
Finance
What Is The Current Market Risk Premium?
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about the current market risk premium in finance and how it impacts investments. Gain insights into the factors influencing this key financial metric.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Investing in the financial markets comes with inherent risks. One of the key concepts that investors need to understand is the market risk premium. This is a crucial factor in determining the expected return on an investment, as it represents the additional return an investor requires for taking on the risk associated with investing in the overall market.
The market risk premium is influenced by various factors, such as economic conditions, investor sentiment, and geopolitical events. It plays a significant role in asset pricing and is used to assess the potential return of an investment relative to the risk-free rate of return. Understanding the current market risk premium is essential for making informed investment decisions and managing portfolio risk.
In this article, we will explore the concept of market risk premium, examine the factors that influence it, discuss different methods for calculating it, and delve into historical and current market risk premium estimates. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of the importance of the market risk premium in the world of finance.
Definition of Market Risk Premium
The market risk premium is a critical concept in finance that represents the additional return an investor expects to earn for assuming the risk of investing in the overall market. It measures the compensation for bearing the systematic risk that cannot be eliminated through diversification.
Systematic risk, also known as market risk, refers to the risk that affects the entire market or a particular segment of it. It includes factors such as macroeconomic conditions, geopolitical events, and industry-specific risks. On the other hand, unsystematic risk, also known as idiosyncratic risk, can be diversified away by holding a diverse portfolio of investments.
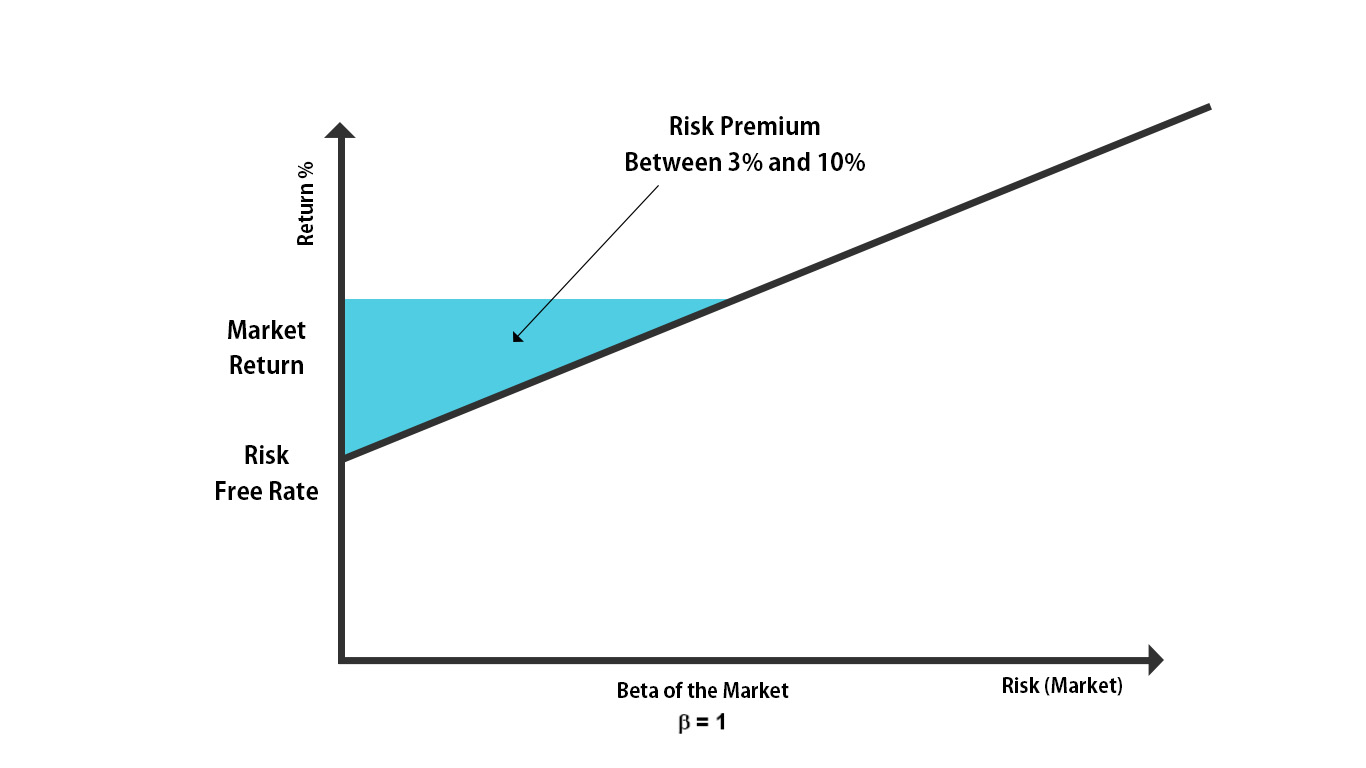
The market risk premium is the difference between the expected return on the market (usually represented by a benchmark index such as the S&P 500) and the risk-free rate of return. The risk-free rate is often approximated by the yield on government bonds, such as US Treasury bonds, which are considered to have negligible default risk.
