a good credit score, practicing safe behavior, and taking advantage of available discounts. These strategies can help reduce insurance costs while maintaining the necessary coverage.
Remember, insurance premiums are not set in stone, and by being proactive and informed, individuals can explore options to lower their premiums without compromising on coverage.
In conclusion, having a comprehensive understanding of insurance premium calculations, the factors affecting premiums, and practical tips for lowering them can empower individuals to navigate the insurance landscape more effectively. By making wise choices, individuals can secure the coverage they need at a price that fits their budget, achieving financial peace of mind in the process.