
Finance
How To Read An IRS Transcript
Published: November 1, 2023
Learn how to read an IRS transcript and understand your financial information.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of IRS transcripts! If you have ever dealt with taxes or faced an audit, you have likely come across the term “IRS transcript.” But what exactly is an IRS transcript, and why is it important to understand how to read it? In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of IRS transcripts and provide you with the knowledge you need to navigate them confidently.
An IRS transcript is a detailed summary of your tax return information that is maintained by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It contains a wealth of information about your tax account, including personal details, income, deductions, payments, and any adjustments or changes made to your return.
Now you may be wondering, why would you need to read an IRS transcript in the first place? Well, there are several reasons. First and foremost, if you are facing an audit or have questions about your tax account, an IRS transcript can provide valuable insights and help you understand what the IRS has on record. It can also be useful if you need to provide proof of income or tax history for loan applications, financial aid, or legal purposes.
Accessing an IRS transcript is easier than you might think. The IRS provides several methods to obtain your transcript, including online, by mail, or through a phone request. You will need to provide some identifying information, such as your Social Security number, date of birth, and filing status, to authenticate your request. Once you have successfully accessed your transcript, it’s time to dive into the different sections and understand what each one represents.
The first section you will encounter is the Personal Information section. This includes your name, address, Social Security number, and other identifying details. It is essential to review this section carefully and ensure that all the information is correct. Any discrepancies should be reported to the IRS to ensure the accuracy of your tax records.
What is an IRS Transcript?
An IRS transcript is a document issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) that provides a summarized record of your tax return information. It serves as an official record of your tax account and includes details about your income, deductions, payments, and any adjustments or changes made to your return.
There are several types of IRS transcripts available, including Account Transcripts, Return Transcripts, and Record of Account Transcripts. Each type contains specific information about your tax account and serves different purposes.
The Account Transcript provides a detailed overview of your tax account for a specific tax year. It includes information such as the types of income you reported, any deductions or credits claimed, and your tax liability for that year. In addition, it includes details about any payments you made, any penalties or interest assessed, and any adjustments or changes made to your account.
The Return Transcript, on the other hand, is a summary of the information you reported on your tax return. It does not include any changes or adjustments made by the IRS. The Return Transcript can be useful if you need to provide proof of income or tax history for loan applications, financial aid, or legal purposes.
The Record of Account Transcript provides a combination of the Account and Return Transcripts. It includes a detailed record of your tax account, including both the original information you provided on your tax return and any adjustments made by the IRS. This transcript is valuable if you are facing an audit or have questions about your tax account.
Reading an IRS transcript may seem intimidating at first, but with a little guidance, you can easily decipher the information it contains. The transcript is divided into various sections, including personal information, account summary, transaction codes, and more. Understanding these sections will allow you to navigate the transcript effectively and gain valuable insights into your tax account.
Why Would You Need to Read an IRS Transcript?
There are several reasons why you might need to read an IRS transcript. Whether you’re facing an audit, applying for a loan, or need to provide proof of income or tax history, understanding how to read an IRS transcript is essential. Here are a few specific scenarios where reading an IRS transcript can be beneficial:
Audit: If you are selected for an audit by the IRS, reading your IRS transcript is crucial. It will provide you with a detailed account of your tax information, allowing you to compare it with your records and understand what the IRS is focusing on during the audit. By reviewing the transcript, you can identify potential discrepancies or errors and gather the necessary documentation to support your position.
Discrepancies or Errors: If you discover any discrepancies or errors in your tax records, reading your IRS transcript can help you understand where the issue lies. The transcript will provide a comprehensive overview of your tax account, including any adjustments or changes made by the IRS. By identifying the specific areas of concern, you can take the necessary steps to rectify the situation.
Proof of Income: When applying for a loan, such as a mortgage or car loan, lenders often require proof of income. An IRS transcript can serve as official documentation of your income history, providing lenders with a reliable source of information. By reading the transcript, you can ensure that the income reported matches the amounts you provided to the lender.
Tax History Verification: In some cases, you may need to provide proof of your tax history for legal or financial purposes. This could be required for court proceedings, divorce settlements, or applying for financial aid. By reading an IRS transcript, you can verify the accuracy of your tax history and present it as evidence when needed.