Investors demand a higher return for taking on the additional risk associated with investing in the market compared to holding risk-free assets. The market risk premium serves as compensation for this risk and is a crucial component of the required rate of return for an investment.
The concept of market risk premium is closely related to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which provides a framework for determining the expected return of an investment based on its beta, a measure of systematic risk. According to CAPM, the expected return of an investment is equal to the risk-free rate plus the product of its beta and the market risk premium.
In summary, the market risk premium represents the compensation investors expect for taking on market risk. It is the difference between the expected return on the market and the risk-free rate of return. Understanding this concept is essential for evaluating the potential return and risk of investments and making informed investment decisions.
Factors Affecting Market Risk Premium
The market risk premium is influenced by a variety of factors that can impact the expected return on investments in the market. These factors can fluctuate over time and can significantly impact the level of risk and potential reward associated with investing in the market. Here are some of the key factors that affect the market risk premium:
- Economic Conditions: The overall health of the economy, including factors such as inflation, GDP growth, and unemployment rates, can have a significant impact on the market risk premium. During periods of economic expansion and strong growth, investors may demand a lower risk premium as they anticipate higher returns. Conversely, during economic downturns, investors may demand a higher risk premium to compensate for the increased uncertainty and potential loss of value in their investments.
- Investor Sentiment: Investor sentiment plays a crucial role in determining the market risk premium. Positive sentiment and confidence in the market can lead to lower risk premiums as investors are willing to take on more risk for potentially higher returns. Conversely, negative sentiment and increased risk aversion can drive up the market risk premium as investors demand a higher return for the perceived risk.
- Geopolitical Events: Geopolitical events, such as political instability, trade tensions, and wars, can significantly impact the market risk premium. These events introduce uncertainty and increase the perceived risk of investing in the market, leading to higher risk premiums. On the other hand, positive geopolitical developments, such as trade agreements or peaceful resolutions, can lower the risk premium as investor confidence improves.
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can have a direct impact on the market risk premium. When interest rates are low, investors may demand a lower risk premium as the opportunity cost of investing in risk-free assets, such as bonds, decreases. Conversely, when interest rates rise, investors may demand a higher risk premium to compensate for the increased cost of financing and the potential for lower returns in other asset classes.
- Market Volatility: Market volatility, measured by indicators such as the VIX (Volatility Index), can impact the market risk premium. Higher levels of volatility indicate increased uncertainty and risk, leading to higher risk premiums. Conversely, lower volatility levels may result in lower risk premiums as investors perceive a reduced level of market risk.
It is important to note that these factors are interconnected and can influence each other. For example, economic conditions can affect investor sentiment, which in turn can impact market volatility. Additionally, the relative importance of each factor can vary depending on the specific market and time period.
By understanding the factors that affect the market risk premium, investors can gain insight into the dynamics of the market and make more informed investment decisions. It is crucial to stay informed about economic indicators, geopolitical developments, interest rate movements, and market volatility to assess the current level of risk premium and its potential impact on investments.
Calculation Methods for Market Risk Premium
There are several methods used to calculate the market risk premium, each with its own advantages and limitations. These methods aim to estimate the additional return that investors require for taking on the systematic risk associated with investing in the market. Here are three commonly used calculation methods:
- Historical Approach: The historical approach to calculating the market risk premium involves analyzing historical data to determine the average excess return of the market over the risk-free rate. This method uses historical returns of a broad market index, such as the S&P 500, and subtracts the risk-free rate from the average return over a specific time period. While this method provides an empirical estimate, it assumes that historical returns are representative of future performance and does not account for changes in economic conditions or market dynamics.
