Finance
How To Reduce Market Risk
Modified: December 30, 2023
Learn essential finance strategies to reduce market risk and protect your investments. Discover how to navigate uncertain economic conditions and make informed financial decisions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Market risk is an inherent aspect of investing that every investor needs to be aware of and manage effectively. It refers to the potential for losses arising from fluctuations in the overall market conditions, such as economic factors, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment. Understanding and mitigating market risk is essential for preserving capital and achieving long-term investment success.
In this article, we will explore various strategies and techniques to reduce market risk. By diversifying portfolios, assessing individual stock risk, using asset allocation, employing derivative instruments, and considering market timing, investors can mitigate the impact of adverse market movements. Additionally, we will discuss the importance of investor behavior in managing market risk.
It is crucial to note that while market risk cannot be entirely eliminated, it can be effectively managed and controlled to minimize potential losses. By implementing the strategies outlined in this article, investors can navigate through market volatility with more confidence and protect their investment portfolios.
So, let’s delve deeper into the world of market risk and discover how to alleviate its impact on our investment outcomes.
Understanding Market Risk
Market risk refers to the potential for investment losses due to adverse movements in the overall market. It encompasses various factors that affect market conditions, such as economic indicators, political events, and investor sentiment. Understanding market risk is crucial for investors to make informed decisions and protect their portfolios.
One of the key components of market risk is systematic risk, also known as undiversifiable risk. This type of risk cannot be eliminated through diversification because it affects the entire market. Systematic risk includes factors like interest rate fluctuations, inflation, and economic recessions. For example, during a recession, stock prices tend to decline, impacting the value of a diversified portfolio.
Another aspect of market risk is idiosyncratic risk, also referred to as unsystematic risk. This risk is specific to individual stocks or sectors and can be reduced through diversification. By investing in a variety of assets across different industries and sectors, investors can mitigate the impact of idiosyncratic events that may negatively affect one particular investment.
Market risk can also be influenced by external factors such as geopolitical events, natural disasters, and changes in government policies. These events can have a significant impact on market sentiment and result in increased volatility and potential losses.
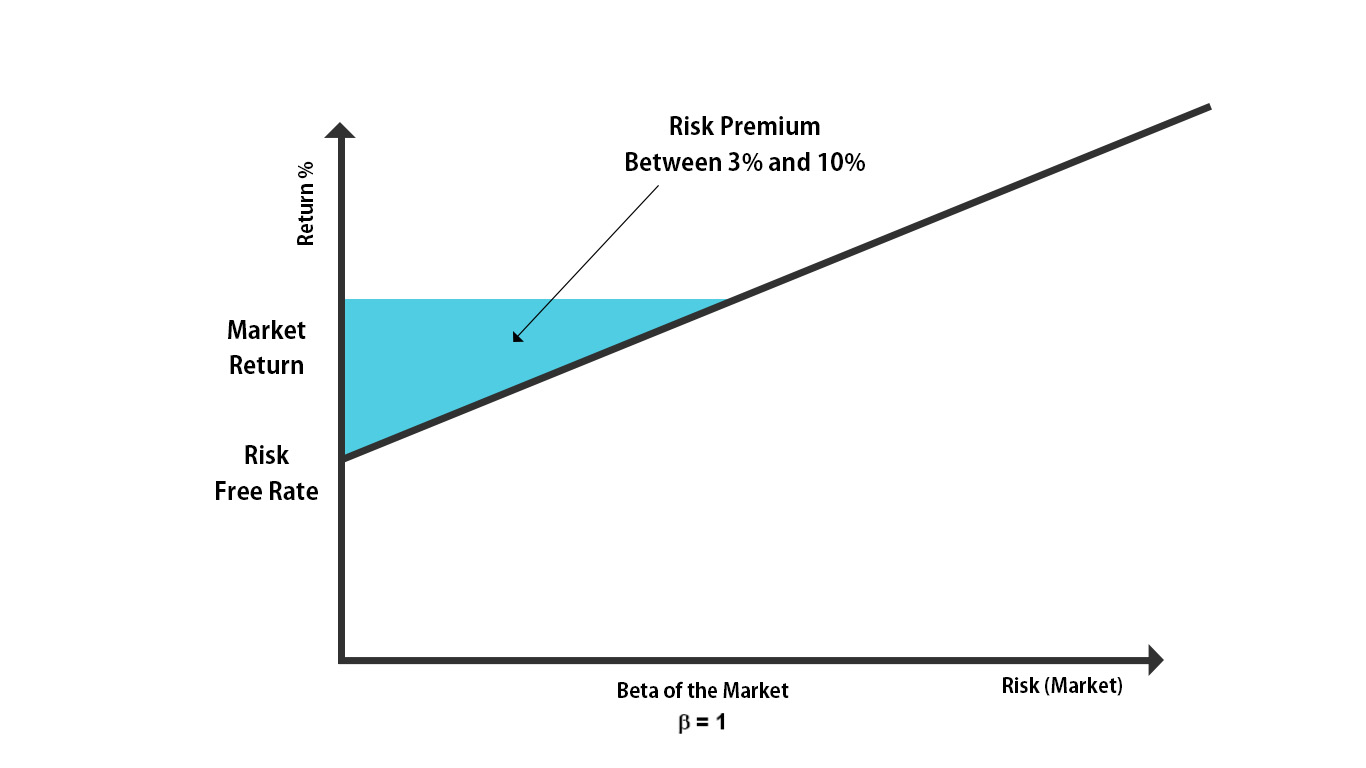
Investors should also be aware of the concept of beta when assessing market risk. Beta measures the sensitivity of a stock or portfolio to market movements. A beta of 1 indicates that the investment is expected to move in line with the market, while a beta greater than 1 suggests higher volatility compared to the market. Understanding the beta of their investments can help investors gauge the level of market risk associated with those assets.