Tax Planning: Understanding how to read an IRS transcript can also be beneficial for tax planning purposes. By reviewing your past tax information, you can identify trends, deductions, or credits that you may have missed. This can help you optimize your tax strategy for future returns and potentially minimize your tax liability.
Overall, reading an IRS transcript is essential in various situations where you need to gain a deeper understanding of your tax account, provide proof of income, or rectify errors or discrepancies. By familiarizing yourself with the information presented in an IRS transcript, you can navigate the process more confidently and ensure the accuracy of your tax records.
How to Access an IRS Transcript
Accessing an IRS transcript is a relatively straightforward process. The IRS provides several methods for obtaining your transcript, including online, by mail, or through a phone request. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to access your IRS transcript:
- Online: The quickest and most convenient way to access your IRS transcript is through the IRS website. Visit the IRS Transcript Delivery System at www.irs.gov/individuals/get-transcript and follow the instructions to set up an account or log in if you already have one. Once logged in, you can view and download your transcripts instantly.
- By Mail: If you prefer to receive your IRS transcript by mail, you can complete Form 4506-T, Request for Transcript of Tax Return. This form is available on the IRS website or can be obtained by calling the IRS. Fill out the form with the necessary information, including the tax year(s) you need the transcript for, and mail it to the address specified on the form. It may take several days or weeks to receive the transcript, depending on the IRS processing time.
- By Phone: Another option is to request your IRS transcript by phone. Call the IRS at their Transcript Ordering Line at 1-800-908-9946 and follow the automated instructions to request your transcript. You will need to provide your Social Security number, date of birth, and the tax year(s) you need the transcript for. The transcript will be mailed to your address on record, and it may take some time to receive it.
When accessing your IRS transcript, it’s important to have certain information ready to verify your identity. This may include your Social Security number, date of birth, filing status, and mailing address. Ensuring the accuracy of the provided information is crucial to successfully accessing your transcript.
Once you have obtained your IRS transcript, whether online, by mail, or by phone, it’s time to familiarize yourself with the different sections and understand how to read the information presented. This will allow you to make sense of the details and gain valuable insights into your tax account.
Remember, IRS transcripts contain sensitive information, so it’s important to keep them secure. Only provide transcripts to authorized individuals or entities who require them for legitimate purposes.
Understanding the Different Sections of an IRS Transcript
When you receive an IRS transcript, it may appear overwhelming at first glance. However, by understanding the different sections and what they represent, you can navigate the information effectively. Here are the key sections you’ll come across on an IRS transcript:
- Personal Information: This section contains your name, taxpayer identification number (such as your Social Security number), address, and other identifying details. It is crucial to review this section carefully and ensure that all the information is correct. Any discrepancies should be reported to the IRS to maintain accurate tax records.
- Account Transcript: The Account Transcript provides a summary of your tax account for a specific tax year. It includes information such as the types of income reported, any deductions or credits claimed, and your tax liability. It also lists any payments made, penalties or interest assessed, and any adjustments or changes made by the IRS. This section provides a comprehensive overview of your tax account activity.
- Return Transcript: The Return Transcript is a summary of the information you reported on your tax return. It does not include any changes or adjustments made by the IRS. This section is useful for verifying the accuracy of the information you provided on your tax return and can be used as proof of income or tax history for loan applications or other purposes.
- Record of Account: The Record of Account Transcript combines the Account and Return Transcripts. It includes a detailed record of your tax account, including both the original information you provided on your tax return and any adjustments made by the IRS. This section is particularly helpful if you are facing an audit or have questions about your tax account.
- Transaction Codes: The Transaction Codes section provides a list of codes that represent specific actions or events related to your tax account. Each code has a specific meaning, such as posting a payment, assessing a penalty, or adjusting a return. Understanding these codes can help you decipher the IRS’s actions and identify any changes made to your account.
It’s important to note that while the layout and terminology may vary slightly on different types of IRS transcripts, the overall structure remains consistent. By familiarizing yourself with these sections, you can better interpret the information presented in an IRS transcript and gain insights into your tax account. Remember, if you have any questions or concerns about the information in your IRS transcript, it’s always advisable to consult with a tax professional or contact the IRS directly.