- Survey-Based Approach: The survey-based approach involves collecting data by surveying market participants, such as investment professionals or analysts, to gather their estimates of the market risk premium. These surveys typically ask for estimates of expected returns on the market and the risk-free rate. The average of these estimates is then calculated to obtain an estimate of the market risk premium. The advantage of this method is that it incorporates the collective wisdom and insights of market participants. However, it relies on subjective opinions and may be influenced by biases or market sentiment.
- Equity Risk Premium Models: Equity risk premium models attempt to estimate the market risk premium based on fundamental factors. One commonly used model is the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which calculates the market risk premium as the product of beta, a measure of systematic risk, and the equity risk premium. Beta represents the sensitivity of an investment’s returns to market movements. Another model is the Dividend Discount Model (DDM), which estimates the market risk premium by comparing the expected dividend yield of equities to the risk-free rate. These models provide a theoretical framework for estimating the market risk premium but are dependent on the accuracy of input assumptions and can be sensitive to model parameter estimation.
It is important to note that these calculation methods are not definitive and can yield different results. The choice of method depends on the available data, the investor’s preference, and the specific context in which the market risk premium is being calculated. Many investors rely on a combination of approaches and exercise judgment in determining an appropriate market risk premium for their investment analyses.
Regardless of the calculation method used, it is advised to regularly review and update the market risk premium estimation based on changing market conditions and new information. The market risk premium is a dynamic concept that can vary over time, and it is crucial for investors to have updated estimates to inform their investment decisions and risk management strategies.
Historical Market Risk Premiums
Examining historical market risk premiums can provide valuable insights into the long-term relationship between risk and reward in the financial markets. Tracking the historical trends of the market risk premium can help investors understand the potential returns they can expect for taking on market risk. However, it is important to note that historical data is not indicative of future performance.
Over the past several decades, the historical market risk premium has varied significantly. On average, the long-term historical market risk premium has been estimated to range between 4% and 8%. This means that investors have historically demanded a premium of 4-8% above the risk-free rate to compensate for the additional risk associated with investing in the broader market.
It is essential to consider the time period over which the historical market risk premium is calculated. Different periods can yield different results due to variations in economic conditions, market cycles, and investor sentiment. For example, during periods of economic expansion and bullish market conditions, the risk premium may be lower as investors are more optimistic about potential returns. Conversely, during periods of economic downturns or financial crises, the risk premium tends to be higher as investors demand a higher return for taking on more risk.
An analysis of historical market risk premiums indicates that the risk premium tends to be higher in emerging markets compared to developed markets. This is primarily due to the higher levels of political and economic uncertainties associated with investing in emerging economies.
It is important to note that historical market risk premiums are subject to interpretation and estimation methods. Different calculation methods and assumptions can yield varying results. Additionally, factors such as survivorship bias, data limitations, and changing market dynamics should be considered when interpreting historical market risk premium data.
Investors should use historical market risk premium data as a reference point and consider it in conjunction with other relevant factors, such as current economic conditions, market outlook, and individual risk tolerance. Consulting with financial professionals or conducting comprehensive research can help in making informed investment decisions based on historical market risk premiums.
Current Market Risk Premium Estimates
Estimating the current market risk premium is a key concern for investors seeking to assess the potential returns and risks associated with investing in the market. However, determining the precise value of the current market risk premium is a complex task that involves analyzing various factors and methodologies. Different experts and organizations may provide different estimates based on their assessment of the market conditions. Here, we discuss some of the current market risk premium estimates based on recent data and analysis.
One widely referenced source for market risk premium estimates is the implied equity risk premium (IERP) approach. This approach calculates the market risk premium as the difference between the expected return on equities and the risk-free rate. The expected return on equities is often estimated using analysts’ earnings forecasts and market price data. Based on this approach, the current market risk premium for major market indices, such as the S&P 500, is estimated to be in the range of 4% to 6%.
Another approach to estimating the current market risk premium is through surveying market participants and investment professionals. These surveys seek to gather insights and opinions on the expected return of the market and the risk-free rate. The average of these estimates can be used to estimate the market risk premium. However, it is important to note that survey-based estimates can vary depending on the participants’ perspectives and market sentiment. Currently, survey-based estimates suggest a market risk premium in the range of 5% to 7%.
In addition to these approaches, some financial institutions and research organizations provide their own estimates of the current market risk premium based on their analysis and models. These estimates can vary depending on the specific methodologies and assumptions used. As of the latest available data, estimates from these sources range from 3% to 8% for developed markets, and higher for emerging markets, reflecting the higher perceived risks associated with investing in these economies.