To effectively manage market risk, investors must stay informed about economic trends, monitor global events, and conduct thorough research before making investment decisions. By understanding the factors that influence market movements, investors can position themselves better to navigate through various market conditions.
Evaluating Individual Stock Risk
When it comes to managing market risk, evaluating the risk associated with individual stocks is essential. While market risk affects all investments, the specific risks associated with individual stocks can vary significantly. It is crucial for investors to assess these risks before making investment decisions.
One of the key factors to consider when evaluating individual stock risk is the company’s financial health. This includes analyzing its balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement to assess its profitability, debt levels, and liquidity. A company with strong financials is generally considered to be less risky compared to a company with weak financials.
It is also important to evaluate the industry and sector in which the company operates. Different industries and sectors have varying levels of inherent risk. For example, sectors such as technology and biotechnology tend to be more volatile and therefore carry higher risk compared to more stable sectors like utilities or consumer staples. Understanding the risks associated with a specific industry can help investors make informed decisions about individual stock investments.
Another aspect to consider is the company’s competitive position within its industry. Companies with strong competitive advantages, such as a unique product or a dominant market position, tend to be more resilient to market downturns and have a lower risk profile. On the other hand, companies with weaker competitive positions may face greater risk and volatility.
Investors should also assess the management team and their track record. A capable and experienced management team can help navigate through challenges and make sound business decisions, reducing the overall risk associated with the stock. On the contrary, poor management can increase the company’s risk profile and negatively impact stock performance.
Lastly, it is crucial to consider the valuation of the stock. Investing in stocks that are significantly overvalued can increase the risk of losses if the market corrects. Evaluating key valuation metrics such as price-to-earnings ratio, price-to-sales ratio, and price-to-book ratio can help investors assess whether a stock is trading at a reasonable valuation.
By evaluating the individual stock risks, investors can make informed decisions and construct a portfolio that aligns with their risk tolerance and investment objectives. It is important to diversify across different stocks and sectors to reduce the concentration risk associated with individual stocks.
Diversification as a Risk Reduction Strategy
Diversification is a fundamental risk reduction strategy that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions. By diversifying their portfolios, investors aim to reduce the impact of any individual investment’s poor performance on the overall portfolio. Diversification is considered to be an effective way to manage market risk.
The rationale behind diversification is that different types of assets perform differently under various market conditions. When one asset class or sector is experiencing a downturn, another may be performing well. By including a mix of assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities, investors can potentially offset losses in one area with gains in another.
Furthermore, diversification helps mitigate the risk specific to individual stocks or sectors. By spreading investments across multiple stocks within different sectors, the impact of any negative news or events affecting a single company or industry is reduced. This helps protect the overall portfolio from substantial losses.
However, it is important to note that diversification does not guarantee a profit or protect against all types of risk. It is still possible for all asset classes to decline simultaneously in turbulent market conditions. Therefore, diversification should be combined with other risk management strategies to create a well-rounded investment approach.
There are several ways to achieve diversification. One approach is to invest in mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that offer exposure to a broad range of assets. These funds typically invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks or bonds, providing instant diversification for investors with limited resources or expertise.
Another approach is to build a diversified portfolio of individual stocks. Investors can choose stocks from different industries and sectors, ensuring a balanced representation across the market. Additionally, diversification can extend beyond domestic markets by investing in international stocks, which can provide exposure to different economies and currencies.
Lastly, diversification can also be achieved through asset allocation, which involves strategically dividing investments among different asset classes based on their risk and return characteristics. By determining an appropriate asset allocation that aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance, investors can effectively manage market risk.