Personal Information
The Personal Information section of an IRS transcript contains essential details about the taxpayer. It includes information such as the taxpayer’s name, taxpayer identification number (such as the Social Security number), address, and filing status. This section serves as the foundation of the transcript and ensures that the correct taxpayer’s records are being accessed.
When reviewing your Personal Information section, it is crucial to carefully check for accuracy. Verify that your name is spelled correctly and matches the name on your tax returns, as well as any changes in your address or filing status. Discrepancies in personal information may lead to issues with the processing and verification of your tax records.
It is important to note that if you find any errors or outdated information in the Personal Information section, you should take immediate steps to rectify them. Contact the IRS to update your personal information by providing the necessary documentation and supporting evidence of the correct information.
Additionally, it is essential to ensure that the taxpayer identification number (TIN), typically the Social Security number, is accurate. The TIN is a unique identifier that ties your tax records to your personal information. Any errors in this section can lead to complications in IRS correspondence and the processing of your tax returns.
Overall, the Personal Information section of an IRS transcript is the first section to review when you receive your transcript. It establishes the foundation for the rest of the information contained within the transcript. By ensuring the accuracy of your personal details, you can ensure that your tax records are correctly attributed to you and mitigate any potential issues with your tax account.
Account Transcript
The Account Transcript is a vital section of an IRS transcript as it provides a comprehensive summary of your tax account for a specific tax year. This section contains valuable information about your income, deductions, payments, penalties, interest, and any adjustments or changes made by the IRS.
When reviewing the Account Transcript, you will find details about the types of income you reported, such as wages, self-employment income, dividends, or interest. It also includes information about any deductions or credits you claimed, such as education expenses, mortgage interest, or business expenses.
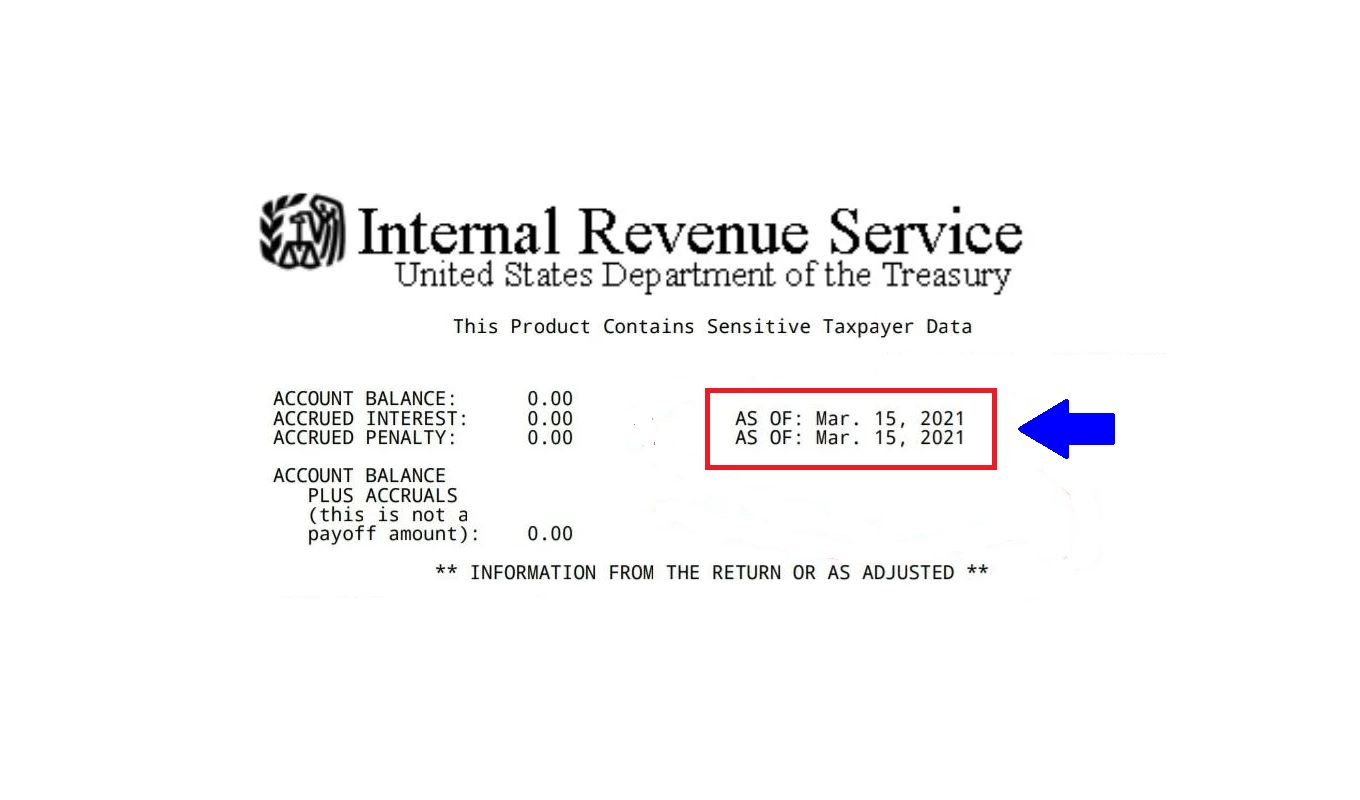
The Account Transcript displays your tax liability for the specific tax year and provides insights into how your payments and credits have been applied. It shows any payments you made, including estimated tax payments or withholding, and any penalties or interest assessed if you did not pay the full amount owed by the due date.
One crucial aspect of the Account Transcript is that it documents any adjustments or changes made by the IRS. This includes corrections to errors on your tax return, adjustments based on information received from third parties (such as W-2 or 1099 forms), or changes due to an audit or examination. It is important to review these adjustments carefully to understand the impact on your tax liability.
In addition, the Account Transcript may reflect any collection actions taken by the IRS, such as the filing of a federal tax lien or the initiation of an installment agreement. It can provide insights into the status of any unresolved issues or outstanding balances.