It is important to remember that market risk premium estimates are ultimately subjective and based on various assumptions and factors. They serve as a reference point for investors but should not be considered as definitive values. The actual future market risk premium can deviate from these estimates due to changing economic conditions, market dynamics, and unforeseen events.
Investors should approach market risk premium estimates with caution. It is recommended to consult with financial professionals and consider a range of estimates to develop a more comprehensive understanding of the current market risk premium. Additionally, staying informed about economic indicators, market trends, and geopolitical developments can further enhance the evaluation of the current market risk premium.
Importance of Understanding the Current Market Risk Premium
Understanding the current market risk premium is of paramount importance for investors and financial professionals. It provides valuable insights into the relationship between risk and return, allowing for informed decision-making when it comes to investment strategies and portfolio management. Here are some key reasons why understanding the current market risk premium is crucial:
- Assessing Expected Returns: The market risk premium helps investors evaluate the potential returns they can expect from investing in the market. By comparing the expected return of an investment to the risk-free rate, investors can gauge whether the potential rewards justify the additional risk they are taking. Understanding the current market risk premium allows for more accurate estimations of expected returns, enabling investors to make well-informed investment decisions.
- Setting Risk Management Strategies: Managing risk is a crucial aspect of successful investing. By understanding the current market risk premium, investors can develop effective risk management strategies. They can assess the likelihood and magnitude of potential market downturns or volatility, and determine an appropriate level of portfolio diversification, asset allocation, and hedging strategies. Incorporating the current market risk premium into risk management allows investors to prudently balance risk and reward.
- Comparing Investment Opportunities: When evaluating different investment opportunities, understanding the current market risk premium is essential. It provides a common benchmark for comparing the potential returns of various investments. By comparing the expected returns of different assets or investment vehicles to the market risk premium, investors can identify potentially undervalued or overvalued opportunities. This information helps investors make informed decisions about asset allocation and investment selection.
- Evaluating Investment Performance: Analysis of investment performance requires considering the market risk premium. Comparing the actual returns of an investment with the expected returns based on the market risk premium can help assess the success of an investment strategy. Positive or negative deviations from expected performance can be evaluated in light of the prevailing market risk premium to determine if the investment was successful or if adjustments are needed.
- Responding to Changing Market Conditions: The market risk premium is not a static value and can change over time. Understanding the current market risk premium allows investors to adapt their strategies to changing market conditions. If the market risk premium is high, investors may opt for a more conservative approach, whereas a low market risk premium may warrant taking on additional risk to pursue higher returns. By staying informed about the current market risk premium, investors can make timely adjustments to their investment strategies.
In summary, understanding the current market risk premium is essential for investors to assess expected returns, develop sound risk management strategies, compare investment opportunities, evaluate investment performance, and adapt to changing market conditions. By incorporating the market risk premium into investment analysis and decision-making, investors can make more informed choices and improve their overall investment outcomes.
Conclusion
The market risk premium plays a crucial role in the world of finance, providing insights into the additional return investors require for assuming the risks associated with investing in the overall market. Understanding the current market risk premium is essential for making informed investment decisions, managing portfolio risk, and assessing the potential rewards and risks of investments.
In this article, we explored the definition of market risk premium and its significance in asset pricing. We discussed the factors that affect the market risk premium, including economic conditions, investor sentiment, geopolitical events, interest rates, and market volatility. These factors interplay to determine the level of risk premium investors demand for investing in the market.
We delved into different methods for calculating the market risk premium, such as the historical approach, survey-based approach, and equity risk premium models. Each method provides a unique perspective but requires careful consideration of various assumptions and limitations.
Additionally, we examined historical market risk premiums and their variability over time, providing insights into the long-term relationship between risk and reward. It is crucial to interpret historical data in the context of specific economic conditions and market cycles.
We also discussed current market risk premium estimates and the importance of understanding them in assessing expected returns, setting risk management strategies, comparing investment opportunities, and evaluating investment performance. The market risk premium serves as a benchmark for decision-making and can guide investors in navigating the dynamic nature of the financial markets.
In conclusion, the market risk premium is a fundamental concept that investors need to comprehend to effectively manage their investments. By staying informed about the current market risk premium and considering it alongside other relevant factors, investors can make informed decisions, strike an optimal balance between risk and return, and achieve their financial goals.