Overall, diversification is a valuable risk reduction strategy that helps investors navigate through market volatility. By spreading investments across different assets, sectors, and regions, diversification can minimize the impact of any single investment’s poor performance and provide a more stable and balanced portfolio.
Asset Allocation to Reduce Market Risk
Asset allocation is a strategic approach to managing market risk by dividing investments among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, cash, and alternative investments. This strategy aims to optimize the risk and return characteristics of a portfolio based on an investor’s objectives and risk tolerance.
By diversifying investments across different asset classes, investors can reduce their exposure to any single market or economic event. This is because different asset classes tend to perform differently under varying market conditions. For example, during periods of economic expansion, stocks might outperform bonds, while during downturns, bonds may provide more stability. By including a mix of assets, investors have the potential to decrease the overall volatility of their portfolio and mitigate market risk.
One of the key considerations in asset allocation is determining the appropriate mix of assets based on an investor’s risk tolerance and investment goals. Aggressive investors might allocate a higher proportion of their portfolio to stocks, which historically offer higher returns but also come with higher volatility. On the other hand, conservative investors might opt for a higher allocation to bonds and cash, which are generally considered less risky.
Investors can further refine their asset allocation by considering factors such as market conditions, economic outlook, and their investment time horizon. During periods of uncertainty or market volatility, a more conservative allocation might be favored to reduce potential downside risk. Conversely, during periods of economic growth, a more aggressive allocation might be appropriate to capture potential market gains.
Asset allocation is a dynamic process and should be reviewed and adjusted periodically. As an investor’s circumstances and market conditions change, their asset allocation may need to be rebalanced. For example, if one asset class has significantly outperformed others, it may become overweight in the portfolio. Rebalancing involves selling some of the overweight asset class and reallocating those funds to the underweight asset classes to restore the desired allocation.
Investors can implement asset allocation strategies through various investment vehicles, including mutual funds, ETFs, or individual securities. Additionally, target-date funds, also known as lifecycle funds, are designed to automatically adjust the asset allocation based on the investor’s target retirement date.
It is important for investors to remember that asset allocation does not guarantee profits or protect against all risks. However, by strategically diversifying investments across different asset classes, investors can potentially reduce market risk and achieve a more balanced and optimal portfolio that aligns with their long-term financial goals.
Using Derivative Instruments for Hedging
Derivative instruments are financial contracts that derive their value from an underlying asset or benchmark. They are commonly used by investors to hedge against market risk and protect their portfolios from adverse price movements. Derivatives provide a means to offset potential losses by taking an opposite position to an existing investment.
One common derivative used for hedging purposes is options. Options give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. Put options allow investors to protect against potential declines in the value of an asset, while call options can help mitigate the risk of missing out on potential gains.
By purchasing put options on individual stocks or market indices, investors can hedge their positions in case of a downturn. If the stock or index declines in value, the put option will increase in value, thereby offsetting the losses in the underlying asset. This hedging strategy provides a form of insurance against adverse market movements.
Another derivative instrument commonly used for hedging is futures contracts. Futures contracts obligate the buyer to purchase an underlying asset at a specified price and time in the future. By entering into a futures contract, investors can hedge against potential price fluctuations. For example, a commodity producer might use futures contracts to lock in prices for their production, thereby reducing their exposure to price volatility.
It is important to note that while derivative instruments can be powerful hedging tools, they also come with their own risks. Misuse or misinterpretation of derivatives can result in significant losses. Therefore, it is crucial for investors to fully understand the risks and intricacies of these instruments before incorporating them into their investment strategies. Consulting with a financial advisor or derivatives expert can provide valuable insights and guidance.
Additionally, derivatives are typically more commonly used by professional investors and institutions due to their complex nature. Individual retail investors should approach derivatives with caution and ensure they have the requisite knowledge and experience to use them effectively.
Overall, derivatives offer investors the ability to hedge against market risk by offsetting potential losses. By using options or futures contracts strategically, investors can protect their portfolios and minimize the impact of adverse market movements.
Market Timing to Mitigate Risk
Market timing refers to the practice of attempting to predict the future direction of the market and making investment decisions based on these predictions. The goal is to buy investments at low points and sell them at high points to achieve better returns and reduce the risk of losses. While market timing can be challenging and risky, it is considered a strategy to mitigate market risk if executed correctly.
Timing the market effectively requires a deep understanding of market trends, economic indicators, and investor sentiment. It relies on analysis and forecasting techniques to identify potential market turning points. However, accurately predicting market movements consistently is extremely difficult, if not impossible, even for experienced investors and professionals.
One common market timing strategy is called “buying the dip.” This approach involves purchasing investments during market downturns when prices are lower, with the expectation that they will eventually recover and provide higher returns. It is based on the belief that markets are cyclical and will eventually rebound after a decline.