Understanding the Account Transcript is essential if you are facing an audit or have questions about specific entries on your tax return. It allows you to compare the information on your tax return with the IRS’s records and identify any discrepancies or errors that may need to be addressed.
Overall, the Account Transcript section provides a comprehensive overview of your tax account for a specific tax year. By carefully reviewing this section, you can gain valuable insights into your income, deductions, payments, and any changes made by the IRS, helping you understand your tax liability and address any discrepancies or issues.
Return Transcript
The Return Transcript section of an IRS transcript provides a summarized version of the information you reported on your tax return. It serves as a valuable document for verifying the accuracy of the information you provided and can be used as proof of income or tax history for various purposes.
When reviewing the Return Transcript, you will find a condensed version of your tax return details. This includes information about your filing status, sources of income, deductions, credits, and other relevant entries. It reflects the data you reported on your original tax return without any adjustments or changes made by the IRS.
The Return Transcript can be particularly useful when applying for loans, such as mortgages or car loans. Lenders often require proof of income and tax history to assess your creditworthiness. By providing a Return Transcript, you can provide a reliable source of information to support your loan application.
Additionally, the Return Transcript can be beneficial for financial aid applications. When applying for student loans or grants, educational institutions may require proof of income and tax information. The Return Transcript can serve as documentation to demonstrate your financial circumstances.
It’s important to note that the Return Transcript does not include any adjustments or changes made by the IRS. If you have been through an audit or examination, or if the IRS has made corrections to your tax return, those adjustments will not be reflected in the Return Transcript.
The Return Transcript section can also be helpful when reviewing your own tax records. By comparing the information on the Return Transcript with your own records, you can ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies. This is especially important if you believe there may be errors or if you are taking steps to amend your tax return.
Overall, the Return Transcript section provides a concise summary of the information you reported on your tax return. It can be used as proof of income or tax history, allowing you to verify the accuracy of your tax records and support various financial applications. It is a valuable tool for managing your tax information and ensuring the consistency of your financial records.
Record of Account
The Record of Account section in an IRS transcript is a comprehensive record that combines both the Account Transcript and the Return Transcript. It provides a detailed history of your tax account, including the original information you reported on your tax return and any adjustments or changes made by the IRS.
When reviewing the Record of Account section, you will find a chronological summary of your tax account activities. It includes the types of income you reported, deductions and credits claimed, payments made, penalties or interest assessed, and any adjustments made by the IRS.
By combining the information from the Account Transcript and the Return Transcript, the Record of Account allows you to review your tax account history as a cohesive and complete picture. It provides insights into any changes or corrections made by the IRS, ensuring that you have an accurate record of your tax liabilities and payments.
The Record of Account is especially useful if you are facing an audit, examination, or have questions about specific entries on your tax return. It allows you to see the adjustments made by the IRS and the justification behind them. This information empowers you to provide supporting documentation or address any discrepancies with the IRS.
It is important to review the Record of Account section carefully, as it can help you identify any unresolved issues or outstanding balances. If you notice any errors or discrepancies, it is advisable to contact the IRS or consult with a tax professional to address the matter promptly.
Furthermore, the Record of Account can be valuable for financial planning purposes. By analyzing your tax account history, you can identify patterns or trends in your income, deductions, or credits. This information can help you make informed decisions and optimize your tax strategy for future tax returns.
Overall, the Record of Account section provides a comprehensive and detailed overview of your tax account history. By carefully examining this section, you can ensure the accuracy of your tax records, address any discrepancies, and make informed decisions regarding your tax planning and filing activities.
Transaction Codes
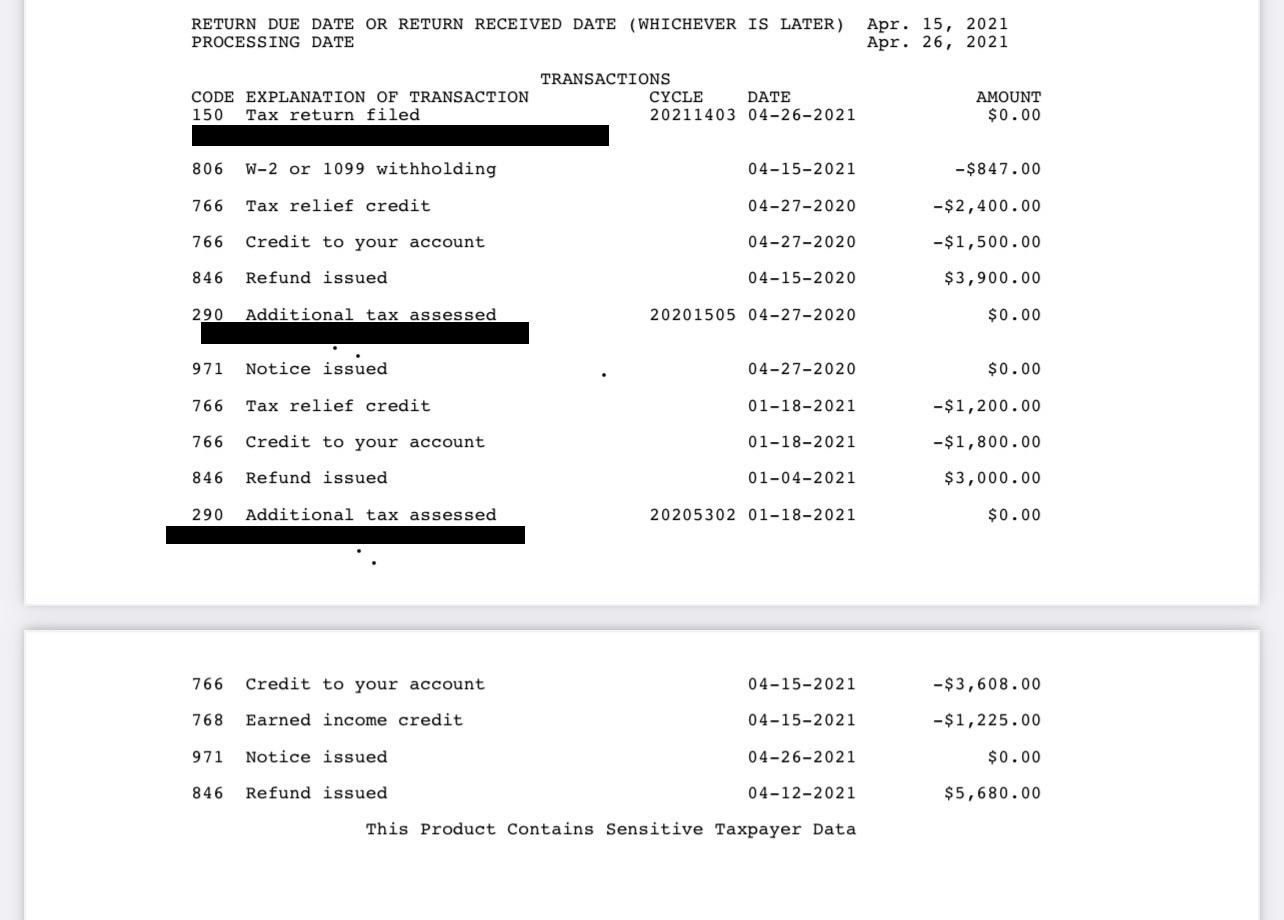
The Transaction Codes section in an IRS transcript contains a list of codes that represent specific actions or events related to your tax account. Each code serves as a shorthand notation for a particular transaction that has occurred between you and the IRS. Understanding these codes is crucial to interpreting the actions taken and changes made to your tax account.