Another market timing strategy is “selling the rally,” which involves selling investments during periods of market upswings. The rationale behind this strategy is to take profits when prices are high and potentially avoid losses if a market correction occurs.
However, it is important to note that market timing comes with its share of risks. The market is unpredictable, and attempting to time it can lead to missed opportunities and potential losses. Market timing requires making multiple accurate decisions consistently, which is challenging even for seasoned professionals.
Furthermore, the emotional aspect of investing can negatively impact market timing strategies. Fear and greed often drive investors’ decision-making, leading them to buy at the peak and sell at the bottom. Emotion-driven behavior can result in poor market timing decisions and ultimately detract from overall portfolio performance.
Investors should approach market timing with caution and be aware of the limitations and risks involved. It is generally recommended for long-term investors to adopt a more disciplined approach, such as dollar-cost averaging, where investments are made regularly regardless of market conditions. This approach helps to mitigate the impact of short-term market volatility and reduces the reliance on timing the market accurately.
Ultimately, market timing should be approached with careful analysis, realistic expectations, and a thorough understanding of the risks involved. It may be best suited for investors with a high-risk tolerance and the ability to actively monitor and adjust their positions based on market conditions. For the average individual investor, a long-term, diversified investment approach is generally more prudent.
The Role of Investor Behavior in Managing Market Risk
Investor behavior plays a significant role in managing market risk. How investors react to market fluctuations, their emotions, and their decision-making process can greatly impact their investment outcomes and overall portfolio performance. Understanding and managing investor behavior is crucial for effectively mitigating market risk.
One of the key aspects of investor behavior is emotional decision-making. During periods of market volatility, fear and panic can lead to impulsive decisions, such as selling investments at a loss or abandoning long-term investment strategies. Conversely, during periods of market euphoria, greed can drive investors to take on excessive risk or chase speculative investments.
To manage market risk, it is important for investors to remain disciplined and avoid making impulsive decisions based solely on emotions. Developing a well-defined investment plan, setting realistic goals, and sticking to a long-term strategy can help mitigate the impact of emotional decision-making. Regularly reviewing and rebalancing the portfolio based on predetermined criteria rather than reacting to short-term market fluctuations can also contribute to better risk management.
Another aspect of investor behavior is overconfidence. Overconfident investors might believe they can outperform the market consistently and take on excessive risk, potentially exposing themselves to significant losses. It is important for investors to remain vigilant, acknowledge their limitations, and avoid taking on undue risks that may jeopardize their long-term financial goals.
Additionally, the herd mentality or following the crowd can also impact investor behavior and increase market risk. When everyone is buying a certain investment or asset class, prices can become inflated, leading to potential bubbles and subsequent market corrections. Conversely, when everyone is selling, investment opportunities may arise. It is essential for investors to assess investments based on their own research and analysis rather than blindly following the crowd.
Education and awareness are key in managing investor behavior and market risk. Investors should stay informed about market trends, economic indicators, and the fundamentals of their investments. A solid understanding of investment principles and risk management strategies can help investors make more rational and informed decisions.
Finally, seeking professional guidance can provide valuable insights and help investors navigate through market volatility. Financial advisors can provide objective advice, help manage emotions, and provide a disciplined approach to investing.
In summary, investor behavior plays a crucial role in managing market risk. Emotional decision-making, overconfidence, and following the herd can lead to poor investment outcomes. Staying disciplined, maintaining a long-term perspective, and being aware of behavioral biases are essential for effectively managing market risk and achieving long-term investment success.
Conclusion
Managing market risk is a vital aspect of investing to protect portfolios and achieve long-term financial goals. Through a combination of strategies and techniques, investors can mitigate the impact of market fluctuations and reduce potential losses. Understanding market risk and evaluating individual stock risk are crucial in making informed investment decisions.
Diversification, by spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions, is an effective risk reduction strategy. Asset allocation helps to further optimize risk and return by strategically dividing investments based on risk tolerance and investment goals.
Derivative instruments, such as options and futures contracts, offer hedging opportunities to offset potential losses. However, these instruments should be used with caution due to their complexity and associated risks.
Market timing, while challenging, can be used to mitigate risk if executed accurately. However, a more disciplined and long-term investment approach, such as dollar-cost averaging, is often recommended for most investors.
Lastly, investor behavior plays a significant role in managing market risk. Emotional decision-making, overconfidence, and following the crowd can lead to poor investment outcomes. By remaining disciplined, staying informed, and seeking professional guidance when necessary, investors can mitigate the impact of behavioral biases and improve their investment outcomes.
In conclusion, managing market risk requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses risk evaluation, diversification, asset allocation, and consideration of derivative instruments. It also entails understanding and managing investor behavior to make rational and informed investment decisions. By implementing these strategies and techniques, investors can navigate through market volatility with greater confidence and work towards achieving their financial objectives.