The Transaction Codes can vary depending on the type of transaction or event. Some common codes include:
- Payment Codes: These codes indicate payments made towards your tax liabilities. They may include codes for different types of payments, such as estimated tax payments, payroll withholdings, or credits applied to your account.
- Audit or Examination Codes: These codes represent actions related to an audit or examination of your tax return. They can indicate the selection for audit, scheduled appointments, requests for documentation, or final audit decisions.
- Penalty or Interest Codes: These codes signify the assessment of penalties or interest on your tax account. They indicate the specific nature of the penalty or interest charged and the corresponding amount.
- Adjustment Codes: These codes indicate changes or adjustments made by the IRS to your tax return or account. They can reflect corrections to errors, adjustments based on additional information received, or changes resulting from an audit or examination.
- Refund Codes: These codes represent the issuance of a refund by the IRS. They indicate the type of refund, such as a direct deposit or paper check, and the amount refunded.
Understanding these transaction codes can provide valuable insights into the actions taken by the IRS and any changes made to your tax account. By reviewing the codes, you can decipher the events that have occurred, track the progress of specific transactions, and identify any discrepancies or issues that need to be addressed.
If you come across transaction codes that you do not understand or have concerns about, it is advisable to consult with a tax professional or contact the IRS directly for clarification. They can provide further guidance and explanations specific to your tax situation.
Overall, the Transaction Codes section in an IRS transcript serves as a roadmap to understanding the actions and changes made to your tax account. By familiarizing yourself with these codes, you can better comprehend the IRS’s actions, ensure accuracy in your tax records, and effectively address any issues that arise.
Closing Thoughts
Understanding how to read an IRS transcript is an essential skill for anyone dealing with taxes or facing an audit. The transcript provides a detailed summary of your tax account, including personal information, income, deductions, payments, penalties, interest, and any adjustments made by the IRS.
By gaining familiarity with the different sections of an IRS transcript, such as the Personal Information, Account Transcript, Return Transcript, Record of Account, and Transaction Codes, you can navigate the information more effectively. Reviewing these sections allows you to verify the accuracy of your tax records, address any discrepancies, and gain valuable insights into your tax account history.
Accessing an IRS transcript is easier than ever, with online, mail, and phone options available. The online platform provides quick access to your transcripts, while the mail and phone methods are suitable alternatives for those who prefer a physical copy or require assistance.
Whether you need to provide proof of income, verify tax history, or address issues with your tax account, understanding how to read an IRS transcript is vital. It empowers you to navigate through the complexities of tax records, make informed decisions regarding tax planning and filings, and ensure the accuracy of your financial records.
If at any point you feel overwhelmed or unsure about the information in your IRS transcript, it is recommended to seek guidance from a tax professional or contact the IRS directly. They can provide personalized assistance and clarification based on your specific tax situation.
Remember, an IRS transcript is a powerful tool that can give you insights and control over your tax account. By mastering the art of reading an IRS transcript, you can confidently handle tax-related matters and make informed choices to optimize your tax situation.